Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
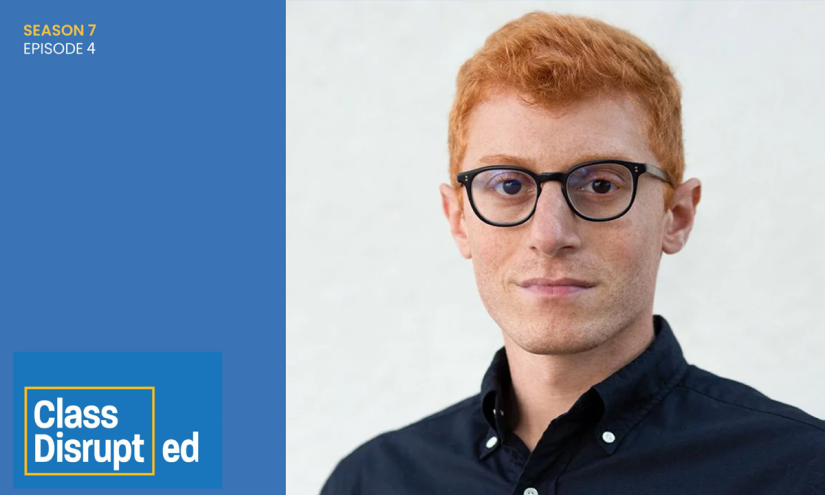
Class Disrupted is an education podcast featuring author Michael Horn and Futre’s Diane Tavenner in conversation with educators, school leaders, students and other members of school communities as they investigate the challenges facing the education system in the aftermath of the pandemic — and where we should go from here. Find every episode by bookmarking our Class Disrupted page or subscribing on Apple Podcasts, Google Play or Spotify.
Michael and Diane sit down with Alex Kotran, founder and CEO of the AI Education Project (AIEDU), to dive into what true “AI readiness” means for today’s students, educators and schools. They explore the difference between basic AI literacy and the broader, more dynamic goal of preparing young people to thrive in a world fundamentally changed by technology. The conversation ranged from the challenges schools face in adapting assessments and teaching practices for the age of AI, to the uncertainties surrounding the future of work. The episode asks key questions about the role of education, the need for adaptable skills, and how we can collectively steer the education system toward a future where all students can benefit from the rise of AI.
Listen to the episode below. A full transcript follows.
*Correction: At 17:40, Michael attributes an idea to Andy Rotherham, The idea should have been attributed to Andy Smarick.
Diane Tavenner: Hey, Michael.
Michael Horn: Hey, Diane. It is good to see you as always. Looking forward to this conversation today.
AI Education and Literacy Insights
Diane Tavenner: Me, too. You know what I’m noticing, first of all, I’m loving that we’re doing a whole season on AI because I felt like the short one was really crowded. And now we get to be very expansive in our exploration, which is fun. And that means we’ve opened ourselves up. And so there’s so much going on behind the scenes of us constantly pinging each other and reading things and sending things and trying to make sense of all the noise. And just this morning, you opened it up super big. And so it works out perfectly with our guest today. So I’m very excited to be here.
Michael Horn: No, I think that’s right. And we’re having similar feelings as we go through the series. And I’m, I’m really excited for today’s guest and because I think, you know, there are a lot of headlines right now around executive actions with regards to AI or, you know, different countries making quote, unquote, bold moves, whether it’s South Korea or Singapore or China and how much they’re using AI in education or not. We’re going to learn a lot more today, I suspect, from our guest, and he’s going to help put it all in the context, hopefully, because we’ve got Alex Kotran, excuse me, joining us. He’s the founder and CEO of the AI Education Project, or AIEDU. And AIEDU is a nonprofit that is designed to make sure that every single student, not just a select few, understands and can benefit from the rise of artificial intelligence. Alex is working to build a national movement to bring AI literacy and readiness into K12 classrooms, help educators and students explore what AI means for their lives, their work, and their futures.
And so with all that, I’m really excited because, as I said, I think he’s going to shed a little bit of light on these topics for us today. I’m sure we’re only going to get to scratch the surface with him because he knows so much, but he’s really got his pulse on the currents at play with AI and education, and perhaps he can help us separate some of the hype from reality, or at least the very real questions that we ought to be asking. So, Alex, with all that said, no pressure, but welcome. We’re excited to have you.
Alex Kotran: I’ll do my best.
Michael Horn: Sounds good. Well, let’s start maybe just your personal story right into this work and what motivates you around this topic in particular, to spend your time on it.
Alex Kotran: I’ve been in the AI space for about 10 years. But you know, besides being sort of proximate to all these conversations about AI, you know, I don’t have a background in software, computer science. I don’t think I have ever written a line of code. I mean, my dad was a software engineer. He teaches CS now. No background in technology or CS, no background in education. And so I actually, I had funders ask me this when I first launched AIEDU like, well like, why are you here? Like, what’s, what’s your role in all of this? You know, my background is in really political organizing. I started my career working on a presidential campaign, went and worked for the White House for the Obama administration, doing outreach for the Affordable Care act and other stuff like Ebola and Medicare and, and then found myself in D.C.
and after I just kind of got burned out of politics for reasons people probably don’t need to hear and can completely understand. And so it wasn’t that I was so smart to like, oh, I knew AI was the next thing. I just was like, I really want to move to San Francisco. I visited there, visited the city like twice and just fell in love and sort of fell into tech and an AI company that was working in cleantech. And so I was sort of doing AI work before it was really cool. It was like back in 2015, 2016. And then I ended up getting like what at the time was a kind of a really random job that I had a lot of mentors who were like, I don’t know, Alex, like AI, like this is just like a fringe, you know, emerging technology kind of like, you know, 3D printing and VR and XR and the Metaverse, you know, is that really like what you should do? And I just had like, nah, I just want to learn.
It seems really interesting. And that’s why I joined this AI company essentially working for the family office for the CEO. It was like, sort of a hybrid family office, corporate job, doing CSR, corporate social responsibility in the legal sector. This is the first company to build AI tools for use in the law. And so I was sort of charged with how do we advance the governance of AI and sort of like the safe and ethical use of AI and the rule of law. And so I basically had a blank canvas and ended up building the world’s first AI literacy program for judges. I worked with the National Judicial College in Stanford and NYU Law, trained thousands of judges around the world in partnership, by the way, with non profits like the Future Society and organizations like UNESCO. And because my parents are educators, I, you know, and my parents are foreign immigrants as well.
And so they always ask me about my job and really trying to convince me to go back, to go to law school or get a PhD or something. And I was like, well, no, but, you know, I actually, I’m, I don’t need to go to law school. I’m actually training judges. Like, they’re, they’re coming to learn from me about this thing called AI. And my mom was like, oh, like, well, that sounds so interesting. You know, have you thought about coming, you should come to my school and teach my kids about AI. And she teaches high school math in Akron, Ohio. And I was just like, surely your kids are learning about AI.
That’s, you know, my assumption is that we’re at a minimum talking to the future workers about the future of work. I just assume that, you know, like, you know, judges who tend to be older, like, they kind of need to be caught up. And after I started looking around to see, like, is there other curriculum that I could share with my mom’s school, I found that there really wasn’t anything. And that was back in 2019. 2018/2019. So way before ChatGPT and thus AIEDU was born when I realized, OK, this doesn’t exist. This actually seems like a really big problem because even as, even as early as 2018, frankly, as early as 2013, people in the know, technologists, people in Silicon Valley, labor economists, were sounding the alarms, like, AI is, you know, automation is going to replace like tens of millions of jobs.
This is going to be one of the huge disruptors. You had the World Economic Forum talking about the fourth Industrial Revolution. Really, this wasn’t much of a secret. It was just, you know, like, esoteric and like, you know, in the realm of like certain nerdy wonky circles. And it just, there wasn’t a bridge between those, the people that were meeting at the AI conferences and the people in education. And I would really say, like, our work now is still anchored in this question of, like, how do you make sure that there is a bridge between the cutting edge of technology and the leadership and decision makers who are trying to chart a course not over the next two years, which is sort of like how a lot of, I think Silicon Valley is thinking in the sort of like, very immediate reward system where they’re just, you know, like, they’re, they’re looking at the next fundraise. But in education, you’re thinking about the next 10 years. These are huge tanker ships that we’re trying to navigate now and we’re entering.
I think this is such a trope, but, like, we are really entering uncharted waters. And so, like, steering that. That supertanker is hard and I suppose to really belabor it as maybe AIEDU is sort of like the nimble tugboat, you know, that’s trying to just sort of like, nudge everybody along and sort of like guide folks into the future. And that demands answering some of this core question of the future of work, which hopefully we’ll get some more time to talk about.
Michael Horn: Yeah, I want to, I want to move there in a moment, but I, but first, like, I maybe I don’t know that all of our audience will be caught up with all the, you know, sort of this macro environment right where. Where we sit right now in terms of the national policy, executive actions as it pertains to AI and education. They’ve probably heard about it, but don’t know what it actually means, if anything. And so maybe sort of set the scene around where we are today nationally on these actions? What if it is actually meaningful or impactful? What if it is maybe more lip service around the necessity of having the conversation rather than moving the ball, just sort of set the stage for us where we are right now.
Alex Kotran: It’s really hard to say. I mean, there’s been a lot of action at the federal level and at state levels and schools have implemented AI strategies. The education space is inundated with, like, discussion and initiatives at working groups and bills and, you know, like, pushes for, like, AI and education. I think the challenge now is, like, we really haven’t agreed on, like, to what end? Like, is this, you know, are we talking about using AI to advance education as a tool? So, like, can AI allow us to personalize learning and address learning gaps and help teachers save time, or are we talking about the future of work and how do we make sure kids are ready to thrive? And there are some that say, well, they. We just need to get them really good at using tools. Which is a conversation I literally had earlier today where there was like a college to career nonprofit and they were like, well, we’re trying to figure out what tools that help kids learn because we want them to be able to get jobs.
