Artificial intelligence has rapidly evolved from experimental pilots into practical tools in higher education. Colleges and universities are now adopting AI agents, intelligent, autonomous systems designed to perform tasks, learn continuously from data, and act proactively to support students and staff throughout the entire enrollment and student journey.
Unlike traditional chatbots that offer scripted responses, AI agents for colleges can analyze behavior, adapt to changing inputs, and take meaningful actions based on goals or context. They can handle tasks like personalized communication, lead nurturing, application guidance, and even predicting student attrition, all with minimal human intervention.
For higher ed leaders, enrollment managers, and marketing teams, the question is no longer if AI will play a role in education; it’s how to use it strategically, ethically, and effectively. The potential is significant: smarter outreach, streamlined operations, and stronger support for students.
In this article, we’ll unpack what AI agents are, how they differ from simpler tools, how institutions are using them today, and what practical steps schools can take to get started or scale up AI-powered initiatives.
What Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a dynamic, intelligent system designed to perform tasks autonomously on behalf of users or institutions. Unlike static tools or rule-based chatbots, AI agents can analyze data, interpret complex intent, and act independently in pursuit of defined goals. They are capable of:
- Understanding and responding to user intent across multiple interactions
- Taking proactive actions based on predefined goals, real-time context, or behavioral triggers
- Continuously learning and improving from user inputs and outcomes
- Integrating with core institutional platforms such as CRMs, student information systems (SIS), learning management systems (LMS), and communication tools
In a higher education context, AI agents are not simply answering questions; they’re helping institutions solve problems. These agents can assist with lead nurturing, application guidance, appointment scheduling, academic advising, and more. Their ultimate purpose is to support institutional goals such as improving enrollment conversion, enhancing student engagement, and reducing the manual workload on admissions, marketing, and student services teams.
Key Characteristics of AI Agents in Higher Education
AI agents for colleges are defined by several core capabilities that set them apart from traditional tools or scripted chatbots:
- Autonomy: They operate independently, completing tasks or initiating interactions without requiring constant human oversight.
- Context Awareness: AI agents can recognize a student’s position within the enrollment or academic lifecycle and adjust their responses accordingly.
- Goal-Oriented Behavior: They are built with specific institutional outcomes in mind, such as increasing conversion rates, reducing summer melt, or improving retention.
- Continuous Learning: These systems improve over time by analyzing data patterns and learning from past interactions.
Together, these characteristics enable AI agents to act as proactive, adaptive partners in student engagement, going well beyond static digital assistants to drive meaningful institutional impact.
AI Agent vs. Chatbot: What’s the Difference?
A common source of confusion in higher education is the distinction between traditional chatbots and AI agents. While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, the capabilities and strategic impact of each are vastly different.
Traditional Chatbots
Chatbots are typically rule-based or scripted tools that respond to user prompts. They are reactive rather than proactive, meaning they wait for a user to initiate contact. Most chatbots are limited in scope: they may answer FAQs or provide links to resources, but they cannot understand context or evolve. Their utility is often confined to narrow use cases like answering admissions deadlines or sharing campus event information.
AI Agents
AI agents, by contrast, are intelligent, goal-driven systems that can operate autonomously across platforms. They are capable of interpreting complex intent, initiating actions, and retaining memory across sessions and channels. These agents integrate with CRMs, SIS, and learning platforms to deliver personalized experiences. More importantly, AI agents can adapt their strategies based on behavioral data and outcomes. For example, an AI agent might detect that an admitted student has not opened key onboarding emails and proactively reach out with a nudge or alternative format.
The Key Distinction
What makes an AI agent different from a chatbot? AI agents are autonomous, goal-driven systems that understand context, learn over time, and take proactive actions. Unlike chatbots, which respond to scripted prompts, AI agents can guide users through processes and initiate engagement across multiple platforms.
In essence, chatbots answer questions, but AI agents help move students through a process. They not only provide information but also drive outcomes like enrollment completion, financial aid submission, and course registration. As institutions seek to improve service quality and efficiency at scale, AI agents offer a more strategic, integrated approach than chatbots alone.
Why AI Agents Matter for Colleges Today
Higher education is undergoing a seismic shift. Institutions are under mounting pressure from multiple directions: growing competition for a shrinking pool of prospective students, fluctuating domestic enrollment in many regions, rising expectations for personalized and digital-first engagement, and increasingly limited internal resources. In this environment, colleges and universities need tools that enable them to do more with less without sacrificing student experience.
AI agents offer a powerful solution. These intelligent systems enable colleges to shift from reactive service models to proactive, anticipatory engagement across the student lifecycle. Whether guiding prospective applicants through the admissions process or supporting enrolled students with course selection and financial aid navigation, AI agents help scale operations while preserving a sense of personal touch.
Core Education AI Use Cases for Colleges
1. AI in Enrollment Management
One of the most transformative applications of AI agents is in enrollment management. Traditional outreach methods often rely on bulk communications and static timelines. AI agents, by contrast, enable real-time, tailored engagement based on where each student is in the funnel.
Key functions include:
- Sending automated, personalized nudges to incomplete applicants
- Identifying prospects who show signs of disengagement or drop-off
- Providing 24/7 responses to common admissions questions
- Supporting post-admit engagement and reducing summer melt
Rather than replacing admissions professionals, these agents act as digital extensions of the team, helping manage volume while maintaining quality interactions.
2. Intelligent Assistants in Higher Education Recruitment
On websites, landing pages, and student portals, intelligent AI assistants for higher ed help convert interest into action. These systems can dynamically guide users to the most relevant content or next steps based on browsing behavior, geography, or persona.
Use cases include:
- Directing students to matching academic programs
- Surfacing key dates and requirements based on applicant type
- Offering localized content or multilingual support for international visitors
- Capturing high-intent inquiries for CRM integration and follow-up
When embedded at strategic touchpoints, these tools improve the prospective student experience and boost lead conversion rates.
3. Student Services and Academic Support
Beyond recruitment, AI agents are increasingly being used to reduce administrative burden and expand access to essential student services. This is especially valuable for institutions serving diverse populations, including adult learners, international students, and part-time students who may need help outside of regular office hours.
Key areas of support:
- Assisting with course registration logistics and policies
- Answering financial aid questions and helping students navigate fees
- Referring students to on-campus services based on need (e.g., mental health, tutoring, IT help)
- Acting as a triage point for academic advising requests
By handling routine inquiries, AI agents free up staff to focus on more complex or sensitive cases.
4. Retention and Student Success
Student success teams often lack real-time visibility into which students are disengaging. AI agents can analyze signals such as missed logins, dropped classes, or overdue assignments to flag early risk indicators.
Once identified, agents can:
- Trigger automated check-ins or reminders
- Recommend helpful resources (e.g., peer tutoring)
- Notify academic advisors or success coaches
- Encourage re-engagement through timely, personalized outreach
These interventions help prevent attrition by reaching students before they fully disengage.
5. Marketing and Communications Automation
AI agents also bring efficiency to enrollment marketing operations. They can support:
- Real-time content personalization on websites
- Automated follow-up workflows based on behavior (e.g., abandoned form fill)
- Cross-channel engagement across email, SMS, and chat
- Handling campaign-related inquiries or call-to-action responses instantly
For marketing teams, this means campaigns can scale without losing relevance. AI ensures that prospective students receive the right message, at the right time, via the right channel, improving conversion rates and ROI.
In short, AI agents are not a future-facing concept. They’re a current strategic advantage. By embedding intelligence and automation into student engagement, colleges can improve outcomes, reduce strain on staff, and create experiences that meet the expectations of today’s digital-native learners.
How Are Colleges Using AI Agents Today?
Across Canada, the United States, and internationally, colleges and universities are already deploying AI agents to support critical areas like enrollment, student services, academic advising, and marketing. These are no longer just experimental tools or isolated pilot projects. Instead, many institutions are integrating AI agents into their core strategies, using them to improve responsiveness, personalize outreach, and ease the burden on staff.
From automating admissions follow-ups to guiding students through financial aid, real-world use cases are multiplying. The focus has shifted from “if” to “how best” to implement these tools.
(See the curated examples at the end of this article.)
Do AI Agents Replace College Staff?
This is a common concern, and the answer is no. AI agents are not designed to replace college staff, but to support them.
These intelligent tools handle routine, high-volume, and time-sensitive tasks that can overwhelm busy teams. They can respond instantly to frequently asked questions, guide users to resources, and even operate around the clock, especially useful during evenings, weekends, or high-traffic application periods.
By managing first-line support, AI agents free up staff to concentrate on what matters most: personalized advising, meaningful relationship-building, and strategic planning. They also surface real-time data and student behavior insights that staff can use to make more informed decisions.
Importantly, human expertise remains essential for nuanced conversations, equity-based support, and complex decision-making. Rather than replacing staff, AI agents extend their capacity, allowing institutions to offer more consistent, timely, and personalized service without adding headcount. When implemented thoughtfully, AI agents strengthen, not diminish, the human touch in education.
Ethical and Practical Considerations
As colleges adopt AI agents, ethical implementation is paramount. Institutions must ensure these tools align with institutional values and uphold trust.
Data Privacy and Security:
AI agents must comply with relevant privacy laws such as PIPEDA or GDPR. Clear, transparent data usage policies help reassure users and safeguard institutional integrity.
Bias and Fairness:
To prevent unintended bias, especially in areas like admissions or advising, institutions should conduct regular audits, use diverse training data, and maintain human oversight in high-stakes decisions.
Governance and Oversight:
Successful AI initiatives require clear accountability. Define who owns the AI agent, how it’s monitored, and when human staff should step in.
Ultimately, AI agents should enhance equitable access, not compromise it. Thoughtful design and oversight are essential.
How Can Colleges Get Started with AI Agents?
For colleges and universities exploring AI agents for the first time, a phased and strategic approach ensures alignment with institutional goals while minimizing risks.
Step 1: Identify High-Impact Use Cases
Start by targeting clear, high-volume needs where automation delivers immediate value. Common entry points include admissions inquiries, application follow-ups, and frequently asked questions in student services. These areas typically require timely, consistent responses and are ideal for early pilots.
Step 2: Align with Enrollment and Marketing Strategy
AI agents should reinforce your institution’s enrollment goals, not operate in a silo. Ensure that the use cases support broader priorities such as inquiry-to-application conversion, yield improvement, or retention. Collaboration between admissions, marketing, and IT is key.
Step 3: Integrate with Existing Systems
To be effective, AI agents must connect with your existing technology stack. Integrate them with CRM platforms, student portals, and marketing automation tools to ensure seamless data flow and actionable insights.
Step 4: Pilot, Measure, Optimize
Launch a limited-scope pilot with clear objectives. Track metrics like reduced response times, increased application completion, or staff time saved. Use feedback and data to refine both the agent’s responses and its integration with team workflows.
Step 5: Scale Thoughtfully
Once the agent has proven value, consider expanding to new functions (e.g., academic support or financial aid). Establish governance policies, ensure ongoing training and monitoring, and communicate transparently with users.
With the right foundation, AI agents can scale intelligently, becoming a long-term asset for your institution.
Examples of Higher Education Institutions Demonstrating AI Agent Use
Georgia State University (USA): Georgia State pioneered an AI chatbot named “Pounce” to assist incoming students with admissions queries, financial aid forms, and other enrollment steps. By answering thousands of questions 24/7 via text messages, Pounce helped reduce “summer melt” (admitted students failing to enroll) by 22% in its first year, meaning hundreds more freshmen made it to campus. This AI assistant continues to guide students through registration and financial processes, improving support for new Panthers.
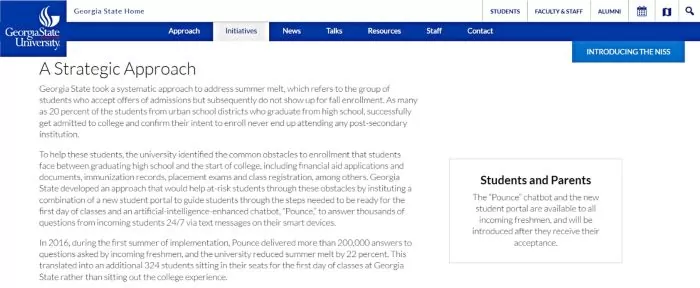

Source: Georgia State University
University of Toronto (Canada): U of T is actively exploring AI-driven tools to enhance student advising and services. A university-wide AI task force has recommended integrating AI into student support and administration. Initiatives include pilot projects for AI chatbots and data analytics to assist academic advisors, streamline routine administrative queries, and personalize student services. By embracing these technologies with a human-centric approach, U of T aims to improve how students receive guidance and navigate campus resources.
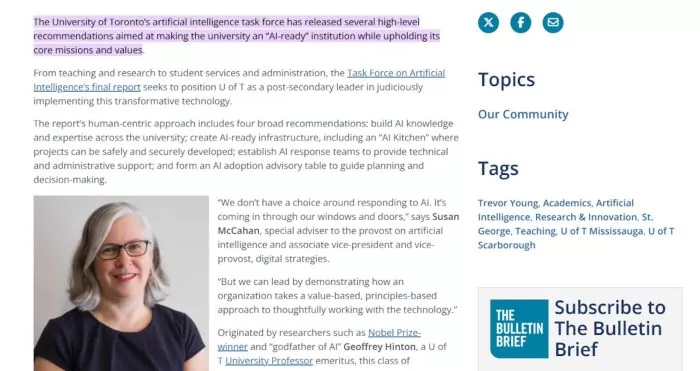

Source: University of Toronto
Arizona State University (USA): ASU has implemented AI-enabled digital assistants (including voice-activated tools) to guide prospective and current students. Notably, ASU partnered with Amazon to create a voice-based campus chatbot via Alexa, allowing users to ask the “ASU” skill about campus events, library hours, dining menus, and more. In residence halls, students received Echo Dot devices as part of a smart campus initiative, making it easy to get instant answers about enrollment or campus life. These AI assistants augment student engagement by conversationally providing on-demand information and support.
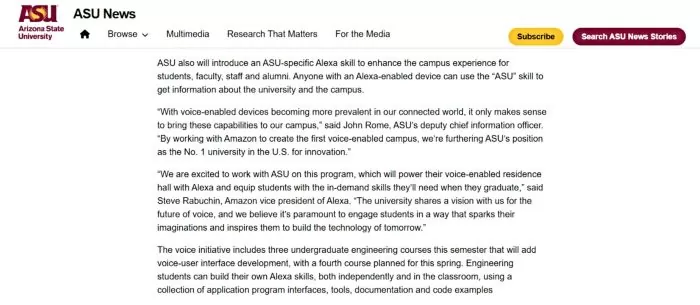

Source: Arizona State University
University of British Columbia (Canada): UBC leverages AI in both research and practical applications to improve student experiences. The university deploys AI chatbots and advising assistants to help answer student questions and streamline services. For example, UBC’s “AskCali” project is an AI-driven advising tool that uses generative AI to answer academic planning questions and direct students to resources. UBC Okanagan’s campus also introduced an AI chatbot across departments like IT support and Student Services, automating routine inquiries and reducing wait times by handling ~99% of chats, which frees up staff for complex issues. Through these efforts, UBC enhances student support while improving operational efficiency.


Source: UBC
Harvard University (USA): Harvard is applying AI systems to enhance academic advising, streamline administrative tasks, and bolster student engagement. The university’s digital strategy encourages responsible use of AI in advising and student services. For example, Harvard has explored AI chatbots for answering routine student questions and experimented with AI tutors to augment academic advising. These AI initiatives are aimed at improving the efficiency of advising processes and enriching how students interact with academic support, all while maintaining a human-centered approach (Harvard’s advisors and faculty guide AI use to ensure it aligns with educational values).

Source: Harvard University
University of Michigan (USA): U-M has rolled out AI-powered tools to support student services, including conversational assistants for advising and campus information. The College of LSA launched “Maizey,” a 24/7 AI academic advising chatbot that answers questions on course requirements, policies, and study tips, providing a “smart sidekick” for students seeking guidance after hours. Additionally, U-M developed “MiMaizey,” a personalized AI campus assistant that helps students find information on dining, events, organizations, and more in a chat interface. By deploying these AI-supported services, Michigan offers instant help and tailored support to students while complementing its human advisors.

Source: University of Michigan
University of Alberta (Canada): UAlberta is integrating AI into student services and campus operations to improve efficiency and support. The university’s AI committees explicitly guide the use of AI to “improve university operations, services, resource management, and administrative tasks.” This means deploying AI tools in areas like student advising, where chatbots or predictive analytics can assist with inquiries, and in back-office processes, where automation can streamline workflows. By embracing these technologies, the U of A seeks to enhance the student service experience (faster responses, 24/7 support) and optimize institutional decision-making and resource use.


Source: University of Alberta
Stanford University (USA): Stanford has been a leader in leveraging AI agents for student support, learning analytics, and administrative innovation. Researchers at Stanford have developed AI systems that detect when students are struggling in digital courses and then recommend interventions to instructors, effectively acting as an AI tutor/assistant to keep students on track. In student services, Stanford has experimented with chatbots and AI-driven data analysis to personalize learning and improve advising. These efforts—from AI “teaching assistants” that answer student questions to predictive models that inform advisors—illustrate Stanford’s use of AI to enhance learning outcomes and streamline academic administration.


Source: Stanford University
The Strategic Opportunity Ahead
AI agents represent a transformative opportunity for colleges and universities that approach them with purpose and alignment. When embedded within broader strategies for enrollment management, student success, and marketing, these tools can significantly enhance institutional impact.
By automating high-volume tasks and providing real-time, personalized support, AI agents help institutions engage students earlier in their journey, offer more relevant touchpoints, and deliver a seamless digital experience that today’s learners expect. At the same time, they free up staff to focus on strategic, human-centered work, creating a more agile and efficient institution.
The real value lies not in simply deploying AI tools, but in how they’re integrated across departments and designed to serve long-term goals. For higher education leaders, this means shifting the conversation from technology for its own sake to technology as an enabler of student-centric transformation. With thoughtful implementation, AI agents can become a cornerstone of modern, resilient, and responsive institutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What makes an AI agent different from a chatbot?
Answer: AI agents are autonomous, goal-driven systems that understand context, learn over time, and take proactive actions. Unlike chatbots, which respond to scripted prompts, AI agents can guide users through processes and initiate engagement across multiple platforms.
Question: How are colleges using AI agents today?
Answer: Across Canada, the United States, and internationally, colleges and universities are already deploying AI agents to support critical areas like enrollment, student services, academic advising, and marketing.
Question: Do AI agents replace college staff?
Answer: This is a common concern, and the answer is no. AI agents are not designed to replace college staff, but to support them. These intelligent tools handle routine, high-volume, and time-sensitive tasks that can overwhelm busy teams.