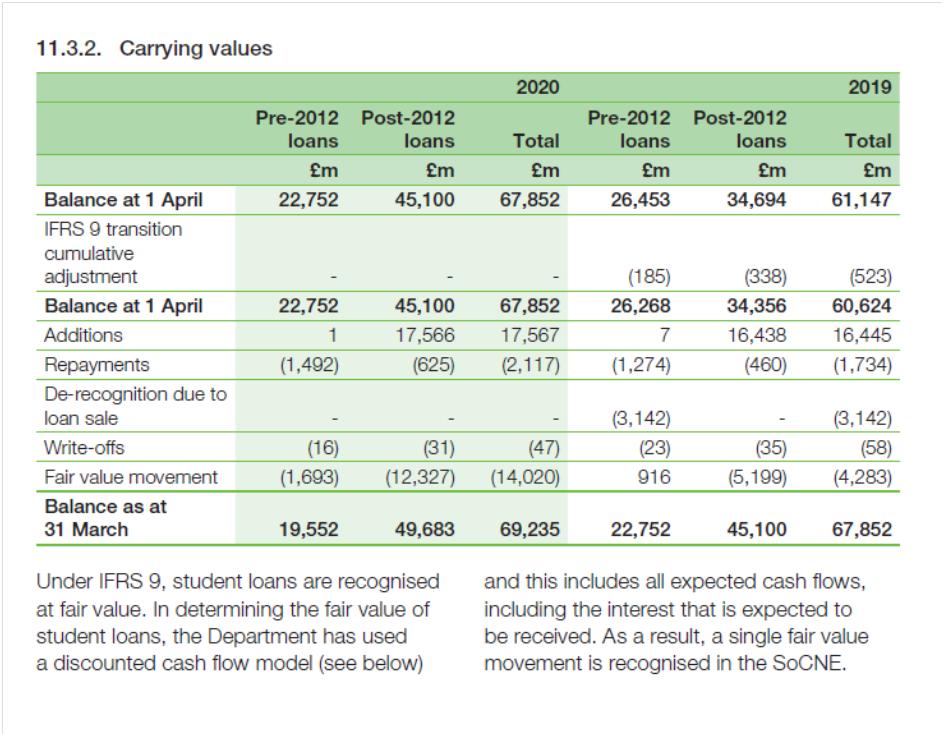
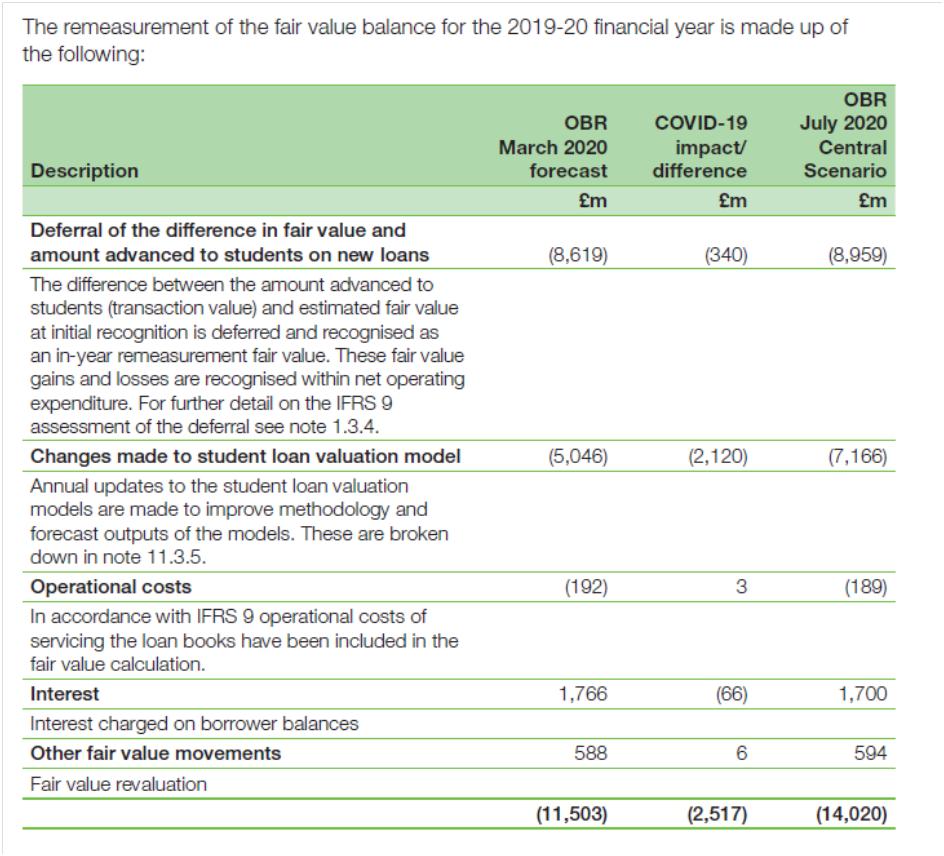
I have seen some confusions recently on twitter regarding university finances. Here are four recommendations:
- Avoid using sector aggregate figures to make your arguments
The sector is very uneven both in terms of size of institutions and in financial performance, make sure you are familiar with your institution and how it fits into the sector. - Avoid using figures for “reserves” when you mean cash
In accounting terms, “reserves” does not mean cash. Cash is included in reserves but that is because reserves names the excess of assets over liabilities: that the institution owns more than it owes. If it didn’t have reserves it would be insolvent. But its assets include buildings and land, which can dominate the reserves figure.
It is a confusion that crops up regularly and is often associated with right-wing arguments about the sector being “awash with cash”. If you want to talk about cash, use the figures for cash – but bear in mind that it is good management to hold significant levels of cash or other liquid assets to manage the day-to-day running of the organisation. Universities are large and have large outgoings! - Revolving Credit Facilities (RCFs) are like overdrafts …
If you have one, you aren’t necessarily planning to use it.
It provides extra headroom or is there for an emergency. Universities might simply be using it in their “liquidity” calculations to assure OfS that they have sufficient resources to cover 30 days of expenditure – falling below that level is a “reportable event” – and never intend to use it.
That your institution negotiated one, but haven’t used it, is not per se a sign of bad management. - Avoid confusing one-off costs with recurrent costs
There is a clear difference between spending £1million on a one-off purchase and an annual outgoing of £1million.
Your management may not always present the difference between such items in a very clear way, particularly when they have a certain narrative they wish to present or when they need to hit targets or covenants.
One to be wary of is “vacancy savings”. Are these higher because of a recruitment freeze? Are these one-offs or recurrent savings? Technically, the former; they would only become recurrent savings, if the posts are made redundant.
A management highlighting a certain level of vacancy savings may want to convey discipline to governors or lenders, but it can mask issues of sustainability: it isn’t a way to address persistent deficits. If there is an underlying deficit of, say, £2million, you shouldn’t be confident because they covered that through a recruitment freeze this year. And that’s solely from the numbers perspective: before you consider the implications for workload …
There are a few resources on this site for thinking about university finances. There is also a blog and recorded seminar for UCU on getting started with university accounts and “challenging the financial narrative”.
If you want more help, please get in touch.
I have worked with more than 40 UCU branches over the last few years to help with negotiations. Get in touch for details.
A testimonial: