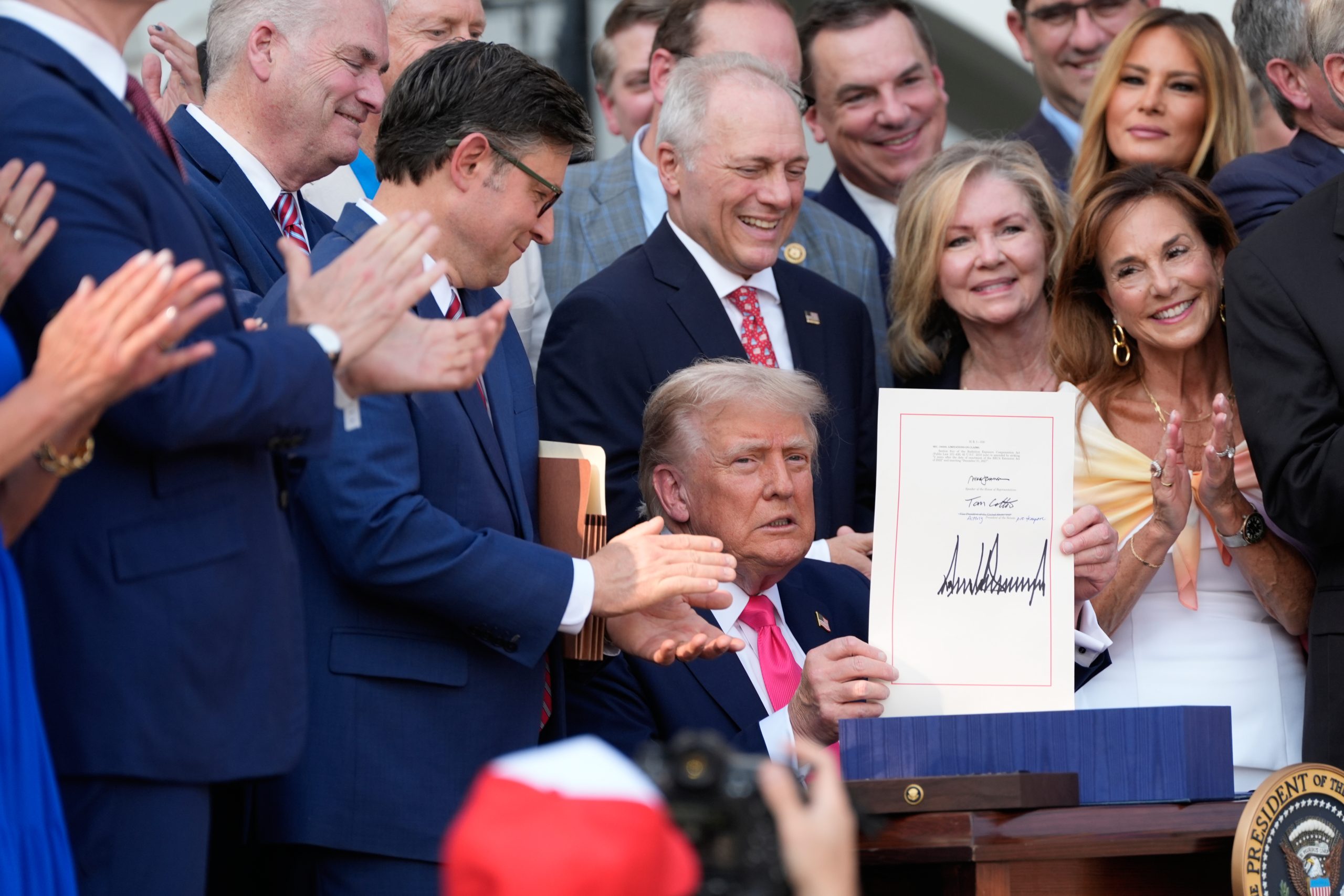
After decades of trying, conservatives this year succeeded in creating the first national school voucher program.
The Republican megabill that President Donald Trump signed into law in July will establish new tax credit scholarships for families to use at private schools, including religious ones — a long-held goal of school privatization advocates who argue parents should get taxpayer support if they want to opt out of their neighborhood school.
Under the “big, beautiful bill,” donors can receive dollar-for-dollar tax credits of up to $1,700 for contributions to scholarship-granting nonprofits. Those groups then distribute the money to families seeking help paying for private school, tutoring and other educational expenses.
The program, while significant, is less expansive than in earlier drafts of the legislation. Previous versions gave donors larger tax credits — a match up to $5,000 or 10 percent of their income, whichever is greater — and mandated that all states participate rather than allowing them to opt in.
Related: A lot goes on in classrooms from kindergarten to high school. Keep up with our free weekly newsletter on K-12 education.
Here are 10 things to know about the program. If you have other questions or there’s more you’d like to know, write to us: [email protected].
When does it start?
Jan. 1, 2027. Families have until then to research where they might want to spend a scholarship — and if the school in mind even plans to accept one. Taxpayers who want to contribute to support the scholarships can do so beginning in late 2026.
How will the scholarships work?
The law opens the door to churches, universities, education nonprofits, rotary clubs and potentially even public schools (more on that below) to accept and distribute donations for the program. These “scholarship-granting organizations,” or SGOs, can keep up to 10 percent of the donations for administrative costs.
In some states with existing scholarship programs, families apply with a third-party contractor that works with eligible schools and selects students for awards. Other states allow religious groups and other nonprofits to create and manage their own scholarship funds. The federal bill gives states wide flexibility to make those sorts of decisions about how the program is administered, experts say.
Who’s eligible for the scholarships?
To qualify, students need to check these boxes: They must be eligible to attend a public school, their state must opt in to the program, and their families must earn no more than three times the area median income — a threshold that would include households with incomes nearing $500,000 in some parts of the United States.
Students who already attend private school qualify, since they are eligible for public school, even if they don’t attend one. The scholarships also may cover home-schoolers. (Keep reading for more on that.)
How much money will families receive?
While the bill set a $1,700 cap on how much individual donors can contribute through their taxes, it’s unclear whether it limits how much an individual student could collect in scholarships.
In theory, a student could apply for several scholarships. An SGO might also offer a scholarship that reimburses a family for all costs associated with attending their preferred school. In states that already offer similar school choice programs, a student might be able to collect scholarships from both the new program and the existing state program. Still, the average cost of private school tuition is roughly $13,000, so even students who combine several scholarships may not receive enough to cover the full cost of attending.
The Treasury Department is expected to issue regulations on the program, and we may not know these kinds of details until it does.
Related: Arizona gave families public money for private schools. Then private schools raised tuition
What can the scholarship money be used for?
Quite a lot. The legislation suggests that families could use the money not only to help pay for private school tuition, but also for room and board, services for students with disabilities, transportation, tutoring, and school supplies like books, computers and uniforms.
The rules may depend on the individual state and its definition of an “eligible school.” In some states, home schooling might qualify students for the scholarships, but in other states it might not, said Robert Enlow, president of EdChoice, a pro-school choice group.
It’s also possible that public schools could charge scholarship students — as some do with home-schoolers — for services like tutoring, special education or advanced courses.
So students can use the money at public schools? How would that work?
Yes, potentially. In some states, schools already charge activity or participation fees for non-enrolled students who want to join clubs and sports. Marguerite Roza, director of the Edunomics Lab at Georgetown University, said some states may write their own rules that allow schools to extend the menu of services they could charge for.
Meanwhile, most school districts — roughly 4 in 5 — already partner with foundations that raise money to help students with transportation, school supplies and basic needs. Both Enlow and Roza said they expected nonprofits and districts to partner on finding ways to tap the federal scholarship dollars as well.
“Imagine you could have a public school foundation going out and helping with transportation and books and computers and tutors and all sorts of stuff, right?” Enlow said. “The potential is huge.”
Will all private schools accept the scholarships?
No, private schools are not required to accept the scholarships, and many states that offer school choice don’t require private schools to participate. Private schools generally can accept or reject a student for any reason, whether they have a scholarship or not.
In Arizona, for example, the tax credit program provided scholarships to students at 348 schools last year. More than 400 private schools operated in the state as of 2022.
Related: Tracking Trump: His actions to dismantle the Education Department, and more
Which states will participate?
Roughly 21 states — including Arizona, Georgia and Montana — offer their own tax credit scholarships, according to the group EdChoice, so it’s expected they would opt into the federal program. Conservative lawmakers in North Carolina already introduced a bill to allow families there to take part in the federal scholarships.
If public schools can benefit too, even Democratic governors may consider joining the program, said Roza.
“Ultimately if the state can open this to summer camp and tutoring, obviously there would be a lot of pressure to unlock so much money with this,” she said.
How much will the scholarships cost the government?
It depends on how many taxpayers claim the credit.
While an earlier version of the bill would have capped the tax credits at $10 billion a year, the final legislation contains no such limit — so the exact amount in lost revenue won’t be known until much later. That said, an analysis by the nonpartisan Joint Committee on Taxation found that the legislation would cost the Treasury up to $4 billion per year.
Others think the cost will be higher. The Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, a left-leaning research group, placed its projection closer to $51 billion, while Roza estimated the cost at $28 billion per year. Still, she hesitated to count that as a direct loss to K-12 funding. “It’s new money in the sense that it doesn’t go into or out of the federal pie,” Roza said.
What’s been the reaction to the plan?
Critics, including teachers unions and many education experts, have been quick to raise alarms about the voucher program, arguing that it’s a handout for wealthy families and will harm public schools by reducing funding for them.
“It’s the centerpiece of the Great American Heist — a privatization scheme wrapped in tax policy,” Denise Forte, president of the left-leaning nonprofit EdTrust, said at a hearing before the Senate Democratic Caucus in July.
Advocates for the separation of church and state worry about the program channeling money from government coffers to religious schools, while disability advocates note that private schools are not required to serve students with disabilities.
Some supporters of school vouchers, meanwhile, wish the legislation had gone further.
“This is a very positive program for taxpayers in America. You can help families get better education and claim a tax credit for it,” said EdChoice’s Enlow. “It’s going to benefit middle- and low-income families.” But he added, “It’s not as generous as we would like, which is universal.”
Others are focused now on encouraging states to participate in the program. “The fight doesn’t end with the passing of the bill,” said Sydney Altfield, national director of Teach Coalition, which advocates for Jewish schools to get access to government funding. “States must opt into the program.”
Contact staff writer Neal Morton at 212-678-8247, on Signal at nealmorton.99, or via email at [email protected].
This story about school voucher programs was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for the Hechinger newsletter.
The Hechinger Report provides in-depth, fact-based, unbiased reporting on education that is free to all readers. But that doesn’t mean it’s free to produce. Our work keeps educators and the public informed about pressing issues at schools and on campuses throughout the country. We tell the whole story, even when the details are inconvenient. Help us keep doing that.
Join us today.