null
Source link
Author: admin
-

Don’t let Texas criminalize free political speech in the name of AI regulation
This essay was originally published by the Austin American-Statesman on May 2, 2025.
Texans aren’t exactly shy about speaking their minds — whether it’s at city hall, in the town square, or all over social media. But a slate of bills now moving through the Texas Legislature threatens to make that proud tradition a criminal offense.
In the name of regulating artificial intelligence, lawmakers are proposing bills that could turn political memes, commentary and satire into crimes.
Senate Bills 893 and 228, and House Bills 366 and 556, might be attempting to protect election integrity, but these bills actually impose sweeping restrictions that could silence ordinary Texans just trying to express their opinions.
Take SB 893 and its companion HB 2795. These would make it a crime to create and share AI-generated images, audio recordings, or videos if done with the intent to “deceive” and “influence the result of an election.” The bill offers a limited safeguard: If you want to share any images covered by the bill, you must edit them to add a government-mandated warning label.
But the bills never define what counts as “deceptive,” handing prosecutors a blank check to decide what speech crosses the line. That’s a recipe for selective enforcement and criminalizing unpopular opinions. And SB 893 has already passed the Senate.
Vague laws and open-ended definitions shouldn’t dictate what Texans can say, how they can say it, or which tools they’re allowed to use.
HB 366, which just passed the House, goes even further. It would require a disclaimer on any political ad that contains “altered media,” even when the content isn’t misleading. With the provisions applying to anyone spending at least $100 on political advertising, which is easily the amount a person could spend to boost a social media post or to print some flyers, a private citizen could be subject to the law.
Once this threshold is met, an AI-generated meme, a five-second clip on social media, or a goofy Photoshop that gives the opponent a giant cartoon head would all suddenly need a legal warning label. No exceptions for satire, parody or commentary are included. If it didn’t happen in real life, you’re legally obligated to slap a disclaimer on it.
HB 556 and SB 228 take a similarly broad approach, treating all generative AI as suspect and criminalizing creative political expression.
These proposals aren’t just overkill, they’re unconstitutional. Courts have long held that parody, satire and even sharp political attacks are protected speech. Requiring Texans to add disclaimers to their opinions simply because they used modern tools to express them is not transparency. It’s compelled speech.
Besides, Texas already has laws on the books to address defamation, fraud and election interference. What these bills do is expand government control over how Texans express themselves while turning political expression into a legal minefield.
Fighting deception at the ballot box shouldn’t mean criminalizing creativity or chilling free speech online. Texans shouldn’t need a lawyer to know whether they can post a meme they made on social media or make a joke about a candidate.
Political life in Texas has been known to be colorful, rowdy and fiercely independent — and that’s how it should stay. Vague laws and open-ended definitions shouldn’t dictate what Texans can say, how they can say it, or which tools they’re allowed to use.
The Texas Legislature should scrap these overbroad AI bills and defend the Lone Star state’s real legacy: fearless, unapologetic free speech.
-

Trump Proposes Deep Cuts to Education and Research
President Donald Trump wants to end funding for TRIO, Federal Work-Study and other grant programs that support students on campus as part of a broader plan to cut $163 billion in nondefense programs.
The funding cuts were outlined in a budget proposal released Friday. The document, considered a “skinny budget,” is essentially a wish list for the fiscal year 2026 budget for Congress to consider. The proposal kicks off what will likely be a yearlong effort to adopt a budget for the next fiscal year, which starts Oct. 1. Trump is unlikely to get all of his plan through Congress, though Republicans have seemed especially willing this year to support his agenda.
If enacted, the plan would codify Trump’s efforts over the last three months to cut spending and reduce the size of the federal government—moves that some have argued were illegal. (Congress technically has final say over the budget, but Trump and his officials have raised questions about the legality of laws that require the president to spend federal funds as directed by the legislative branch.)
The proposed budget plan slashes nearly $18 billion from the National Institutes of Health, $12 billion from the Education Department, and nearly $5 billion from the National Science Foundation. The skinny budget also eliminates funding for the Institute of Museum and Library Sciences, AmeriCorps, National Endowment for the Arts, and National Endowment for the Humanities. Trump has already made deep cuts at those agencies and put most—if not all—of their employees on leave.
A fuller budget with more specifics is expected later this month.
Democrats were quick to blast Trump’s plan, saying it would set the country “back decades by decimating investments to help families afford the basics.” But Republicans countered that the proposal would rein in “Washington’s runaway spending” and right-size “the bloated federal bureaucracy.”
For higher ed groups and advocates, the proposed cuts could further jeopardize the country’s standing as a leader in global innovation and put college out of reach for some students.
“Rather than ushering in a new Golden Age, the administration is proposing cuts to higher education and scientific research of an astonishing magnitude that would decimate U.S. innovation, productivity, and national security,” said Mark Becker, president of the Association of Public and Land-grant Universities, in a statement. “We call on Congress to reject these deeply misguided proposed cuts and instead invest in the nation’s future through education and pathbreaking research.”
Zeroing Out ED Programs
At the Education Department, the Trump administration is proposing to end a number of programs and reduce funding to others.
The president wants to eliminate the department altogether; Education Secretary Linda McMahon said in a statement that the proposal reflects “an agency that is responsibly winding down, shifting some responsibilities to the states, and thoughtfully preparing a plan to delegate other critical functions to more appropriate entities.”
McMahon laid off nearly half of the agency’s staff in March, so the budget also addresses those cuts.
To compensate for the cuts to programs that directly support students or institutions, the administration argued colleges, states and local communities should on take that responsibility. Other justifications for the cuts reflect the administration’s crackdown on diversity, equity and inclusion programs and higher ed.
For instance, officials from the Office of Management and Budget wrote that the SEOG program “contributes to rising college costs that [institutes of higher education] have used to fund radical leftist ideology instead of investing in students and their success.” (The SEOG program provides $100 to $4,000 to students “with exceptional financial need,” according to the department.)
On TRIO and GEAR UP, which help low-income students get to college, the administration said those programs were a “relic of the past when financial incentives were needed to motivate Institutions of Higher Education to engage with low-income students and increase access … Today, the pendulum has swung and access to college is not the obstacle it was for students of limited means.”
Additionally, the administration wants to cut the Office for Civil Rights’ budget by $49 million, or 35 percent. The budget document says this cut will refocus OCR “away from DEI and Title IX transgender cases.” In recent years, the Biden administration pleaded with Congress to boost OCR’s funding in order to address an increasing number of complaints. The office received 22,687 complaints in fiscal year 2024, and the Biden administration projected that number to grow to nearly 24,000 in 2025.
But the OMB document claims that OCR will clear its “massive backlog” this year. “This rightsizing is consistent with the reduction across the Department and an overall smaller Federal role in K-12 and postsecondary education,” officials wrote.
The administration also proposed cutting the Education Department’s overall budget for program administration by 30 percent. The $127 million cut reflects the staffing cuts and other efforts to wind down the department’s operations.
“President Trump’s proposed budget puts students and parents above the bureaucracy,” McMahon said. “The federal government has invested trillions of taxpayer dollars into an education system that is not driving improved student outcomes—we must change course and reorient taxpayer dollars toward proven programs that generate results for American students.”
Science and Research Cuts
Agencies that fund research at colleges and universities are also facing deep cuts. The $4.9 billion proposed cut at the National Science Foundation is about half of what the agency received in fiscal year 2024—the last year Congress adopted a full budget.
The cuts will end NSF programs aimed at broadening participation in the STEM fields, which totaled just over $1 billion, as well as $3.45 billion in general research and education.
“The budget cuts funding for: climate; clean energy; woke social, behavioral, and economic sciences; and programs in low priority areas of science,” the officials wrote in budget documents. “NSF has fueled research with dubious public value, like speculative impacts from extreme climate scenarios and niche social studies.”
As examples of “research with dubious public value,” officials specifically highlighted a $13.8 million NSF grant at Columbia University to “advance livable, safe, and inclusive communities” and a $15.2 million grant to the University of Delaware focused on achieving “sustainable equity, economic prosperity, and coastal resilience in the context of climate change.” The administration is maintaining the funding for research into artificial intelligence and quantum information sciences.
The budget plan also aims to make significant reforms at the National Institutes of Health while slashing the agency’s budget by $17.9 billion. NIH received $47 billion in fiscal 2024.
The plan would consolidate NIH programs into five areas: the National Institute on Body Systems Research; National Institute on Neuroscience and Brain Research; National Institute of General Medical Sciences; National Institute of Disability Related Research; and National Institute on Behavioral Health.
The National Institute on Minority and Health Disparities, the Fogarty International Center, the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health and the National Institute of Nursing Research would all be cut. The administration is planning to maintain $27 billion for NIH research.
“The administration is committed to restoring accountability, public trust, and transparency at the NIH,” officials wrote. “NIH has broken the trust of the American people with wasteful spending, misleading information, risky research, and the promotion of dangerous ideologies that undermine public health.”
-

Eliminating grade inflation isn’t as easy as ABC
A perfect grade point average isn’t what it used to be. As grade inflation continues worldwide, more students are earning top marks, but it isn’t always deserved. Critics argue that inflated grades make it harder to distinguish truly exceptional students, while supporters say they reduce stress and improve confidence.
From high schools in the United States to universities in Europe, the debate over grade inflation is shaping education systems and college admissions. But is this trend helping students succeed, or is it setting them up for failure?
Grade inflation is the trend of rising student grades over time without a corresponding increase in academic achievement, often making higher grades less reflective of actual learning or ability.
High school is meant to prepare students for higher education, but with grade inflation, many students feel unprepared.
Take high school senior Ruby Schwelm. “As a student who has dealt with inflation, I’ve noticed I don’t receive grades and feedback that reflect my actual understanding of the content,” Schwelm said. “I feel like I’m just going through the motions of my courses, completing assignments without really engaging with the material. This makes it hard to track progress, see where I need improvement and feel prepared for college.”
The rising GPA
According to a study by ACT, a non-profit organization that runs one of two standardized tests used in the United States used for college admissions, the average adjusted grade point average (GPA) of students in the United States has risen from 3.17 in 2010 to 3.36 in 2021.
The report said that grade inflation “calls into question the degree to which we should rely on grades to measure academic achievement or predict future grades.” This shift challenges the typical role of grades as a reliable measure of knowledge, starting a debate over whether they still hold value in measuring students’ abilities.
Many educators believe that the shift in grading has led to a lack of rigor and academic accountability. Josh Hsu, a high school English teacher at the Tatnall School in Wilmington, Delaware where I go to high school, said that many students now equate a C with failure, despite it being historically recognized as an average grade.
“There seems to be a threshold of how low grades will go, and that bar gets pushed higher and higher,” Hsu said.
This trend has caused concern among educators who feel that the traditional grading system no longer differentiates students based on their academic performance.
“What does an A mean if everybody has an A, right?” Hsu said.
The psychological effects of grade inflation
Proponents of grade inflation argue that it helps students maintain self-confidence and reduces academic stress.
Sara Gartland, a high school math teacher at the Tatnall School and adjunct professor at the University of Delaware School of Education, said that “there’s a lot of tension in what a grade is.”
She worries that students today see grades as a measure of their worth rather than as a tool for learning. Grades should function as a feedback loop between teachers and students rather than a rigid measure of success, Gartland said.
She also emphasized the importance of second chances. “I tend to see that really what students are looking for is, ‘Do I have a second chance if today is not my best day?’,” she said.
This perspective aligns with educational philosophies that prioritize mastery over memorization. Many teachers now allow students the opportunity to make corrections and retake assessments to make sure that students truly understand the material, which can also lift the burden of test stress off of students.
Elevated grades and equity
While grade inflation is happening across the country, there have been concerns over whether grade inflation is proportionally impacting students of different incomes and communities.
Hsu said that parents of students in private schools often expect their children to earn high grades to get into a top college in return for the price of tuition. While this belief may lead people to assume that wealthier students have proportionately higher grades than lower-income students, this actually is not the case.
The ACT’s study shows that the average GPA of students in a household with an income of under $36,000 a year has grown much faster than the GPA of students in a household with an income of $100,000 from 2012 to 2021. This could be due to teachers inadvertently trying to give a break to students from low-income families to try and level the playing field.
Gartland argues that teachers should provide students with the tools they need for success and take into consideration things that may impact a student’s performance outside of the classroom.
“That [grade on a test] doesn’t necessarily take into consideration your drive to school that day, whether or not you forgot your lunch that day, or let’s say you had a particularly exciting life event or a particularly upsetting life event, and you didn’t get to spend the amount of time studying that other students did, all sorts of other things,” she said.
With this mindset in education, students are being treated with equity, allowing them the opportunity to experience the same academic success, even if there are barriers in their way.
Global patterns in how students are graded
While the issue of grade inflation is often discussed in the context of schools in the United States, grade inflation is a global issue. A 2024 study, by researchers at the College of New Jersey, found that many countries, including the United Kingdom, Germany and Canada have all experienced rising average grades over time.
However, the extent of grade inflation varies from country to country. Australia, for example, maintains relatively strict grading standards through the use of relative grading and limited reliance on student achievement.
This study also showed that there are many differences in grading practices from region to region. In the United States, professors were significantly more likely to use curved grading, a practice strongly associated with grade inflation.
In contrast, educators in Europe and the South Pacific gave lower average grades and curved fewer grades, suggesting a more conservative approach to grading. Asian countries showed grading patterns similar to the United States, with higher usage of grade curves and slightly elevated grade averages.
These disparities have real implications. Grade inflation complicates international admissions, making it harder to fairly compare students from different educational systems.
It can also distort hiring practices. The international study on grade inflation found that in Sweden, students from schools with inflated grades were shown to earn up to 5% more than peers with equivalent abilities. Ultimately, when grades become inflated, they lose their value as an objective measure of performance, creating global challenges in education, employment, and equity.
A shift in college admissions
As I went through the process of applying to college, I learned from my college counselors how grade inflation has affected the college admissions process. As grade inflation rises, colleges and employers are shifting their focus away from GPAs and toward other indications of student potential. Admissions officers are increasingly looking at extracurricular activities, personal essays and recommendation letters to evaluate applicants.
According to a report by the group FairTest, which works for equity in educational assessments, standardized tests, which once served as a counterbalance to inflated grades, are also becoming optional at many colleges and universities, further complicating the process of evaluating students.
Hsu said he worries that without clear academic standards, the education system could lose its credibility. “If you don’t have a set of standards, then it just becomes the Wild West, and then you have everyone getting A’s and B’s and you have students with GPAs that they didn’t earn,” he said.
Employers, too, are placing greater emphasis on internships and real-world experience rather than assuming high grades equate to a strong work ethic and mastery of material.
With the recent trends of grade inflation, we can expect the average GPAs of students across the country to continue to rise. Hsu worries some students have become lazier in recent years. This raises concerns about how this will impact the future of education and if students will be prepared for life post-graduation.
“Everyone wants instant gratification now,” Hsu said. “They don’t want to work at things as hard because if they have challenges, they’re not willing to stumble through those challenges or fight through them.”
Questions to consider:
• What is meant by grade inflation?
• How can student achievement be measured without letter or number grades?
• Do you think that getting an A on an assignment should be difficult? Why?
-
Career-connected learning builds a more employable, future-ready generation
Key points:
Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a fundamental psychological theory that explains human motivation. At its base are physiological and safety needs, followed by love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization at the peak. While this theory is universally recognized for understanding personal growth in human development, it can also be applied to an individual’s educational journey.
Had Maslow been an educator, he might have reconsidered the foundation of our education system to one that would align student aptitudes and interests to sustain the rapidly changing workforce. Consider the phrase, “If you give a man a fish, he will be hungry tomorrow. If you teach a man to fish, he will be richer forever.” It could be applied here, too. If we pair students’ strengths and aptitudes with in-demand careers through personalized learning, we are ensuring the success of our students and tomorrow’s workforce, thus realigning motivation and fulfilling the individuals Hierarchy of Needs.
States have begun investing in career-connected learning (CCL) to connect learning to career pathways as a means to boost employability and inevitably support businesses and the local economy.
Students are rarely guided toward career paths that match their aptitudes (or natural talents). But if our districts began doing so, we would likely see higher levels of employment and job satisfaction, and lower economic instability and gaps in the job market. This could ultimately impact our communities and the national economy at large.
While work is being done, there is still plenty to do as the career exposure gap grows, particularly in IT, manufacturing, finance, and more. It’s time for educational stakeholders–policy, K-12 decision makers, guidance counselors and parents alike–to rethink how we prepare young people for their futures.
The foundation: Addressing basic needs first
It has become ever so clear that every student, starting as early as junior high, should have the opportunity to take an aptitude assessment. Researchers have identified that students’ natural aptitudes solidify by age 14, forming the foundation for understanding what they’re inherently good at. If Maslow were designing today’s educational experience, this would be the starting point–helping students discover their strengths and setting the stage for growth.
Students’ ability to learn, and therefore their level of education, has always shown to have direct correlations to their physical well-being and sense of security. Often, students feel discouraged and unengaged in their coursework because it doesn’t connect to their innate strengths, making it harder to feel confident in their abilities and motivated to tap into potential future pathways for employment.
When these foundational supports are provided, students are likely to feel ready to explore career opportunities and develop the workplace-ready skills needed in today’s economy.
Building confidence: Belonging and self-esteem in education
Students thrive when they feel a sense of belonging–both in the classroom and in the broader community. They also need to build self-esteem by experiencing achievement, recognition, and purpose. Connecting education with natural aptitudes and real-world career experiences can foster this sense of belonging and achievement.
Encouraging students to participate in internships, apprenticeships, or mentorship programs can bridge the connection between their talents and real-world job opportunities. This fosters a sense of community and a personal identity tied to their future careers and success. CCL helps students understand that they have valuable contributions to make, both in school and beyond, which often leads to students taking ownership of their educational journeys.
Path to self-actualization: Unlocking career potential
At the pinnacle of Maslow’s hierarchy is self-actualization. Students are no longer just attending school to pass tests–they are actively seeking knowledge and skills to help them achieve their dreams. Students are often more motivated when they see the relevance of their learning, especially when they understand how it connects to their future aspirations.
Tech solutions have helped districts provide personalized career assessments and work-based learning experiences for students, which empowers them to explore their career interests in-depth. When we offer students opportunities for hands-on exploration and real-world application, they find greater fulfillment in their educational experiences and a stronger desire to achieve higher learning goals.
The crisis: How the current system is failing to meet Maslow’s vision
Most high school graduates (75 percent) do not feel prepared to make college or career decisions after graduation.
Simultaneously, 40 percent of employers stated that educational institutions do not sufficiently prepare students for their future careers, and 90 percent emphasized the need for stronger partnerships between K-12 schools and postsecondary institutions.
Despite the clear benefits of linking education to career pathways, more often schools solely focus on academic success, neglecting the broader skills students need to thrive in the workforce. And CCL is frequently seen as a nice-to-have, rather than an essential piece of education. The growing career exposure gap is evidence of this disconnect.
Closing this disconnect begins with helping people understand where to invest in their skills.
A new model: Career-connected learning as the solution
By ensuring basic needs are met, fostering belonging and esteem, and unlocking students’ potential, we equip students with the real-world skills they need to succeed. CCL benefits every student and should be seen as an essential part of education, not just a nice-to-have.
Personalized learning platforms, aptitude assessments, career identification, and skill-based learning tools provide the foundation for this transformation. But it’s the convergence among educators, employers, policymakers, and technology providers that will ultimately ensure that every student has the opportunity to realize their full potential.
My final thoughts: Maslow would remind us that education isn’t just about filling students’ heads with knowledge–it’s about inspiring them to dream, grow, and discover their limitless opportunities. This vision offers not just hope for individual students, but economic benefits for society as a whole.
Latest posts by eSchool Media Contributors (see all) -

Reimagining readiness in Indiana education
Key points:
Across the country, education is on the brink of significant change. As schools, districts, and policymakers grapple with the realities of a rapidly evolving workforce that requires discipline-specific knowledge, high-tech know-how, and hands-on skills, there is a growing recognition that the traditional approaches to preparing students for the real world no longer suffice.
This shift brings uncertainty and anxiety for district leaders here in Indiana. Change can be intimidating, especially when the stakes are as high as the future success of our students. Yet, this moment also holds immense potential to redefine what it means to truly ready them for a workplace that is continually reinventing itself.
To confront the challenges future-focused schools face, we’re sharing our approach from two distinct, but complementary, perspectives. One, from the superintendent of Eastern Hancock Schools, a small, rural district in Indiana that is deeply rooted in its community and focused on creating opportunities for students through strong local partnerships. The other, from the president and CEO of Project Lead The Way (PLTW), a national nonprofit organization that provides schools with innovative, hands-on, project-based STEM curriculum designed to develop critical skills and knowledge, while preparing students for careers beyond the classroom.
While we work in different contexts, our shared mission of preparing students and educators for an ever-changing world unites us. Together, we aim to highlight the excitement and possibility that change can bring when approached with readiness and purpose.
