Author: admin
-
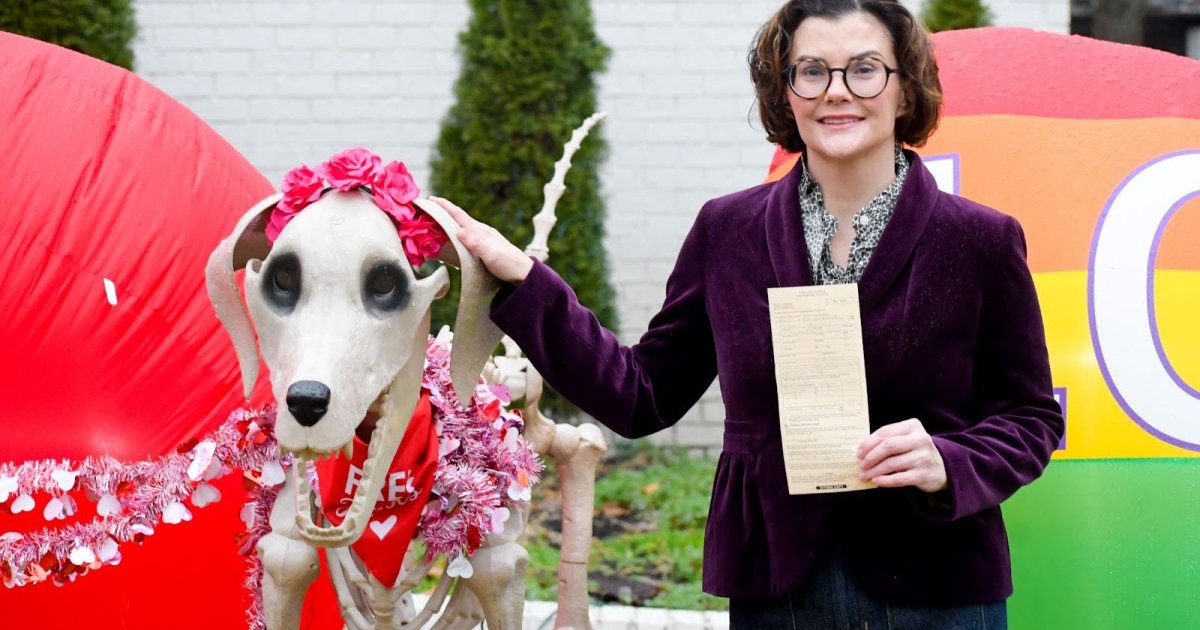

VICTORY! Charges dropped against TN woman cited for using skeletons in Christmas decorations
GERMANTOWN, Tenn., March 10, 2025 —Less than a month after the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression filed a First Amendment lawsuit against Germantown, Tennessee, the city has voluntarily dismissed charges against its resident Alexis Luttrell for keeping skeletons in her yard after Halloween.
“We are thrilled that Alexis will no longer have to stand trial because government officials disapproved of her decorative skeletons,” said FIRE attorney Colin McDonell. “Punishing Alexis for her choice of expressing holiday cheer would have been a bone-chilling restriction on her First Amendment rights.”
“I’m beyond pleased that I’m no longer on trial for nothing more than decorating my yard in a way that City Hall didn’t like,” said Alexis. “That these charges were ever brought in the first place was utterly surreal, but I’m glad that they’re dead and buried — and my skeletons aren’t.”
Alexis set up a decorative skeleton and skeleton dog in her front yard to celebrate Halloween last year, and then redressed them for Election Day and Christmas as well. But in December, a Germantown code officer left a notice that said that she had violated Ordinance 11-33, which says that yard decorations “shall not be installed or placed more than 45 days before the date of the holiday” and must be removed within “30 days, following the date of the holiday.”
On Jan. 6, she received a citation from the Memphis suburb saying she was still in violation and that she would have to appear before a local judge. If found guilty, she would have been subject to fines and a court order prohibiting skeletons in her holiday displays.
All this violated Alexis’s First Amendment rights. Americans have the right to put up skeletal decorations in September, October, November, December —- whenever they want. And by refusing to acknowledge Alexis’s Christmas-themed skeletons as Christmas decorations, the city engaged in viewpoint discrimination by enforcing an arbitrary and narrow idea of the “right” way to celebrate Christmas.
COURTESY PHOTOS OF ALEXIS AND HER HOLIDAY DISPLAYS
FIRE jumped into action, agreeing to represent Alexis in Germantown municipal court and filing a federal lawsuit seeking to overturn the Germantown ordinance on First Amendment grounds.
