Can we close the “knowledge gap”?
Source link
Category: education
-

When young people ask big questions and seek answers
Cliffrene Haffner attended the African Leadership Academy (ALA) in South Africa during the Covid-19 pandemic. Her university applications were stalling and she felt stressed and anxious.
“Life felt unstable, as if I were hanging by a thin thread,” Haffner said. But it was at ALA that she discovered News Decoder.
“Joining News Decoder helped me rebuild my voice,” she wrote. “It created a place to write honestly and with purpose whilst supporting others in telling their stories. At a time when the world felt numb and disconnected, we used storytelling to bring back hope on campus by sharing our fears, thoughts and expectations.”
At News Decoder, students work with professional editors and news correspondents to explore complicated, global topics. They have the opportunity to report and write news stories, research and present findings in global webinars with students from other countries, produce podcasts and sit in on live video roundtables with experts and their peers across the globe.
Many get their articles published on News Decoder’s global news site.
A different way of seeing the world
Out of these experiential learning activities, they take away important skills valuable in their later careers, whatever those careers might be: How to communicate clearly, how to recognize multiple perspectives, how to cut through jargon and propaganda and separate facts from opinion and speculation.
One milestone for many of these is our Pitch, Report, Draft and Revise process, which we call PRDR. In it, students pitch a story topic to News Decoder with a plan on how to research and report it. We ask them to identify different perspectives on problems they want to explore and experts they can reach out to for information and context.
Then we guide them through a process of introspection, if the story is a personal reflection on their own experience, or a process of reporting and interviewing. News Decoder doesn’t promise students that their stories will get published at the end of the process. They have to work for that — revising their drafts until the finished story is clear and relevant to a global audience.
One student who went through the process was Joshua Glazer, now a student at Emory University in the United States. Glazer came to News Decoder in high school as an exchange student in Spain with School Year Abroad.
“I think the skills that I got out of that went on to really change the course of my education and how I view the world,” Glazer said. “Because when you step into the world of journalism you learn a different way of seeing the world.”
Recognizing our biases
Glazer learned that for journalism, he had to be less opinionated. “You have to really approach things kind of as they are in the world,” Glazer said. “And that is hard to do. That is not an easy skill that we can do as humans because we inherently have biases.”
He said it challenged him to look inwards and recognize his biases and counter them with evidence.
“So I think those skills have really changed the course of how I view having an argument with somebody because all of a sudden, you know, when you have an argument with someone, it’s all opinion,” he said.
For Haffner, who is now a business administration student at Ritsumeikan Asia Pacific University in Japan, News Decoder reshaped how she and her peers understood storytelling.
“It taught us to let go of rigid biases and to make authenticity the centre of our work,” Haffner said. “Students from different backgrounds found a space where their voices were heard, respected and valued. Our stories formed a shared map, each one opening a new room to explore, each voice strengthening the collective journey we were on. In that chaotic period, we created something meaningful together. Something bigger than us.”
Working through the complexity of a topic
Marouane El Bahraoui, a research intern at The Carter Center in the U.S. state of Georgia, also discovered News Decoder at the African Leadership Academy. At the time, he was interested in writing about the effectiveness of the Arab Maghreb Union — an economic bloc of five North African countries. He grew up in Morocco but didn’t want to approach the topic from a purely Moroccan perspective.
“It was like a very raw idea,” he said.
He pitched the story and worked with both News Decoder Founder Nelson Graves and correspondent Tom Heneghan to refine the idea. They guided him in the reporting and writing process.
“One aspect that I liked a lot from my research was the people that I had the chance to talk to,” he said. “It was during Covid and I was just at home and I’m talking to, you know, professors in U.S. universities, I’m talking to UN officials, experts working in think tanks in D.C. and I was thinking oh those people are just so far, you can’t even reach them. And then you have a conversation with them and they’re just normal people.”
He also found writing the story daunting. “It was a little bit overwhelming for me at the time,” he said. “You know, you’re not writing like an academic essay.”
Graves encouraged him to write in a straightforward manner. In school, he had been taught to write in a beautiful way to impress.
“From News Decoder, something I learned is to always keep the audience in mind who you are speaking to, who are you writing to,” he said.
He took away the importance of letting readers make their own conclusions. “You’re not writing to tell the reader what to think,” he said. “You are writing to give them ideas and arguments, facts and leave the thinking for them.”
-

Have Democrats Lost Voters’ Trust on Education? Not According to Most Polls – The 74
Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
Chalkbeat Ideas is a new section featuring reported columns on the big ideas and debates shaping American schools. Sign up for the Ideas newsletter to follow our work.
Democrats are in disarray on education — according to a growing chorus of Democrats.
A variety of left-leaning journalists, politicians, and advocates have all recently claimed that voters have become disillusioned with the party’s approach to schools. Often, these commentators cite anger over pandemic-era closures and argue that Democrats need to embrace tougher academic standards or school choice.
“For decades, when pollsters asked voters which party they trusted more on education, Democrats maintained, on average, a 14-point advantage. More recently that gap closed, then flipped to favor Republicans,” wrote former Chicago Mayor Rahm Emanuel last month.
Is this emerging conventional wisdom true, though? This assertion has typically relied on one or two surveys, rather than a comprehensive look at the data. So I compiled all publicly available polls I could find that asked voters which party they preferred on education.
The verdict was clear: In more than a dozen surveys conducted this year by eight different organizations, all but one showed Democrats with an edge on education. This ranged from 4 to 15 points. Among all 14 polls, the median advantage was 9 points. Although Democrats appear to have briefly lost this edge a few years ago, voters again now tend to trust Democrats on the issue of education, broadly defined.
The narrative that Republicans had wrested the issue of education from Democrats emerged in 2021, after Virginia’s Glenn Youngkin won a come-from-behind victory in the governor’s race after campaigning on parents’ rights.
Long-running data from the Winston Group, a political consulting firm, showed that in late 2021 and early 2022 Republicans really had eroded Democrats’ lead on education. The parties were even briefly tied for the first time since the early 2000s, when former President George W. Bush was championing No Child Left Behind. Polling commissioned in 2022 and 2023 by Democrats for Education Reform, a group that backs charter schools and vouchers, also showed Democrats falling behind on education.
Since then, though, Democrats appear to have regained their edge. In the run-up to the 2024 presidential election, the party held at least a 10-point lead, according to Winston Group. Other polls from last year also found that more voters preferred Democrats’ approach on education, even as the party lost the presidency.
Emanuel pointed me to polling from 2022. “Democrats have not gained ground as much as Trump has cost GOP gains they have made,” he says when asked about the more recent surveys.
This year in Virginia, Democrat Abigail Spanberger easily won in her bid to replace Youngkin. Education was one of her stronger issues, according to a Washington Post survey.
Some argue that these election results disprove the idea that Democrats are losing on schools. “That’s not what panned out at all,” says Jennifer Berkshire, a progressive author who writes and teaches about education. She notes that the Republican governor candidate in New Jersey also tried to make schools an issue and lost badly.
The Winston poll shows Democrats’ advantage is currently below its peak between 2006 and 2009 but is comparable to many other periods, including the tail end of the Obama administration and part of the first Trump administration.
Keep in mind: These surveys ask about education broadly, not just K-12 schools. When given the option, a good chunk of voters don’t endorse either party’s approach. For instance, a YouGov survey found Democrats up 39%-32% on education with another 29% saying they weren’t sure or that the parties were about the same.
The one public poll in which Democrats did not have an advantage came from Blue Rose Research, a Democratic-aligned firm. Ali Mortell, its head of research, says different survey methodologies can lead to different results.
Regardless, she wants to see Democratic politicians lean into the issue more. “Say they do have that trust advantage right now, [education] is still not something that they’re really talking about a lot,” Mortell says.
One of the top messages that resonates with voters focuses on addressing teachers’ concerns about stagnant pay and large class sizes, Blue Rose polling finds.
Democrats’ lead on education doesn’t appear to have grown much over the last year, according to surveys from Winston, YouGov, and Ipsos. That’s somewhat surprising since Trump’s approval has sunk generally and is low on education specifically.
Jorge Elorza, the CEO of Democrats for Education Reform, points to a survey it commissioned showing the two parties tied when it comes to making sure schools emphasize academic achievement. “Democrats should be focused on delivering results,” he says. “When we ask voters about that, it’s a toss up.” A separate DFER poll found the party with only a 1-point lead on who voters trust to ensure “students are prepared for success after high school.”
Democrats’ overall polling advantage on education does not necessarily speak to the substantive merits of their policies, however. One analysis found that Democratic-leaning states have seen bigger declines in student test scores in recent years. At a national level, Democrats have not offered a particularly clear message on K-12 education, unlike Trump.
“For the last six years there’s [been] no proactive agenda for Democrats on educational excellence,” says Emanuel.
The party’s approach to schools has clearly lost a segment of America’s political tastemakers including center-left nonprofit executives, political strategists, and even some Democratic politicians. Yet, despite insistent assertions otherwise, regular voters don’t seem to share this view, at least at the moment.
I relied on the following polls from this year, with Democrats’ lead in parentheses: Blue Rose Research (February, tied); Fox News (July +15); Ipsos (February +6, April +4, October +7); Napolitan News Service (August +9, October +6); Navigator (August +9); Strength in Numbers (May +11, October +15); YouGov (May +7); Winston (April +15, June +14, August/September +11). To find these surveys, I conducted my own search and asked a variety of large pollsters, as well as a number of advocates. Differences in results between polls can come from random error, as well as differences in sampling and question wording. Although the precise wording varied, each poll asked voters which party they preferred on education.