Redefining what it means to be ready
The jobs of tomorrow will demand far more than technical knowledge. As industries transform at warp speed, accelerated by AI, automation, and other technological advancements, many of today’s students will enter careers that don’t yet exist.
Preparing them for this reality requires educators to focus on more than just meeting academic benchmarks or prepping for the next standardized test. It demands fostering critical thinking, collaboration, communication skills, and, perhaps most importantly, confidence–characteristics many employers say are lacking among today’s graduates.
At Eastern Hancock, this preparation begins by creating opportunities for students to connect their learning to real-world applications. The district’s robust work-based learning program allows juniors and seniors to spend part of their day in professional placements across industries, such as construction, healthcare, engineering, and education, where they receive hands-on training. These experiences not only provide exposure to potential careers but also help students develop soft skills, including teamwork and problem-solving, that are critical for success in any field.
We also know that when students have earlier access to STEM learning and concepts, they are more inclined to pursue a STEM-driven career, such as computer science and engineering. Students in PLTW programs tackle meaningful problems as capable contributors, such as designing prototypes to address environmental issues, exploring biomedical innovations, and solving arising problems like cybersecurity and information safety.
Preparation, however, is about more than providing opportunities. Many students dismiss career paths because they lack the self-assurance to see themselves thriving in those roles. Both Eastern Hancock and PLTW work to break down these barriers–helping students build self-esteem, explore new possibilities, and develop confidence in chosen fields they may have once considered out of reach.
Empowering educators to lead with confidence
While students are at the heart of these changes, educators are the driving force behind them. For many teachers, however, change can feel overwhelming, even threatening. Resistance to new approaches often stems from a fear of irrelevance or a lack of preparation. To truly transform education, it is essential to support teachers with the resources, tools, and confidence they need to thrive in evolving classrooms.
PLTW’s professional development programs equip educators with training that builds their capacity to lead transformative learning experiences. Teachers leave PLTW sessions with practical strategies, a renewed sense of purpose, and the self-assurance to inspire their students through immersive classroom experiences.
At Eastern Hancock, the promise of growth drives efforts to support educators through professional development that aligns with their goals and the district’s vision. Teachers collaborate to set meaningful objectives, fostering a culture of innovation and shared purpose. This approach ensures that educators feel prepared not only to guide students but also to grow alongside them.
Blending a local approach and national reach illustrates how schools and organizations at every level can work together to address the shared challenge of preparing and supporting educators for the future. By empowering teachers with the tools and confidence they need, both Eastern Hancock and PLTW demonstrate how readiness can ripple outward to transform entire communities.
Delivering on the promises of education
Indiana’s reimagined graduation requirements offer schools the chance to redefine what it means to be truly prepared for the future. At Eastern Hancock, we’ve seen how aligned values–like those we share with PLTW–can inspire new ways of thinking about career readiness. We’re both deeply committed to ensuring students are equipped with the skills, experiences, and confidence they need to thrive in an unpredictable world.
Change may cause anxiety, but it also creates opportunities for innovation, growth, and excitement. When educators, students, and communities embrace readiness, the future of education becomes a source of hope and possibility-for Indiana and for the nation.
Latest posts by eSchool Media Contributors (see all) -

Education Department unveils guidance to make switching accreditors easier
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.The U.S. Department of Education unveiled guidance Thursday intended to make it easier for colleges to change accreditors and lifted a pause on its review of applications for new accrediting agencies.
The guidance comes a week after President Donald Trump signed an executive order to reshape the accreditation system and make it easier for new agencies to come onto the scene.
Trump’s order also took aim at accreditor criteria related to diversity, equity and inclusion and directed U.S. Education Secretary Linda McMahon to ensure colleges prioritize “intellectual diversity” among their faculty — a mandate that raised concerns about academic freedom among some higher education experts.
“President Trump’s Executive Order and our actions today will ensure this Department no longer stands as a gatekeeper to block aspiring innovators from becoming new accreditors nor will this Department unnecessarily micromanage an institution’s choice of accreditor,” McMahon said in a Thursday statement.
The Education Department also revoked guidance issued in 2022 that outlined a more rigorous review process for colleges to switch accreditors. The Biden-era guidance said the department would review whether a college wanted to change accreditors to lessen oversight and if moving to a new agency would strengthen its institutional quality, among other factors.
At the time, the Biden administration said the guidance sought to ensure colleges weren’t attempting to evade oversight from their current accreditor by switching to a new one.
The Trump administration’s new guidance, however, says the agency will reestablish “a simple process that will remove unnecessary requirements and barriers to institutional innovation.” Under the policy, colleges must submit a two-page form to serve as documentation of their prior accreditation, as well as “materials demonstrating reasonable cause” for changing or adding an accreditor.
The form includes a checklist of reasons institutions may seek to switch accreditors, along with a section requiring colleges to certify that they have not had their accreditation withdrawn or faced accreditor sanctions in the past two years. Colleges must also attach their most recent letter renewing their accreditation.
Wesley Whistle, project director for student success and affordability at New America, a left-leaning think tank, criticized the new process, arguing that making it easier to switch accreditors could lead institutions to move to agencies with less rigorous standards.
“This new guidance says all they have to do is fill out this checklist and provide them [with] their most recent letter of reaffirmation,” Whistle said. “That letter could be almost a decade old.”
Moreover, that letter wouldn’t indicate if a college is currently under investigation by its accreditor, Whistle said.
“Just because an institution may not be on probation today, they could still be under investigation,” Whistle added.
The Education Department also said it will have 30 days to approve an application to switch accreditors. If not, the change will be automatically granted unless a college failed to meet the eligibility requirements.
Whistle described the policy as a “30-day rubber stamp.”
“It’s irresponsible,” Whistle said. “There’s nearly 6,000 colleges and universities that are eligible for Title IV aid, so conducting even a modest review takes time and expertise.”
The Trump administration’s new guidance also permits colleges to switch to new accreditors if required by state law. Other recognized reasons include seeking an accreditor that better aligns with a college’s religious mission, changing the types of academic programs offered or objecting to current accreditation standards, including DEI requirements.
The Biden administration’s guidance was in part prompted by a 2022 Florida law requiring the state’s public colleges to switch accrediting agencies every accreditation cycle. This sparked concerns that colleges weren’t voluntarily choosing to switch to new accreditors, even though department regulations require colleges to be voluntary members of their accrediting agencies.
Still, the Education Department gave approval to at least one public Florida college to change accreditors in 2023, Inside Higher Ed reported. However, some have faced a time-intensive process that has required the submission of hundreds of pages of documents, according to the publication.
In the department’s new guidance, Deputy Under Secretary James Bergeron said the agency recognizes the significance of voluntary membership “but does not believe that an institution’s change in accrediting agency due to State law compliance constitutes involuntary membership.”
-

This week in 5 numbers: Sweeping higher ed bill advances
The federal funding that the Trump administration suspended to University of Pennsylvania in March, citing the Ivy League institution’s participation policies for transgender athletes. The U.S. Department of Education concluded this week Penn violated Title IX, though university leaders have said the institution is complying with current law and NCAA policies. -
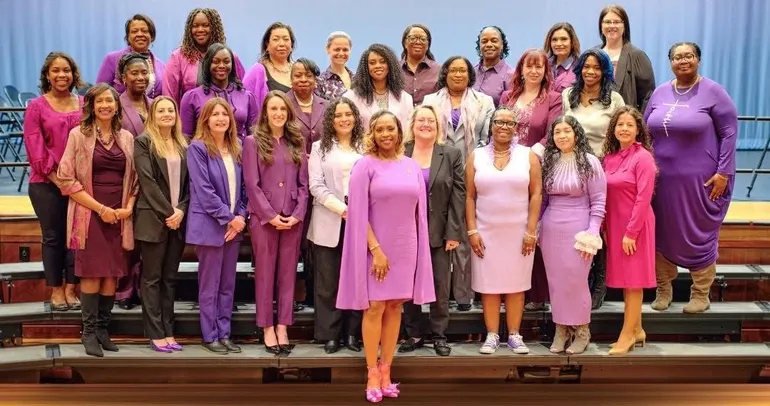

The Women of Westbury: How a district diversified leadership and strengthened schools
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.Tahira DuPree Chase is superintendent of Westbury Union Free School District In New York and a member of the Institute for Education Innovation.
Rising through the ranks to a school leadership role can be an arduous journey for even the most qualified female educators. And once we reach our final destination, we’re not always welcomed. We often face challenges our male counterparts never experience.
Only 30% of superintendents in the U.S. are female, and less than 1.5% are Black women. Across the country, female school leaders are targeted by unwarranted criticism, experience significant gender pay gaps, and receive less coaching and support than their male colleagues. We’re also a powerful force to be reckoned with — fierce, committed and experienced — and when united, we are reshaping education to better fit our students’ diverse needs.

Tahira DuPree Chase
Permission granted by Tahira DuPree Chase
To break down barriers, female leaders must find their own tribe of like-minded women who sit in a similar seat, both in the education field and outside of it. There are formal and informal, national, regional, and local support systems composed of incredible individuals who understand one another’s struggles. In these groups, we talk about our experiences, share ideas and uplift our fellow women.
Here in Long Island’s Westbury Union Free School District, that collective commitment on a local level is powering our schools forward.
Westbury is an anomaly in K-12 education, with women in 93% of administrative roles. Under the leadership of “The Women of Westbury,” otherwise known as “WOW,” the district’s graduation rate has skyrocketed to 90% in a district where nearly 70% of children qualify for free or reduced-price lunch. We have implemented top-tier security measures to better protect our students, improved facilities and operations, and done it all while successfully managing our schools’ finances.
Building this team of professionals and helping them thrive hasn’t been without its challenges, but by aligning our recruitment and retention strategies with three critical guidelines, we’ve reached this incredible time in Westbury’s history.
Hire with an open mind
At Westbury, we knew we needed to diversify our leadership, but the goal did not dictate our hiring process. We followed a traditional interview path, and it just so happened that female applicants rose to the top. The individuals we’ve hired are credentialed, well-versed and highly qualified. These aren’t so-called “DEI hires”; they are common-sense hires.
As a Black female leader in education, I’ve had my credentials questioned due to unconscious — and sometimes blatant — bias. I’m required to hold multiple advanced degrees and jump through endless hoops to be on the same playing field as many of my male counterparts in the hiring process. Based on my own experiences, I find it no surprise that female candidates often self-select from applying for management roles, because they believe men have an advantage or assume they lack the experience to meet every vague qualification listed in the job announcement.
It has been disheartening to watch other women struggle with similar challenges and become disenchanted with the entire education system. That’s why Westbury has strived to create a more equitable space where all individuals are encouraged to take the next step in their careers.
Encourage leaders to embrace their vulnerability
Superintendents are expected to shoulder a heavy load in their role, but for female leaders, the stress can feel overwhelming. Ninety-five percent of female administrators said they struggled to find a healthy work-life balance and were forced to make personal and professional sacrifices their male colleagues did not.
At Westbury, we stress the importance of self-care for all educators and administrators in the district by hosting wellness fairs and offering a mental health day focused solely on our team’s well-being. A board-certified psychotherapist is on staff to provide social-emotional support on both a group and individual level. In addition, we help school leaders develop their own professional support system that includes not just their fellow women, but male allies who have their best interests at heart.
We have found that when we provide educators the space to find that self-care sweet spot, they better maintain their focus, think more clearly, and allow ideas to flow. In turn, our schools become centers of innovation where we are improving our students’ academic experience.
Help lift up the women behind you
As female school leaders, we have an obligation to empower the next generation of women. Becoming a mentor to future leaders and watching them thrive is one of the greatest honors we can experience in our leadership roles. When someone trusts me to be their sounding board and values my insights, it fuels me to keep moving forward.
All leaders in the district are automatically assigned a mentor to help guide them in their administrative path. I’ve also extended myself to be a secondary mentor if a leader requests extra support. Furthermore, Westbury encourages our leaders to consider roles with professional organizations, like the Institute for Education Innovation and AASA, to offer their expertise to female colleagues nationwide.
This professional community is incredibly powerful. Research has found that women who have a close inner circle of female colleagues are more likely to secure leadership positions, have higher pay and greater authority. In comparison, there is no link for men’s success in terms of the gender composition of their networks.
Over the years, the “Women of Westbury” have encountered their fair share of detours, roadblocks and bumps to get to a place where their talents and expertise are celebrated. Today, we’re not just a support system for each other, we are paving the way for the women coming up behind us to receive the roles they rightly deserve.
We recognized that diversifying our administration is one of the best things we can do for students, ensuring they see themselves reflected in their leaders and understand there is no limit to what they can achieve in their future careers.


