Did you know that beyond powering multi-million dollar Giving Days and dynamic crowdfunding initiatives, ScaleFunder also offers functionality for creating simple and easy to use giving forms?
This versatility is why ScaleFunder Giving Forms are rapidly gaining momentum! If your institution is already a ScaleFunder Crowdfunding partner, you automatically have unlimited access to create as many Giving Forms as you need. Continue reading to explore how consolidating all your giving initiatives to the ScaleFunder platform can strengthen cross-campus collaboration, simplify the donor experience, and offer operational flexibility.
Stay friends with your gift processing team
Keep your gift processing team smiling, because fewer platforms mean fewer headaches. With every gift flowing through the same trusted payment processor (of your choice), your payment mapping fields stay consistent across all ScaleFunder Giving Day and crowdfunding campaigns. Plus, digital wallet options activated through your payment integration let donors give how they prefer without throwing your processing pals a curveball. In addition, you can now easily add opt-in questions for university-wide texts and emails, making it easier than ever to gather big-picture data while keeping your systems (and friendships) running smoothly.
Build consistency with donors
Familiarity builds confidence, and ScaleFunder keeps things beautifully consistent. Whether a donor is supporting your Giving Day, a crowdfunding project, or a giving form, the experience looks and feels consistent once they land on the donation form. After a few gifts, they’ll be pros at checkout…breezing through the form with ease. That comfort can translate to higher completion rates, faster transactions, and more donors exploring other opportunities on your platform.
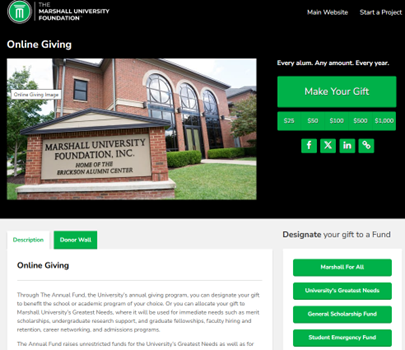
Plus, once they’ve landed on one Giving Form, connecting them to others is a snap. Link to additional forms—like athletics, annual fund, or individual colleges and schools—just like our partners at Michigan Tech do, making it effortless for donors to discover new ways to give.
Pictured: The Michigan Technological University annual fund giving page.
Enjoy the flexibility you know and love
Creating a universal giving form has never been easier—you can do it in under five minutes! Need a simple form for one fund? Done. Want to showcase all 3,000 of your institution’s funds on a single page? Easy. The athletic director dreaming of a QR code in the banquet program that links to every athletic fund? Consider it handled.
You can add unlimited custom questions to make your form as fun—or as functional—as you like. Ask for T-shirt sizes, invite donors to share their stories, or let them vote for their favorite residence hall. The options are limitless, and the setup is a breeze.
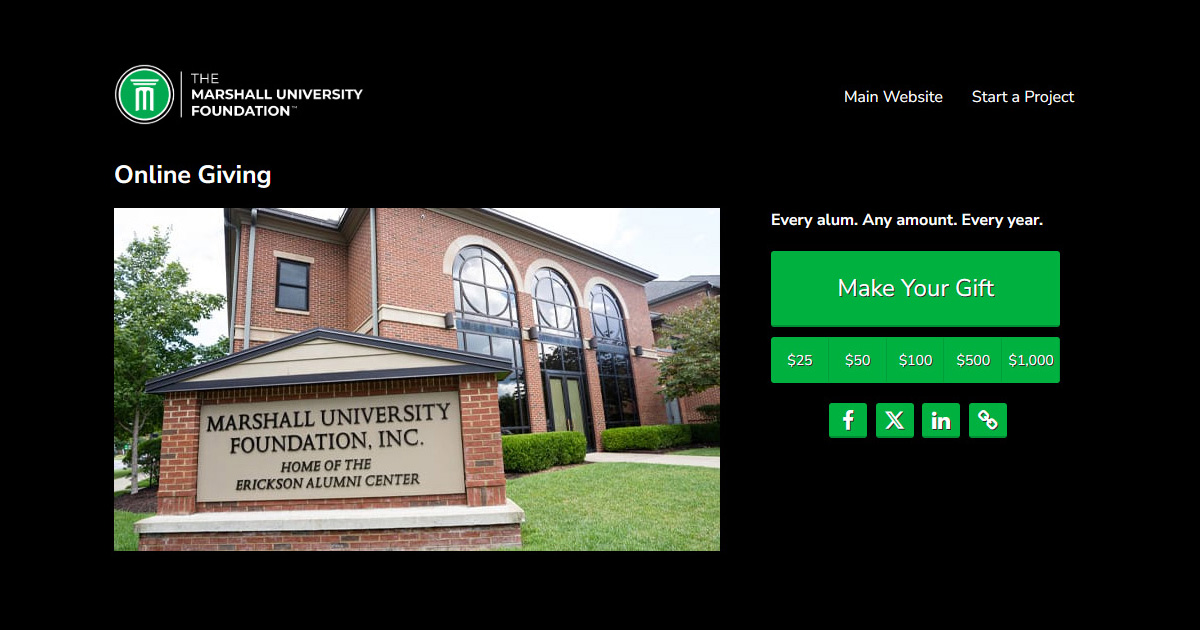
Pictured: Our partners at Marshall University have identified nearly 20 priority funds on their Giving Form, which appear in two ways: visually appealing buttons on the project page and a searchable, scrollable list on the Giving Form.
Maintain your identity
Your brand is uniquely yours and it should shine through every click, color, and contribution. When you join the ScaleFunder family, our team crafts a custom site design and background that aligns with your institution’s brand standards, colors, and tone. Every page carries that same cohesive look and feel, so donors always know they’re in your world.
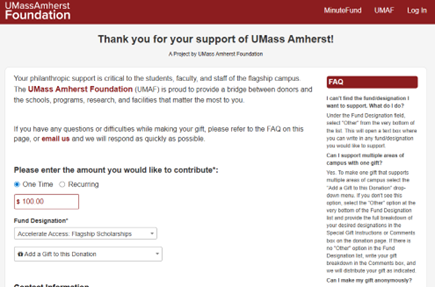
From your logo and language to your custom domain, everything says “you,” while Google reCAPTCHA quietly works behind the scenes to reassure them that every gift is safe and secure. This consistency of branding also means it’s easy to link to your Giving Forms from external pages, just like our partners at UMass Amherst have done from their main foundation website.
Pictured: The UMass Amherst Foundation giving page.
Ready to learn more?
Whether you’re exploring digital fundraising platforms or already part of the ScaleFunder family, we’d love to help you get the most out of your tools. Connect with Courtney Pourciaux, senior consultant, to learn how Giving Forms and ScaleFunder can elevate your fundraising strategy. Reach out and we can schedule a demo as well as discuss how to make your giving experience easy and consistent for your donors.
Talk with our digital giving experts
RNL works with institutions on digital giving and donor engagement, including crowdfunding, giving days, and omnichannel fundraising. Set up a time to talk with our fundraising experts to find your optimal strategies.