How effective are Snapchat school campaigns? Snapchat may no longer be the “shiny new toy” in the social media landscape, but it continues to offer something few platforms can match: authentic, ephemeral connection with Gen Z. While platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube dominate the headlines, Snapchat remains deeply embedded in the daily lives of many teens and young adults, especially in North America, Europe, and parts of the Middle East.
For education marketers targeting younger demographics, Snapchat’s low-friction, high-engagement environment makes it a powerful, if often underutilized, channel. From personalized outreach and peer-led takeovers to geofilter-powered event promotion, Snapchat school digital marketing campaigns meet students on their terms with content that feels spontaneous, creative, and real.
This blog post explores how different types of institutions: business schools, language schools, career colleges, K–12 schools, and universities, can use Snapchat strategically to support their enrollment goals, community engagement, and brand building.
Why Snapchat Still Matters
Globally, Snapchat’s active user base tops 850 million. In key recruitment markets like North America, parts of Europe, and the Middle East, teens and young adults continue to use Snapchat as a daily communication hub. What makes it especially powerful for education marketing is the way it enables institutions to meet students where they are in their preferred format, tone, and space.
How does Snapchat college work? Snapchat’s college features, like School Communities, offer institutions a way to foster peer-to-peer engagement within a verified, digital campus environment. It strengthens school spirit, encourages student interaction, and creates new touchpoints for community-building in a format Gen Z prefers.
Snapchat offers unique features that make it a great tool for engaging students and supporting education marketing. Its main appeal is that content, like photos and 10-second videos, disappears after being viewed, which makes it feel immediate and personal, unlike traditional social media. Some key features include:
Stories: Stories allow users to string together multiple snaps (photos or videos) that are viewable for 24 hours. This feature helps schools showcase campus life, events, and student takeovers in a way that feels immediate and engaging. Schools can post regular updates, highlights of campus activities, and even have students take over the account for a day to give a personal perspective on student life.
Snapchat School Communities: In 2024, Snapchat introduced School Communities, which let students join private groups for their school. Members can view and contribute to shared Campus Stories visible only to classmates. These communities help students connect with peers in a secure, school-specific space, making it easier to share experiences, participate in group chats, and discuss common interests. Snapchat verifies members using their official school email addresses and gives them a special badge on their profiles.
Geofilters and AR Lenses: Geofilters are custom-designed overlays available to users in a specific location. Schools use geofilters for events like campus tours, admitted student days, or graduations, turning these moments into shareable, branded experiences. Augmented reality (AR) lenses, which add fun virtual elements to photos, can also be used to promote school spirit and engagement.
User-Generated Content (UGC): Snapchat thrives on content created by its users. Schools encourage UGC through activities like account takeovers, contests, and Q&As. These features allow students to contribute their own content, giving a more authentic, behind-the-scenes view of campus life.
Example: NYU (Snapchat username: nyuniversity) has leveraged Snapchat’s geofilter feature to welcome and engage prospective students. In 2016, NYU introduced a custom Snapchat geofilter for its Admitted Students Day event, even running a student design contest to create the filter. The winning filter gave visiting admits a fun way to announce their presence at NYU on Snapchat. NYU’s official news release also encouraged the community to “Add us on Snapchat” for behind-the-scenes campus glimpses and student takeovers.


Source: NYU
Snapchat Ads and Discover: In addition to organic content, Snapchat offers a robust ads platform and a Discover media section. While Discover is mostly for professional media partners, schools can utilize Snapchat Ads Manager to run targeted ad campaigns for recruitment. From short video ads to swipe-up web forms, Snap ads can reach users by age, location, interests, and more, crucial for enrollment marketing.
What does putting your school on Snapchat do? Listing your institution on Snapchat enables a digital community where students connect, share, and engage under your brand. While not managed by the school, this community becomes a valuable extension of campus life and student culture.
How does Snapchat verify your school? Snapchat confirms membership by requiring students to use their institutional email address for verification. This automated system ensures only enrolled individuals access the community, minimizing moderation needs while maintaining student privacy and authenticity.
With expertise in education marketing, agencies like HEM help schools navigate these ad tools as part of an integrated digital marketing strategy, ensuring Snapchat campaigns align with enrollment goals and complement efforts on other platforms.
To learn more about crafting cross-platform campaigns, see HEM’s digital marketing services specifically for education organizations, which cover social media, paid ads, content, and more.
With this foundation, let’s examine how various types of educational institutions are using Snapchat in practice, from the tech-savvy prep school to the global MBA program.
K–12 Schools: Building School Spirit With Caution and Creativity
K–12 schools, particularly high schools, face a unique challenge when it comes to Snapchat. While teens are highly active on the platform, schools must balance the need for engagement with a duty of care, especially considering their minor student populations. Despite these concerns, some schools have found creative ways to use Snapchat to build school spirit, communicate with students, and engage parents and alumni, all while ensuring privacy and safety.
One common use of Snapchat in schools is to share quick glimpses of campus life and events, offering a more personal and immediate connection than traditional communications like newsletters.
Schools also leverage Snapchat’s geofilters for major events like prom, graduation, or sports games, encouraging students to use school-branded filters. These geofilters, often featuring the school name or mascot, help increase visibility and pride as students share their celebratory moments with their networks.
Example: At Lincoln School in Costa Rica, a student designed an official Snapchat geofilter for the campus, enabling students to overlay a custom school graphic on their snaps. Geofilters like this rally school spirit during events and make it easy for students to share branded moments from school.
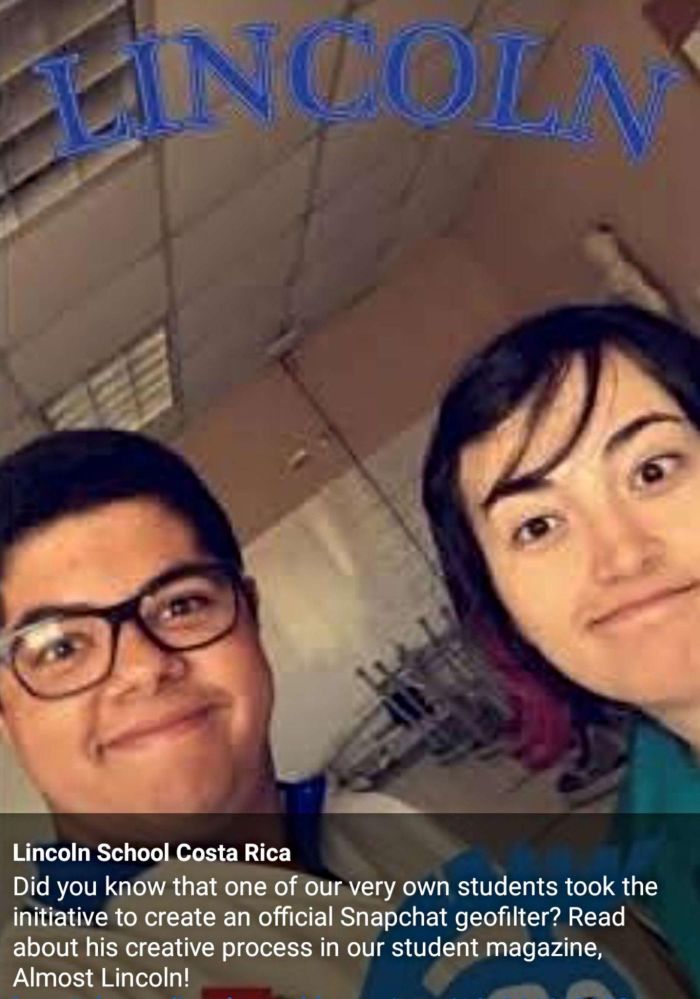


Source: Facebook
While Snapchat offers numerous opportunities for engagement, schools must exercise caution. Privacy concerns are paramount, and schools typically avoid following students back on the platform. They also direct more serious inquiries to email or in-person discussions.
Ultimately, Snapchat can be a powerful tool for K–12 schools when used thoughtfully with clear goals, safety protocols, and creative student involvement. However, schools should evaluate their resources and decide if the platform aligns with their communication strategy.
For those who are unsure about how to get started, education marketing consultants HEM can offer guidance to help schools develop effective, safe social media strategies.
Language Schools: Capturing Culture, Fun, and Learning in Real Time
Language schools, including ESL institutes, immersion camps, and university pathway programs, serve a naturally youthful audience: students who are eager to share their cultural and educational experiences. For this reason, Snapchat is a fitting addition to their marketing strategy. With over 38% of Snapchat’s users aged 18 to 24, it offers a great opportunity to reach teen learners who are already on the platform.
Snapchat’s popularity among this age group makes it ideal for language schools looking to connect with students where they spend their time. While platforms like Facebook may be better suited for reaching parents, Snapchat helps schools tap into the social, youthful energy of their student base.
Language schools use Snapchat in several ways to engage their audience. One key strategy is showcasing student life and local culture in real-time. By giving students control of the school’s Snapchat account, schools allow them to share their experiences, from excursions to daily activities.
Example: CEA ran a campaign called “10 Stages of Study Abroad,” where students shared their personal journeys through Snapchat, from arrival to cultural experiences. This user-generated content, filled with emojis and candid moments, felt real and approachable, making it an ideal way to engage teens considering studying abroad.


Additionally, language schools use Snapchat for quick-hit teaching and engagement. Posting a “word of the day” with a fun illustration or running mini-quizzes encourages interaction and reinforces learning. These spontaneous, playful posts not only engage current students but also expand reach as followers share and respond.
Finally, Snapchat can be used for international recruitment, particularly in regions where the platform is popular. Snapchat school campaigns can target specific countries where teens are heavy Snapchat users and run geo-targeted ads to promote their programs.
While Snapchat offers valuable engagement opportunities, not every language school may have the resources to manage it. If maintaining a regular presence is challenging, schools may choose to focus on other platforms like Instagram or YouTube.
However, if Snapchat aligns with your target demographic and storytelling style, it can be a powerful tool in your marketing mix, provided you post consistently and keep the tone light and authentic. Language learning is filled with fun and cultural moments, making Snapchat’s informal style the perfect vehicle for sharing these experiences.
Colleges: Bringing Practical Learning to Life
Colleges, ranging from community colleges to vocational institutes, serve a diverse audience, from recent high school grads to working adults seeking new skills. To connect with these students, platforms like Snapchat offer a unique opportunity.
Although adoption has been slow, career colleges that have embraced Snapchat report high engagement and significant benefits. Snapchat allows these institutions to showcase hands-on learning experiences and workforce outcomes in a way that feels authentic and immediate, which resonates with prospective students, particularly those focused on practical skills and career outcomes.
One major way career colleges leverage Snapchat is by giving students the platform to share real-time glimpses of their training. For instance, technical institutes may use Snapchat Stories to offer behind-the-scenes looks into workshops or classrooms. This content provides a dynamic, visually engaging alternative to traditional brochures, showcasing students’ day-to-day experiences in fields like auto mechanics or culinary arts.
Example: Owens Community College empowers student content producers to share everything from welding sparks to nursing students practicing IVs. This hands-on, visual storytelling appeals directly to prospective enrollees, giving them a taste of life in their chosen field.


Source: Owens Community College
In addition to showcasing student life, career colleges use Snapchat to bring workforce outcomes to life. Through alumni takeovers, schools can give prospective students a “day in the life” of a graduate, showing how their programs led to real career success. This adds a personal, relatable touch that resonates more than statistics alone.
Snapchat’s advertising tools also play a pivotal role in recruitment. Career colleges can use Snapchat Ads to target specific age groups or demographics, promoting relevant programs or seasonal events. For example, a cosmetology school could run an ad campaign targeting local teens to promote an open house, encouraging immediate sign-ups through Snapchat’s lead-gen feature.
While Snapchat offers clear benefits, career colleges must be cautious about the content they share, especially when dealing with sensitive or confidential aspects of certain programs. Social media policies must be in place to protect privacy and ensure safety protocols are not compromised. Additionally, moderation is crucial to maintain professionalism, particularly when engaging with prospective students via interactive features like Q&As.
Despite these considerations, career colleges that embrace Snapchat can build a modern, relatable brand, connect with a younger audience, and showcase their unique offerings. With the right strategy, Snapchat can be a powerful tool to attract the next generation of students. For colleges unsure where to start, digital marketing specialists can help create a strategy that includes content planning, staff training, and targeted ad campaigns to maximize impact.
Universities: Scaling Engagement With Personalization
Universities have been early adopters of Snapchat in the education space, using it to engage prospective students and strengthen their campus communities.
The platform’s youth-driven, real-time, and personal nature makes it a perfect fit for engaging 17–18-year-old prospects and meeting them where they already spend their time. Universities have utilized Snapchat for everything from personalized admissions outreach to virtual campus tours, showcasing the immediate and authentic experiences that Gen Z craves.
One standout use of Snapchat is personalized admissions and outreach. The University of Wisconsin–Green Bay gained attention by notifying hundreds of accepted students through Snapchat, offering a personal touch with fun campus photos and a message like “Welcome to the Phoenix family!” This creative approach made a lasting impression, fostering a sense of connection with incoming students. Many other universities have followed suit, using Snapchat to welcome students or remind them about key deadlines, creating an interpersonal feel that’s hard to achieve with traditional email.
Example: UW–Green Bay’s Snapchat notifications let students engage by snapping selfies back, creating an interactive and memorable admissions experience.
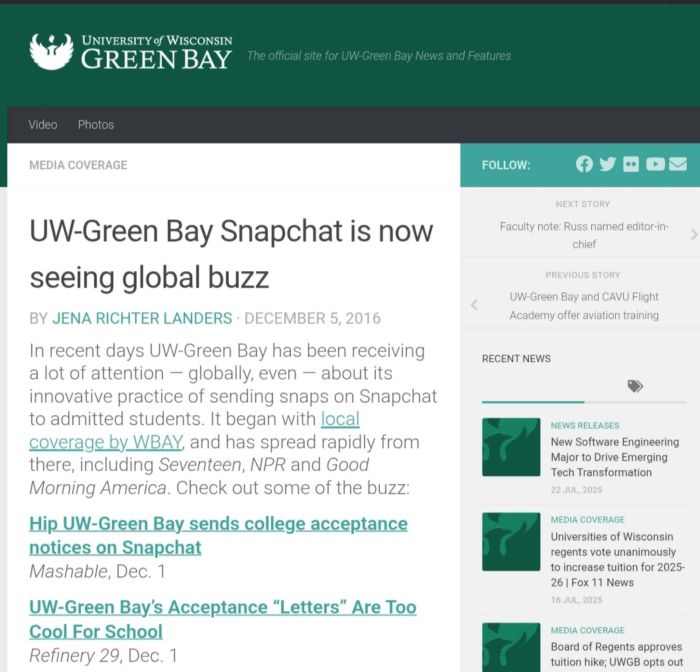

Source: UW–Green Bay
Another common strategy is virtual campus tours and Q&As. Before virtual tours became widespread, universities like UW–Green Bay were already using Snapchat to show prospective students around campus, from dorms to dining halls, answering questions along the way. These casual, behind-the-scenes tours are an engaging way to help students envision themselves on campus, giving them a more authentic and intimate view of student life. This approach also allows universities to reach thousands of potential students in a relaxed, informal way.
- Example: UW–Green Bay used Snapchat to host Q&A sessions on topics like financial aid and study abroad, allowing students to ask questions privately, making the experience feel more personal and accessible.
In addition to these strategies, many universities leverage student takeovers and ambassador programs, where students take over the Snapchat account for a week to share their day-to-day experiences. This approach humanizes the institution, allowing prospective students to connect with real students in an authentic way. Universities like UNC–Chapel Hill have seen success with this model, using cross-platform promotion to ensure maximum visibility for the takeovers.
- Example: At UNC–Chapel Hill, Snapchat takeovers are often cross-promoted on Twitter, with students sharing everything from campus life to personal milestones.
For contests and user-generated campaigns, universities often run engagement initiatives like Snapchat scavenger hunts or spirit photo contests. These campaigns incentivize students to engage with the platform and promote the school while integrating online interaction with offline connections. Such contests increase visibility and drive student participation, making them a fun, interactive way to build community.
- Example: Princeton’s “Snap as You Pack” contest encouraged incoming students to send snaps of their packing process, with winners receiving prizes at a campus event, turning digital interactions into real-world connections.
Universities also utilize Snapchat ads for recruitment and yield campaigns, with many seeing impressive returns. Finally, community building and retention is a growing area for Snapchat. With features like School Communities, universities are creating digital spaces for current students and alumni to share experiences and connect.
In conclusion, universities have effectively integrated Snapchat into their recruitment and engagement strategies. The key takeaway is the importance of authenticity and timeliness—students respond far more to real, relatable content than polished marketing. With careful planning, universities can use Snapchat not just as a novelty but as a core element of their digital strategy, driving awareness, engagement, and ultimately, enrollment.
Business Schools: Elevating Outcomes With Authentic Storytelling
Business schools, though often catering to older students focused on career advancement, are increasingly turning to Snapchat to humanize their brand and engage digital-native prospects. Snapchat’s bite-sized, authentic content resonates with younger audiences, offering business schools a unique opportunity to showcase their community and career outcomes in a dynamic, engaging way.
One of the most effective strategies employed by business schools is Snapchat alumni takeovers. Bentley University, for example, hosts monthly takeovers where alumni share “a day in the life” from their workplace, whether it’s at a Big Four accounting firm or a tech startup. These takeovers provide prospective students with a candid, behind-the-scenes look at life after graduation, helping them envision themselves in similar roles. This strategy not only promotes outcomes but also activates the alumni network, turning graduates into ambassadors for the school.
Example: Bentley University’s alumni takeovers offer a real-life glimpse into successful careers, showcasing alumni in cities across the country working for top companies.


Business schools also use Snapchat’s interactive features to engage prospects during admissions events. NYU’s Stern School of Business, for instance, leveraged geofilters during its admitted students’ day, allowing attendees to personalize their snaps with an NYU-themed graphic. This not only built excitement among admitted students but also turned their snaps into organic promotion for the school, reaching their personal networks and marking a milestone moment.
- Example: NYU Stern’s geofilter campaign allowed admitted students to broadcast their campus visit excitement, effectively turning their posts into branded, organic promotions.
In addition to these strategies, Snapchat offers a platform for student-driven content. Schools use Snapchat Stories to share authentic glimpses of student life, from MBA orientation week to team-building exercises. This unfiltered, real-time content helps prospective students connect with current students, creating a peer-to-peer relationship that traditional marketing cannot replicate.
- Example: The University of Michigan has used Snapchat to show prospective students what the school is truly about, with current students or young alumni sharing experiences directly with their peers.
Although Snapchat may play a supplementary role in business school marketing, especially with slightly older audiences who might prefer platforms like LinkedIn or YouTube, it offers a way to engage younger undergraduate prospects and keep them connected. As more Gen Z students enter graduate programs, Snapchat will likely become a more central tool in business school marketing strategies.
The key takeaway from early adopters like Bentley and NYU Stern is that authenticity sells. By letting students and alumni take the lead, business schools create meaningful, relatable content that stands out. Snapchat’s interactive elements, like geofilters, contests, and Q&As, add another layer of engagement, making it a valuable tool for creating memorable touchpoints that differentiate a school’s brand.
For business schools looking to implement these strategies, HEM offers expert support in crafting campaigns that resonate with younger audiences without compromising the professional brand. From structuring alumni takeover series to designing custom Snapchat filters, professional guidance ensures that schools’ Snapchat campaigns remain on-message and platform-appropriate.
Best Practices for Schools Using Snapchat
To use Snapchat effectively in education marketing:
- Set Clear Goals: Whether you’re aiming for inquiries, event sign-ups, or community engagement, define what success looks like.
- Assign Resources: Content doesn’t make itself. Designate staff, interns, or ambassadors. Even 1–2 days per week of content can be enough if it’s consistent.
- Cross-Promote Aggressively: Share your Snapcode on all channels. Post reminders when live sessions or takeovers happen.
- Encourage Participation: Ask students to snap their dorm move-ins, study setups, or event moments. Share user-submitted content with consent.
- Use Native Features: Stickers, polls, doodles, filters; these keep your content aligned with Snapchat’s playful vibe.
- Set Policies and Respect Privacy: Create a short social media usage policy. Don’t follow students back. Don’t show private info. Always get permission.
- Measure Performance: Monitor views, screenshots, swipe-ups, and conversions. Define KPIs like “50 open house signups” and track accordingly.
- Stay Flexible: Social trends shift fast. Listen to your students. If they say they love takeovers and ignore admin posts, adjust your campaign accordingly.
Snapchat is not a magic bullet. But as the examples show, with strategy, creativity, and the right guardrails, it can drive measurable results.
Snapchat: A Platform for the Brave and Strategic
Snapchat isn’t right for every school. But when used strategically, it can yield exceptional engagement and even tangible ROI. From intimate glimpses into student life to full-funnel recruitment campaigns, the platform gives institutions a way to be authentic, relatable, and modern.
Schools that embrace Snapchat thoughtfully, backed by clear goals, content planning, and a dose of Gen Z creativity, can stand out in a crowded market. And for schools unsure of how to begin, partnering with Higher Education Marketing can accelerate results, providing campaign support, creative strategy, and platform-specific training.
Snapchat may be temporary by design, but its impact on student perception can last much longer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: How does Snapchat college work?
Answer: Snapchat’s college features, like School Communities, offer institutions a way to foster peer-to-peer engagement within a verified, digital campus environment. It strengthens school spirit, encourages student interaction, and creates new touchpoints for community-building in a format Gen Z prefers.
Question: How does Snapchat verify your school?
Answer: Snapchat confirms membership by requiring students to use their institutional email address for verification. This automated system ensures only enrolled individuals access the community, minimizing moderation needs while maintaining student privacy and authenticity.
Question: What does putting your school on Snapchat do?
Answer: Listing your institution on Snapchat enables a digital community where students connect, share, and engage under your brand. While not managed by the school, this community becomes a valuable extension of campus life and student culture.