Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
This story was originally published by CalMatters. Sign up for their newsletters.
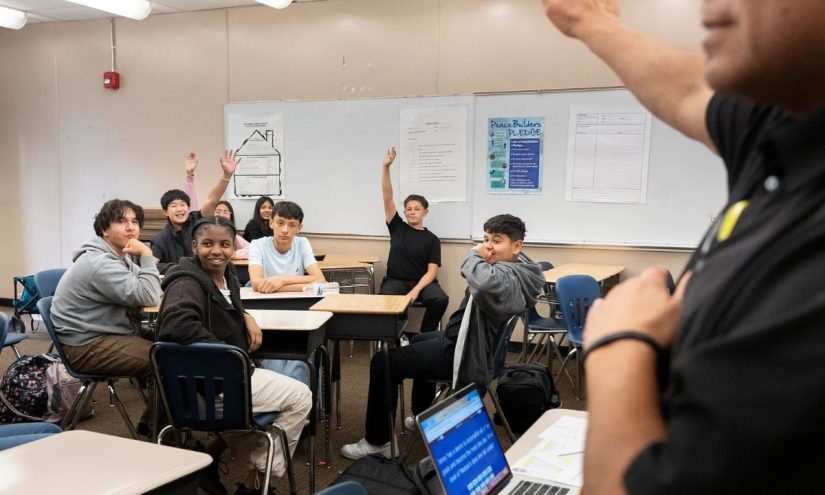
By 2:45 p.m. the regular school day at August Boeger Middle School had already ended, but one class is about to start. More than 20 eighth graders drop their backpacks and settle into desks — not for extra credit but for college credit.
These 13- and 14-year-old students in East San Jose are taking their first college course, an entry-level class on career planning. This middle school is one of the first in the state to offer a college-level course. In the coming years, the San Jose Evergreen Community College District wants all middle school students in this school district to be able to complete three college courses before they start high school, and soon, the district plans to offer other courses, such as sociology and ethnic studies, said Beatriz Chaidez, the chancellor for the community college district.
Middle schoolers have long been eligible to enroll in college classes in California, though only a few, high-achieving students actually do it. By offering a college class at a middle school — especially one in a high-poverty area — the community college district is looking to make that enrollment easier. The class is taught by a middle school staff member, and it’s reserved exclusively for middle school students.
But with so few programs, there is little research about whether students are benefitting, and the local faculty union is worried middle school students might not be ready.
Chaidez disagrees. “Navigating (college) as early as middle school is unheard of in their community,” she said. “So when they experience success, it really motivates them to continue.”
California is increasingly pushing high schools to offer community college classes directly to students during the regular school day, a set-up known as “dual enrollment.” Unlike AP classes, which include expensive exams and are limited to certain subjects and high-performing students, these community college classes cover a range of topics and are open to all students. By 2030, California Community Colleges Chancellor Sonya Chiristian wants all high school students to graduate with at least four college courses completed.
Chaidez wants to go further. She wants every local high school student to be able to complete about 20 college courses by the time they graduate — enough to earn an associate’s degree.
CalMatters reached out to the college district’s faculty union, which was surprised to learn the district is offering classes at a middle school.
“This opens up some problems,” said Jessica Breheny, an English professor and the union’s vice president. “I’m sure there are 12-year-olds that are college-ready, but there are just less of them and it’s less likely. Developmentally, they have other things going on.”
Research shows that high schoolers who take college classes are more likely to attend college and graduate, but there’s little research on how middle school students fare, said John Fink, a senior researcher at Columbia University’s Community College Research Center. “Nationally, and in most states, this is very, very rare, and in many states this is not allowed.” Instead, he said the focus is typically on enrolling more 10th, 11th and 12th graders in college courses.
A college-level course, with a few middle school games
About 10% of California’s high school students took a community college class in the 2021-22 school year, according to an analysis by professors at UC Davis using the most recent data. California’s community college system doesn’t track how many middle school students take college courses.
So far, the Mount Pleasant Elementary School District, which includes August Boeger Middle School, offers only one college course, called “Career Planning,” and it’s almost indistinguishable from any other class on its campus. The college course is taught in a regular middle school classroom, and the professor, Oscar Lamas, already works at the middle school, where he’s a counselor. Perhaps the only noticeable difference is the timing: The middle school day ends at 2:30 p.m. and Lamas’ course starts at 2:45. He’s paid separately by the community college to teach the course.
Career Planning helps students learn about career paths, practice resume-writing and learn psychological theories related to professional success. A governing board of college district professors, known as the Academic Senate, sets the objectives for each college course, but Lamas has broad discretion in teaching it. The Academic Senate responsible for setting the parameters of Lamas’ course did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
The dean of the community college’s counseling department, Victor Garza, refused an interview request from CalMatters but issued a written statement. Garza said the middle school class is akin to other dual enrollment courses, which maintain the college’s “academic rigor.”
“Some adjustments might be needed to cater to the unique needs and experiences” of students, he added.
On a Thursday before spring break, Lamas tries to make his class more fun by breaking the students into five teams to play a Jeopardy-style quiz game on the topic of the day, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
Natalie Mendoza, 14, becomes the default spokesperson of her team, named the “Tacos R Us Club,” but she answers the first question wrong, putting her team back 300 points and prompting her classmates to burst into chatter and analyze their mistakes.
As part of the class, she has to study a career, write a short essay about it and present it at a career fair. She picked intellectual property law. “A lot of people say I’m assertive,” she said. “I think that’s a really good trait for a lawyer, and I think it’d be fun to fight for people who have created stuff.”
Natalie said she’d be the first in her family to attend college but she’s already planning to go and has a few schools in mind, including UC Berkeley and San Jose State. If she does attend one of those schools, her grade in this counseling class would be part of her official college transcript.
Breheny, with the union, said she’s concerned about the quality of the classes, especially once the college district begins teaching other subjects, such as ethnic studies.
“Faculty designed their courses for adult learners,” Breheny said. An ethnic studies class may cover topics such as sexual violence and genocide, she added — topics that may be difficult to convey to a middle schooler. “Some of the material assumes a certain knowledge about the world, about politics, which you may not have at 11, 12, 13 years old.”
High schools offer few dual enrollment classes
August Boeger Middle School sits at the base of the Diablo Range mountains, tucked between the ranch-style homes and strip malls that color East San Jose. Teachers and staff greet each other with mucho gusto instead of hello. All around the open-air campus, murals tell the story of the region’s multi-cultural heritage, especially its Mexican and Chicano roots.
That celebration of culture is a direct response to a history of adversity, Lamas said. “East San Jose has always been a marginalized, disadvantaged environment.” As a result, schools in the community contend with education disparities, he said, such as a high dropout rate and a high teen pregnancy rate.
Offering a college class to these middle school students allows them to “see a possibility for their future that doesn’t exist within these walls here” and can inspire them to reach for a higher goal, said Marisa Peña, a school advisor.
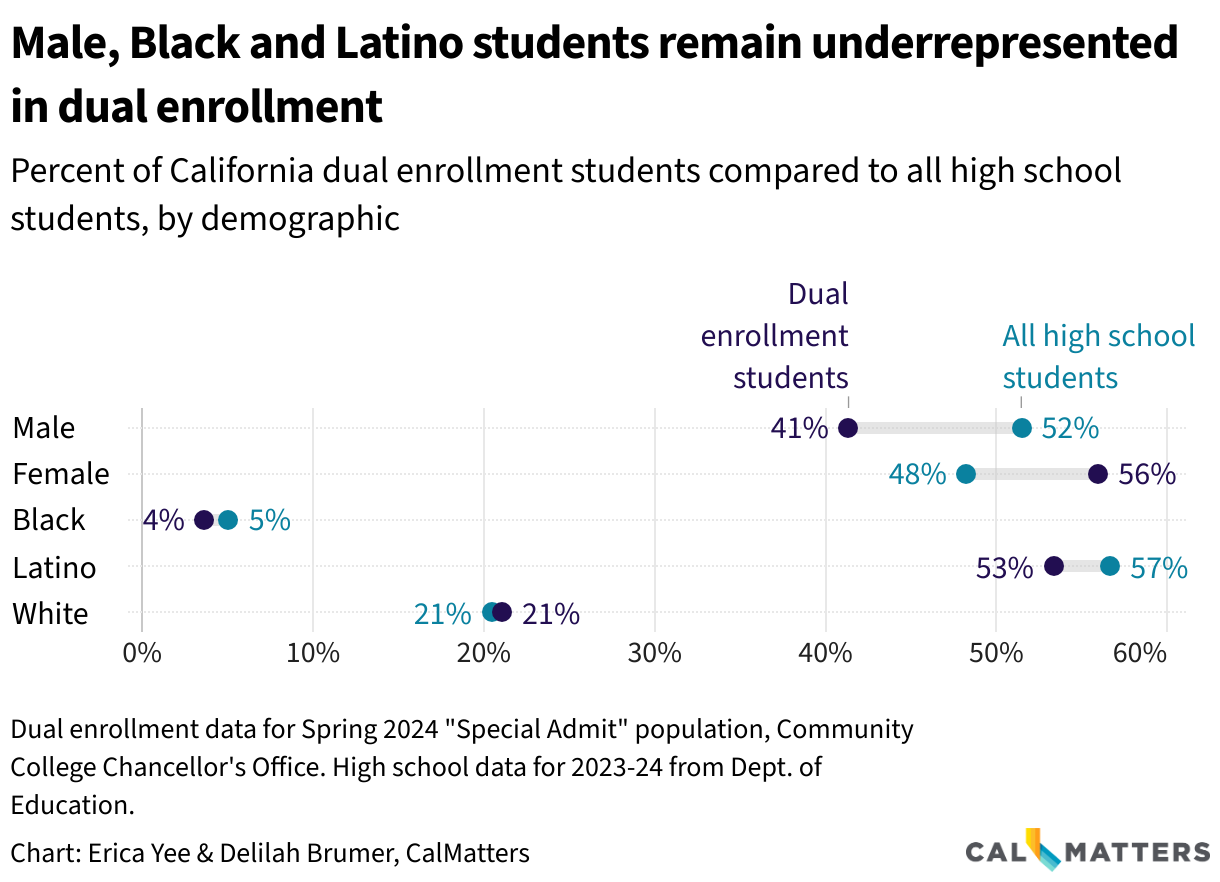
Male students, Black and Latino students and students from rural areas are underrepresented in the community college courses offered at California’s school districts. California lawmakers have signed numerous bills in the hopes of expanding access but certain regions in the state, such as Los Angeles, enroll a higher percentage of students.
Natalie said she hopes to continue taking college courses when she starts at Mount Pleasant High School this fall, which is just around the corner from her middle school. But her options are limited.
Mount Pleasant High School offers just three community college courses, which serve about 10% of the school’s roughly 1,000 students, said Kyle Kleckner, the school district’s director of instructional services. All of the classes are in “multimedia” studies, he said, which teaches students how to create their own podcasts or YouTube channels, along with other digital marketing skills.
Although Mount Pleasant High School’s dual enrollment is about on par with the state average, it trails other districts in the region. Less than 20 miles away, at high schools in the Milpitas Unified School District, roughly 25% of students enrolled in a community college class in 2021-22, according to the UC Davis analysis.
Finding professors to teach middle school
Part of the dual enrollment challenge is finding qualified college professors who are willing and able to work at a high school or middle school. Existing middle and high school teachers are allowed to teach college courses but they have to meet the qualifications, which usually include a master’s degree in the area of instruction. Most of California’s high school and middle school instructors lack a master’s degree, according to a study by the Public Policy Institute of California.
“We have graduation requirements that students have to accomplish,” Kleckner said. “The trick is finding that community college course that also fulfills those requirements and also finding a teacher who can teach it.” He said Mount Pleasant High School is committed to expanding the number of college courses but noted that it’s smaller and therefore has fewer teachers who meet the requirements to teach a college course.
In turn, many college professors lack experience teaching children, said Breheny, who teaches at San Jose City College. “We have had some problems already with dual enrollment where faculty have gone to different (high schools) to teach and have dealt with classroom management issues that they wouldn’t have in a college course.” In one case, she said a college faculty member saw bullying in a high school classroom but didn’t feel equipped to respond.
Lamas has a master’s degree, which is required for most school counselors. He’s gentle with the middle school students in his class, occasionally awarding points in the Jeopardy game even when the answer isn’t perfect. Lamas had two quiz games planned that day, each one covering a different topic, but the first game took up almost all of the class time.
He ends class by taking questions about the upcoming final project. Although spring break is minutes away, the students sit still through the final minutes, except for the occasional joke and bursts of laughter. Not a single phone was in sight.
Once class ends, however, chatter ensues, the students pull out their phones, and staff escort them to the parking lot. While they may be taking a college course, they still must wait for their parents to pick them up.
This article was originally published on CalMatters and was republished under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives license.
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter