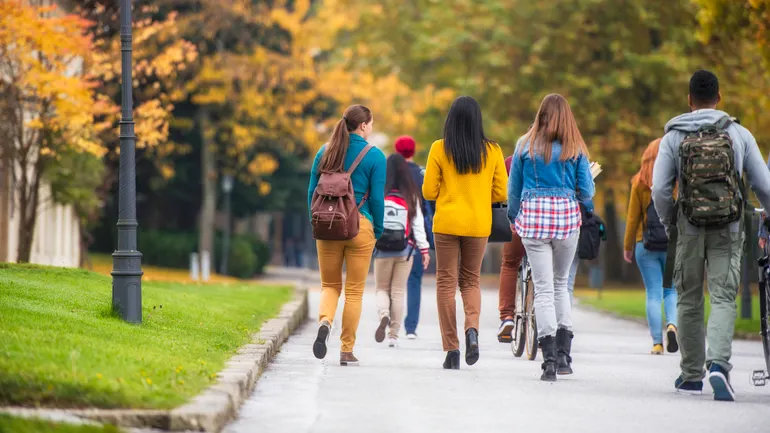
This fall, North Carolina is one of the latest states rolling out a direct admission program that offers high school seniors acceptance to a range of public and private colleges.
Through direct admissions, colleges proactively admit students based on high school academic performance metrics such as GPA, SAT scores, or the amount of credits they received.
Around the start of the school year, more than 62,000 public high school seniors in North Carolina were offered direct admission to select colleges through the NC College Connect Program. Eleven of the University of North Carolina System’s 16 colleges, 29 private colleges and all 58 of the state’s community colleges are participating.
The UNC System first piloted NC College Connect last year in partnership with state agencies, the governor’s office and North Carolina’s community college system. The system launched the program to increase access to higher education in the state, Shun Robertson, UNC’s senior vice president for strategy and policy, said in an email.
For many high school seniors, “the process of applying to college, transferring between institutions, and navigating the maze of financial aid feels like an insurmountable series of hurdles,” said Robertson. “Eliminating these barriers has been a high priority.”
Over the past decade, direct admissions policies have increased the likelihood that in-state students both apply to college and apply to more colleges, said John Lane, vice president for academic affairs at the State Higher Education Executive Officers Association, in an email. In turn, that shift has effectively increased college enrollment, he said.
“Direct admissions policies and programs are impactful because they eliminate the complications and uncertainties of longstanding college application processes,” said Lane. “Instead, students are proactively admitted.”
UNC’s program
The UNC System piloted its direct admissions initiative last fall and notified over 70,000 high school seniors with GPAs of 2.8 or higher of their eligibility for the program, Robertson said.
Those seniors could apply to six UNC institutions and all 58 state community colleges for the 2025-26 academic year by sharing on an online portal their email address, their potential major, and when they’d like to start college, he said.
UNC System officials haven’t been able to review outcome data yet for the pilot program, a spokesperson said. But over 5,000 students responded to the letter during the pilot, the spokesperson said.
The system simplified the program this fall. Students won’t have to formally apply to get into one of the colleges on their list, rather they are provided direct admission to institutions based on their GPA and whether they meet the program’s requirements, Robertson said. Then they just need to submit a program form to accept their admission, he said.
Students accepting admission to community colleges must still fill out applications, but they will already be admitted, according to the initiative’s website.
The program also expanded to include private colleges in the state and added more UNC institutions, said Robertson. The University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, the system’s highly selective flagship, remains excluded from the program.
Some of the private institutions in the program have additional direct admission qualification requirements, such as foreign language course requirements.
UNC System officials hope direct admissions will help the state’s institutions enrollment numbers long term by tapping into a growing college-aged student population.
Like most of the country, North Carolina is expected to see a decline in high school graduates between 2025 and 2030, according to a report last year from the Western Interstate Commission for Higher Education. However, that pool of students is expected to grow again in North Carolina after that year.
WICHE predicts that North Carolina will be one of 12 states, along with the District of Columbia, to have growing numbers of high school students between 2023 and 2041. Overall, North Carolina should see a 6% increase in high school graduates over that period, per WICHE projections.
“As more students and families choose to live in North Carolina, the UNC System is making sure that we serve as a gateway to opportunity for postsecondary education for them and building an educated workforce for our state,” said Robertson.
An effective trend
Idaho launched the nation’s first state direct admissions program in 2015, hoping to improve enrollment at its public institutions.
Research from 2022 on Idaho’s direct admissions program found a 4% to 8% increase in first-time undergraduate enrollment per campus. Those enrollments were driven by an increase in attendance at two-year institutions, the research found.
Such programs have since expanded at institutions in more than a dozen states, including Minnesota, Wisconsin, Hawai’i, Connecticut, California, Illinois, Indiana, Utah, Oregon and West Virginia.
Direct admissions programs have also been attributed to increases in applications among Black, Latinx, multiracial, first-generation and low-income students, according to a 2023 study by researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
That study also found that students offered direct admissions were more likely to apply to a college or university and twice as likely to apply to an institution that offered them guaranteed acceptance.