

by CUPA-HR | January 29, 2025
Along with several immigration-related executive orders and actions issued on Inauguration Day, President Trump signed an executive order titled “Protecting the American People Against Invasion.” The EO sets several directives for U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) and U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) to enforce immigration law against immigrants without permanent legal status in the U.S. and could implicate employers the government deems as “facilitating” the presence of such individuals.
Sections 4 and 5 of the EO establish civil and criminal enforcement priorities for relevant federal agencies. Specifically, the EO directs the secretary of Homeland Security to enable ICE and USCIS to set priorities for their agencies that would ensure successful enforcement of final orders of removal. Additionally, Section 8 of the EO directs increased enforcement action in the form of civil fines and penalties. The EO directs the secretary of Homeland Security to ensure assessment and collection of all fines and penalties from individuals unlawfully present in the U.S. and, notably, those who facilitate such individuals’ presence in the U.S.
Depending on how the agencies respond to this order, these three sections of the EO could lead to an uptick in worksite enforcement action. As a result of this EO, agencies could take increased enforcement action for employment-related immigration law, which could lead to agency actions such as Form I-9 audits and potential investigations and worksite visits related to immigration compliance. Employers who are not in compliance with federal immigration laws could be considered as entities that potentially “facilitate” the presence of immigrants without permanent legal status, which could lead to significant fines and other penalties for the employers.
CUPA-HR has always worked to help you ensure that your institution’s Form I-9 processes are in compliance with federal requirements, and we’ve partnered with USCIS for many years to provide periodic guidance, support and resources. We also understand that it is sometimes a challenge to ensure total compliance for large, sprawling campuses and that some of you have employees at worksites across your state, the country and the globe. Through speeches and actions like this executive order, the Trump administration has made it clear that they intend to focus enforcement efforts on immigrants without permanent legal status and businesses employing them. As noted above, it is possible that there could be I-9 audits and site visits to ensure compliance. Penalties for noncompliance could include very large fines and loss of federal funding.
In light of this EO, it is vital for institutions to review their compliance with immigration laws regarding employment eligibility and work authorization. There are several questions HR leaders should ask themselves when reviewing compliance:
CUPA-HR will continue to monitor for any additional updates related to the Form I-9 and other hiring processes related to work authorization. If you need additional guidance or resources, please review the CUPA-HR I-9/E-Verify Toolkit.

Albert Camus’s philosophy of Absurdism provides a unique approach to the meaning of life. He explores the tension between humanity’s deep desire for meaning and the universe’s lack of answers, coining this contradiction as “the absurd.” His philosophy rejects nihilism and encourages us to embrace life’s limitations, living fully in the present and finding purpose through personal choices rather than ultimate truths.
In The Myth of Sisyphus, Camus likens life to Sisyphus’s endless task of pushing a boulder up a hill, only for it to roll back down—a metaphor for the repetitive, sometimes purposeless cycle of human existence. Instead of succumbing to despair, Camus suggests that we imagine Sisyphus finding joy in the struggle itself, symbolizing a resilient, defiant spirit.

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Undergraduates’ level of trust in their institution has been positively linked to individual student outcomes, as well as the broader institutional culture and reputation. So trust matters. And a new analysis of data from Inside Higher Ed’s annual Student Voice survey with Generation Lab shows which groups of campus employees students trust the most—and least—to promote an enriching experience.
Asked to rate their level of trust in the people in various roles across campus to ensure that they and other students have a positive college experience, nearly all students have some (43 percent) or a lot (44 percent) of trust in professors. This is consistent across institution size, classification (both two-year and four-year) and sector, though students at private nonprofit institutions are somewhat more likely than their peers at public institutions to say they have the highest level of trust in their professors (51 percent versus 42 percent, respectively).
Nearly three in 10 respondents (28 percent) to Inside Higher Ed’s annual Student Voice survey, fielded in May 2024 in partnership with Generation Lab, attend two-year institutions, and closer to four in 10 (37 percent) are post-traditional students, meaning they attend two-year institutions and/or are 25 or older. The 5,025-student sample is nationally representative. The survey’s margin of error is 1.4 percent.
Other highlights from the full survey and from follow-up student polls on key issues can be found here, while the full main survey data set, with interactive visualizations, is available here. In addition to questions about academic life, the main annual survey asked questions on health and wellness, the college experience, and preparation for life after college.
Trust in professors is also relatively consistent across a swath of student characteristics, including gender, household income level and even political affiliation, with 47 percent and 44 percent of Democratic- and Republican-identifying students, respectively, having a lot of trust in them. By race, however, Black students (32 percent) are less likely to say they have a lot of trust in professors than are white (47 percent), Asian American and Pacific Islander (42 percent), and Hispanic students (41 percent).
Academic advisers come next in the list of which groups students trust a lot (36 percent), followed by campus safety and security officers (32 percent). The trust in security is perhaps surprising, giving heightened concerns about overpolicing in the U.S., but some general public opinion polling—including this 2024 study by Gallup—indicates that confidence in policing is up year over year. That’s as confidence in other institutions (including higher education) remains at a low. In a 2022 Student Voice survey, undergraduates were about equally likely to have a lot of trust in campus safety officers.
Toward the bottom of the list of campus groups students trust a lot is financial aid staff (23 percent). This finding may be influenced by the tenor of national conversations about college costs and value, as well as last year’s chaotic Free Application for Federal Student Aid overhaul. Revised national data suggests that the FAFSA mess did not have the negative impact on enrollment that was feared. But another Inside Higher Ed/Generation Lab flash survey in 2024 found that a third of students disapproved of the way their institution communicated with them about the changes, with lower-income students especially likely to say this communication had been poor.
Victoria Nguyen, a teaching fellow at Harvard’s Graduate School of Education and a program coordinator in the Office for Community Conduct at the university, recalls worrying about the financial aid process during her undergraduate years. “The issue is transparency and understanding … Did my scholarship go through? Are they going to reimburse me [for tuition paid]? … It’s not a lack of trust, but since there’s no transparency it feels as though financial aid staff does not have that care,” says Nguyen, who earned her bachelor of science degree in 2023.
At the very bottom of the trust hierarchy are presidents and other executive-level college and university leaders, with just 18 percent of students expressing a lot of trust in this group. It’s been a tough few semesters for college leaders, with presidents, in particular, in the hot seat—including before Congress—over their responses to campus dynamics surrounding the war in Gaza. And those current tensions aside, the presidency appears to be getting harder and harder to hold on to, with average tenures shrinking.
In any case, the newly released Student Voice data shows that students, too, may be losing faith in presidents and other senior leaders. These findings are relatively consistent across institution and student type.
One recent study that sought to identify essential competencies for any modern college president ranked trust-building No. 1 in a list of seven that emerged from focus groups and surveys of presidents themselves: Some 96 percent emphasized that presidents need to behave “in a way that is trustworthy, consistent and accountable.”
Jorge Burmicky, assistant professor of higher education leaders and policy studies at Howard University and co-author of that study, says that while this particular survey item on trust-building was drafted without a specific population in mind, presidents in focus groups emphasized the importance of building trust with students, as well as with faculty members. Participants’ ideas for building trust included bringing campus stakeholders into decision-making processes, minimizing surprises, supporting shared governance and showing consistency by aligning actions with personal and institutional values. Respondents also identified listening to and understanding the needs of various campus groups as a related, critical skill.
Presidents “shared that it was important for them to maintain visibility on campus and that they often took time to visit with students as a way of staying connected to their campus,” Burmicky notes. He also encourages further study on what students—not just presidents—think about core competencies for presidents and means of building trust, including and perhaps especially around communication. Some presidents in his study shared feelings of frustration that students were not reading weekly or monthly presidential newsletters, and he advises that presidents develop trust in a way that works for their campus. Town hall–style gatherings might work in smaller settings, but not others, for instance.
“There is clearly a perception gap between students and presidents on important issues such as trust-building and feeling heard,” he says. “Presidents ought to reach students where they’re at by using outlets that are relevant to their day-to-day lives,” such as social media or athletic events.
Nguyen of Harvard would like to see college presidents showing care by attending more events where they can listen to students’ concerns, such as student organization meetings and workshops, or meetings of task forces that include students. Leaders’ “presence in the room matters so much more than they think,” she says.
Tone and authenticity are additional considerations: Generic messages “do not resonate with most people as they lack empathy, as expressed by our participants,” says Burmicky.
Nguyen adds that campus leaders should assess their communication to ensure they’re not “using tactics from 20 years ago that don’t match our student population anymore.”
Another study published last month shed new light on the concept of student-faculty trust, seeking to better understand how students perceive its value. The study, involving hundreds of engineering students in Sweden, identified showing care and concern as the most important trust-building approach for professors. Teaching skills also mattered.
Co-author Rachel Forsyth, of Lund University, explains that students “seem to want to have confidence that the teacher knows what they are talking about, is able to communicate their ideas and will attempt to build an effective relationship with them.” Student participants indicated that they could learn without trust, “but that the process felt more effective if it were present and that they had more options in terms of supporting that learning and extending their engagement with the materials.”
The question of faculty trust is only gaining urgency with the rise of artificial intelligence–powered teaching tools, she adds.
Peter Felten, executive director of the Center for Engaged Learning, professor of history and assistant provost for teaching and learning at Elon University, notes that prior research in this area has defined trust as both “students’ willingness to take risks based on their judgment that the teacher is committed to student success” (original study here) and as “the perception that the instructor understands the challenges facing students as they progress through the course, accepts students for who they are and cares about the educational welfare of students.”
Felten says that his own research—completed with Forsyth and involving experienced faculty members teaching large science, engineering, technology and math courses—found there are four categories of “trust moves” faculty can make in their teaching:
These trust moves, Felton says, include “not only what instructors do and say, but how they design their courses, how they assess students and more.”
What do you do to build trust in your classroom or on your campus? Let us know by sharing your ideas here.

Katherine Franke, formerly a law professor at Columbia University, is just the latest of many academics who have found themselves in hot water because of something they said outside the classroom. Others have been fired or resigned under pressure for what they posted online or said in other off-campus venues.
In each of those cases, the “offending party” invoked academic freedom or freedom of speech as a defense to pressures brought on them, or procedures initiated against them, by university administrators. The traditional discourse of academic freedom or free speech on campus has focused on threats from inside the academy of the kind that led Franke and others to leave their positions.
Today, threats to academic freedom and free speech are being mounted from the outside by governments or advocacy groups intent on policing colleges and universities and exposing what they see as a suffocating orthodoxy. As Darrell M. West wrote in 2022, “In recent years, we have seen a number of cases where political leaders upset about criticism have challenged professors and sought to intimidate them into silence.”
We have seen this act before, and the record of universities is not pretty.
During the 1940s and 1950s, an anticommunist crusade swept the nation, and universities were prime targets. In that period, “faculty and staff at institutions of higher learning across the country experienced increased scrutiny from college administrators and trustees, as well as Congress and the FBI, for their speech, their academic work, and their political activities.”
And many universities put up no resistance.
Today, some believe, as Nina Jankowicz puts it, that we are entering “an era of real censorship the likes of which the United States has never seen. How will universities respond?”
If academic freedom and freedom of expression are to be meaningful, colleges and universities must not only resist the temptation to punish or purge people whose speech they and others may find offensive; they must provide new protections against external threats, especially when it comes to extramural speech by members of their faculties.
They must become active protectors and allies of faculty who are targeted.
As has long been recognized, academic freedom and free speech are not identical. In 2007, Rachel Levinson, then the AAUP senior counsel, wrote, “It can … be difficult to explain the distinction between ‘academic freedom’ and ‘free speech rights under the First Amendment’—two related but analytically distinct legal concepts.”
Levinson explained, “Academic freedom … addresses rights within the educational contexts of teaching, learning, and research both in and outside the classroom.” Free speech requires that there be no regulation of expression on “all sorts of topics and in all sorts of settings.”
Ten years after Levinson, Stanley Fish made a splash when he argued, “Freedom of speech is not an academic value.” As Fish explained, “Accuracy of speech is an academic value … [because of] the goal of academic inquiry: getting a matter of fact right.” Free speech, in contrast, means “something like a Hyde Park corner or a town-hall meeting where people take turns offering their opinions on pressing social matters.”
But as Keith Whittington observes, the boundaries that Levinson and Fish think can be drawn between academic freedom and free speech are not always recognized, even by organizations like the AAUP. “In its foundational 1915 Declaration of Principles on Academic Freedom and Academic Tenure,” Whittington writes, “the AAUP asserted that academic freedom consists of three elements: freedom of research, freedom of teaching, and ‘freedom of extramural utterance and action.’”
In 1940, Whittington explains, “the organization reemphasized its position that ‘when they speak or write as citizens,’ professors ‘should be free from institutional censorship or discipline.’”
Like the AAUP, Whittington opposes “institutional censorship” for extramural speech. That is crucially important.
But in the era in which academics now live and work, is it enough?
We know that academics report a decrease in their sense of academic freedom. A fall 2024 survey by Inside Higher Ed found that 49 percent of professors experienced a decline over the prior year in their sense of academic freedom as it pertains to extramural speech.
To foster academic freedom and free speech on campus or in the world beyond the campus, colleges and universities need to move from merely tolerating the expression of unpopular ideas to a more affirmative stance in which they take responsibility for fostering it. It is not enough to tell faculty that the university will respect academic freedom and free expression if they are afraid to exercise those very rights.
Faculty may be fearful that saying the “wrong” thing will result in being ostracized or shunned. John Stuart Mill, one of the great advocates for free expression, warned about what he called “the tyranny of the prevailing opinion and feeling.” That tyranny could chill the expression of unpopular ideas.
In 1952, during the McCarthy era, Supreme Court justice Felix Frankfurter also worried about efforts to intimidate academics that had “an unmistakable tendency to chill that free play of the spirit which all teachers ought especially to cultivate and practice.”
Beyond the campus, faculty may rightly fear that if they say things that offend powerful people or government officials, they will be quickly caught up in an online frenzy or will be targeted. If they think their academic institutions will not have their back, they may choose the safety of silence over the risk of saying what they think.
Whittington gets it right when he argues that “Colleges and universities should encourage faculty to bring their expertise to bear on matters of public concern and express their informed judgments to public audiences when doing so might be relevant to ongoing public debates.” The public interest is served when we “design institutions and practices that facilitate the diffusion of that knowledge.”
Those institutions and practices need to be adapted to the political environment in which we live. That is why it is so important that colleges and universities examine their policies and practices and develop new ways of supporting their faculty if extramural speech gets them in trouble. This may mean providing financial resources as well as making public statements in defense of those faculty members.
Colleges and universities should also consider making their legal counsel available to offer advice and representation and using whatever political influence they wield on behalf of a faculty member who is under attack.
Without those things, academics may be “free from” the kind of university action that led Franke to leave Columbia but still not be “free to” use their academic freedom and right of free expression for the benefit of their students, their professions and the society at large.

Approaching a critical vote on its accreditation status next month, Saint Augustine’s University has made controversial moves in recent months to stabilize its shaky financial position, but so far none have paid off, putting the beleaguered institution in a more precarious position.
