This post is one of many, related to my participation in Harold Jarche’s Personal Knowledge Mastery workshop.
Sometimes we think we need experts, sure. But we shouldn’t dismiss the power of finding fellow seekers. There are times when an expert might help us, but also times they leave us behind or otherwise are unable to contribute to our growth. They may not have sufficient beginner’s mind or childlike curiosity. We may need the empathy and lack of judgement that can be possible with someone who is still wrestling through these same ideas, themselves.
I’ve often tried to coach students in showing them the ways that they can help their professors, when they often think their only possible role is as one being the receiver of help. Similarly, when we are in a seeking role, we aren’t able to see the ways we can add value to the learning process for ourselves and others. We can wrestle with trying to give the appearance of competence versus staying in the seeker’s mindset and focusing on curiosity and wonder. This hesitance at potentially looking foolish to others in our incompetence can not only hold us back from learning, but also cause us to feel alone. It is vital to connect with other seekers and experience the benefits of those roles within our networks.
Jarche writes:
Your fellow seekers can help you on a journey to become a Knowledge Catalyst, which takes parts of the Expert and the Connector and combines them to be a highly contributing node in a knowledge network. We can become knowledge catalysts — filtering, curating, thinking, and doing — in conjunction with others. Only in collaboration with others will we understand complex issues and create new ways of addressing them. As expertise is getting eroded in many fields, innovation across disciplines is increasing. We need to reach across these disciplines.
I sure hope Harold is right about cross-disciplinary innovation expanding, as we need that more than ever. In Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World, David Epstein instructs:
Compare yourself to yourself yesterday, not to younger people who aren’t you. Everyone progresses at a different rate, so don’t let anyone else make you feel behind. You probably don’t even know where exactly you’re going, so feeling behind doesn’t help. Instead… start planning experiments.
The Value of Experiments
What are experiments? Epstein describes them by introducing physicist Andre Geim and his “Friday night experiments” (FNEs). It was through these endeavors that Geim won not a fancy Nobel Prize, but an Ig Nobel (which Geim shares with collaborator M V Berry via their Of Flying Frogs and Levitrons piece, available through the Internet Wayback Machine). The Ig Nobel is bestowed on those who at first seem like they’re doing something ridiculous. From Wikipedia:
The Ig Nobel Prize (/ˌɪɡ noʊˈbɛl/) is a satirical prize awarded annually since 1991 to promote public engagement with scientific research. Its aim is to “honor achievements that first make people laugh, and then make them think.” The name of the award is a pun on the Nobel Prize, which it parodies, and on the word “ignoble”.
A serious researcher, Geim is (as of 2025) the only person to both win a Nobel and an Ig Nobel prize. Those who are in line to potentially win an Ig Nobel are first informed, such that they can determine if the satirical nature of the designation might be detrimental to their research careers. For his FNEs, Geim was experimenting with levitating frogs with magnets and was awarded the satirical prize for that less “serious” work. Through another FNE, Geim wound up developing “gecko tape,” which was based on the properties of geckos’ feet. These less serious experiments contributed to his more “serious” research, which ultimately led to his prestigious receipt of a Nobel Prize.
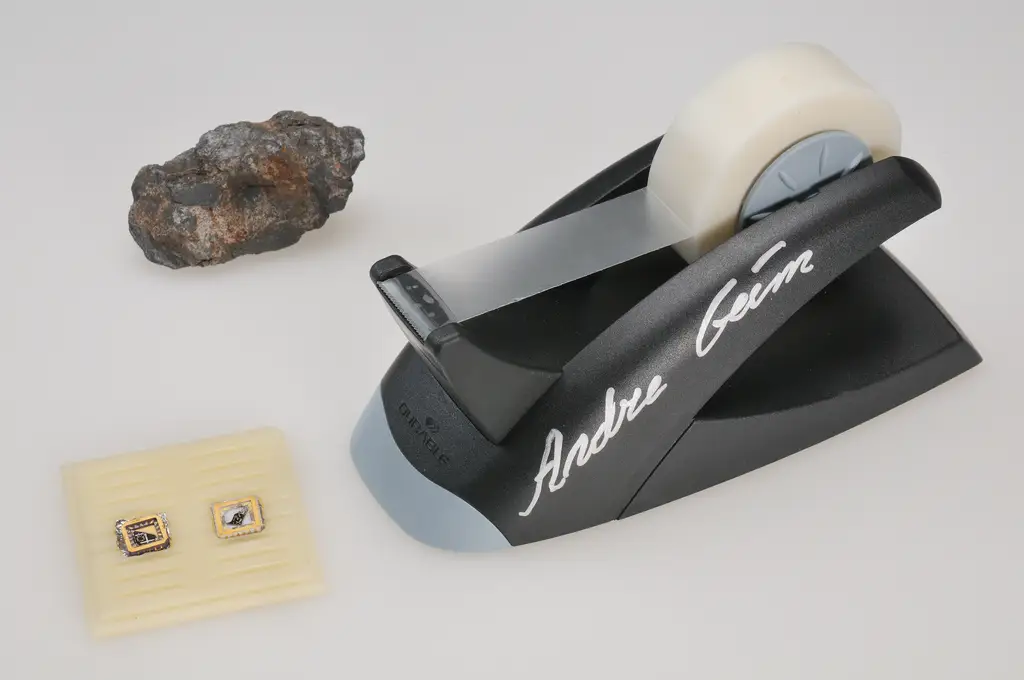

This 2010 image of a lump of graphite, a graphene transistor, and a tape dispenser, items that were given to the Nobel Museum by researchers Andrew Geim and Konstantin Novoselov to reflect their Nobel research. Before their discoveries, it was believed to be impossible to create material that could conduct electricity in such thin layers as graphene is now able to, which has opened up even more possibilities in both material science and electronics.
In his first-person narrative from his 2010 Nobel Prize, he describes how his Russian literature tutor critiqued his writing for trying too hard to parrot experts vs trusting his own intuition. Geim writes:
My tutor said that what I was writing was good but it was clear from my essays that I tried to recall and repeat the thoughts of famous writers and literature critics, not trusting my own judgement, afraid that my own thoughts were not interesting, important or correct enough. Her advice was to try and explain my own opinions and ideas and to use those authoritative phrases only occasionally, to support and strengthen my writing. This simple advice was crucial for me – it changed the way I wrote. Years later I noticed that I was better at explaining my thoughts in writing than my fellow students.
I once was able to interview a recipient of the Ig Nobel for Teaching in Higher Ed: Episode 591 – Rethinking Student Attendance Policies for Deeper Engagement and Learning with Simon Cullen and Danny Oppenheimer. Danny is the one of these two collaborators with this great honor. Take a look at the incredible title of the piece that won him the Ig Nobel: Consequences of Erudite Vernacular Utilized Irrespective of Necessity: Problems with Using Long Words Needlessly, by Daniel M. Oppenheimer Imagine how bummed I was that despite me being so excited to ask him more about it, my nerves got the best of me and I entirely forgot to ever mention it during our conversation for the podcast.
Researching Versus Searching
Epstein describes in Range the ways in which the novice mindset gets weaved together with the expert mindset in such transformative ways. He reveals how us being willing to be vulnerable in our not knowing and early experimentation through an art historian’s description of how Geim is emblematic of this willingness to stay in the not knowing longer. Epstein tells how:
Art historian Sarah Lewis studies creative achievement, and described Geim’s mindset as representative of the “deliberate amateur.” The word “amateur,” she pointed out, did not originate as an insult, but comes from the Latin word for a person who adores a particular endeavor. “A paradox of innovation and mastery is that breakthroughs often occur when you start down a road, but wander off for a ways and pretend as if you have just begun,” Lewis wrote.
My friend, Naomi, and I always joke with each other about our “rabbit trail” emails back and forth to each other. I often wish there were a better expression that more precisely evokes the delight that can come from a diversion. Two years before he won the Nobel, Geim was asked to explain his research process. He described how instead of always going deep, he likes to stay in the shallow and move around. He described:
I don’t want to carry on studying the same thing from cradle to grave. Sometimes I joke that I am not interested in doing re-search, only search.
Seeking as Doing
Jarche illustrates how when trust is low that doers, connectors, and catalysts can address the limitations of credibility that exist in the roles of professors, stewards, and experts. He asserts: We Need Less Professing and More Doing. He describes how someone like Zeynep Tukekci can be not a medical professional herself, but so gifted at weaving “knowledge from many disciplines into a coherent narrative.”
Jarche stressing the doing part made me think of Mike Caulfield, who says that novice fact checkers need not to solely focus on critical thinking, but he would rather we all get far better at teaching critical doing skills. I’ve been having a blast following Mike’s own critical doing skills as he documents his experiments with in what ways AI may be able to help with critical thinking/doing. He is in the process of learning out loud, as he identifies the less helpful approaches for trying to use AI for fact checking and where he sees promise for achieving better results than most people would be able to come up with, themselves.
In a lot of ways, I’m seeing Harold Jarche’s Personal Knowledge Mastery Workshop as my own set of small experiments. In Dave’s recent Coaching for Leaders Episode 747, he interviews Laure Le Cunff, author of Tiny Experiments: How to Live Freely in a Goal-Obsessed World. Le Cunff explains how:
The secret to designing growth loops is not better knowledge or skills, but your ability to think about your own thinking, question your automatic responses, and know your mind.
Sounds a lot like PKM to me… Until next time. For now, it is dinnertime around here and we ordered Cheesecake Factory. It’s good to be back home. In the meantime, here’s for our individual and collective ability to see clearly now, as we practice PKM together.