“The Holiday Decorations Ordinance violates the First Amendment,” the civil rights complaint read. “It is a content-based and viewpoint-discriminatory restriction on speech. It is not narrowly tailored to a compelling government interest. And it is unconstitutionally vague, allowing government officials to arbitrarily punish holiday expression based on their subjective beliefs.”
Alexis’s municipal court date was originally scheduled for Feb. 13, but it was postponed for a month after FIRE filed the federal lawsuit. But ahead of the March 13 hearing, the city’s attorneys dropped the charges, meaning Alexis is no longer at immediate risk of being punished for exorcising — er, exercising her rights.
FIRE’s federal lawsuit challenging Germantown’s ordinance is still pending, but with charges dropped, Alexis’s skeletons will stay up and dressed to the nines as the lawsuit progresses through the courts. Alexis has continued dressing the skeletons to celebrate every new holiday season. Last month, it was Valentine’s Day, now they’re dressed for St. Patrick’s Day, and Easter and Pride Month displays are set to follow.
“Holidays come and go, but the First Amendment is here year-round,” said McDonell. “We look forward to seeing all the ways Alexis will express herself for the holidays this year, without government interference.”
The Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression (FIRE) is a nonpartisan, nonprofit organization dedicated to defending and sustaining the individual rights of all Americans to free speech and free thought — the most essential qualities of liberty. FIRE educates Americans about the importance of these inalienable rights, promotes a culture of respect for these rights, and provides the means to preserve them.
CONTACT:
Alex Griswold, Communications Campaign Manager, FIRE: 215-717-3473; [email protected]
-

VICTORY! Charges dropped against Tenn. woman cited for using skeletons in Christmas decorations
GERMANTOWN, Tenn., March 10, 2025 —Less than a month after the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression filed a First Amendment lawsuit against Germantown, Tennessee, the city has voluntarily dismissed charges against its resident Alexis Luttrell for keeping skeletons in her yard after Halloween.
“We are thrilled that Alexis will no longer have to stand trial because government officials disapproved of her decorative skeletons,” said FIRE attorney Colin McDonell. “Punishing Alexis for her choice of expressing holiday cheer would have been a bone-chilling restriction on her First Amendment rights.”
“I’m beyond pleased that I’m no longer on trial for nothing more than decorating my yard in a way that City Hall didn’t like,” said Alexis. “That these charges were ever brought in the first place was utterly surreal, but I’m glad that they’re dead and buried — and my skeletons aren’t.”
Alexis set up a decorative skeleton and skeleton dog in her front yard to celebrate Halloween last year, and then redressed them for Election Day and Christmas as well. But in December, a Germantown code officer left a notice that said that she had violated Ordinance 11-33, which says that yard decorations “shall not be installed or placed more than 45 days before the date of the holiday” and must be removed within “30 days, following the date of the holiday.”
On Jan. 6, she received a citation from the Memphis suburb saying she was still in violation and that she would have to appear before a local judge. If found guilty, she would have been subject to fines and a court order prohibiting skeletons in her holiday displays.
All this violated Alexis’s First Amendment rights. Americans have the right to put up skeletal decorations in September, October, November, December —- whenever they want. And by refusing to acknowledge Alexis’s Christmas-themed skeletons as Christmas decorations, the city engaged in viewpoint discrimination by enforcing an arbitrary and narrow idea of the “right” way to celebrate Christmas.
COURTESY PHOTOS OF ALEXIS AND HER HOLIDAY DISPLAYS
FIRE jumped into action, agreeing to represent Alexis in Germantown municipal court and filing a federal lawsuit seeking to overturn the Germantown ordinance on First Amendment grounds.
“The Holiday Decorations Ordinance violates the First Amendment,” the civil rights complaint read. “It is a content-based and viewpoint-discriminatory restriction on speech. It is not narrowly tailored to a compelling government interest. And it is unconstitutionally vague, allowing government officials to arbitrarily punish holiday expression based on their subjective beliefs.”
Alexis’s municipal court date was originally scheduled for Feb. 13, but it was postponed for a month after FIRE filed the federal lawsuit. But ahead of the March 13 hearing, the city’s attorneys dropped the charges, meaning Alexis is no longer at immediate risk of being punished for exorcising — er, exercising her rights.
FIRE’s federal lawsuit challenging Germantown’s ordinance is still pending, but with charges dropped, Alexis’s skeletons will stay up and dressed to the nines as the lawsuit progresses through the courts. Alexis has continued dressing the skeletons to celebrate every new holiday season. Last month, it was Valentine’s Day, now they’re dressed for St. Patrick’s Day, and Easter and Pride Month displays are set to follow.
“Holidays come and go, but the First Amendment is here year-round,” said McDonell. “We look forward to seeing all the ways Alexis will express herself for the holidays this year, without government interference.”
The Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression (FIRE) is a nonpartisan, nonprofit organization dedicated to defending and sustaining the individual rights of all Americans to free speech and free thought — the most essential qualities of liberty. FIRE educates Americans about the importance of these inalienable rights, promotes a culture of respect for these rights, and provides the means to preserve them.
CONTACT:
Alex Griswold, Communications Campaign Manager, FIRE: 215-717-3473; [email protected]
-

Building Infrastructure for Non-Degree Credentials
Title: A Global Review of Non-degree Credential Quality Frameworks: Matching Aspirations to Available Data
Authors: Kyle Albert and Thomas Weko
Source: George Washington University (GWU) Program on Skills, Credentials & Workforce Policy (PSCWP)
With the continued increase of alternative, non-degree credentials, education and professional stakeholders have developed quality frameworks meant to guide these credentials.
The authors of a new report from PSCWP examine and evaluate criteria and data used in current credential quality frameworks. The brief highlights the growing need for institutions to consider and build out data sources for these non-degree frameworks. Whereas foundations, nonprofits, and policy organizations shape frameworks in the United States, government ministries do so outside of the U.S. The U.S. does not recognize non-degree credentials in the Higher Education Act, meaning that such credentials are not required to be reported to the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System and other government databases.
A 2024 GWU/UPCEA survey showed that for non-degree, credit-based credentials, quality standards and procedures are primarily established at the institutional level and are modified forms of standards for degree programs. For non-degree, non-credit credentials, however, there is a “far greater decentralization of responsibility” (p.15). Standards for these programs are often established at the faculty or departmental level, and only about 10 percent of respondents reported that their institution could link learner data from these programs to external data systems.
Given the variation among commonly used datasets as well as processes within institutions, private actors hold substantial power in refining quality frameworks. The authors suggest the following ways to improve data standardization when it comes to quality frameworks:
- Use consistent language: Using consistent language across non-degree credentials can support organizations not only in how they describe and distinguish between programs but also in how they measure outcomes.
- Make data accessible: Membership and research-based organizations can empower the field to be more transparent and develop legal and technical guidelines for data sharing beyond the confines of the organization.
To see the full report, click here.
—Kara Seidel
If you have any questions or comments about this blog post, please contact us.
-

Simulations and AI: Critical Thinking Improvement
Reading Time: 4 minutesAs an educator teaching undergraduates and graduates, both online and face-to-face, it’s always a challenge to find meaningful ways to engage students. Now that artificial intelligence has come into play, that challenge has become even greater. This has resulted in a need to address ways to create “AI-proof” assignments and content.
Simulations in different types of courses
According to Boston College, simulations are designed to engage students “directly with the information or the skills being learned in a simulated authentic challenge.” In my teaching over the past decade plus, I have gone from using simulations in one primary operations management course to using them in almost every course I teach. And I don’t necessarily use them in a stand-alone assignment, although they can be used as such. How I use a simulation is course dependent.
Face-to-face
In some face-to-face courses, I will run the simulation in class with everyone participating. Sometimes I will have teams work in a “department,” or have true, open discussions. Sometimes I will run the room, ensuring every single student is paying attention and contributing. Using simulations in this fashion gives flexibility in the classroom. It shows me who truly gets the concepts and who is going through the motions. The dynamic of the class itself can dictate how I run the simulation.
Online
In online courses, I typically assign simulation work. This can be one simulation assignment or a progressive unit of simulations. It’s a great way to see students improve as they move through various concepts, ideas, and applications of the topics covered. Creating assignments which are both relative to the simulation and comparative to the work environment make assignments AI-proof. Students must think about what they have actually done in class and relate it to their workplace environment and/or position.
Why simulations work for all levels
There are many simulations that can be used and incorporated in both undergraduate and graduate level courses. As much as we don’t think of graduate students relying on AI to complete work, I have seen this happen multiple times. The results aren’t always ideal. Using simulations at the graduate level, and ensuring your assignments reflect both the simulation and real-world comparisons, can help your students use AI to gather thoughts, but not rely on it for the answers.
Student benefits
Using simulations will have many benefits for your students. I have gotten feedback from many students over the years regarding their ability to make decisions and see the results that simulations give. My capstone students often want to continue running the simulation, just to see how well they can do with their “business.” I have had students in lower-level management courses ask me how they can get full access to run these when I have them as “in-class only” options. The majority of feedback includes:
- Anything is better than lecture!
- Being able to see how students’ decisions impact other areas can be very helpful for them. They actually remember it, enforcing more than reading or watching can do.
- Students want more simulations throughout their courses, rather than just one or two. They will have the ability to make those decisions and see those impacts. And they feel it will prepare them even more for the workforce.
As a retention and engagement tool, simulations seem to be one of the best I have found. Are there students that don’t like them? Yes, there always are. Even so, they’re forced to think through solutions and determine a best course of action to get that optimal result. From an instructor’s perspective, there’s nothing better than seeing those wheels turn. Students are guided on how to recover from an issue, and are advised on what may happen if different solutions were attempted. The questions gained are often better than the results.
Instructor benefits
For instructors, there are many benefits. As I stated earlier, you can see improvements in student behavior. They ask questions and have a defined interest in the results of their actions. In classes when you have teams, it can become friendly competition. If they are individual assignments, you get more questions, which is something we always want to see. More questions show interest.
Ease of use
Although I usually include recorded instructions and tips for simulations in my online courses, I prefer my personal recordings, since I also give examples relevant to student majors and interests. For example, in an entrepreneurial class, I would go through a simulation piece and include how this might affect the new business in the market vs. how it might impact an established business.
Auto-grading
When assigning simulations, they are usually auto-graded. This can drastically lighten our workload. I personally have around 150-200 students each term, so being able to streamline the grading function is a huge benefit. However, with this, there are trade-offs. Since I also create simulation-based questions and assignments, there are no textbook answers to refer to. You must know the simulations and be the content expert, so you can effectively guide your students.
Thoughtful responses
AI can be a great tool when used productively. But seeing overuse of the tool is what led me to learn more simulations. This adjustment on my end has resulted in students presenting me with more thoughtful, accurate, and relevant responses. Feedback from students has been positive.
Sims for all industries
An additional benefit of simulations is that there are basically sims for all industries. Pilot and healthcare sims have existed for a very long time. But even if you only have access to one or two, you have the ability to make it relatable to any field. If you’re like me and teach a variety of classes, you can use one simulation for almost any class.
Overall success
I was using simulations before AI became so influential. The extensive and current use of AI has driven me to use more simulations in all of my courses. By adjusting what tools I use, I have been able to encourage more thorough problem solving, active listening and reasoning. Plus, I get strategic and effective questions from my students. The overall results include intense engagement, better critical thinking skills, and content retention.
Written by Therese Gedemer, Adjunct Instructor and Workforce Development Trainer, Marian University, Moraine Park Tech College and Bryant & Stratton College
-

Gettysburg College – Edu Alliance Journal
March 10, 2025, by Dean Hoke: This profile of Gettysburg College is the fifth in a series presenting small colleges throughout the United States.
Background
Founded in 1832, Gettysburg College is a private liberal arts institution located in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The 225-acre campus is steeped in history, having served as a field hospital during the Battle of Gettysburg. An alumnus (David Wills, Class of 1851) invited President Abraham Lincoln to deliver the Gettysburg Address in 1863, tying the college to this pivotal moment in American history. Gettysburg’s historical significance (from its Civil War connections to President Dwight D. Eisenhower’s post-presidency involvement on its Board of Trustees) contributes to its distinctive identity.
The college is known for its rigorous academics, close faculty-student mentorship, and emphasis on leadership development. Gettysburg maintains a 10:1 student-to-faculty ratio, ensuring personalized instruction. It enrolls approximately 2,200 students from across the country and abroad, fostering a diverse and engaged learning community.
Curricula
Gettysburg College offers more than 40 majors and 40 minors, spanning the arts, humanities, sciences, and social sciences. Popular programs include Business, Political Science, Economics, Psychology, and Health Sciences. The college is home to the Eisenhower Institute provides students with opportunities to engage in public policy and leadership development, while the Civil War Era Studies minor leverages the college’s historical location for in-depth academic exploration. Five years after graduation (as of Fall 2021), 45 percent of this graduating class had received and/or were enrolled in a graduate/professional degree program five years after graduating from Gettysburg. Graduation rates have remained high. The latest 6-year graduation rate was 83%
Strengths
- Strong Post-Graduate Outcomes: 98% of graduates are employed or enrolled in graduate school within a year of graduation.
- Experiential Learning: Over 78% of students complete at least one internship, and 55% participate in faculty-mentored research.
- Leadership Development: Programs such as the Eisenhower Institute provide hands-on training in policy and governance.
- Historical and Civic Engagement: The college’s proximity to the Gettysburg Battlefield and its Civil War Era Studies program offer students a unique educational experience.