I think like AIEDU, like, our work is actually, we don’t build tools. We don’t even have a software engineer on our team, which we’re trying to fix, like, if there’s a funder out there that would like to help fund an engineer, we’d love to have one. But our work is really systems change. Because if you like, zoom out and like, this is, I think, where I do have this skill set. And it’s kind of like, again, it’s a bit niche.
The education system is not. It’s not one thing. It’s like, it’s sort of like an organism. The same way that like redwood trees are organisms. Like, they’re kind of all connected, the root structure. But it’s actually like you’re looking at a forest that looks very different, you know, that’s not centralized. You know, every state kind of has their own strategy. And frankly, every district, in many cases, you’re talking about, you know, in some cases, like government scale, procurement, discussion, bureaucracy involved.
Advancing AI Readiness in Education
Alex Kotran: So if you’re trying to do systems change, this is really a project of like, how do you move a really heterogeneous group of humans and different audiences and stakeholders with different motivations and different priorities? And so our work is all about, OK, like, setting a North Star for everybody, which is like defining where we’re actually trying to go, what. And we use the word AI readiness, not AI literacy. Because what we’re, what we care about is kind of irrespective of whether kids are really good at using AI. Like, are they thriving in the world? And then like, how do you get there? Like, like most of our budget goes to delivering that work, you know, doing actual services, where we’re building the human, basically building the human capital and like, the content. So like training teachers, building curriculum, adapting existing curriculum, more so than building new curriculum, but like integrating learning experiences into core subjects that build the skills that students are going to need. And those skills, by the way, are not just AI literacy, but durable skills like problem solving, communication, and core content knowledge frankly, like being able to read and write and do math, we think is actually really important still, if not more important. And then sort of the third pillar to our work is really catalyzing the ecosystem.
And because the only way to do this is by building a movement, right? Like, sure, there. There’s an opportunity for someone to build a successful nonprofit that’s delivering services today. But if you actually want to change the world and really solve this problem on the timescale required, you have to somehow rally the entire, there’s like a million K12 nonprofits. We need all of them. This is like an all hands on deck moment. And so our organization is really obsessed with, like, how do we stay small and almost like operate as the intel inside to empower, like, the existing nonprofits so that they don’t have to all pivot and, like, become AI because, like, there’s just not enough AI experts to go around. If every school and every nonprofit wanted to hire an AI transformation officer.
Like, there just wouldn’t be enough people for them to hire.
Diane Tavenner: Yeah, they’re still trying to hire a good tech lead in schools. We’re definitely not getting an AI expert in every school soon. So you’re, you’re speaking my language, you know, sort of change management, vision, leadership 101, etc. I’m wondering, you know, sort of not necessarily the place we were thinking we’d go in this conversation, but I think it’d be fun to go, like, really deep for a moment that I think is related to your North Star comment. What does school look like in the age of AI? When kids are flourishing, when young people are flourishing, and when they’re successfully launching? I think that’s what the North Star has to describe.
And you just started naming a whole bunch of things that are still important in school, which feel very familiar to me. They’re all parts of the schools that I’ve built and designed and whatnot. And so I think one of the interesting things is maybe we’ll then build back up to policy and whatnot. But, like, what does it look like if we succeed, if there is this national movement, we’re successful. We have schools or whatever they are that are enabling young people to flourish. What do you think that that looks like?
Alex Kotran: Yeah, this is the question of our day. Right. I mean, I think this is where, I mean, just to go back to this, like, state of play. I think, like, we’re kind of. It’s very clear that we are in the age of AI, right? This is no longer some future state. And frankly, like, ignore all the talk about AI bubbles because it kind of doesn’t matter. I mean, there was, there was like, there’s always a bubble. There was a bubble when we had railroads.
There was a bubble when we had, like, in the oil boom. There was a bubble with the Internet. You know, there probably will be some kind of a bubble with AI, but that’s kind of like part and parcel with transformational technologies. Nobody who’s really spent time digging these technologies believes that there’s not going to be AI sort of totally proliferated throughout our work in society in like, 10 years, which is, again, the timeframe that we’re thinking about. The key question is, though, like, what is it? Like, what does it mean to thrive? And so there’s more than just getting a job. But I think most people would admit that, like, having a job is really important. So maybe we start there and we can also talk about, you know, the, the social, emotional components of just sort of like, being able, being resilient to some of like, the onslaught of synthetic media and like, AI companions as other stuff. One of, if not the most important thing is, like, how do you get a job and like, have like, you know, be able to support yourself and, and that question is really unanswered right now.
Uncertainty in AI and Future Jobs
Alex Kotran: And so everybody in the education system is trying to figure out, like, well, what is our strategy? But we don’t know where we’re going? Like, we really do not know what the jobs of the future are. And like, I’ve, like, you hear platitudes like, well, it’s not that AI is going to take your job, it’s that somebody using AI is going to take your job. Which is a kind of a dumb thing to say because it’s, it’s correct. I mean, it’s like, it’s like, basically like, okay, either AI is going to do all the jobs, which I don’t like, like, that actually may happen, some people say, sooner than later. I just assume it’s going to be a long, long time if it ever, if we ever get there. And so until we get there, that means that there are humans doing jobs and AI and technology doing other aspects of work. So, like, what are the humans doing is really the important question. Not just like, are they using AI? But like, how are they using AI? How aren’t they using AI? Until we get more fidelity about what the future of work looks like, what are the skills you should be teaching? Because, like, you know, like, I think a lot about, like, cell phones.
And you go back to 2005 and you can imagine a conversation where it’s like, and all this is completely true, right? In 2005, it would be correct to say that, you know, you will not be able to get a job if you don’t know how to use a cell phone. You will be using a cell phone every single day, whether you’re a plumber or a mathematician or an engineer or an astrophysicist. And yet I think most of us would agree that, like, we shouldn’t have, like, totally pivoted education to focus on, like, cell phone literacy because, like, nobody’s going to hire you because you know how to use a phone and AI like, probably is going to some degree get there. I mean, it’s already sort of there, right? Like, sure, there are people who will charge you money to teach you prompt engineering, but you could also just open up Gemini and say, help me write a prompt. Here’s what I want to do. And it will basically tell you how to do it.
Diane Tavenner: I mean, we. You’ve seen this. You might not be old enough to remember this, but I was a teacher when everyone thought it was a really good idea to teach keyboarding in school. It’s like a class. What we discovered is actually if you just have people using technology, they learn how to use the keyboard. Right? Like, it happens in the natural course of things and you don’t have a class for it. So what I hear you saying is like, your approach is not about this sort of, you know, there’s some finite set of information or skill, you know, not even skills in many ways that we’re going to teach kids. But it’s like, what does it look like to have them ready for the world that honestly is here to today and then keeps evolving and changing over the next 10 years? And so where to even go with that, Michael because.
Michael Horn: I mean, part of me wonders, Alex, like, if I start to name the things that remain relevant, what, like, maybe the conversation to have is like, what’s less relevant in your view, based on what the world of work and society is going to look like?
What’s the stuff that we do today that you know, will feel quaint? Right, that we should be pruning from?
Diane Tavenner: Yeah, cursive handwriting. That is still hotly debated by, by the way.
Alex Kotran: But, you know, although you get like Deerfield Prep and they’re going back to pen and paper.
Michael Horn: Right. So that, I mean, that’s kind of where I’m curious. Like, what practices would you lean into? What would you pull away from? Because, I mean, that’s part of the debate as well. Like our friend Andy Rotherham, I believe at the time we’re recording it, just had a post around how it’s time for a, you know, a pause on AI in all schools. Right. Not sure that’s possible for a variety of reasons. But, like, what would you pull back on? What would you lean into? What would you stop doing that’s in schools today, as you think about that readiness for the world that will be here in your, we’re all guessing, but 10 years from now.
Alex Kotran: Now, what to pull back on? I mean, look, take home essays are dead. Don’t assign take-home essays like the detectors are imperfect. It’s like, and as a teacher, do you really want to be like an, you know, a cyber forensics specialist? Like that’s not the right use of your time. And also you’re using AI. So it’s a bit weird to the dissonance of like, oh, like empowering teachers with AI, but then like, we need to prevent kids from using it. But I think they’re like low hanging fruit. Like, OK, don’t assign take-home essays.
The way to abstract, that is students are. You can call it cheating, let’s just call it shortcuts. What we do need to do is figure out, OK, how can AI, how is AI being used as a shortcut? And whether you ban it in schools, kids are going to use it out of school. And so teachers need to figure out how to create assessments and homework and projects that design such that you can’t just use AI as a shortcut. And there’s like, this is a whole separate conversation. But just like to give one example, having students demonstrate learning by coming into the class and presenting and importantly having to answer questions in real time about a topic. You can use all the AI you want, but if you’re going to be on the spot and you don’t understand whatever the thing is that you’re presenting about and you’re being asked questions like, you know, that’s the kind of thing where sure, use all the AI. If it’s helpful, you might just.
But ultimately you just need to learn the thing. But like the more important question is like, I don’t know if school changes as much as people might think. I think it does change. I think there’s a lot that we know needs to change that is kind of irrespective of AI. Like we need learning to be more engaging. We need more project based learning. We need to shift away from just sort of like pure content knowledge, memorization. But that’s not necessarily new or novel because of AI.
I think it is more urgent than ever before.
Michael Horn: I’m curious, like what’s. Because I do think this is also hotly debated, right? Like in terms of the role of knowledge and being able to develop skills and things of that nature. And so I’m just sort of curious, like what’s the thin layer of knowledge you think we need to have? Or, or like Steven Pinker’s phrase, common knowledge Right
And what’s the stuff we don’t have? Like we don’t have to memorize state capitals, right? Maybe.
Diane Tavenner: No. Yeah, I don’t think we need to memorize the state capital, because, yeah, but keep going.
Michael Horn: Yeah, yeah, I’m curious now. It’s like, right, like as we think about, because we do have this powerful assistant serving us now and we think about what that means for work. And I, but I guess I’m just curious, like, what does that really mean in terms of that balance, right? Like, what is all knowledge learned through the project or this, you know, how do we think about, you know, and it’s a lot of just in time learning perhaps, which is more motivating. I’m curious, like, how you think about that.
Alex Kotran: I think this needs to be like, backed by, like research, right? Like, sure, it probably is, right, that you don’t need to memorize all the state capitals. But then I think you, you start to get to a place where like, OK, well, but do you even need to learn math? Because AI is really good at math and I think math is actually a good analog because I don’t really use math very much or I use relatively simplistic math day to day. I, I think it was really valuable for me to like, have spent the time building computational thinking skills and logic. And also just math was really hard for me and it was challenging. And like the process of learning a new abstract, hard thing. I do use that skill, even some of the rote memorization stuff. You know, my brother went to med school and like they spent a lot of time just memorizing like completely just like every tiny aspect of the human body.
They like have to learn it. It’s actually like, I think doctors are really interesting, a great way to kind of double click on this because if doctors don’t go through all of that and don’t understand the body and go through all of the rote process of literally taking like thousand question tests where they have to know like random things about blood vessels. And even if they’re never going to deal with that specific aspect of the human body, doctors kind of like build this sort of like generalized set of knowledge and then also they spend all this time like interacting with real world cases. And you, you start to build instincts based on that and, and you talk to hospitals about like, oh, what about, you know, AI to help with diagnosis? And one of the things I hear a lot of is, well, we’re worried about doctors losing the capacity to be a check on the AI because ultimately we hear a lot about the human in the loop. The human in the loop is only relevant if they understand the thing that they’re looped into. So, yeah, so like, I don’t know, I mean, maybe we.
Diane Tavenner: Yeah, you’re onto something. You’re spurring something for me that I, I actually think is the new thing to do and haven’t been doing and aren’t talking about. And that is this, let me see if I can describe it as I’m understanding it, unfold the way you’re talking about it. So I had a reaction to the idea of memorizing the state capitals because memorizing them is pretty old school, right? It calls back to a time where you aren’t going to be able to go get your encyclopedia off the shelf and look up the capitals. Like you have to have that working knowledge in your mind, if you will, to have any sense of geography and, you know, whatever you might be doing. And it was pretty binary.
Like it really wasn’t easy to access knowledge like that. So you really did have to like memorize these things. Math, multiplication tables get cited often and whatnot for fluency in thinking and whatnot. So I don’t think that goes away. But it’s different because we have such easy access to AI and so there isn’t this like dependency on, you’re the only source of that knowledge, otherwise you’re not going to be able to go get it. But it doesn’t take away the need to have that working understanding of the world and so many things in order to do the heavier lifting thinking that we’re talking about and the big skills. And I think that, I don’t think there’s a lot of research on that in between pieces, like, how do you teach for that level of knowledge acquisition and internalization and whatnot? And how do you then have a, you know, a more seamless integration with the use of that knowledge in the age of AI when it’s so easily accessible? So that feels like a really interesting frontier to me. That doesn’t look exactly the same as what we’ve been doing, but isn’t totally in a different world either.
It is restricted, responsive and reflective of the technology we have and how it will get used now.
Rethinking Assessments and Learning Strategies
Alex Kotran: Yeah, it’s, it’s a helpful push because like, what I’m not saying is that I know everything in school is fine. I don’t think I’ve ever talked to a superintendent who would say, oh, I’m feeling good about our assessment strategy. Like, we’ve known that and because really what you’re describing is assessments like what, like what are we assessing in terms of knowledge, which becomes the driver and incentive structure for teachers to like, you know, because to your point. Are you spending five weeks just memorizing capitals or are you spending two weeks and then also then saying, OK, now that you’ve learned that, I want you to actually apply that knowledge and like come up with a political campaign for governor of, you know, a state that you learned about and like, tell us about like why you’re going to be picking those. You know, tell us about your campaign platform. Right. And you know, like, how is it connected to what you learned about the geography of that state? So it’s like adapting, integrating project based learning and more engaging and relevant learning experiences. And then like the mix and the balance of what, what’s happening in the classroom is sort of, and this is the, the challenging thing because it’s like the assessments will inform that, but it’s also there the assessments are downstream of sort of like it’s not just about getting the assessments right, but it’s like, why are we assessing these things? And so that you very quickly get to like, well like, what is the future of work? And because like, yeah, I mean like, you probably don’t need to learn the Dewey Decimal system anymore.
Even though being able to navigate knowledge is maybe one of the most important things, certainly something I use every day.
Diane Tavenner: One of the things we tend to do in US Education, Alex, is be so US centric and we forget that other people on the planet might be grappling with some of these things. I know you track a lot of what happens around the globe. What can we look at as models or interesting, you know, experiments or explorations. Everything from like big system change work, which I know we have different systems across the world, so that’s different. It’s a little bit, it’s not groundswell, it’s a top down but like anything from policy, big system all the way down to like who, who might be doing interesting things in the classroom. Where are you looking for inspiration or models across the globe?
Alex Kotran: I mean, South Korea is a really interesting case study. You mentioned South Korea. I think at the beginning of this, during the intro they were just in headlines because they had done this big push. They would like roll out personalized learning nationwide. And then they announced that they were rolling back or sort of slowing down or pausing on the strategy. I forget if it was a rollback or a pause, but they’re basically like, wait, this isn’t working. And what they found is that they hadn’t made a requisite investment in the teacher capacity. And that was clear.
And so part of the reason I’m tracking that is because I don’t know that there’s very much for us to learn from what any school is doing right now, beyond, like, there’s a lot for us to learn in the sense of like, how can we empower teacher, like, how do we empower teachers to run with this stuff? Because they are doing that. You know, like, I think there’s a lot to learn from a, like a mechanical standpoint of like, implementation strategies. But I don’t know that anybody has figured this out because like, nobody can yet describe what the future of work looks like. And I know this because the AI companies can’t even describe what the future of work looks like. You know, you had like Dario Amodei at Anthropic seven months ago, saying in six months, 90% of code is going to be written by AI, which is not the case. Not even close.
Diane Tavenner: And Amazon’s going to lay off 30,000 white collar workers this week,
Alex Kotran: Which they did.. Yes. And so you have. But is that really because of AI or is that because of overhiring from interest rates? I mean there’s like, so, so until we answer this question of like, what is like. And really the way to say what is the future of work is like, to put it in educational terms, how are you going to add value to the labor market? Like, David Otter has this like, example which I think is really important. It’s like, you know, the crosswalk coordinator versus the air traffic controller. And then, like, we pay the air traffic controller four times as much because any one of us could go, be a crosswalk coordinator like today, just give us a vest and a stop sign. I don’t, I assume you’re not moonlighting as an air traffic controller. I’m certainly not.
It would take us, I think, I don’t know what the process is, but I think years to acquire the expertise. And so there is this barrier of expertise to do certain things. And what AI will do is lower the barriers to entry for certain types of expertise, things like writing, things like math. And so in those environments where AI is increasingly going to be automating certain types of expertise, then, well, for people to still get wages that are good or to be employed, they have to be adding something additional. And so the question of like, what are the humans adding? Again, we get to stuff like durable skills. We get to stuff like a human in the loop. But I think it’s much more nuanced than that. And the reason I know that is because there’s the MIT study.
I think it was a survey, but let’s call it a study. I think they called it a study. So there’s a study from MIT that found that 95% of businesses, AI implementations failed, have not been successful. So really what we’re seeing is, yes, AI is blowing up, but for the most part, most organizations have not actually cracked the code on like, how to like, unlock productivity and like. And so I think that there’s actually quite a lot of business change management and organizational change that’s coming. And so actually kind of trying to hone in on what does that look like, I think is maybe the key, because that will take 10 years if you look at computers. Computers, like, could have revolutionized businesses long before, but they ended up getting adopted. I mean, it took like decades actually for, you know, spreadsheets and things like that to become ubiquitous.
And like Excel is a great example of something. I was just talking to this, this expert from the mobile industry who was talking about, like, the interesting thing about spreadsheets was it didn’t just automate because there were people who literally would hand write, you know, ledgers before Excel. And so obviously that work got automated. But the other thing that spreadsheets did, where they created a new category of work, which is like the business analysts, because. Because before spreadsheets there was really the only way to get that information was to like, call somebody and sort of like compile it manually. And now you had a new way to look at information which actually unlocked a new sort of function that didn’t exist. And that meant, like, businesses now have teams of people that are like, doing layers of analysis that they didn’t realize that they could do before. And so
Diane Tavenner: I wonder, what you’re saying is sparking two things for me. And again, we could talk probably all day, but we don’t have all day. So sadly, I think this might be bringing us to a close here for the moment. But I’m curious what both of you think on this because you brought up air traffic controllers. And in my new life and work, I’m very obsessed with careers and how people get into them and whatnot. I’ve done deep dives on air traffic controllers. And it’s, my macro point here is going to be.
I do wonder if this moment of AI is also just extreme, exposing existing challenges and problems and bringing them to the forefront. Because let me be clear, training air traffic controllers in the US was a massive problem before AI came around, before any of this happened. It’s a really messed up system. It is so constrained. It’s not set up for success. Like, it’s just such a disaster and a mess and it’s such a critical role that we have. And it’s probably going to change with AI. Like, so you’ve just got all these things going on.
And I’m wondering, Michael, from your perspective, is that what happens in these, you know, moments of disruption and is that all predictable and how do we get out of it? And then, Alex, you’re talking about. I was having a conversation this morning about this idea that all these companies no longer are hiring sort of those entry level analysts, or they’re hiring far fewer of them. And my wondering is no one can seem to answer this question yet. Great. Where’s your manager coming from? Because if you don’t employ any people at that level and they haven’t sort of learned the business and learned things, what do you think they’re just sitting on the sidelines for seven, eight years and then they’re ready to slide in there into, you know, the roles that you are keeping? And so are these just problems that already existed that are now just being exposed, you know, what’s going on? What do you all think?
Job Market Trends and AI
Alex Kotran: So, first of all, we really don’t know if the, like, I’m not convinced that the reason that there’s high unemployment among college grads is because of AI. I mean, I think there was overhiring because of interest, low interest rates. I think that companies are trying to free up cash flow to pay for the inference costs of these tools. And, and I think in general, like, you know, we’re, there’s going to be like, sort of like boom, bust cycles in terms of hiring in general. And we’ve been in a really good period of high employment for a long time. I think what, what is clear is if you talk to like earlier stage companies, you know, I was talking to a friend of mine at Cursor, which is like one of the big vibe coding companies, like blowing up, worth lots and lots of money. And I asked them about, like, oh, like I keep hearing about like, you know, companies aren’t hiring entry level engineers anymore because like, you’re better off having someone with experience.
And he’s like, all of our engineers are in like their early 20s. Huh. OK, that’s interesting. Well, yeah, because actually it’s a lot faster and easier to train somebody who’s an AI native who learned software engineering while vibe coding. But he’s like, but we’re a small organization that’s like basically building out our structure as we go so we don’t have to like operate within sort of like the confines. I think there’s going to be this idea of like incumbent organizations. They have the existing hierarchy because ultimately you’re looking for people who are like really fast learners who can like learn new technology, who are adaptable and who are good at like doing hard stuff. If you’re a small organization, you’re probably better off just like hiring young people that like, you know, have those instincts.
If you’re a large organization, what you might do is just maybe you’re laying off some of the really slow movers and then retaining and promoting the people that are already in place and have those characteristics. And then your point about like training the next generation, like law firms are thinking about this a lot because like you could, maybe you could automate all the entry level associates, but you do need a pipeline. But then you get to do you need middle managers? I mean like if the business models are less hierarchical because you just don’t need all those layers, then maybe you don’t worry so much about whether you need middle management and it’s more about do you need more. I think what companies are going to realize is they actually need more systems thinkers and technology native employees that are integrated into other verticals of knowledge work that outside of tech. So like, if you think about marketing and like business and customer success and you know, like non profit world fundraising and policy analysts, like all of these teams that generally have like people from the humanities. You know, I think companies are going to say, OK, how do we actually get people that like can do some vibe coding and have a little bit of like CS chops to build out some, you know, much more efficient and productive ways for these teams to operate. But like nobody knows. Nobody knows.
I don’t know. Michael?
Michael Horn: I love this point, Alex, where you’re ending and that like, and I like the humility frankly in a lot of the guests that we’ve had around. This is like the honesty that we’re all guessing a little bit at this future and we’re looking at different signals right. As we do. I think my quick take off this and I’ll try to give my version of it, I guess is you mentioned David Otter earlier at mit, Alex. Right. And part of his contention is that actually, right, it levels expertise between jobs that we’ve paid a lot for and jobs that we haven’t and more people like, as opposed to technology that is increasing inequality. This may be a technology that actually decreases inequality. And I guess it goes to my second thing, Diane, around what the question you asked and air traffic control training is a great example.
But like, fundamentally, the organizations and processes we have in place have a very scarcity mindset. And I suspect they’re going to fight change and we’re going to need new disruptive organizations, similar to what Alex was just saying, that look very differently to come in. And it gets to a little bit of, I think what everyone says with technology, like the short term predictions are huge. They tend to disappoint on that. The long term change is bigger than we can imagine. And I guess I kind of wonder is the long term change what we. Alex, earlier on this season we had Reed Hastings and you know, he has a very abundant sort of society mindset where the robots plus AI plus probably quantum computing, like, are doing a lot of the things, or is it frankly sort of what you or I think Paul LeBlanc would argue, which is that a lot of these things that require trust and we want people like, yes, you can build an AI that does fundraising for you. But like, do I really trust both sides of that equation? I’d rather interact with someone.
Right. There’s a lot of social capital that sort of greases these wheels ultimately in society. And I guess that’s a bit of the question. And Diane, I guess part of me thinks, you know, Carlota Perez, who’s written about technology revolutions, right. She says that there will be some very uncomfortable parts of this, right. And a bit of upheaval. Part of me keeps wondering if we can grease the wheels for new orgs to come in organically, can we avoid some of that upheaval because they’ll actually more naturally move to paying people for these jobs in a more organic way.
And I, right now we have a, I’m not sure we have that mindset in place. That’s a bit of my question.
Diane Tavenner: More questions than answers. More questions than answers. Really. This has been, wow, really provocative.
Michael Horn: Yeah. So let’s, let’s, let’s leave. We could go on for a while. Let’s leave the conversation here for the moment. Alex, A segment we have on the show as we wrap up always is things we’re reading, watching, listening to either inside work or we try to be outside of work. You know, podcasts, TV shows, movies, books, whatever it might be. What’s on your night table or in your ear or in front of your eyes right now that you might share with us.
Alex Kotran: I’m reading a book about salt. It’s called Salt.
Michael Horn: This came out a few years ago. Yeah. Yeah. My wife read it.
Alex Kotran: Yeah, I’m actually reading it for the second time. But it is, you know, it’s interesting because we. It’s something that’s, like, now you take for granted. But, you know, there’s a time when, you know, wars were fought. You know, it sort of spurred entire new sorts of technologies around. Like, the Erie Canal was basically, you know, like, salt was a big component of, you know, why we even built the Erie Canal. It’s. It’s actually nicknamed a ditch that salt built, you know, spurring new mining techniques.
Technology’s Interconnected Conversation
Alex Kotran: And, you know, I just find it fascinating that, like, you know, there are these, like, technology is so interconnected not to bring it back. I know this is supposed to be outside, but all I read, I only read nonfiction, so it’s going to be connected in some way. I just, like, fascinated by, like, you know, there are these sort of, like, layers behind the scenes that we sometimes take for granted that, you know, can actually be, like, you know, quietly, you know, monumental. I think what’s cool about this moment with technology is it’s like everybody’s a part of this conversation. Like, before, it was, like, much more cloistered. And so I think that’s just, like, good. Even though, yes, there’s a lot of noise and hype and, you know, snake oil and all that stuff, but I think in general, like, we are better off by, like, having folks like you, like, asking folk, asking people for, like, you know, like, driving conversation about this and not just leaving it to a small group of experts to dictate.
Diane Tavenner: So I think this is cheating, but I’ve done this one before. But I’m gonna cheat anyway because, as you know, Michael, because you hear me talk about it a lot, the. The one news source I religiously read is called Tangle News. It’s a newsletter now and a podcast. It’s grown like crazy since I first started listening. I love it. It’s like a startup.
It started, I think when I started reading, it was like, under 50,000 subscribers or something. Now up half a million. Executive editor, Isaac Saul, who I’m going to say this about a news person I trust, which I think is just a miracle. And I’m bringing it up this week because he wrote a piece last Friday that, honestly, I had to break over a couple days because it was really brutal to read. That’s just a very honest accounting of where we are in this moment. The best piece I’ve heard, I’ve read or, or heard about it. And then on Monday, he did another piece where, you know, they do what’s the left saying? What’s the right saying? What’s his take? You know, what are dissenting opinions? I just love the format. I love what they’re doing.
I was getting ready to write them a thank you note slash love letter, which I do periodically. And I thought I’d just say it on here.
Michael Horn: I was gonna say now you can just excerpt this and send them a video clip.
Diane Tavenner: So I hope, I hope people will check it out. I love, love, love the work they’re doing, and I think you will too.
Michael Horn: I’m gonna go historical fiction. Diane, I’m like, surprising you multiple weeks in a row here, I think. Right? Yeah. Because, Alex, I’m like you. I’m normally just nonfiction all the time, but I don’t know. Tracy said you have to read this book, Brother’s Keeper by Julie Lee.
It’s based on. It’s historical fiction based on a. About a family’s migration from North Korea to South Korea during the Korean War. It is a tear jerker. I was crying like, literally sobbing as I was reading last night. And Tracy was like, you OK? And I was like, I think I won’t get through the book. But I did, and it’s fantastic.
So we’ll leave it there. But, Alex, huge thanks. You spurred a great conversation. Looking forward to picking up a bunch of these strands as we continue. And for all you listening again, keep the comments, questions coming. It’s spurring us to think through different aspects of this and invite other guests who have good answers or at least the right questions and signals we ought to be paying attention to. So we’ll see you next time on Class Disrupted.
Did you use this article in your work?
We’d love to hear how The 74’s reporting is helping educators, researchers, and policymakers. Tell us how