First, the historically Black university in North Carolina took out a $7 million loan last fall that many critics have described as predatory given its 24 percent interest rate and 2 percent management fee. The university also put real estate up as collateral in case of a loan default.
Then, in November, SAU officials also struck a $70 million deal with 50 Plus 1 Sports, a fledgling Florida company, to lease its campus and develop university property for 99 years. The deal would have provided a much-needed financial lifeline for the cash-strapped university that needs to urgently fix its finances before the accreditation review. (The college was previously stripped of accreditation due to university financial and governance issues but appealed.)
But that lifeline is in legal limbo after the North Carolina attorney general declined to sign off on the deal Monday.
The North Carolina attorney general’s office, which reviewed the deal due to state law on the transfer of assets from a nonprofit, announced it would not approve the arrangement with 50 Plus 1 Sports as written due to a lack of “sufficient documentation to support the proposal” and concerns that the payout “is too low to justify transfer of the lease rights” for SAU’s campus, which is appraised at $198 million. The attorney general’s Office also expressed concerns about SAU’s “ability to continue to operate.”
Saint Augustine’s has faced rising pressures since December 2023 when it fired then-president Christine McPhail, who subsequently lodged a gender-based discrimination complaint against the board. That same week the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges announced it had voted to strip SAU’s accreditation due to board and finance issues.
(SAU lost an appeal to that decision but won a reprieve in court in July before SACSCOC voted again in December to strip accreditation. The accreditor will vote on SAU’s appeal next month.)
Since early 2024—under the guidance of interim president Marcus Burgess—SAU has navigated a series of challenges in a bid to stay afloat. In February, it was hit with a $7.9 million tax lien. That same month, local officials encouraged SAU to explore a merger with nearby Shaw University, another HBCU. Months later, SAU board chair Brian Boulware cast the proposal as an aggressive effort to ramrod a partnership. (Local officials have denied his account.) In May, a group called the Save SAU Coalition sued Boulware and other trustees, alleging malfeasance and self-dealing by the board.
That case was later dismissed due to a lack of standing.
Enrollment has also plummeted, falling from more than 1,100 students in fall 2022 to a head count of around 200 students last fall, according to recent estimates. SAU has also announced major staff reductions.
As its financial pressures added up, Saint Augustine’s borrowed $7 million from Gothic Ventures, an investment firm, and secured a $30 million line of credit. The deal, which came with a 24 percent interest rate and a 2 percent loan management fee, sparked alumni protests in the fall.
Mark DeFusco, a senior consultant with Higher Ed Consolidation Solutions and sector finance expert, told Inside Higher Ed the terms of the Gothic Ventures loan were “crazy” and “irresponsible.” DeFusco agreed with the description of the loan as “predatory.”
SAU officials have defended the agreement, writing that the deal is “crucial for maintaining educational services” and securing the loan contradicted “claims of irresponsibility in financial dealings” leveled by critics. SAU has cast criticism of the deal as a “smear campaign.”
Earlier this month, two local publications, INDY Week and The Assembly, reported that last fall SAU turned down a more favorable loan offer of $19.5 million with a 9 percent interest rate. That offer, from Self-Help Credit Union, stipulated that two board members, including Boulware, resign, and would have included purchasing the existing Gothic Ventures loan. The university balked at the attached conditions.
To DeFusco, the board resignations as part of the loan conditions were a reasonable request.
“There are provisions in leadership for all kinds of lending. And with all due respect, it was a wise provision, because you have a board that’s allowed [financial issues] to go on for several years now. This isn’t something new,” DeFusco said. “They haven’t broken even for at least five years from what I could see in their records, and their accrediting body was going to close them down, except for that arbitration. And now they’re about to close them down again.”
Continued financial struggles ultimately led SAU to a deal with 50 Plus 1 Sports, which describes itself on its website as a financing and development firm. That agreement, according to a university statement, would “generate a $70 million upfront investment” from the company.
But the North Carolina attorney general’s office shut down that proposed deal.
Beyond the lack of documentation on the proposal and the low payout, Assistant Attorney General Kunal Choksi also raised questions about the university’s due diligence of the deal.
“SAU’s board and trustees were obligated to perform due diligence on whether 50+ can meet its obligations under the transaction and has the experience to develop revenue-generating property on the leased land,” Choksi wrote in a letter shared with Inside Higher Ed.
Choksi added that the attorney general’s office had requested “sufficient proof that 50+ has the financial ability to comply with its obligations to SAU and avoid default with its financiers” and “details about similar deals 50+ has developed, including deals with other universities, or the company’s audited financial statements.” Choksi indicated in his letter that SAU had not yet provided those details on the proposal.
In a Tuesday statement, SAU officials said little about the concerns raised by the attorney general about the 50 Plus 1 Sports deal or its ability to operate. Instead, university officials took aim at Self-Help Credit Union.
SAU noted concerns “about the process that led to the recent rejection” of the agreement. Specifically, they pointed to a meeting between Marin Eakes of Self-Help Credit Union and alleged that the attorney general’s letter reflected comments made by Eakes in unspecified media coverage and alleged the 50 Plus 1 Sports proposal was shared without SAU’s consent.
SAU officials wrote in the statement that they “suspect that the Attorney General’s Office used Mr. Eakes’ counsel and input to subsequently influence their decision. Such interference by Self-Help raises significant concerns about fairness. It suggests their attempt to weaponize the NC Attorney General’s Office to obstruct the approval process for the 50 Plus 1 Sports deal.”
With the North Carolina attorney general’s office shutting down the 50 Plus 1 deal, SAU has little time to fix its finances ahead of a looming vote on its accreditation status in late February.
And questions about both the deal and the company linger.
Information on 50 Plus 1 Sports is sparse and it is unclear, as noted by the attorney general’s office, whether the nascent company has the resources to back the deal. Little is known about 50 Plus 1 Sports, which unsuccessfully big on a $800 million stadium development deal in St. Petersburg, Fla., in early 2023. The firm was not selected for the project amid questions from local officials about how it would finance the deal and a lack of experience as a lead developer.
In its St. Petersburg proposal, 50 Plus Sports listed a $1.4 billion deal to develop a sports and entertainment district for the University of New Orleans among its reference projects. However, a UNO spokesperson told Inside Higher Ed by email it is not “moving forward with the project.”
Monti Valrie, founder and CEO of 50 Plus 1 Sports, did not respond to a request for comment.
The attorney general’s office did leave the door open to reconsider the deal. But the university would have to provide more details to the office, including evidence that SAU conducted due diligence on 50 Plus 1 Sports and its finances.
SAU officials noted in their statement that “despite these challenges, SAU remains committed to working collaboratively with the Attorney General’s Office. We believe transparency and open dialogue are essential in securing the funding for our university’s sustainability and growth.”
But SAU is facing a ticking clock to get that information to the attorney general or rework the deal. University officials have said that the deal needed to close by Jan. 31. Otherwise, “SAU risks failing to demonstrate financial sustainability” before its appeal hearing next month, according to a university statement.
But DeFusco wonders if SAU’s finances are too far gone to fix.
“Their finances are so bad they may be criminal,” he said, pointing to payroll and tax issues. (The university also allegedly failed to maintain worker’s compensation for employees recently.)
As pressure mounts, DeFusco believes the board needs more scrutiny for SAU’s financial problems, arguing “they missed it for years” as the university slipped deeper into the red.
“Now the question is, is the board acting as a fiduciary?” DeFusco said.

By Peter Gray, Chief Executive and Chair of the JS Group.
As the higher education sector starts to plan its next budget cycle and many may need to make savings, there is a concern about the impact of any cuts on students and how this could negatively affect their university experience and performance.
Universities are bound to look at a range of options to save money, especially given the stormy operating context. But one less-often highlighted aspect of university finances is the cost (and benefit) of the additional financial support universities devote to many of their students. Through cash, vouchers and other means, many universities provide financial help to support with the costs of living and learning.
Using Universities UK’s annual sector figures as one indicator, roughly 5% of universities’ overall expenditure has gone towards financial support and outreach, equivalent to around £2.5 billion. Although some of this money will inevitably not go directly to students themselves, this is still a significant amount of spending.
There are, naturally, competing tensions when it comes to considering any changes to targeted financial support. With significant financial pressures on students, exacerbated by the cost-of-living crisis, there is always a very justifiable case for more money. However, with the significant financial pressures universities are facing, there is an equally justifiable case to control costs to ensure financial sustainability. Every university has to manage this tension and trade-offs are inevitable when understanding just how much financial support to give and to whom.
In many respects, the answers to those questions are partially governed by Access & Participation Plans, with the clear intention that these financial interventions really change student outcomes. However, properly measuring those outcomes is incredibly difficult without a much deeper understanding of student ‘need’ – and understanding these needs comes from being able to identify student spending behaviour (and often doing this in real-time).
It always amazes me that some APPs will state that financial support ‘has had a positive impact on retention’ and some quite the opposite and I think part of this is a result of positioning financial support from the university end of the telescope rather than the student end.
Understanding real and actual ‘need’ helps to change this. Knowing perhaps that certain groups (for example Asylum Seekers or Gypsy, Roma, Traveller, Showman and Boater students) across the sector will have similar needs would be helpful and data really help here. Having, using, and sharing data will allow us to draw a bigger picture and better signpost to where interventions are most effectively deployed so those particular groups of students who need support are achieving the right outcomes.
Technology is at hand to help: Open Banking (for example) is an incredible tool that not only can transform how financial support can be delivered but also helps to build an understanding of student behaviour.
Lifting the bonnet and understanding behaviour poses additional questions, such as: When is the right time to give that support? And what form should that support take?
I am a big proponent of providing financial support as soon as a student starts. When I talk to universities, however, it is clear that the data needed to identify particular groups of students are not readily available at the point of entry and students’ needs are not met. Giving a student financial support in December, when they needed it in September, is not delivering at the point of student need, it is delivering at the point where the university can identify the student. I think there is a growing body of evidence that suggests the large drop off in students between September and December is, in part, because of this.
Some universities in the sector give a small amount of support to all students at the start of the year, knowing that by doing so they will ensure that they can meet the immediate needs of some students. But clearly, some money must also go to those who do not necessarily need it.
However, and this is where the maths comes in, if the impact of that investment keeps more students in need at university, then I would argue that investment is worth the return. And the maths is simple: it really doesn’t take many additional students to stay to have a profoundly positive impact on university finances. Thus it is certainly worthy of consideration.
To me, this is about using financial support to drive the ultimate goal of improving student outcomes, especially the retention of students between September and December, which is when the first return is made, where the largest withdrawal is seen and where the least amount of financial support is given.
As to the nature or format of support: of course, in most cases, it is easier to provide cash. However, again, this is about your investment in your student, and, for example, if you have students on a course with higher material and resource costs, or students who are commuting, then there is an argument to consider more in-kind support and using data to support that decision.
Again, I am a proponent of not just saying ‘one size fits all’. Understanding student need is complex, but solutions are out there. It is important to work together to identify patterns of real student need and understand the benefits of doing so.
My knowledge draws on JS Group’s data, based on the direct use of £40 million of specialist student financial support to more than 160,000 students across 30 UK universities in the last full academic cycle.
I have also looked at the student views on such funding and there is an emerging picture that connects student financial support with continuation, participation and progress. A summary of student feedback is here: https://jsgroup.co.uk/news-and-views/news/student-feedback-report-january-2025/
The real positive of this is that everyone wants the same goal: for fewer students to withdraw from their courses and for those students to thrive at university and be successful. We need to widen the debate on how financial support is delivered, when, and in what format to draw together a better collective understanding of student need and behaviour to achieve that goal.

The kids are not bouncing back.
The results of a major national test released Wednesday showed that in 2024, reading and math skills of fourth and eighth grade students were still significantly below those of students in 2019, the last administration of the test before the pandemic. In reading, students slid below the devastatingly low achievement levels of 2022, which many educators had hoped would be a nadir.
The test, the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), is often called the nation’s report card. Administered by the federal government, it tracks student performance in fourth and eighth grades and serves as a national yardstick of achievement. Scores for the nation’s lowest-performing students were worse in both reading and math than those of students two years ago. The only bright spot was progress by higher-achieving children in math.
The NAEP report offers no explanation for why students are faltering, and the results were especially disappointing after the federal government gave schools $190 billion to aid in pandemic recovery.
“These 2024 results clearly show that students are not where they need to be or where we want them to be,” said Peggy Carr, the commissioner of the National Center for Education Statistics, in a briefing with journalists.
Related: Our free weekly newsletter alerts you to what research says about schools and classrooms.
More than 450,000 fourth and eighth graders, selected to be representative of the U.S. population, took the biennial reading and math tests between January and March of 2024.
Depressed student achievement was pervasive across the country, regardless of state policies or instructional mandates. Student performance in every state remained below what it was in 2019 on at least one of the four reading or math tests. In addition to state and national results, the NAEP report also lists the academic performance for 26 large cities that volunteer for extra testing.
The results also highlighted the sharp divergence between higher- and lower- achieving students. The modest progress in fourth grade math was entirely driven by high-achieving students. And the deterioration in both fourth and eighth grade reading was driven by declines among low-achieving students.
“Certainly the most striking thing in the results is the increase in inequality,” said Martin West, a professor of education at Harvard University and vice chair of the National Assessment Governing Board, which oversees the NAEP test. “That’s a big deal. It’s something that we hadn’t paid a lot of attention to traditionally.”
The starkest example of growing inequality is in eighth grade math, where the achievement gap grew to the largest in the history of the test.
The chart above shows that the math scores of all eighth graders fell between 2019 and 2022. Afterward, high-achieving students in the top 10 percent and 25 percent of the nation (labeled as the 90th and 75th percentiles above) began to improve, recovering about a quarter of the setbacks for high achievers during the pandemic. That’s still far behind high-performing eighth graders in 2019, but at least it’s a positive trend.
The more disturbing result is the continuing deterioration of scores by low-performing students in the bottom 10 percent and 25 percent. The huge pandemic learning losses for students in the bottom 10 percent grew 70 percent larger between 2022 and 2024. Learning losses for students in the bottom 25 percent grew 25 percent larger.
“The rich get richer and the poor are getting shafted,” said Scott Marion, who serves on the NAEP’s governing board and is the executive director of the National Center for the Improvement of Educational Assessment, a nonprofit consultancy. “It’s almost criminal.”
More than two-thirds of students in the bottom 25 percent are economically disadvantaged. A quarter of these low performers are white and another quarter are Black. More than 40 percent are Hispanic. A third of these students have a disability and a quarter are classified as English learners.
By contrast, fewer than a quarter of the students in the top 25 percent are economically disadvantaged. They are disproportionately white (61 percent) and Asian American (14 percent). Only 5 percent are Black and 15 percent are Hispanic. Three percent or fewer of students at the top have a disability or are classified as English learners.
Related: Six puzzling questions from the disastrous [2022] NAEP results
Although average math scores among all eighth grade students were unchanged between 2022 and 2024, that average masks the improvements at the top and the deterioration at the bottom. They offset each other.
The NAEP test does not track individual students. The eighth graders who took the exam in 2024 were a different group of students than the eighth graders who took the exam in 2022 and who are now older. Individual students have certainly learned new skills since 2019. When NAEP scores drop, it’s not that students have regressed and cannot do things they used to be able to do. It means that they’re learning less each year. Kids today aren’t able to read or solve math problems as well as kids their same age in the past.
Students who were in eighth grade in early 2024, when this exam was administered, were in fourth grade when the pandemic first shuttered schools in March 2020. Their fifth grade year, when students should have learned how to add fractions and round decimals, was profoundly disrupted. School days began returning to normal during their sixth and seventh grade years.
Harvard’s West explained that it was incorrect to assume that children could bounce back academically. That would require students to learn more in a year than they historically have, even during the best of times.
“There’s nothing in the science of learning and development that would lead us to expect students to learn at a faster rate after they’ve experienced disruption and setbacks,” West said. “Absent a massive effort society-wide to address the challenge, and I just haven’t seen an effort on the scale that I think would be needed, we shouldn’t expect more positive results.”
Learning isn’t like physical exercise, West said. When our conditioning deteriorates after an injury, the first workouts might be a grind but we can get back to our pre-injury fitness level relatively quickly.
“The better metaphor is saving for retirement,” said West. “If you miss a deposit into your account because of a short-term emergency, you have to find a way to make up that shortfall, and you have to make it up with interest.”
What we may be seeing now are the enduring consequences of gaps in basic skills. As the gaps accumulate, it becomes harder and harder for students to keep up with grade-level content.
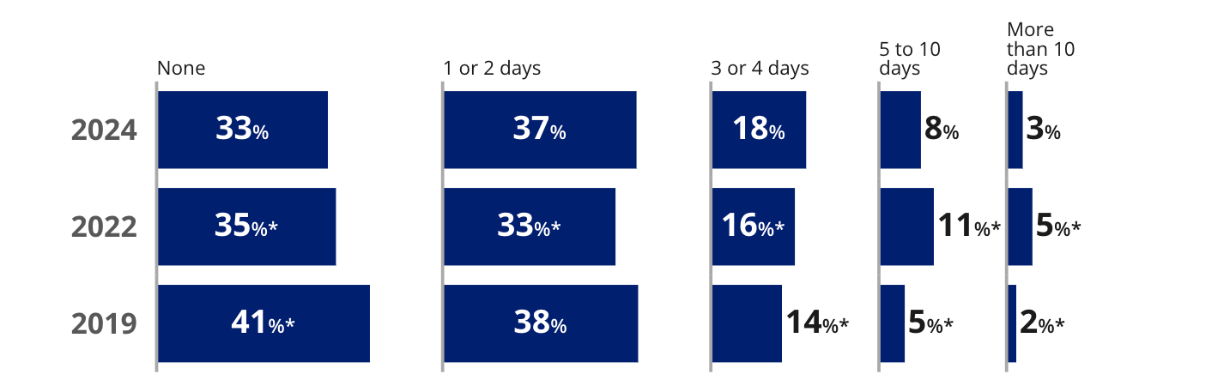
Another factor weighing down student achievement is rampant absenteeism. In survey questions that accompany the test, students reported attending school slightly more often than they had in 2022, but still far below their 2019 attendance rates. Eleven percent of eighth graders said that they had missed five or more school days in the past month, down from 16 percent in 2022, but still far more than the 7 percent of students who missed that much school in 2019.
“We also see that lower-performing readers aren’t coming to school,” said NCES Commissioner Carr. “There’s a strong relationship between absenteeism and performance in these data that we’re looking at today.”
Fourth grade math results were more hopeful. Top-performing children fully recovered back to 2019 achievement levels and can do math about as well as their previous peers. However, lower-performing children in the bottom 10 percent and 25 percent did not rebound at all. Their scores were unchanged between 2022 and 2024. These students were in kindergarten when the pandemic first hit in 2020 and missed basic instruction in counting and arithmetic.
Reading scores showed a similar divergence between high- and low- achievers.
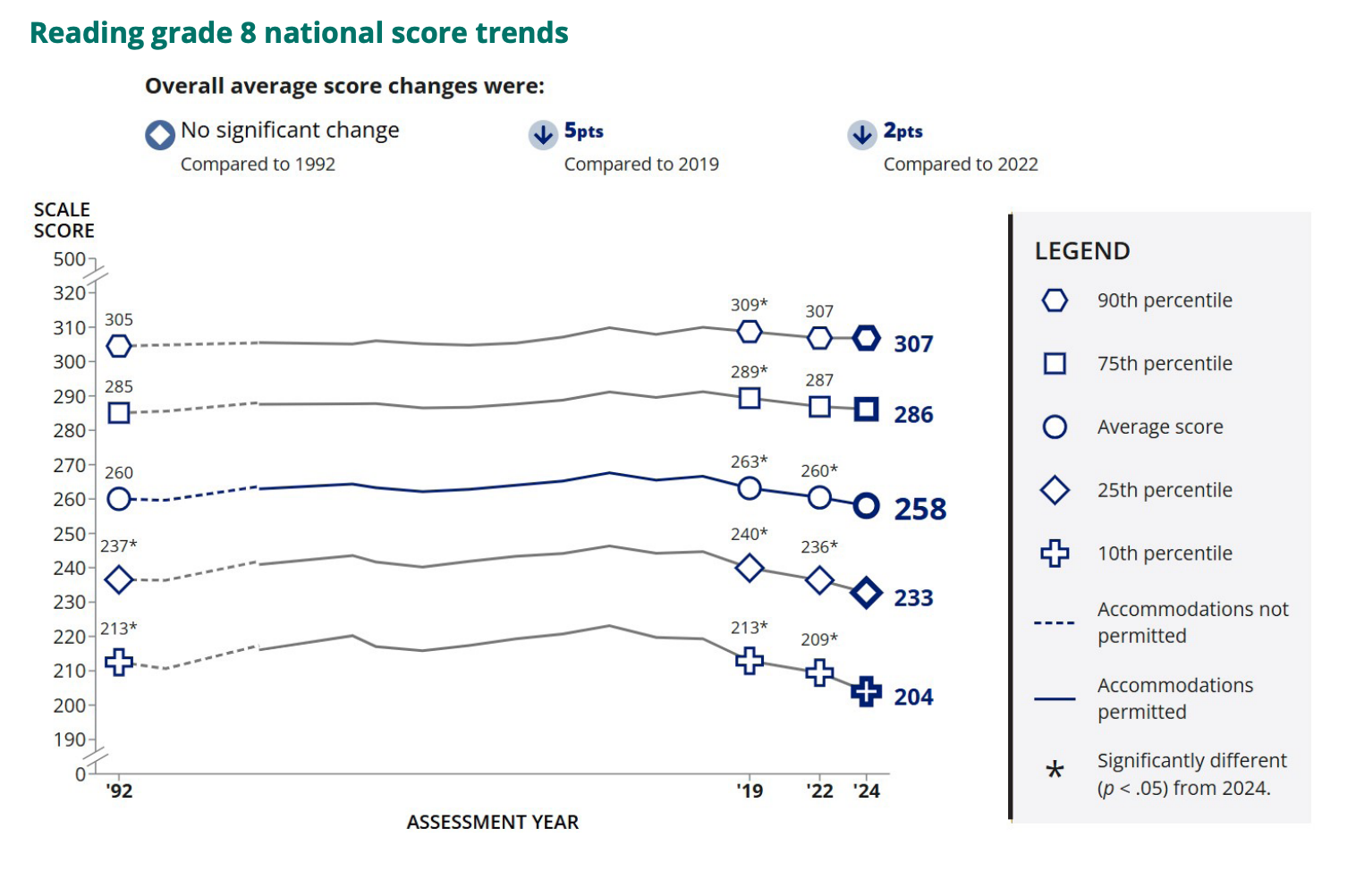
This chart above shows that the highest-performing eighth graders failed to catch up to what high-achieving eighth graders used to be able to do on reading comprehension tests. But it’s not a giant difference. What’s startling is the steep decline in reading scores for low-achieving students. The pandemic drops have now doubled in size. Reading comprehension is much, much worse for many middle schoolers.
It’s difficult to say how much of this deterioration is pandemic related. Reading comprehension scores for middle schoolers had been declining for a decade since 2013. Separate surveys show that students are reading less for pleasure, and many educators speculate that cellphone use has replaced reading time.
Related: Why reading comprehension is deteriorating
The biggest surprise was fourth grade reading. Over the past decade, a majority of states have passed new “science of reading” laws or implemented policies that emphasize phonics in classrooms. There have been reports of improved reading performance in Mississippi, Florida, Tennessee and elsewhere. But scores for most fourth graders, from the highest to the lowest achievers, have deteriorated since 2022.
One possibility, said Harvard’s West, is that it’s “premature” to see the benefits of improved instruction, which could take years. Another possibility, according to assessment expert Marion, is that being able to read words is important, but it’s not enough to do well on the NAEP, which is a test of comprehension. More elementary school students may be better at decoding words, but they have to make sense of those words to do well on the NAEP.
Carr cited the example of Louisiana as proof that it is possible to turn things around. The state exceeded its 2019 achievement levels in fourth grade reading. “They did focus heavily on the science of reading but they didn’t start yesterday,” said Carr. “I wouldn’t say that hope is lost.”
The results show that many more children lack even the most basic skills. In math, 24 percent of fourth graders and 39 percent of eighth graders cannot reach the lowest of three achievement levels, called “basic.” (The others are “proficient” and “advanced.”) These are fourth graders who cannot locate whole numbers on a number line or eighth graders who cannot understand scientific notation.
The share of students reading below basic was the highest it’s ever been for eighth graders, and the highest in 20 years for fourth graders. Forty percent of fourth graders cannot put events from a story into sequential order, and one third of eighth graders cannot determine the meaning of a word in the context of a reading passage.
“To me, this is the most pressing challenge facing American education,” said West.
Contact staff writer Jill Barshay at 212-678-3595 or [email protected].
This story about the 2024 NAEP test was written by Jill Barshay and produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for Hechinger newsletters.