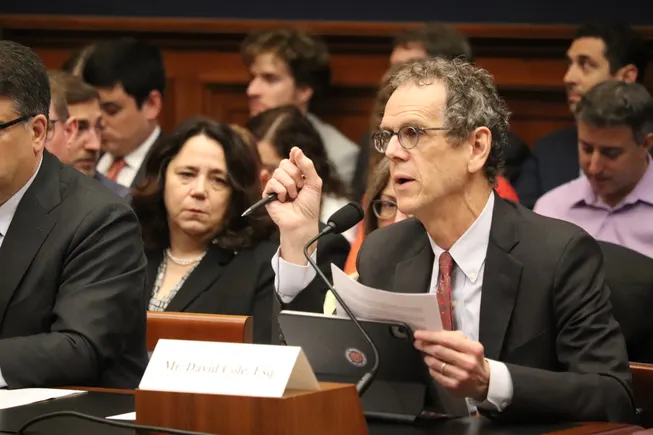
Republicans on the House’s education committee grilled three college presidents Wednesday about how they’ve handled alleged incidents of antisemitism in the wake of the Israel-Hamas war, expanding their probe beyond the Ivy League and other well-known research universities.
The leaders came from Haverford College, a small private liberal arts college in Pennsylvania; DePaul University, a private Catholic research university in Chicago; and California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, a public institution in California.
All three institutions have been a hotbed of political activity for over a year. Pro-Palestinian protesters set up encampments at both Haverford and DePaul last year. Cal Poly also saw demonstrations, including a pro-Palestinian protest held around the one-year anniversary of the Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas attack on Israel.
Republicans on the House Committee on Education and Workforce said they sought to crack down on campus antisemitism and uphold Title VI of the Civil Rights Act, which prohibits discrimination based on race, color and national origin in federally funded programs.
However, some Democrats accused the panel’s GOP members of using antisemitism concerns to quell free speech. They also blasted the Trump administration for detaining international students involved in pro-Palestinian demonstrations and for its heavy cuts to the U.S. Department of Education’s Office for Civil Rights, which investigates antisemitism and other discrimination allegations at colleges and schools.
Wednesday’s hearing was the first the House education committee has held on campus antisemitism since President Donald Trump retook office. Since then, his administration has frozen funding at several high-profile institutions that have been probed by the committee, claiming the colleges haven’t done enough to protect students from antisemitism.
“The Trump administration has taken a sledgehammer to due process rights of institutions,” said Virginia Rep. Bobby Scott, the top Democrat on the committee. “The public has seen a barrage of reports of this administration taking action without any investigation, such as taking away federal funding.”
Haverford’s federal funding threatened
Haverford President Wendy Raymond and DePaul President Robert Manuel struck a conciliatory tone in their opening remarks, and all three leaders outlined steps they have recently taken to protect Jewish students from discrimination, including setting up an antisemitism task force and tightening protest rules.
“I recognize that we haven’t always succeeded in living up to our ideals,” Raymond said. “I remain committed to addressing antisemitism and all issues that harm our community members. I am committed to getting this right.”
Last year, a group of Haverford students sued the college over allegations it had denied Jewish students the ability to participate in classes and educational activities “without fear of harassment if they express beliefs about Israel that are anything less than eliminationist.”
The lawsuit contains accounts of several incidents and comments it says are antisemitic, including one professor sharing a social media post on Oct. 11, 2023. The post included an image the lawsuit described as Hamas breaking through the border between Gaza and Israel and stating, “We should never have to apologize for celebrating these scenes of an imprisoned people breaking free from their chains.”
A federal judge dismissed the case in January but allowed plaintiffs to file an amended lawsuit, which they did that month.
Rep. Elise Stefanik, a Republican from New York, asked Raymond whether the professor who shared the post had faced disciplinary action, but the Haverford president declined throughout the hearing to talk about individual cases or share specific figures on disciplinary actions. The professor, Tarik Aougab, is listed on Haverford’s website as a faculty member.
“Many people have sat in this position who are no longer in the positions as president of universities for their failure to answer straightforward questions,” Stefanik replied.
During a similar hearing in 2023, Stefanik questioned the presidents of Harvard University, the University of Pennsylvania and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, asking all three leaders whether calling for the genocide of Jewish people would violate campus rules.
They all declined to give a yes-or-no answer, contending that the language could cross the line into harassment depending on the situation.
The moment went viral, and Elizabeth Magill, then leader of Penn, resigned only days later. Claudine Gay stepped down as president of Harvard about a month later, amid allegations of plagiarism and growing calls for her ouster following the hearing.
During Wednesday’s hearing, Rep. Mark Messmer, a Republican from Indiana, asked whether calls for the genocide of Jews would violate university policies. All three said these types of calls would be subject to disciplinary action.
However, other Republican lawmakers criticized Raymond’s refusal to detail disciplinary actions, with some threatening Haverford’s federal funding.
“I suppose it’s your First Amendment right to be evasive, but it’s also our right to decide that such institutions are not deserving of taxpayer money,” Rep. Bob Onder, a Republican from Missouri, told her.
An anti-higher education agenda?
Democrats on the committee frequently lambasted recent cuts to the Office for Civil Rights, which lost roughly half of its staff and regional offices as part of the Trump administration’s moves to downsize — and eventually eliminate — the Education Department.
“For those of us who do want to stop the rise of antisemitism on college campuses, I remind you that the federal government already has an entity in place to investigate and resolve antisemitic instances” — OCR, said Rep. Suzanne Bonamici, a Democrat from Oregon.
She also pointed to reports from John Kelly, Trump’s former chief of staff, that the president privately said multiple times during his first term that Adolf Hitler “did some good things.” Bonamici likewise accused some congressional Republicans of promoting antisemitic conspiracy theories.
“It is unconscionable to weaponize the real problems of the Jewish community for political gain, and I’m not going to engage in more back-and-forth in this hearing with people who call out antisemitism when it’s part of their anti-higher education agenda but not when it’s coming from their side of the aisle,” Bonamici said.
Additionally, Bonamici pointed to a recent statement from 10 Jewish organizations, led by the Jewish Council for Public Affairs, which accused the Trump administration of stripping due process rights from students and threatening academic research under “the guise of fighting antisemitism.”
David Cole, a law and public policy professor at Georgetown University and the Democratic witness, didn’t mince words. Cole likened the House education committee’s use of hearings on antisemitism to McCarthyism and the work of the House Un-American Activities Committee, which probed suspected communists during that era.
Cole argued the committee had made “no effort to discern the difference between protected speech and discrimination.”
“That’s why I draw the comparison to HUAC,” Cole said.
He also said that Title VI does not prohibit antisemitic speech.
“Antisemitic speech, while lamentable, is constitutionally protected, just like racist speech, sexist speech and homophobic speech,” Cole said. “While such speech obviously causes deep harm, the greater danger is giving government officials the power to censor speech by labeling it antisemitic, racist or sexist.”
Antisemitic speech “implicates Title VI,” he said, when it constitutes harassment targeting an individual because of their Jewish identity or when it is “so severe, pervasive and objectively offensive that it denies equal access to an education.”
Determining whether speech has crossed into prohibited discrimination requires a fact-intensive investigation, Cole said. Moreover, colleges only violate Title VI when they were “deliberately indifferent” to the discrimination, he added.
Cole argued that the House hearings weren’t the right place to engage in these types of investigations, which he said require testimony from those involved in the alleged incidents. Instead, he called on the committee to bring in U.S. Education Secretary Linda McMahon.
“They should be calling Secretary of Education McMahon before the committee and asking her why she has decimated the very office that is supposed to be enforcing antidiscrimination law,” Cole said.
Clarification: This article has been updated to reflect that a group of Jewish organizations issued the statement led by the Jewish Council for Public Affairs.




 Because our brains interpret emotional threats in the same way as physical threats, feeling unsafe at work can provoke a similar feeling to walking alone in a dark parking garage or seeing a snake on a hiking trail. But when we feel a sense of psychological safety and social belonging, our brains shift into connected mode. When we feel safe, we’re more likely to collaborate with our team, be less resistant to change and feel creative.
Because our brains interpret emotional threats in the same way as physical threats, feeling unsafe at work can provoke a similar feeling to walking alone in a dark parking garage or seeing a snake on a hiking trail. But when we feel a sense of psychological safety and social belonging, our brains shift into connected mode. When we feel safe, we’re more likely to collaborate with our team, be less resistant to change and feel creative.