Weaknesses
- Financial Resources: Gettysburg’s endowment is moderate compared to some peer institutions, affecting the availability of internal funding for scholarships and program expansion.
- Enrollment Challenges: The college has seen a gradual decline in student enrollment over the past decade, from a peak of over 2,700 students in 2013 to approximately 2,207 in 2024. Gettysburg’s rural location and relatively small town setting may also be a hurdle in recruiting students who prefer an urban environment or a more expansive social scene.
- Diversity Initiatives: About 21% of undergraduates are domestic students of color, and 14% are international. While improving, the college’s domestic student diversity (21%) lags behind national averages.
Economic Impact
Gettysburg College serves as a major economic engine in its local and regional economy. As one of the largest employers in Adams County, the college provides hundreds of jobs for faculty, administrators, and staff, injecting substantial income into the community through payroll and benefits. The college also attracts thousands of visitors annually for events like Orientation, Family Weekend, Homecoming, and Commencement, as well as academic conferences and cultural events at its facilities (such as the Majestic Theater, a college-owned performing arts center). Also, Gettysburg College’s investment in revitalizing downtown Gettysburg through projects like the Majestic Theater restoration and its support of local internships/service programs help strengthen the social and economic fabric of the area.
Broader economic analyses highlight the significant spillover effects of colleges like Gettysburg. Many graduates remain in or return to Pennsylvania, joining the workforce and paying taxes. (Statewide data from the Association of Independent Colleges & Universities of PA suggests that if ~57% of one graduating class stays in Pennsylvania to work, that cohort would add about $1.5 billion to the state economy over their careers.
Enrollment Trends
As of Fall 2024, Gettysburg College enrolls approximately 2,207 students. Over the past five years, undergraduate enrollment has declined from a peak of 2,500 to 2,200. The shift is attributed to demographic changes and increasing competition among liberal arts colleges. Efforts to stabilize enrollment include enhanced recruitment strategies and expanded financial aid options.
In the Fall of 2022, Gettysburg College launched and began offering classes for its first part-time master’s degree program, the Master of Arts in American History, in partnership with the Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History. This fully online, 30-credit program is designed for K-12 educators, district supervisors, librarians, museum professionals, and National Park Service employees affiliated with the Gilder Lehrman Institute. It is growing; new graduate programs are in the process of being offered.
Degrees Awarded by Major
In the 2023 graduating class, Gettysburg College conferred degrees across the various disciplines.

Alumni
According to the college, Gettysburg College has an alumni network of over 32,000 graduates. Approximately 25% of alumni reside in Pennsylvania, with a significant concentration in the greater Washington, D.C., and Philadelphia areas. The college’s alumni are well-represented in fields such as business, law, government, education, and the arts. Career services and networking opportunities ensure that graduates remain engaged and professionally supported.
Notable Alumni
- Michael Bishop (Class of 1957): Nobel Prize-winning biomedical researcher in virology and cancer research.
- Fred Fielding (Class of 1961): 9/11commissioner and White House Council for President Ronald Regan and George W. Bush.
- Carol Bellamy (Class of 1963): Former Executive Director of UNICEF and Peace Corps Director.
- Bruce S. Gordon (Class of 1968): Former President of the NAACP.
- Kathryn Wolford (Class of 1979: Former President of the McKnight Foundation and Past President of Lutheran World Relief.
- Carson Kressley (Class of 1991): Television personality, fashion expert, and actor.
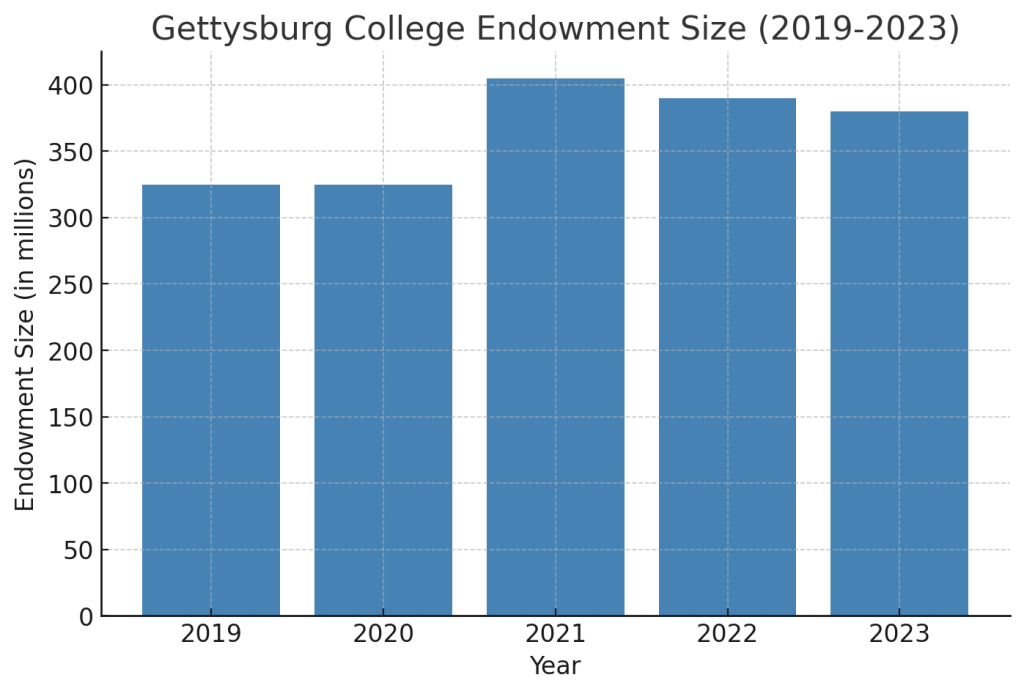
Endowment and Financial Standing
As of 2023, Gettysburg College’s endowment stands at approximately $380–$400 million. While this represents growth over the past five years, the college remains tuition-dependent, with about 80% of its operating budget coming from student fees. Gettysburg College is stable but budget-conscious. Forbes’ 2023 financial health evaluation gave Gettysburg an approximate “B–” grade, with a financial GPA of around 2.71 on a 4.5 scale, indicating that while the college is not financially distressed.
Why is Gettysburg College Important
- Academic Excellence: The college provides a strong liberal arts foundation with small class sizes and individualized instruction.
- High Graduate Success Rates: With 98% of graduates employed or in graduate school within a year, Gettysburg’s outcomes are among the best for liberal arts colleges.
- Leadership Development: Programs such as the Eisenhower Institute and Center for Public Service prepare students for civic engagement and public service careers.
- Historical Significance and Cultural Impact: Its Civil War connections and Lincoln’s legacy make it a unique institution with a strong civic mission. Also Gettysburg College plays a key role in supporting local businesses, employment, and tourism in Gettysburg and beyond.
With its strong commitment to liberal arts education, leadership development, and historical legacy, Gettysburg College remains a distinguished institution that prepares students for success in an ever-changing world.
Dean Hoke is Managing Partner of Edu Alliance Group, a higher education consultancy, and a Senior Fellow with the Sagamore Institute. He formerly served as President/CEO of the American Association of University Administrators (AAUA). With decades of experience in higher education leadership, consulting, and institutional strategy, he brings a wealth of knowledge on small colleges’ challenges and opportunities. Dean, along with Kent Barnds, are co-hosts for the podcast series Small College America. Season two begins on March 11, 2025.
-

Trump Budget Will Reveal How Extensive ED is Dismantled in 2025
Some time this March, President Trump’s US Budget proposal will be submitted. It would not be out of the realm of possibility that budget cuts to the US Department of Education exceed 70 percent if the $1.7 Trillion Student Loan Portfolio is transferred to the US Treasury. President Biden’s 2024 Budget for the US Department of Education was published March 11, 2024. This is what the proposal typically looks like.
-

How does the higher education sector sustain digital transformation in tough times?
Higher education institutions are in a real bind right now. Financial pressures are bearing down on expenditure, and even those institutions not at immediate risk are having to tighten their belts.
Yet institutions also need to continue to evolve and improve – to better educate and support students, enable staff to do their teaching and research, strengthen external ties, and remain attractive to international students. The status quo is not appealing – not just because of competitive and strategic pressures but also because for a lot of institutions the existing systems aren’t really delivering a great experience for students and staff. So, when every penny counts, where should institutions invest to get the best outcomes? Technology is rarely the sole answer but it’s usually part of the answer, so deciding which technologies to deploy and how becomes a critical organisational capability.
Silos breed cynicism
Digital transformation is one of those areas that’s historically had a bit of a tricky reputation. I suspect your sense of the reason for this depends a bit on your standpoint but my take (as a moderately competent user of technology but by no means expert) is that technology procurement and deployment is an area that tends to expose some of higher education’s historic vulnerabilities around coordinated leadership and decision-making, effective application of knowledge and expertise, and anticipation of, and adaptability to change.
