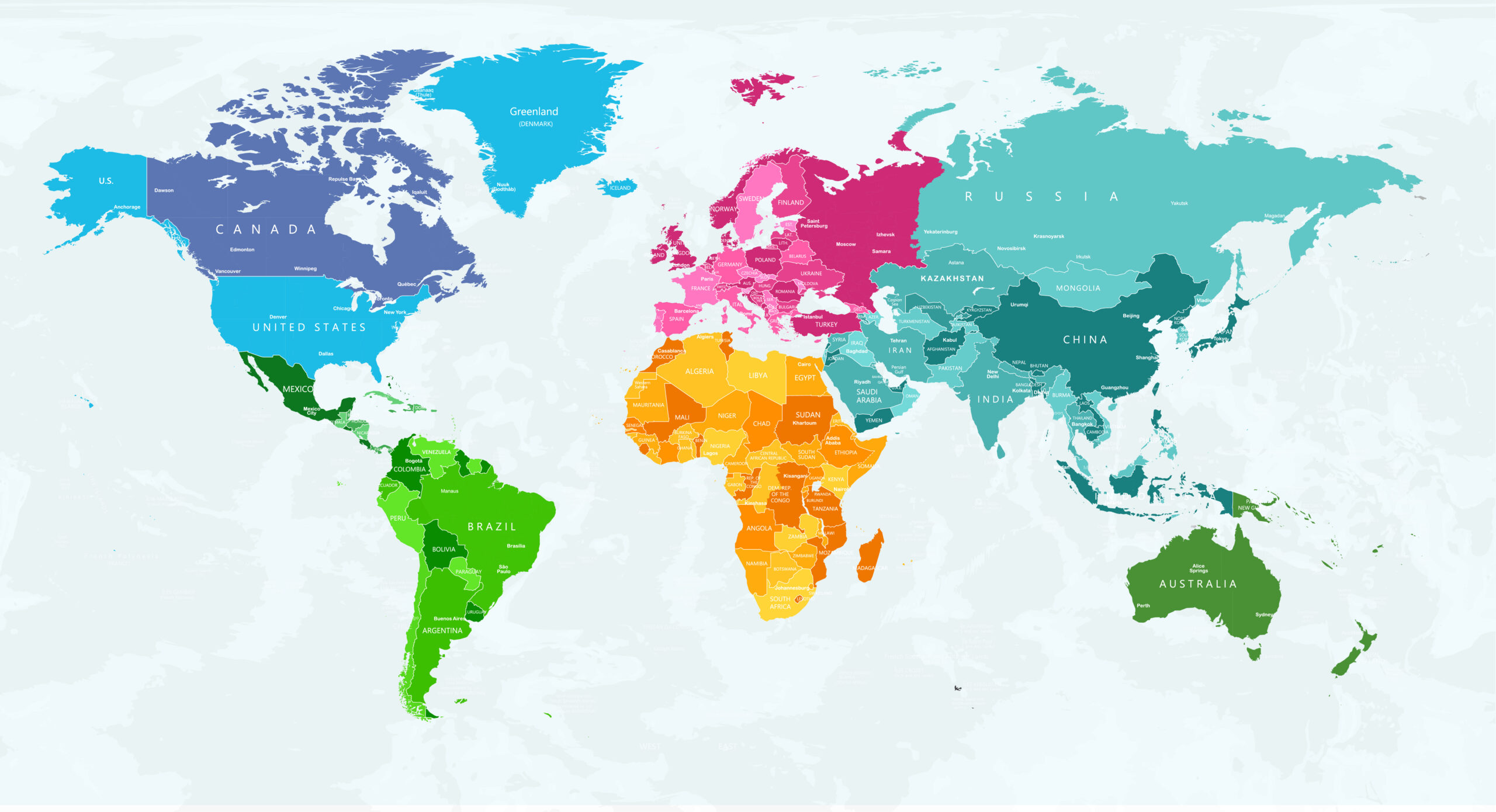
- The HEPI / Kaplan Soft-Power Index looks at the number of very senior world leaders (monarchs, presidents and prime ministers) who studied at a higher level in another country.
- Countries that have educated a significant proportion of the world’s most senior leaders are thought to benefit from a boost to their ‘soft power’.
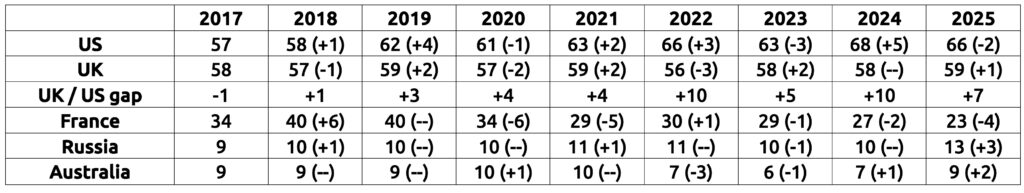
- The results for the leading two countries, the US and the UK, are broadly comparable to those for recent years but other countries, like France and Germany, fare worse than in past years while Russia and India have improved their position.
- For the first time, the results are being published according to the institution that world leaders studied at. Harvard University and the University of Oxford lead the pack, with Sandhurst, the University of Cambridge, the LSE and the University of Manchester making up the rest of the top 6.
When launching the Soft Power Council in early 2025, the UK’s then Foreign Secretary, the Rt Hon. David Lammy MP, said, ‘Soft power is fundamental to the UK’s impact and reputation around the world. I am often struck by the enormous love and respect which our music, sport, education and institutions generate on every continent.’ The HEPI / Kaplan Soft-Power Index offers one way to measure the extent of this soft power.
In 2025, the United States remains comfortably in first place, as their higher education institutions have educated 66 senior world leaders, which is only slightly lower than the US total for 2024 (68). The UK remains in a comfortable second place, having educated 59 world leaders. France performs less well than in the past but stays in third place, with 23 leaders.
The Index is based on a snapshot of world leaders for early August 2025. Changes since then are not reflected in the data. The Index should not be regarded as the only way to measure soft power and should be used alongside other sources of information.
Since the Soft-Power Index was launched in 2017, 81 (42%) of the countries in the world have had at least one very senior leader educated at a higher level in the UK. The Index is regularly quoted by UK Government Ministers – for example, last year’s results featured in this week’s Post-16 Education and Skills white paper.
World leaders educated in countries other than their own
For the first time this year, the results are also being published according to the institution that the leaders attended, with Harvard (15) and Oxford (12) topping the tree.
Harvard alone has educated more senior world leaders than all higher education institutions in Russia (13). Harvard has also educated more senior world leaders than Italy (5), Spain (5) and Germany (4) combined.
Key findings
- The strong performance of the United States represents the country’s second best ever total (equal with 2022 but slightly down on 2024).
- In terms of absolute score, the United Kingdom matches the best it has done since the Index began in 2017 (59), equalising the record that was also hit in 2019 and 2021.
- France fares worse than in the past, with a big drop-off of 17 since 2019 from 40 to 23, but retains third place.
- Russia posts its best performance, with 13 world leaders educated there, beating its previous high of 11 in 2022.
- Australia (9, +2) remains in fifth place, while Switzerland is in sixth place (7, +1).
- India scores its best ever performance. In 2022, only two serving very senior leaders had been educated to a higher level in India; in 2025, five had been – this is the same total as for Spain and also Italy.
- Germany drops out of the top 10 for the first time, having educated just four serving world leaders, the same number as Canada, Germany, Morocco, the Netherlands and South Africa – and the same number as for the LSE alone.
- The higher education institution that has educated the most current world leaders while they were international students is Harvard University (15), closely followed by the University of Oxford (13).
- Five of the six best-performing institutions are situated in the UK, meaning world leaders educated in the UK tend to have been concentrated in a smaller number of institutions. While Harvard is the only US institution to have educated more than three serving world leaders, the UK has five institutions that have educated more than three: Oxford (13); Sandhurst (8); Manchester (6); Cambridge (5); and the LSE (4).
