Please follow and like us:
Richard Feynman the father of Quantum Electrodynamics or “OED” realized the significance of Thompson’s double slit experiment because he felt carefully thinking through its implications would allow one to get complete understanding of the wave particle duality of existence predicted by Quantum Mechanics.
However, one can understand it in terms of the classical properties of wave mechanics and the space-time universe defined by Einstein.
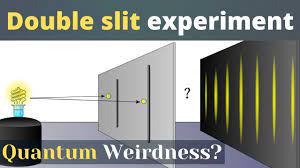
The double slit experiment is made up of a coherent source of photons illuminating a screen after passing through a thin plate with two parallel slits cut in it. Their wave properties cause them to interfere after passing through both slits, creating an interference pattern of bright and dark bands on the screen. However, at the screen, the light is always found to be absorbed as discrete particles, called photons.
When only one slit is open, the pattern on the screen is a diffraction pattern however, when both slits are open, the pattern is similar but with much more detailed. These facts were elucidated by Thomas Young in a paper entitled “Experiments and Calculations Relative to Physical Optics,” published in 1803 wrote “To a very high degree of success, these results could be explained by the method of Huygens–Fresnel principle that is based on the hypothesis that light consists of waves propagated through some medium.
However, discovery of the photoelectric effect made it necessary to go beyond classical physics and take the quantum nature of light into account.
It is a widespread misunderstanding that, when the two slits are open but a detector is added to determine which one a photon has passed through, the interference pattern no longer forms and it yields two simple patterns, one from each slit, without interference.
This is because there are ways to determine which slit it passed through in which the interference pattern will be changed but not be completely wiped out. For instance, by placing an atom at the position of each slit and monitoring whether one of these atoms is influenced by photon passing through it the interference pattern will be changed but not be completely wiped out.
But the most baffling part of this experiment comes when only one photon at a time impacts a barrier with two opened slits because an interference pattern forms which is similar to what it was when multiple photons were impacting the barrier. This is a clear implication the particle called a photon has a wave component, which simultaneously passes through both slits and interferes with itself. (The experiment works with electrons, atoms, and even some molecules too.)”
Many believe the importance of this experiment is that it demonstrates both the duality of the wave and particle properties of photons and the concepts of superposition and quantum interference.
Yet, one can understand this experiment in terms of the classical properties of waves and Relativity because they tell us an electromagnetic wave moves continuously through space-time unless it is prevented from doing so by someone observing or something interacting with it. This would result in its energy being confined in three-dimensional space. The science of wave mechanics also tells us the three-dimensional “walls” of this confinement will result in its energy being reflected back on itself thereby creating a resonant standing wave in three-dimensional space. This would cause its energy to be concentrated at the point in space where a particle would be found. Additionally, wave mechanics also tells us the energy of a resonant system, such as a standing wave which this confinement would create can only take on the discrete or quantized values associated with its fundamental or a harmonic of its fundamental frequency.
Additionally, it also tells us a particle would have an extended volume equal to the wavelength associated with its standing wave.
(Note the boundaries or “walls” of its confinement would be defined by its wave properties. If an electromagnetic wave is prevented from moving through space it will be reflected back on itself. However, that reflected wave still cannot move through space therefore it will be reflected back creating a standing wave. Putting it another way the wave itself defines its boundaries because if it cannot move though space it MUST STAND in place in the form of a standing wave.)
Putting it in the vernacular of Quantum Mechanics when an electromagnetic wave is prevented from moving through space either by being observed or encountering an object its “Collapses” to a form a standing wave that would define the quantized energy Quantum Mechanics associates with a particle.
It shows the reason why the interference pattern remains when one photon at a time is fired at the barrier with both slits open or “the most baffling part of this experiment” is because, as mentioned earlier it is made up of an electromagnetic wave, therefore it occupies an extended volume which is directly related to its wavelength.
This means a portion of its energy could simultaneously pass through both slits, if the diameter of its volume exceeds the separation of the slits and recombine on the other side to generate an interference pattern.
However, if its energy is prevented from moving through space by contacting the screen it will be confined to three-dimensional space causing it to be concentrated in a standing wave that as mentioned earlier would define the energy of the photon that impacted the screen.
Additionally, because the energy of the standing wave which earlier was shown to define the quantum properties of a photon is dependent on its frequency the energy of the particle has when it contacts the screen must have the same energy. Therefore, where it appears on the screen will be determined by where the interference of the wave properties from each slit combine to produce enough energy to support the standing wave associated with its particle properties.
It also explains why the interference pattern disappears, in MOST cases when a detector is added to determine which slit a photon passes through is because the energy required to measure it causes the wavelength of the one being measured to change so that it will not have the same resonant characteristics as one that passed through the other slit. Therefore, the energy passing thought that slit will not be able to interact, in MOST cases with the energy passing through the other one and no interference pattern will form.
However, it also explains why, as was mentioned earlier “there are ways to determine which slit a photon’s energy passed through that will cause a change in the interference pattern but will not completely wipe it out.
The reason for this is if the energy passing through one of the two slits is altered by a relatively small amount compared to what it originally was, classical wave mechanics tells us it will be able to interact to form a slightly different resonant structure with a slightly different interference pattern on the other side than would be the case if no measurement was taken.
However, this also means one should be able to use the science of wave mechanics and the physical properties of space-time to quantify the maximum amount of energy a measuring device can remove from the wave while passing through a slit that will permit the interference pattern although somewhat altered to be re-established on the other side.
For example, if the above interpretation for the double slit experiment is correct one should be able to use the science of wave mechanics to calculate the energy required to cause specific shift in the interference and determine if it matches the energy taken out of the system by the detecting equipment.
This provides an experimental way of determining if the results of the Thompson’s double slit experiment are due to physical properties of space-time or the quantum properties of the wave function because if the pattern disappears above that value and reappears below it would suggest the above explanation is valid. If not, it would suggest the quantum mechanical one is.
Einstein’s Explanation of the Unexplainable
Please follow and like us: