Artisanal gold mining in Kenya’s Western region is raising environmental and public health concerns as mercury contamination threatens both the miners and local water sources.
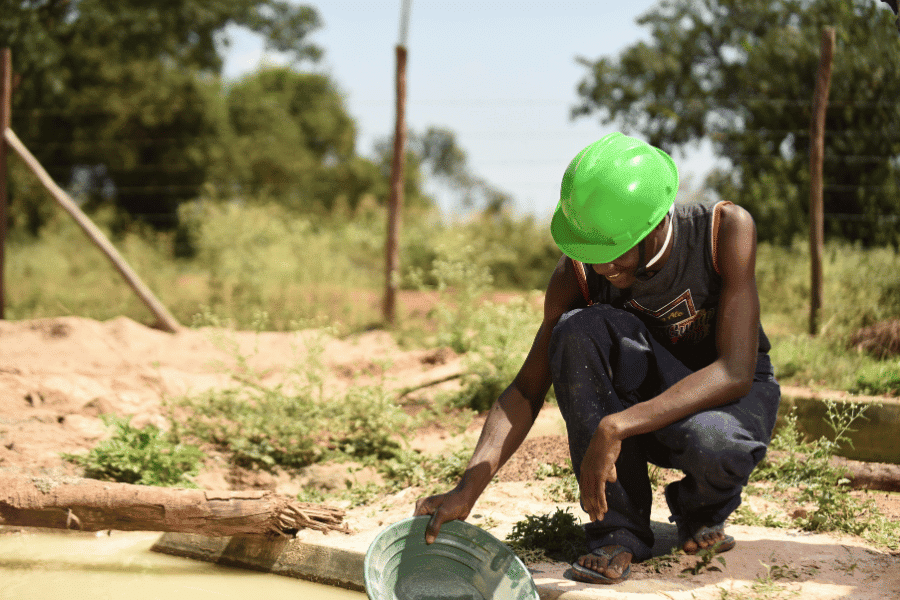
At sunrise in western Kenya’s Migori County, small groups of men and women gather at makeshift gold pits, sifting through soil in search of a precious livelihood. Across Kenya’s western counties, tens of thousands of people have turned to artisanal gold mining — small-scale, informal mining operations, often characterized by manual labor and the use of basic tools and low-tech equipment — as global gold prices rise and traditional farming incomes decline.
But while mining offers a vital economic lifeline, it brings a toxic legacy: mercury contamination that threatens health, water and livelihoods far beyond the mines.
A growing Industry in Western Kenya, small-scale gold mining has expanded rapidly in counties such as Migori, Kakamega and Vihiga. Recent estimates suggest that Kenya is home to more than 250,000 artisanal miners, with more than one million people depending on gold-mining for their livelihoods. In Migori alone, gold mining injects an estimated US$37 million into the local economy each year.
Despite the dangers, mining remains the most viable source of income for many. Surveys in Migori found that a significant majority of miners would not leave the industry, citing a lack of alternatives.
Extracting gold
Women make up an estimated 38% of Kenya’s small-scale gold mining workforce, often involved in ore processing — where mercury exposure is highest — yet receive just 11% of the sector’s revenue.
Nashon Adero, a lecturer at Taita Taveta University and a Kenyan mining policy expert, said that women’s roles and vulnerabilities are often overlooked in policy discussions.
Herman Gibb, a lecturer at George Washington University and managing partner and president of Gibb & O’Leary Epidemiology Consulting said that mercury is widely used by artisanal miners because it is cheap, accessible and effective at extracting gold from ore.
“It’s the easiest way for miners with limited resources to extract gold,” said Gibb, who used to work for the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
The process, known as amalgamation, involves mixing crushed ore with liquid mercury. Mercury binds to gold, creating an amalgam, which is then heated to vaporize and remove the mercury, leaving behind pure gold. But Gibb said that this heating releases toxic mercury vapour, endangering miners and nearby communities.
Mercury poisons
Researchers, including Gibb, have warned that mercury vapour can settle in households, exposing families, particularly children and pregnant women. Biomonitoring studies, including hair sampling, have shown high levels of exposure among women in small-scale gold mining regions.
However, research shows that testing capacity in rural Kenya is limited, and the logistics of sampling, storage and analysis pose additional barriers to effective surveillance. Mercury poses a variety of risks, depending on the form of exposure and who is exposed.
Elemental mercury, the liquid form used in gold extraction, poses serious risks when inhaled as vapour, which can cause neurological symptoms such as tremors, memory loss and cognitive impairment. Prolonged exposure can also cause kidney damage.
“Mercury vapour can damage the brain, especially in children whose nervous systems are still developing,” Gibb said.
Methylmercury, on the other hand, is an organic form of mercury created when elemental mercury enters water bodies and undergoes microbial transformation. It accumulates in fish and other aquatic organisms, entering the food chain. Methylmercury is particularly harmful to pregnant women and children, as exposure can lead to severe developmental disorders, intellectual disabilities and long-term neurological damage.
Chemicals in the food stream
Gibb said that when methylmercury enters the food chain, the risks become even more serious. “This is a toxin that affects the most vulnerable in invisible but lasting ways,” he said.
Although Kenya’s Mining Act of 2016 bans mercury use in mining, enforcement remains weak, and mercury is still widely available in local markets. News reports from the Kenya Chamber of Mines, the main mining industry organization in Kenya, state that many miners lack awareness of its dangers or access to protective equipment.
A 2023 study found that groundwater within six kilometers of mine sites in Migori contained mercury levels exceeding Kenya’s safe drinking water limit of 0.001 mg/L during the dry season. Soil samples from mine tailings (waste materials left over after valuable minerals have been extracted) showed mercury concentrations above 9.6 mg/kg, surpassing the National Environment Management Authority discharge limits.
Kenya’s mercury crisis is part of a wider global problem. Gibb said that the World Health Organization estimates prenatal exposure to methylmercury causes more than 227,000 new cases of intellectual disability each year, contributing to nearly two million “disability-adjusted life years” — a measure of years lost to ill-health or disability.
Mercury ranks among the top chemical threats to global health. Gibb said that its burden is compounded by the fact that most harm is invisible and long-term, making it difficult to prioritize in health budgets.
Science diplomacy
In 2017, Kenya ratified the Minamata Convention, an international treaty designed to protect human health and the environment from releases of mercury, committing to reduce mercury use and emissions. Yet implementation lags. A 2022 Auditor General’s report found that the Ministry of Petroleum and Mining had not mapped or formally designated artisanal mining zones in key counties.
Adero, the Kenyan mining expert emphasized the need for “science diplomacy” — the use of geospatial technologies (mapping tools and location data) and data-driven reports to influence local and national policymakers. Recent GIS-based research (Geographic Information System, or mapping software that shows roads, rivers, houses etc.) show mercury levels remain high in soil and water near mines.
“This highlights enforcement gaps and spatial risks [risks due to location] that many policymakers overlook,” he said.
Monitoring mercury exposure in rural areas is especially challenging due to limited laboratory facilities, transportation and technical capacity.
“We cannot manage what we do not measure,” Adero said. “Without proper exposure tracking, policies are just words on paper. We need data that is local, current and trusted by both governments and communities.”
Enforcing regulations
Gibb said that constraints around sample collection, storage and analysis hinder the ability to track exposure and enforce regulations.
The Migori county government has signed an agreement with the State Department for Environment and Climate Change to establish demonstration sites for mercury-free processing. But while these techniques can be effective, Gibb said, they require up-front investment, training and new equipment and that some alternatives such as cyanide also pose environmental risks.
Adero said that early adoption in countries such as Tanzania and Ghana shows promise but similar scale-up in Kenya remains limited.
Gender and social dimensions organizations such as the Association of Women in Energy and Extractives in Kenya address gender disparities by organizing cooperatives, providing training and advocating for gender-sensitive safety policies.
In his research, Adero found that significant gender gaps remain, with women overrepresented in the most dangerous roles but undercompensated. This research underscores that these disparities are rooted in systemic deprivation and limited access to education and financial literacy, he said.
Bureaucracy and fees
While formalizing small-scale gold mining through Kenya’s Mining Act of 2016 could improve safety and access to technical assistance, progress is slow, hindered by bureaucracy and high fees. Adero advocates simplifying the permitting processes, reducing costs and exempting small-scale miners from fees — learning from successful models such as Ghana’s community mining schemes.
Yet until real changes happen on the ground, artisanal miners remain caught between economic necessity and the invisible dangers of mercury poisoning.
“It’s what we know, and it works — you can see the gold right away,” said a miner from Migori.
But Dr. Adero warns that real progress requires concrete actions, not just policy declarations. Reliable, on-the-ground data to measure mercury exposure and inform decisions is key.
As Kenyan miners struggle with mercury poisoning, consumers around the world unknowingly wear and invest in gold that carries hidden human and environmental costs. Ultimately, addressing mercury contamination is not just a local challenge, it’s a call to action for global accountability, connecting distant luxury markets directly to the miners who risk their health and lives for precious metals.
Questions to consider:
1. Why do some people in Kenya risk their health to mine for gold?
2. What are some things the Kenyan government is doing to improve the lives of gold miners?
3. Why do you think gold is considered so valuable?