So in the past there’s been a sense, not of this exact scenario, but some variation on it: the most senior leaders don’t really have the knowledge or expertise about technology and are constantly getting sold on the latest shiny thing; the director of IT makes decisions without fully coordinating with the needs and workflows of the wider organisation; departments buy in tech for their own needs but don’t coordinate with others. There might even be academic or digital pedagogy expertise in the organisation whose knowledge remains untapped in trying to get the system to make sense. And then the whole thing gets tweaked and updated to try to adapt to the changing needs, introducing layer upon layer of complexity and bureaucracy and general clunkiness, and everyone heaves a massive sigh every time a new system gets rolled out.
This picture is of course a cynical one but it’s striking in our conversations about digital transformation with the sector how frequently these kinds of scenarios are described. The gap between the promise of technology and the reality of making it work is one that can breed quite a lot of cynicism – which is the absolute worst basis from which to embark on any journey of change. People feel as if they are expected to conform to the approved technology, rather than technology helping them do their jobs more effectively.
Towards digital maturity
Back in 2023 Jisc bit the bullet with the publication of its digital transformation toolkit, which explicitly sought to replace what in some cases had been a rather fragmented siloed approach with a “whole institution” framework. When Jisc chief executive Heidi Fraser-Krauss speaks at sector events she frequently argues that technology is the easy bit – it’s the culture change that is hard. Over the past two years Jisc director for digital transformation (HE) Sarah Knight and her team have been working with 24 institutions to test the application of the digital transformation framework and maturity model, with a report capturing the learning of what makes digital transformation work in practice published last month.
I book in a call with Sarah because I’m curious about how institutions are pursuing their digital transformation plans against the backdrop of financial pressure and reductions in expenditure. When every penny counts, institutions need to wring every bit of value from their investments, and technology costs can be a significant part of an institution’s capital and non-staff recurrent expenditure.
“Digital transformation to us is to show the breadth of where digital touches a university,” says Sarah. “Traditionally digital tended to sit more with ‘digital people’ like CIOs and IT teams, but our framework has shown how a whole-institution approach is needed. For those just starting out, our framework helped to focus attention on the breadth of things to consider such as digital culture, engaging staff and students, digital fluency, capability, inclusivity, sustainability – and all the principles underpinning digital transformation.”
Advocating a “whole institution approach” may seem counter-intuitive – making what was already a complicated set of decisions even more so by involving more people. But without creating a pipeline of information flow up, down and across the institution, it’s impossible to see what people need from technology, or understand how the various processes in place in different parts of the university are interacting with the technologies available to see where they could be improved.
“The digital maturity assessment brought people into the conversation at different levels and roles. Doing that can often show up where there is a mismatch in experience and knowledge between organisational leaders and staff and students who are experiencing the digital landscape,” says Sarah.
Drawing on knowledgeable voices whose experience is closer to the lived reality of teaching and research is key. “Leaders are saying they don’t need to know everything about digital but they do need to support the staff who are working in that space to have resources, and have a seat at table and a voice.”
Crucially, working across the institution in this way generates an evidence base that can then be used to drive decision-making about the priorities for investment of resources, both money and time. In the past few years, some institutions have been revising their digital strategies and plans, recognising that with constrained finances, they may need to defer some planned investments, or sequence their projects differently, mindful of the pressures on staff.
For Sarah, leaders who listen, and who assume they don’t already know what’s going on, are those who are the most likely to develop the evidence base that can best inform their decisions:
“When you have leaders who recognise the value of taking a more evidence-informed approach, that enables investment to be more strategically targeted, so you’re less likely to see cuts falling in areas where digital is a priority. Institutions that have senior leadership support, data informed decision making, and evidence of impact, are in the best place to steer in a direction that is forward moving and find the core areas that are going to enable us to reach longer term strategic goals.”
In our conversation I detect a sense of a culture shift behind some of the discussions about how to do digital transformation. Put it like this: nobody is saying that higher education leaders of previous decades didn’t practice empathy, careful listening, and value an evidence base. It’s just that when times are tough, these qualities come to the fore as being among the critical tools for institutional success.
Spirit of collaboration
There’s a wider culture shift going on in the sector as well, as financial pressures and the sense that a competitive approach is not serving higher education well turns minds towards where the sector could be more collaborative in its approach. Digital is an area that can sometimes be thought of as a competitive space – but arguably that’s mistaking the tech for the impact you hope it will have. Institutions working on digital transformation are better served by learning from others’ experience, and finding opportunities to pool resources and risk, than by going it alone.
“Digital can be seen as a competitive space, but collaboration outweighs and has far more benefits than competition,” says Sarah. “We can all learn together as a sector, as long as we can keep sharing that spirit of internal and external collaboration we can continue that momentum and be stronger together.”
This is especially relevant for those institutions whose leaders may secretly feel they are “behind the curve” on digital transformation and experience a sense of anxiety that their institution needs to scramble to “catch up”. The metaphor of the race is less than helpful in this context, creating anxiety rather than a sense of strategic purpose. Sarah believes that no institution can legitimately consider itself “ahead of the curve” – and that all should have the opportunity to learn from each other:
“We are all on a journey, so some might be ahead in some aspects but definitely not all,” says Sarah. “No-one is behind the curve but everyone is approaching this in a slightly different way, so don’t feel ‘we have to do this ourselves’; use networks and seek help – that is our role as Jisc to support the sector.”
Jisc is hosting Digifest in Birmingham on 11-12 March – sign up here for online access to sessions.
-

Ohio University puts Black alumni reunion weekend on hold
Ohio University has postponed its annual Black alumni reunion weekend while it reviews the event in light of the Office for Civil Rights’ Feb. 14 Dear Colleague letter, which declared illegal virtually all race-based activities at public institutions.
While the Black alumni reunion “has always been open to all individuals who have an interest in the event,” read a statement from the university, “based on OCR’s recent guidance related to Title VI compliance, some of the programming historically included in the event may need to be reimagined. The University is obligated to follow OCR’s guidance in order to protect our access to critical federal funding, including students’ continued access to federal financial aid.”
The statement also cited the impact of “proposed State of Ohio legislation,” without specifically mentioning SB 1, a bill the Senate has passed that calls for the elimination of DEI statements, offices and trainings.
“Without question, should this bill pass the House in its current form and be signed into law by the Governor, it will bring changes for all of us,” university president Lori Stewart Gonzalez wrote in an earlier message to the campus community. “However, to define today the specific changes we might make would preempt the legislative process on a bill that is not finalized.”
Still, all signature events planned for Black alumni reunion weekend, which was scheduled for April 10–13 in Athens, were canceled.
“While this is difficult news to share, we remain committed to honoring the legacy and accomplishments of Ohio University’s Black alumni,” said planning committee co-chairs Terry Frazier and Jillian Causey in the statement. “We will continue working with the University to develop a plan that aligns with evolving federal and state guidelines while preserving the significance of this gathering.”
-

ADL, other pro-Israel groups condemn AAUP Palestine webinar
The Anti-Defamation League and four other pro-Israel groups accused the American Association of University Professors of “demonizing Israel” in its framing of and publicity around a webinar titled Scholasticide in Palestine.
Scholasticide is the intentional eradication of an education system. In a joint letter Thursday, the same day as the webinar, the ADL, the Academic Engagement Network, Hillel International, the American Jewish Committee and the Jewish Federations of North America condemned the event’s use of this term.
“Language used in the event’s description—including ‘scholasticide’ and ‘exterminationist’—suggests the adoption and promotion of a one-sided and inflammatory narrative which deviates from the mission of the AAUP,” the letter said. The groups said there’s “no evidence of any intent by Israel to ‘systemically destroy’ the education system in Gaza or elsewhere. The destruction of institutions, including educational ones, is a tragic byproduct of war, exacerbated when terror groups like Hamas embed their operations within school buildings and other civilian centers.”
Six months into the latest war in Gaza, a group of independent United Nations experts said in a news release, “It may be reasonable to ask if there is an intentional effort to comprehensively destroy the Palestinian education system.” By then, the release said, the last Gazan university had already been destroyed and “more than 5,479 students, 261 teachers and 95 university professors have been killed in Gaza, and over 7,819 students and 756 teachers have been injured.”
Miriam Elman, the Academic Engagement Network’s executive director, provided Inside Higher Ed with an email from Donna Murch, a member of the AAUP’s elected national council, inviting members to the webinar. Murch said the event would feature “academics and right-to-education organizers who have experienced, documented and challenged Israel’s ongoing and systematic destruction of the education system in Palestine.”
An AAUP spokesperson told Inside Higher Ed, “We are not aware that anyone who is objecting to AAUP’s programming actually attended the event, which is part of an extended series of conversations about diverse topics of interest to our members. We take antisemitism very seriously and plan our programming consistent with the principles of academic freedom and academic responsibility that AAUP vigorously defends.”
The pro-Israel groups also criticized the AAUP event’s promotional material for not mentioning Hamas’s Oct. 7, 2023, attack on Israelis. The letter says, “We note with dismay that this divisive event is taking place within a wider context of the AAUP being perceived as increasingly moving in a virulently anti-Israel direction.”
The AAUP has received criticism for its council’s August decision to abandon the group’s nearly 20-year categorical opposition to academic boycotts—such as those often called for against Israel.