Institutions attended by very senior world leaders
| Ranking | Higher education institution | Number of world leaders |
| 1 | Harvard | 15 |
| 2 | Oxford | 12 |
| 3 | Sandhurst | 8 |
| 4 | Manchester | 6 |
| 5 | Cambridge | 5 |
| 6 | LSE | 4 |
| 7= | Boston | 3 |
| 7= | Bristol | 3 |
| 7= | George Washington | 3 |
| 7= | New York | 3 |
| 7= | Pennsylvania | 3 |
| 7= | UCL | 3 |
| 7= | US Army Command and Staff College | 3 |
The 15 world leaders educated at Harvard are: i) the Prime Minister of Bhutan (Tshering Tobgay); ii) the President of Botswana (Duma Boko); iii) the Prime Minister of Canada (Mark Carney); iv) the King of Denmark (Frederik X); v) the President of Ecuador (Daniel Noboa); vi) the Prime Minister of Greece (Kyriakos Mitsotakis); vii) the Prime Minister of Israel (Benjamin Netanyahu); viii) the Prime Minister of Jordan (Jafar Hassan); ix) the Prime Minister of Lebanon (Nawaf Salam); x) the Prime Minister of Luxembourg (Luc Frieden); xi) the President of Moldova (Maia Sandu); xii) the Chief Minister of Sierra Leone (David Moinina Sengeh); xiii) the President of Singapore (Tharman Shanmugaratnam); xiv) the Prime Minister of Singapore (Lawrence Wong); and xv) the Prime Minister of South Korea (Kim Min-seok).
The 12 world leaders educated at the University of Oxford are: i) the King of Belgium (Philippe); ii) the King of Bhutan (Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck); iii) the Prime Minister of Canada (Mark Carney); iv) the President of East Timor (José Ramos-Horta); v) the Prime Minister of Hungary (Viktor Orbán); vi) the Emperor of Japan (Naruhito); vii) the King of Jordan (Abdullah II); viii) the President of Montenegro (Jakov Milatović); ix) the King of Norway (Harald V); x) the Sultan and Prime Minister of Oman (Haitham bin Tariq); xi) the President of the Philippines (Bongbong Marcos); and xii) the Prime Minister of the Solomon Islands (Jeremiah Manele).
Nick Hillman OBE, the Director of HEPI, said:
International students bring enormous benefits to the UK. They all spend money while they are here and some then contribute to the UK labour market after studying. The diplomatic benefits are less well understood even though they can be equally important. In 2025, over a quarter of the countries around the world have a very senior leader educated in the UK, which amounts to tremendous soft power.
The current UK Government have established a Soft Power Council and promised a new education exports strategy. These are welcome, but they are counterbalanced by the incoming levy on international students, huge dollops of negative rhetoric and excessive visa costs.
Recent new obstacles standing in the way of people wanting to study in Australia, Canada and the United States provide an opportunity for the UK to steal a march on our main competitors. We are at risk of squandering this opportunity.
Linda Cowan, Managing Director of Kaplan International Pathways, said:
It is fantastic to see how many of our best known universities are educating foreign leaders. This year’s list also highlights the growing diversity and range of institutions contributing to the UK’s soft power, including Cranfield, Leicester, Liverpool and Westminster.
Another trend to watch is the expansion of transnational campuses of British universities abroad, such as in India and the UAE. These initiatives have the potential to further enhance the UK’s soft power by extending the reach of our higher education sector beyond students coming to the UK – a development to watch going forward.
Professor Irene Tracey, Vice-Chancellor of the University of Oxford, said:
That so many world leaders have studied at Oxford speaks to the transformative power of education — to shape ideas, deepen understanding, and inspire service on the global stage.
Professor Duncan Ivison, the President and Vice-Chancellor of the University of Manchester, said:
If soft power is fundamental to the UK’s impact and reputation around the world, then so too are the UK’s outstanding universities.
The HEPI / Kaplan Soft-Power Index makes clear just how important international students are to the UK’s global influence – both now and into the future. Extraordinary future leaders get their start at many of our universities and retain a deep affection for our country long after. And yet the Government is, at the same time, putting up obstacles to welcoming future international students to the UK with a proposed international levy, higher visa costs and reducing the graduate visa route.
We have a once in a lifetime opportunity to make the UK the global destination for the best and the brightest in the world given what is happening elsewhere – and especially in the US and Canada. Let’s not blow it.
The 59 leaders educated in the UK lead 55 countries (as a small number of places – Bahrain, Luxembourg, Namibia and the United Arab Emirates have two very senior leaders educated in the UK). Changes affecting the UK list for 2025 are outlined in the table below. They include:
- The Rt Hon. Mark Carney, the Prime Minister of Canada since early 2025, studied Economics at the University of Oxford.
- Taye Atske Selassie, the President of Ethiopia since late 2024, studied International Relations and Strategic Studies at Lancaster University.
- The President, Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah, and Prime Minister, Elijah Ngurare, of Namibia, who have both been in post since early 2025, studied in the UK – the Namibian President studied at Glasgow Caledonian University as well as Keele University and the Prime Minister studied at University of Dundee.
- The Prime Minister of Rwanda since July 2025, Justin Nsengiyumva, studied Economics at the University of Leicester.
- The Prime Minister of Sri Lanka since autumn 2024, Harini Amarasuriya, studied Social Anthropology at the University of Edinburgh.
Click here to download a table showing all the countries with at least one senior leader educated in the UK for the whole period from 2017 to 2025.
The 66 world leaders from 58 countries educated in the United States head the following countries:
Bahrain (2); Bangladesh; Belgium; Belize; Bhutan (2); Botswana; Bulgaria; Cambodia; Canada; Costa Rica; Denmark; Dominica; Dominican Republic; East Timor; Ecuador; Egypt; Finland; Greece; Guinea-Bissau; Guyana; Haiti (2); Iceland (2); Ireland; Israel (2); Ivory Coast; Jordan (2); Kuwait; Latvia; Lebanon; Liberia; Luxembourg; Malawi; Malaysia; Marshall Islands; Micronesia; Moldova; Monaco; Montenegro; Namibia; Nigeria; Palau; Palestine; Panama; Paraguay; Philippines; Rwanda; Saint Kitts and Nevis; Sierra Leone (2); Singapore (2); Slovenia; Somalia; South Korea; Spain; Sudan; Switzerland; Togo; Tonga; and Vatican City.
Notes for Editors
1. Leaders are defined as heads of state and heads of government (monarchs, presidents and prime ministers). Countries often have more than one (such as a president or monarch and a prime minister).
2. Countries are included if they are members of, or observers at, the United Nations, currently numbering 195 places. Palestine is therefore included but Northern Cyprus, for example, is not.
3. The HEPI / Kaplan Soft-Power Index is a measure of tertiary education. This is defined broadly but distance learning and transnational education are excluded for the soft-power benefits are thought to be less.
4. Leaders change throughout the year, so we provide a snapshot for August 2025. For example, the fieldwork was undertaken prior to the recent change of leadership in Thailand.
5. Each country is treated equally and we do not claim each individual result provides good evidence of positive soft power. No one is excluded on moral grounds.
6. Some people are educated in more than one other country and they can therefore count towards the totals for more than one country.
7. While we use multiple sources to obtain information, the educational background of some national leaders is opaque. HEPI welcomes feedback that would enable us to build up a more complete picture.
8. When new information comes to light, we update the figures. So there are some slight differences in the figures provided here for earlier years compared with what we have published in the past. For example, in the preparation of the 2025 numbers, we found new information that reduced the recent past total for the US (as we discovered two leaders were distance learners rather than in-person learners).
9. King Charles III’s higher education was delivered in the UK (at the University of Cambridge), the country where he was born and lives, and he is head of state of other countries in part by virtue of his position in the UK. So we have opted to exclude this information. This matches how we treat the President of France, Emmanuel Macron, who is one of the heads of state (Co-Prince) of Andorra.
10. The University of the West Indies (UWI) serves 18 countries and territories in the Caribbean. Attempting to unpick the place of study for those world leaders who studied at the UWI is beyond the scope of this study. Therefore, we have assumed that each one studied in their home nation. This is the same practice as followed in earlier years.