

2025 promises to be a disruptive year in higher education and society, not just in DC but across the US. While some now can see two demographic downturns, worsening climate conditions, and a Department of Education in transition, there are other less predictable and lesser-known trends and developments that we hope to cover at the Higher Education Inquirer.
The Trump Economy
Folks are expecting a booming economy in 2025. Crypto and AI mania, along with tax cuts and deregulation, mean that corporate profits should be momentous. The Roaring 2020s will be historic for the US, just as the 1920s were, with little time and thought spent on long-range issues such as climate change, economic inequality, or the potential for an economic crash.
A Pyramid, Two Cliffs, a Wall and a Door
HEI has been reporting about enrollment declines since 2016. Smaller numbers of younger people and large numbers of elderly Baby Boomers and their health and disability concerns spell trouble ahead for states who may not consider higher education a priority. We’ll have to see how Republican promises for mass deportations turn out, but just the threats to do so could be chaotic. There will also be controversies over the Trump/Musk plan to increase the number of H1B visas.
The Shakeup at ED
With Linda McMahon at the helm of the Department of Education, we should expect more deregulation, more cuts, and less student loan debt relief. Mike Rounds has introduced a Senate Bill to close ED, but the Bill does not appear likely to pass. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) efforts may take a hit. However, online K12 education, robocolleges, and surviving online program managers could thrive in the short run.
Policies Against Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
Florida, Texas, Alabama, Iowa and Utah have banned diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) offices at public universities. Idaho, Indiana and Kansas have prohibited colleges from requiring diversity statements in hiring and admissions.
Failing Schools and Strategic Partnerships
People should expect more colleges to fail in the coming months and years, with the possibility that the number of closures could accelerate. Small religious schools are particularly vulnerable. Schools may further privatize their operations to save money and make money in an increasingly competitive market.
Campus Protests and Mass Surveillance
Protests may be limited out of fear of persecution, even if there are a number of legitimate issues to protest, to include human induced climate change, genocide in Palestine, mass deportations, and the resurgence in white supremacy. Things could change if conditions are so extreme that a critical mass is willing to sacrifice. Other issues, such as the growing class war, could bubble up.
The Legitimization of Robocollege Credentials
Online higher education has become mainstream despite questions of its efficacy. Billions of dollars will be spent on ads for robocolleges. Religious robocolleges like Liberty University and Grand Canyon University should continue to grow and more traditional religious schools continue to shrink. University of Southern Hampshire, Purdue Global and Arizona Global will continue to enroll folks with limited federal oversight. Adult students at this point are still willing to take on debt, especially if it leads to job promotions where an advanced credential is needed.
Apollo Global Management is still working to unload the University of Phoenix. The sale of the school to the Idaho Board of Education or some other state organization remains in question.
AI and Cheating
AI will continue to affect society, promising to add more jobs and threatening to take others. One less visible way AI affects society is in academic cheating. As long as there have been grades and competition, students have cheated. But now it’s become an industry. Even the concept of academic dishonesty has changed over the years. One could argue that cheating has been normalized, as Derek Newton of the Cheat Sheet has chronicled. Academic research can also be mass produced with AI.
Under the Radar
A number of schools, companies, and related organizations have flown under the radar, but that could change. This includes Maximus and other Student Loan Servicers, Guild Education, EducationDynamics, South University, Ambow Education, National American University, Perdoceo, Devry University, and Adtalem.
Related links:
The US Working-Class Depression: “Let’s all pretend we couldn’t see it coming.”

Famke Veenstra-Ashmore was an intern at HEPI in the summer of 2024. She previously completed a BA and an MPhil in English at the University of Cambridge and now works as a parliamentary researcher.
My report about the gender awarding gap at Oxbridge has generated a lot of discussion on social media. Though I was astutely warned by HEPI’s Director to expect flak from certain right-wing publications, I was surprised that the only explicit and personal attack came from a female Times columnist.
Melaine McDonagh’s column objected to the report’s suggestion that historic institutions like Oxford and Cambridge ought to consider re-thinking the style and presentation of examinations for certain subjects where large gender awarding gaps exist. McDonagh argued that this suggestion was patronising and underestimated the ability of female students to stand their intellectual ground.
The Times column seemed to pick up on the argumentative threads of much of the discussion about my report online. I noticed a lot of the criticism of the report came from Oxbridge graduates from my parents’ generation, though this view was also held by younger Twitter users, such as Policy Exchange’s Lara Brown.
While debates around the supervision system and examinations are certainly legitimate and acknowledged in the report, the criticism was steeped in a kind of political and institutional nostalgia. A sense that Oxbridge disentangling itself too much from its traditions for the sake of progressive politics.
As a recent graduate of Cambridge, where I spent four years, I understand the urge to herald its unique history and methods of teaching. Personally, I thrived, earned two degrees, and enjoyed both examinations and supervisions. But my report wasn’t about personal experience – it was about systemic flaws which were patently disadvantaging entire groups of students.
Why is it that so many people yearn for the days where women where ‘chewed and spat out’ (to borrow Melanie McDonagh’s phrase) at Oxbridge? David Butterfield’s recent take-down of Cambridge and its ‘infantilising’ approach to teaching also comes to mind when thinking about this surge of ex-Oxbridge students or academics criticising the evolution of institutions in reaction to social change.
From my perspective, this trend of thinking isn’t sincere. It is not rooted in a genuine concern over the way universities operate and how students think and learn and organise. Rather, it stems from a grievance towards the diversification of student cohorts which has caused the uncomfortable recognition, for Oxbridge traditionalists, that as the student body evolves, the manner of teaching and assessing may have to shift accordingly.
Many of these commentators miss this crucial point and their thinking is limited by the belief that all of Oxbridge’s academic traditions should be preserved. Butterfield, for example, claims that the ‘freewheeling process’ of allowing a larger proportion of state school students into Cambridge has ‘placed politics ahead of talent’. With similar logic, McDonagh reasons that adjusting examinations and supervisions to address institutional inequalities would unfairly benefit women, who have done nothing to deserve better outcomes, and should therefore receive no extra consideration when it comes to systemic methods of assessing their academic performance.
Though the comparison between state-school versus private school students and male and female students is limited, I suggest that the arguments offered by Butterfield and McDonagh are motivated by the same emotional basis.
Research by Cambridge Assessment has shown that state school pupils tend to outperform independent school pupils with similar A Level results at university. The study offered two potential explanations for this: that there are simply less incentives for them to perform highly, or they have been ‘coached’ at school to do well in exams but then struggle when left to their own devices.
Are progressive politics, then, getting in the way of talent? Or are they enabling students who have not had the resources in their secondary education to thrive and contribute to an academic community which takes their contributions seriously?
We know that students from academic private schools aren’t entitled to higher marks, nor enjoy higher thresholds of talent, just because of their schooling. In a similar way, we know that Oxbridge was constructed around the education of a very specific, public-school educated, white and able-bodied man. When data suggests there is a problem worthy of addressing, why do ex-students and academics recoil from recognising and addressing this issue?
Many of the detractors of Oxford and Cambridge’s cultural and social modernisation are pushing against the demands of our rapidly shifting present. The desire to keep things the same is not without merit – the supervision system will rightly continue to be lauded by many. Equally, women at Oxbridge, through the criteria by which they are selected, will do well in exams. Change is so incremental at these institutions that I doubt fundamental changes will ever be on the negotiating table.
However, small evidence-based changes, such as the scaffolding of exam questions in specific subjects, can make a huge difference to the experience of female students at Oxbridge. Enabling more women to match their male counter parts will encourage more of them to progress into postgraduate study and strengthen academic departments – not weaken them.
Oxford and Cambridge pride themselves on their reputation for advancing research, technology, and educative practices. In their combined age of around two millennia, why would they stop now?



In a recent article, “Dear Prospective UAGC Students: Stay Away,” a professor from the University of Arizona discourages students from attending the University of Arizona Global Campus (UAGC). Unfortunately, this article was based on the author’s perspective rather than on facts and thus lacked the academic rigor of factual data from credible sources. This opinion piece was a collection of baseless assumptions, completely overlooking the true mission of UAGC, its faculty, and the diverse students we proudly serve. Frankly, the article has no merit.
There is power in knowledge and truth. As such, the article could have accurately depicted the realities of UAGC instead of relying on inaccurate critiques about educational quality, enrollment numbers, adjunct faculty, and alleged student dissatisfaction. To set the record straight, UAGC is committed to providing online higher education for non-traditional students, including working adults, military personnel, parents, and underserved communities. Our students juggle countless responsibilities, and UAGC offers the flexibility and support they need. UAGC is vital in making higher education accessible to those who need it most, breaking barriers that traditional institutions often ignore.
Furthermore, UAGC is unwavering in its commitment to supporting students, staff, and faculty, ensuring consistent educational quality and professional growth. As we continue to evolve, we focus on transparent evolution and collaboration, learning from past oversights to create an environment where our students can improve employment opportunities. Our pursuit of high-quality education is not a destination but an ongoing journey to which UAGC is deeply committed. Like any reputable university, we conduct regular course and program reviews, embrace continuous improvement, and acknowledge areas for development as a perpetual process. This commitment to educational quality is a cornerstone of our institution, ensuring our students receive the best education possible and can be confident in our dedication to their success.
The UAGC faculty, the backbone of our institution, is growing increasingly weary of misleading and disparaging remarks against the university and the faculty. It is time to move forward constructively and collegially. In the name of higher education, we implore you to stop defaming our university, staff, faculty, and students. To that end, we welcome meeting and educating any skeptical faculty or staff on our university’s mission and approach to serving non-traditional adult learners. Above all, we’re eager to clear any misconceptions by providing accurate data, helping to ensure that your words align more closely with the truth moving forward.
As we look to the future (Dr. Cabrera), the late President Franklin D. Roosevelt, who signed the unprecedented G.I. Bill into legislation, stated, “A smooth sea never made a skilled sailor” (Roosevelt, n.d.).”
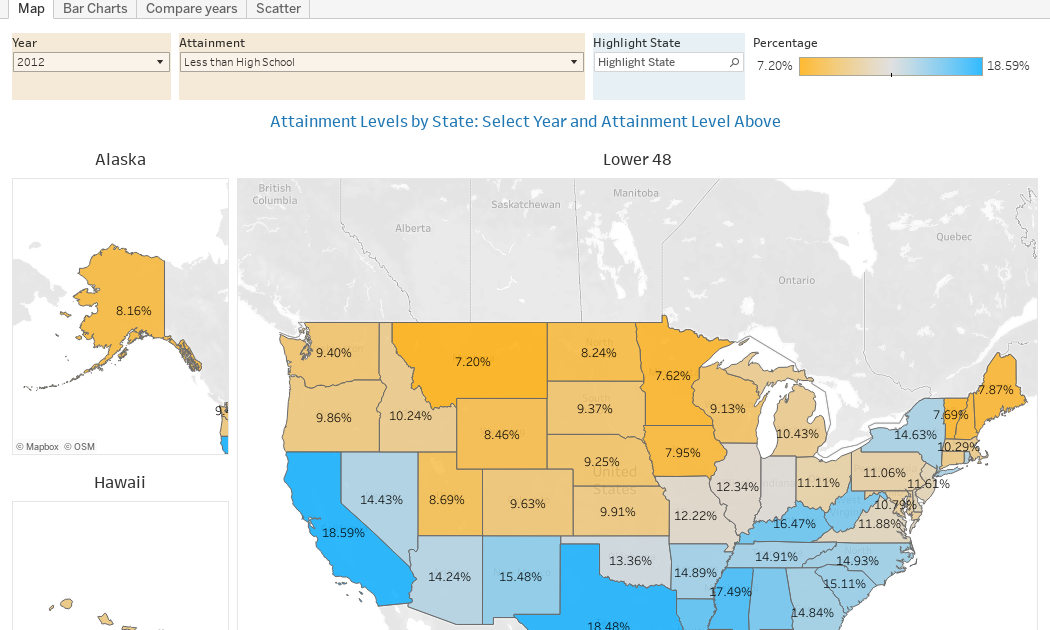
Attainment has always been an interesting topic for me, every since I first got stunned into disbelief when I looked at the data over time. Even looking at shorter periods can lead to some revelations that many don’t make sense at first.
Here is the latest data from NCES, published in the Digest of Education Statistics. Please note that this is for informational purposes only, and I’ve not even attempted to visualize the standard errors in this data, which vary from state-to-state.
There are four views year, all looking at educational attainment by state in 2012 and 2022.
The first shows data on a map: Choose the year, and choose the level of attainment. Note that the top three categories can be confusing: BA means a Bachelor’s degree only; Grad degree means at least a Master’s (or higher, of course); and BA or more presumably combines those two. Again, standard errors might mean the numbers don’t always add up perfectly.
The second shows the data on a bar chart, in three views: 2012 data, 2022 data, and the change, in percentage points. You can choose the attainment level, and then use the control to decide which column to sort the data by.
The third view is a slope chart, where you can see the two years for any state. Choose the attainment level, and then highlight the state you’re interested in. Hover over the points for details.
And finally, the scatter shows the same data, with the same controls; the bubbles are sized by percentage-point change. Additionally, you can use the filter to see which states have changed the most or the least.
If anything surprises you here, drop a comment below, or send me an email.

Earlier this month, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit found that the law to ban TikTok in the United States did not violate Americans’ First Amendment rights. Never before has Congress taken the extraordinary step of effectively banning a platform for communication, let alone one used by half the country.
The First Amendment requires an explanation of why such a dramatic restriction of the right to speak and receive information is necessary, and compelling evidence to support it. The government failed to provide either.
What little Congress did place on the public record includes statements from lawmakers raising diffuse concerns about national security and, more disturbingly, their desire to control the American public’s information diet in a way that strikes at the heart of the First Amendment.
Today, FIRE and a coalition of organizations filed an amicus brief urging the Supreme Court to reverse the decision.
FIRE is proud to be joined by the following organizations and individuals for today’s brief:
Will Creeley, legal director at FIRE: “The government doesn’t have the power to pull the plug on TikTok without demonstrating exactly why such a dramatic step is absolutely necessary. It has failed to publicly lay out the case for cutting off an avenue of expression that 170 million of us use. The First Amendment requires a lot more than just the government’s say-so. Fifty years after the publication of the Pentagon Papers, Americans understand that invoking ‘national security’ doesn’t grant the government free rein to censor. By failing to properly hold the government to its constitutionally required burden of proof, the court’s decision erodes First Amendment rights now and in the future.”
Jacob Mchangama, executive director of The Future of Free Speech and senior fellow at FIRE: “For decades, the United States has been the global gold standard for free speech protections. The unprecedented bipartisan push to effectively shut down TikTok — an online platform where millions exercise their right to free expression and access information — represents a troubling shift from this proud legacy. If enacted, this ban would make the U.S. the first free and open democracy to impose such sweeping restrictions, drawing uncomfortable parallels with authoritarian regimes like Somalia, Iran, and Afghanistan, which use similar measures to suppress dissent and control their populations. This is not just about a single app; it is a litmus test for the resilience of First Amendment principles in the digital age. The Supreme Court must ensure that Congress is held to the highest standard before permitting actions of such profound consequence. A TikTok ban risks setting a dangerous precedent that undermines the very freedoms distinguishing democracies from autocracies.”
The D.C. Circuit’s decision justifies the Act’s sweeping censorship by invoking “free speech fundamentals.” In so doing, it confuses the First Amendment values at stake, and sacrifices our constitutional tradition of debate and dialogue for enforced silence. The D.C. Circuit’s misguided reasoning is sharply at odds with longstanding First Amendment precedent, violating the constitutional protections it claims to preserve. Instead of following the instructive example set by Taiwan, which has eschewed a blanket TikTok ban in favor of robust counterspeech, the D.C. Circuit’s logic echoes the authoritarianism of North Korea and Iran.
READ THE FULL BRIEF BELOW

Social philosopher Herbert Spencer
was wrong in many respects when he coined the term survival of the fittest to discuss human behavior and Victorian social policies. But
social scientists would not be wrong today in comparing humans to other organisms, or to understanding (but not necessarily agreeing with) Spencer’s application of survival of the fittest, especially as the guardrails of government and religion are weakened.
Humans may appear sophisticated in some ways, but we are animals, nevertheless. Many of the laws of human behavior are consistent with the laws of nature, despite commonly held beliefs about human civilization that seemingly make us different. Yet like other animals, humans are prone to disease and vulnerable to the environment. We can adapt to change, and survive using a variety of means which may comport to our values or cause cognitive dissonance. Humans imitate, innovate, manipulate, connive, and steal. Non-human organisms, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and more complex beings, like insects and rodents, can also adapt, and have so for millions of years, much longer than we have. We live in an ecosystem, and in communities. When other organisms thrive or die, it affects us.
This new social reality (or a return to older social realities) should become more apparent in the coming years as humans across the globe deal with a number of existential issues, including war, famine, and disease–and the human-induced climate change that will pour fuel on these issues. Not only must we reexamine Herbert Spencer, we must also reexamine Thomas Malthus and determine what aspects of his theories on population may be coming back to life, and what aspects may not be as relevant.
Related links:
The US Working-Class Depression: “Let’s all pretend we couldn’t see it coming.”