Chalkbeat is a nonprofit news site covering educational change in public schools.
Did you use this article in your work?
We’d love to hear how The 74’s reporting is helping educators, researchers, and policymakers. Tell us how
-

Law Internships For High School Students: Find, Apply, And Succeed
How to Get Started
The Benefits of Law Internships
Different Types of Law Internships for High School Students
Law Office Internships for Teens
Government Internships for High Schoolers
Summer Law Internships
Internships with the FBI for High School Students
White House Internships for High School Students
International Law Internships
How to Help High School Students Get Law Internships
Resources for Schools and Communities
Websites That Can Help You Find Internships
Getting Help and Meeting New People
Conclusion
-
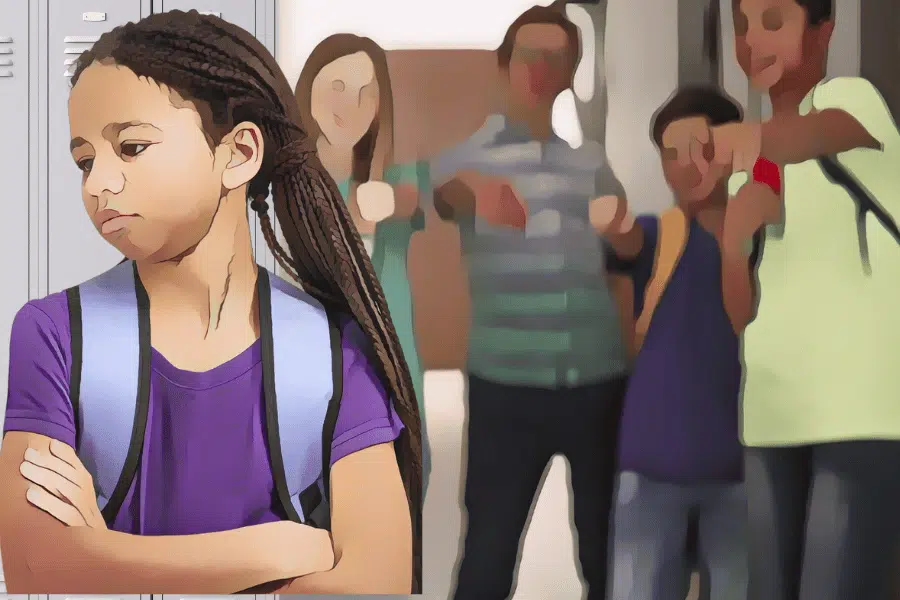
It is up to all of us to stand up to bullies
In the northern part of the country of a thousand hills, amidst volcanoes and the freezing air, there resides a Catholic high school. My name is Anderson and this is my story. I went to study there right after finishing my primary school.
The school was competitive; the smartest, most intelligent and most talented students were found there. It was a school of sciences and it used to be in the top five best high schools in the country. It had an amazing environment. Though strict academically, the teachers were among the best.
When I arrived, it wasn’t that hard to fit in because my elder sister had studied there before me. Some senior students recognized the resemblance and helped me get used to the school. This also gave me the privilege of not being bullied.
Normally, new students in S1 were bullied by seniors and couldn’t report it because they were scared of what might happen. The bullying was actually different based on gender. Boys were beaten severely, while girls were pressured into “dating” seniors. You might think dating sounds harmless, but it often involved bullying too.
There was a male friend of mine who was told to sit on his fork (the one used when we are eating) and say his weight — if he didn’t, the other students would beat him badly. This was also ridiculous because a fork cannot be used to measure someone’s weight. Another was given a leaf from a tree and told to use it to call his parents — again, he was beaten. This was a type of bullying because obviously you can’t talk on the leaf; they wanted him to pretend that the leaf is the phone.
On the other hand, my girlfriend was called out by senior boys, made to greet each one in a way they preferred and surrounded by a big circle of them. In summary, the first year was really hard for some students.
The bullied become bullies
By the second year, we were seniors to new students and some of us began to bully them. At this point, I understood the perspective of bullies — though it didn’t justify their actions. Seeing new students, you feel the tendency to assert your seniority and demand respect.
Some classmates acted out of revenge, targeting new students for what they had endured. On my side, I welcomed them with kindness and tried to help them adapt, knowing how hard it had been.
We used to have shows, which were my favorite part. I loved fashion and wanted to model in the shows, but I was always scared. During the shows, boys would often stand at the entrance, waiting to touch the girls’ bodies; breasts, buttocks, even private parts. Girls could complain, but some students and authorities argued that some girls “wanted to be touched.”
Others said that if girls didn’t want it, they could avoid participating or avoid wearing revealing clothes. Though some authorities promised to investigate, they often ignored the problem. Shows were considered entertainment, so the school left the organization to students. At some point, students feared reporting, worried the school might ban shows entirely.
It wasn’t only during shows. In class, we had a group of bullies we studied with. When the lights went out, girls would run outside immediately, because boys would touch them by force in the darkness.
When harassment is condoned
Once, I was sitting in class, my head on the desk, taking a nap. The lights went out and I didn’t notice. I woke up surrounded by boys. When I tried to leave, they blocked my way. One of them, called Chris, touched my breasts and others grabbed me as well. I felt scared, ashamed and angry. They were about to do more, but fortunately, other students started entering the class, and they left.
I laid my head back on the desk and cried. When people asked what was wrong, I couldn’t say. I had few friends; just my twin sister and another girl. When I reached the dormitory, I cried the whole night. My friend checked on me and though I hesitated at first, she comforted me.
I opened up and told her the story. To my surprise, she had also been harassed by the same boy, Chris. He was undisciplined and we didn’t know how to report him; there was no evidence and I wasn’t ready.
I spent months blaming myself. I was ashamed, hated myself and even had suicidal thoughts. My heart felt broken into pieces and no day passed without crying. But my twin sister was there for me. We cried together and I felt comforted. She suggested that we learn karate so no boy would dare harass me again.
We joined a karate club at school. It was amazing. The group was friendly, teaching discipline, teamwork and flexibility. Chris still mocked me, but I knew he was scared. In class, he never bullied me again. I continued learning karate even in other schools.
Fighting harassment
At other schools, I began my journey in leadership. I was voted Head Girl at two schools, started reading about feminism and realized I was a feminist. I began challenging unfair school policies that hindered one gender. On many campuses, girls were forced to do cleaning chores because culture expected them to be “decent” and “clean.”
Boys were allowed privileges girls could not have, without clear reason. It was a hard battle because authorities were biased. When I finished high school, I was voted Minister of Gender Promotion at my campus.
Reflecting on my high school experience, I realized many other girls knew stories of friends who were sexually assaulted and who couldn’t report it. Sometimes it was done to them by teachers or fellow students or authorities.
Schools often silence reports to protect their reputation. I understand that, but it shouldn’t come at the cost of student safety. There weren’t reporting platforms in place, but when girls tried to report, they were sometimes blamed, told they “wanted it.”
All of this motivated me to start a high school research project to assess the impact of school policies, sexual harassment and sextortion (this means when someone asks for sexual intercourse in exchange for a certain favor. In this context it may be to give you grades or other favors which you can get after having sex with that person offering it) on gender equality outcomes in high schools.
I am still working on my proposal, applying feedback and hoping for approval. As a survivor, I want to help my younger sisters get justice. I want to ensure no other girl cries alone at night, hiding the trauma she endured. I want to be their voice and advocate for solutions as youth.
This is my story — though it is still being written and it is far from over.
Questions to consider:
1. How can someone who is bullied become a bully?
2. Where do you think that some people get the idea that sexual harrassment is acceptable?
3. Have you ever been bullied or felt harrassed at school?
-

Why early STEAM education unlocks the future for all learners
Key points:
When we imagine the future of America’s workforce, we often picture engineers, coders, scientists, and innovators tackling the challenges of tomorrow. However, the truth is that a student’s future does not begin in a college classroom, or even in high school–it starts in the earliest years of a child’s education.
Early exposure to science, technology, engineering, arts, and mathematics (STEAM) builds the foundation for critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity. Research indicates that children introduced to STEAM concepts before the age of eight are significantly more likely to pursue STEM-related fields later in life. Yet for too many children, especially neurodivergent learners and those in underserved communities, STEAM education comes too late or not at all. That gap represents a missed opportunity not only for those children, but also for the industries and communities that will rely on their talents in the future.
The missed opportunity in early education
In most school systems, STEAM instruction ramps up in middle school or high school, long after the formative years when children are naturally most curious and open to exploring. By waiting until later grades, we miss the chance to harness early curiosity, which is the spark that drives innovation.
This late introduction disproportionately affects children with disabilities or learning differences. These learners often benefit from structured, hands-on exploration and thrive when provided with tools to connect abstract concepts to real-world applications. Without early access, they may struggle to build confidence or see themselves as capable contributors to fields like aerospace, technology, or engineering. If STEAM employers fail to cultivate neurodivergent learners, they miss out on theirunique problem-solving skills, specialized strengths, and diverse thinking that drives true innovation. Beyond shrinking the talent pipeline, this oversight risks stalling progress in fields like aerospace, energy, and technology while weakening their competitive edge.
The result is a long-term underrepresentation of neurodivergent individuals in high-demand, high-paying fields. Without access to an early STEAM curriculum, both neurodivergent students and employers will miss opportunities for advancement.
Why neurodivergent learners benefit most
Neurodivergent learners, such as children with autism, ADHD, or dyslexia, often excel when lessons are tactile, visual, and inquiry-based. Early STEAM education naturally aligns with these learning styles. For example, building a simple bridge with blocks is more than play; it’s an exercise in engineering, problem-solving, and teamwork. Programming a toy robot introduces logic, sequencing, and cause-and-effect.
These types of early STEAM experiences also support executive functioning, improve social-emotional development, and build persistence. These are crucial skills in STEM careers, where theories often fail, and continued experimentation is necessary. Additionally, building these skills helps children see themselves as creators and innovators rather than passive participants in their education.
When neurodivergent children are given access to STEAM at an early age, they are not only better equipped academically but also more confident in their ability to belong in spaces that have traditionally excluded them.
Here in Houston, we recognize the importance of early STEAM education in shaping our collective future. As the world’s Energy Capital and a hub for aerospace innovation, Houston’s economy will continue to rely on the next generation of thinkers, builders and problem-solvers. That pipeline begins not in a university laboratory, but in preschool classrooms and afterschool programs.
At Collaborative for Children, we’ve seen this firsthand through our Collab-Lab, a mobile classroom that brings hands-on STEAM experiences to underserved neighborhoods. In these spaces, children experiment with coding, explore engineering principles, and engage in collaborative problem-solving long before they reach middle school. For neurodivergent learners in particular, the Collab-Lab provides an environment where curiosity is encouraged, mistakes are celebrated as part of the learning process, and every child has the chance to succeed. Additionally, we are equipping the teachers in our 125 Centers of Excellence throughout the city in practical teaching modalities for neurodivergent learners. We are committed to creating equal opportunity for all students.
Our approach demonstrates what is possible when early childhood education is viewed not just as childcare, but as workforce development. If we can prioritize early STEAM access in Houston, other cities across the country can also expand access for all students.
To prepare America’s workforce for the challenges ahead, we must treat early STEAM education as a national priority. This requires policymakers, educators and industry leaders to collaborate in new and meaningful ways.
Here are three critical steps we must take:
- Expand funding and resources for early STEAM curriculum. Every preschool and early elementary program should have access to inquiry-based materials that spark curiosity in young learners.
- Ensure inclusion of neurodivergent learners in program design. Curricula and classrooms must reflect diverse learning needs so that all children, regardless of ability, have the opportunity to engage fully.
- Forge stronger partnerships between early education and industry. Employers in aerospace, energy, and technology should see investment in early childhood STEAM as part of their long-term workforce strategy.
The stakes are high. If we delay STEAM learning until later grades, we risk leaving behind countless children and narrowing the talent pipeline that will fuel our nation’s most critical industries. But if we act early, we unlock not just potential careers, but potential lives filled with confidence, creativity and contribution.
The innovators of tomorrow are sitting in preschool classrooms today. They are building with blocks, asking “why,” and imagining worlds we cannot yet see. Among them are children who are neurodivergent–who, with the proper support, may go on to design spacecrafts, engineer renewable energy solutions, or code the next groundbreaking technology.
If we want a future that is diverse, inclusive, and innovative, the path is clear: We must start with STEAM education in the earliest years, for every child.
Latest posts by eSchool Media Contributors (see all) -

Preparing for a new era of teaching and learning
Key points:
When I first started experimenting with AI in my classroom, I saw the same thing repeatedly from students. They treated it like Google. Ask a question, get an answer, move on. It didn’t take long to realize that if my students only engage with AI this way, they miss the bigger opportunity to use AI as a partner in thinking. AI isn’t a magic answer machine. It’s a tool for creativity and problem-solving. The challenge for us as educators is to rethink how we prepare students for the world they’re entering and to use AI with curiosity and fidelity.
Moving from curiosity to fluency
In my district, I wear two hats: history teacher and instructional coach. That combination gives me the space to test ideas in the classroom and support colleagues as they try new tools. What I’ve learned is that AI fluency requires far more than knowing how to log into a platform. Students need to learn how to question outputs, verify information and use results as a springboard for deeper inquiry.
I often remind them, “You never trust your source. You always verify and compare.” If students accept every AI response at face value, they’re not building the critical habits they’ll need in college or in the workforce.
To make this concrete, I teach my students the RISEN framework: Role, Instructions, Steps, Examples, Narrowing. It helps them craft better prompts and think about the kind of response they want. Instead of typing “explain photosynthesis,” they might ask, “Act as a biologist explaining photosynthesis to a tenth grader. Use three steps with an analogy, then provide a short quiz at the end.” Suddenly, the interaction becomes purposeful, structured and reflective of real learning.
AI as a catalyst for equity and personalization
Growing up, I was lucky. My mom was college educated and sat with me to go over almost every paper I wrote. She gave me feedback that helped to sharpen my writing and build my confidence. Many of my students don’t have that luxury. For these learners, AI can be the academic coach they might not otherwise have.
That doesn’t mean AI replaces human connection. Nothing can. But it can provide feedback, ask guiding questions, and provide examples that give students a sounding board and thought partner. It’s one more way to move closer to providing personalized support for learners based on need.
Of course, equity cuts both ways. If only some students have access to AI or if we use it without considering its bias, we risk widening the very gaps we hope to close. That’s why it’s our job as educators to model ethical and critical use, not just the mechanics.
Shifting how we assess learning
One of the biggest shifts I’ve made is rethinking how I assess students. If I only grade the final product, I’m essentially inviting them to use AI as a shortcut. Instead, I focus on the process: How did they engage with the tool? How did they verify and cross-reference results? How did they revise their work based on what they learned? What framework guided their inquiry? In this way, AI becomes part of their learning journey rather than just an endpoint.
I’ve asked students to run the same question through multiple AI platforms and then compare the outputs. What were the differences? Which response feels most accurate or useful? What assumptions might be at play? These conversations push students to defend their thinking and use AI critically, not passively.
Navigating privacy and policy
Another responsibility we carry as educators is protecting our students. Data privacy is a serious concern. In my school, we use a “walled garden” version of AI so that student data doesn’t get used for training. Even with those safeguards in place, I remind colleagues never to enter identifiable student information into a tool.
Policies will continue to evolve, but for day-to-day activities and planning, teachers need to model caution and responsibility. Students are taking our lead.
Professional growth for a changing profession
The truth of the matter is most of us have not been professionally trained to do this. My teacher preparation program certainly did not include modules on prompt engineering or data ethics. That means professional development in this space is a must.
I’ve grown the most in my AI fluency by working alongside other educators who are experimenting, sharing stories, and comparing notes. AI is moving fast. No one has all the answers. But we can build confidence together by trying, reflecting, and adjusting through shared experience and lessons learned. That’s exactly what we’re doing in the Lead for Learners network. It’s a space where educators from across the country connect, learn and support one another in navigating change.
For educators who feel hesitant, I’d say this: You don’t need to be an expert to start. Pick one tool, test it in one lesson, and talk openly with your students about what you’re learning. They’ll respect your honesty and join you in the process.
Preparing students for what’s next
AI is not going away. Whether we’re ready or not, it’s going to shape how our students live and work. That gives us a responsibility not just to keep pace with technology but to prepare young people for what’s ahead. The latest futures forecast reminds us that imagining possibilities is just as important as responding to immediate shifts.
We need to understand both how AI is already reshaping education delivery and how new waves of change will remain on the horizon as tools grow more sophisticated and widespread.
I want my students to leave my classroom with the ability to question, create, and collaborate using AI. I want them to see it not as a shortcut but as a tool for thinking more deeply and expressing themselves more fully. And I want them to watch me modeling those same habits: curiosity, caution, creativity, and ethical decision-making. Because if we don’t show them what responsible use looks like, who will?
The future of education won’t be defined by whether we allow AI into our classrooms. It will be defined by how we teach with it, how we teach about it, and how we prepare our students to thrive in a world where it’s everywhere.
Latest posts by eSchool Media Contributors (see all) -

Why Small Private Colleges Matter More Than Ever – Edu Alliance Journal
Opinion Piece by Dean Hoke — Small College America and Senior Fellow, The Sagamore Institute
A Personal Concern About the Future of Public Education
It’s impossible to ignore the rising level of criticism directed at our nation’s public schools. On cable news, social media channels, political stages, and in school board meetings, teachers and administrators have become easy targets. Public schools are accused of being ineffective, mismanaged, outdated, or, in some corners, ideologically dangerous. Some commentators openly champion the idea of a fully privatized K–12 system, sidelining the public institutions that have educated the vast majority of Americans for generations.
For those of us who have spent our lives in and around education, this rhetoric feels deeply personal. Public schools aren’t an abstraction. They are the places where many of us began our education, where our children discovered their strengths, where immigrants found belonging, where students with disabilities received support, and where caring adults changed the trajectory of young lives.
Behind every one of those moments stood a teacher.
Amid this turbulence, there is one group of institutions still quietly doing the hard work of preparing teachers: small private nonprofit colleges.
Small Private Colleges: An Overlooked Cornerstone of Teacher Preparation
Despite the noise surrounding public education, small private colleges remain committed to the one resource every school depends on: well-prepared, community-rooted teachers.
They rarely make national headlines. They don’t enroll tens of thousands of students. But they are woven into the civic and human infrastructure of their regions—especially in the Midwest, South, and rural America.
This reality became even clearer during a recent episode of Small College America, in which I interviewed Dr. Michael Scarlett, Professor of Education at Augustana College. His insights provide an insider’s view into the challenges—and the opportunities—facing teacher preparation today. Note to hear the entire interview click here https://smallcollegeamerica.transistor.fm/28
I. The Teacher Shortage: A Structural Crisis
Much has been written about the teacher shortage, but too often the conversation focuses on symptoms rather than causes. Here are the forces shaping the crisis.
1. Young people are turning away from teaching
Data from the ACT show that only 4% of students express interest in becoming teachers—down from 11% in the late 1990s. Bachelor’s degrees in education have fallen nearly 50% since the 1970s. Surveys show that fewer than 1 in 5 adults would recommend teaching as a career.
The message is clear: Teaching is meaningful, but many no longer see it as sustainable.
As Dr. Scarlett told us: “The pipeline simply is not as wide as it needs to be.”
Recent data offers a glimmer of hope: teacher preparation enrollment grew 12% nationally between 2018 and 2022. However, this modest rebound is almost entirely driven by alternative certification programs, which increased enrollment by 20%, while traditional college-based programs grew by only 4%. This disparity underscores a critical concern: the very programs that provide comprehensive, relationship-based preparation—including those at small colleges—are not recovering at the same rate as faster, less intensive alternatives.

2. Burnout and attrition have overtaken new entrants
The pandemic accelerated an already-existing national trend: teachers are leaving faster than new ones are entering.
Reasons include:
- Student behavior challenges
- Standardized testing pressure
- Emotional fatigue
- Inequities across districts
- Lack of respect
- Political and social media hostility
As Scarlett notes, these realities weigh heavily on early-career teachers: “What new teachers face today goes far beyond content knowledge. They face inequities, discipline issues, emotional exhaustion… and they’re expected to do it all.”
3. Alternative certification can’t fill the gap
Alternative routes help—but they cannot replace the traditional college-based pipeline. Many alt-cert teachers receive less pedagogical training and leave sooner.
Scarlett captures the trend: “Teaching has always attracted people later in life… we’ve definitely seen an uptick.”
And while alternative routes have seen growth in recent years—increasing 20% between 2018 and 2021—this expansion has not translated into solving the shortage. As of 2025, approximately 1 in 8 teaching positions nationwide remains either unfilled or filled by teachers not fully certified for their assignments. The shortcut approach cannot substitute for comprehensive preparation.
“The national teacher shortage is real… and retention is just as big a challenge as recruitment.” — Dr. Michael Scarlett
II. The Quiet Backbone: How Small Private Colleges Sustain the Teacher Workforce
Small private colleges graduate fewer teachers than large public institutions, but their impact is disproportionately large—especially in rural and suburban America.
1. They prepare the teachers who stay
About 786 private nonprofit colleges offer undergraduate education degrees—representing roughly 20% of all teacher preparation institutions in the United States. Together, they produce approximately 25,119 graduates per year, an average of 32 per institution.

These numbers may seem modest, but these graduates disproportionately:
- Student-teach locally
- Earn licensure in their home state
- Take jobs within 30 miles of campus
- Stay in the profession longer
Public schools desperately need these ‘homegrown’ teachers who understand the communities they serve.
2. Small colleges excel at the one thing teaching requires most: mentoring
Teacher preparation is not transactional. It is relational. And this is where private colleges excel. Scarlett put it plainly: “Close relationships with our students, small classes, a lot of direct supervision… we nurture them throughout the program.” In a profession that relies heavily on modeling and mentorship, this matters enormously.
3. Faculty—not adjuncts—supervise student teachers
One of the most striking differences: “Full professors… working with the students in the classrooms and out in field experiences. Other institutions outsource that.”
This is not a trivial distinction. Faculty supervision affects:
- Preparedness
- Confidence
- Classroom management
- Retention
Where larger institutions rely on external supervisors, small colleges invest the time and human capital to do it right.
4. They serve the regions hit hardest by shortages
Rural districts have the highest percentage of unfilled teaching positions. Many rural counties rely almost exclusively on a nearby private college to produce elementary teachers, special education teachers, and early childhood educators.
When a small college stops offering education degrees, it often leaves entire counties without a sustainable teacher pipeline.
5. They diversify the educator workforce
Small colleges—especially faith-based, minority-serving, or mission-driven institutions—often enroll first-generation students, students of color, adult career-changers, and bilingual students. These educators disproportionately fill shortage fields.
“What we have here is special… students understand the value of a small college experience.” — Dr. Michael Scarlett
III. Should Small Colleges Keep Offering Education Degrees? The Economic Question
Let’s be direct: Teacher preparation is not a high-margin program.
Costs include:
- Intensive field supervision
- CAEP or state accreditation
- High-touch advising
- Small cohort sizes
Education majors also often have lower net tuition revenue compared to business or STEM.
So why should a small college continue offering a program that is expensive and not highly profitable?
Because the alternative is far worse—for the institution and for the region it serves.
1. Cutting teacher-prep weakens a college’s identity and mission
Many private colleges were founded to prepare teachers. Teacher education is often central to institutional mission, community trust, donor expectations, and alumni identity.
Removing education programs sends the message that the college is stepping away from public service.
2. Teacher-prep strengthens community partnerships
Education programs open doors to:
- District partnerships
- Dual-credit pipelines
- Grow Your Own initiatives
- Nonprofit and state grants
- Alumni involvement
These relationships benefit the entire institution, not just the education department.
3. Education majors support other academic areas
Teacher-prep indirectly strengthens:
- Psychology
- English
- Sciences
- Social sciences
- Music and arts
When teacher education disappears, these majors often shrink too.
4. The societal mission outweighs the limited revenue
There are moments when institutional decisions must be driven by mission, not margins. Producing teachers is one of them.
5. Addressing concerns about program quality and scale
Some critics question whether small programs can match the resources and diversity of perspectives available at large universities. This is a fair concern—and the answer is that small colleges offer something different, not lesser.
Graduation and licensure pass rates at small private colleges consistently match or exceed those of larger institutions. What smaller programs may lack in scale, they compensate for through personalized mentorship, faculty continuity, and deep community integration. These are not peripheral benefits—they are the very qualities that predict long-term teacher retention.
IV. Why Students Still Choose Teaching—and Why Small Colleges Are Ideal for Them
Despite all the challenges, students who pursue teaching are deeply motivated by purpose.
Scarlett described his own journey: “I wanted to do something important… something that gives back to society.”
Many education majors choose the field because:
- A teacher changed their life
- They want meaningful work
- They value community and service
- They thrive in supportive, intimate learning environments
This makes small colleges the natural home for future teachers.
V. What Small Colleges Can Do to Strengthen Their Programs
Below are the strategies that are working across the country.
1. Build Grow Your Own (GYO) teacher pipelines
Districts increasingly partner to:
- Co-fund tuition
- Support paraeducator-to-teacher pathways
- Provide paid residencies
- Guarantee interviews for graduates
2. Develop dual-credit and “teacher cadet” high school programs
Scarlett sees this as a major reason for hope: “We’re seeing renewed interest in teaching through high school programs… This gives me hope.”
3. Offer specialized certifications (ESL, special ed, early childhood, STEM)
These areas attract students and meet district needs.
4. Create 4+1 BA/M.Ed pathways
Parents and students love the value.
5. Provide flexible programs for career-changers
The rise of adult learners presents a major opportunity for private colleges. “We prepare our students for the world that exists.” — Dr. Michael Scarlett
VI. Why Small Colleges Must Stay in the Teacher-Prep Business
If small private colleges withdraw from teacher preparation, the consequences will be immediate and dramatic:
- Rural and suburban schools will lose their primary source of new teachers.
- Teacher diversity will shrink.
- More underprepared teachers will enter classrooms.
- Districts will become more dependent on high-turnover alternative routes.
- Student learning will suffer.
And the profession will lose something even more important: the human-centered preparation that small colleges provide so well.
- The teacher shortage will not be solved by legislation alone.
- It will not be solved by fast-track certification mills.
- It will not be solved by online mega-universities.
- It will not be solved by market forces.
- It will be solved in the classrooms, hallways, and mentoring relationships of the small colleges that still believe in the promise of teaching.
If we want public schools to remain strong, we must support the institutions that prepare the teachers who keep them alive. Small private colleges aren’t just participants in the teacher pipeline—they are its foundation.
When these colleges thrive, they produce educators who stay, who care, and who transform communities. That’s not just good for education—it’s essential for American democracy.
Dean Hoke is Managing Partner of Edu Alliance Group, a higher education consultancy firm. He formerly served as President/CEO of the American Association of University Administrators (AAUA). Dean has worked with higher education institutions worldwide. With decades of experience in higher education leadership, consulting, and institutional strategy, he brings a wealth of knowledge on colleges’ challenges and opportunities. Dean is the Executive Producer and co-host for the podcast series Small College America and a Senior Fellow at the Sagamore Institute based in Indianapolis, Indiana.
-

Preserving critical thinking amid AI adoption
Key points:
AI is now at the center of almost every conversation in education technology. It is reshaping how we create content, build assessments, and support learners. The opportunities are enormous. But one quiet risk keeps growing in the background: losing our habit of critical thinking.
I see this risk not as a theory but as something I have felt myself.
The moment I almost outsourced my judgment
A few months ago, I was working on a complex proposal for a client. Pressed for time, I asked an AI tool to draft an analysis of their competitive landscape. The output looked polished and convincing. It was tempting to accept it and move on.
Then I forced myself to pause. I began questioning the sources behind the statements and found a key market shift the model had missed entirely. If I had skipped that short pause, the proposal would have gone out with a blind spot that mattered to the client.
That moment reminded me that AI is fast and useful, but the responsibility for real thinking is still mine. It also showed me how easily convenience can chip away at judgment.
The most powerful way to use AI is to treat it as a partner that widens the field of ideas while leaving the final call to us. AI can collect data in seconds, sketch multiple paths forward, and expose us to perspectives we might never consider on our own.
In my own work at Magic EdTech, for example, our teams have used AI to quickly analyze thousands of pages of curriculum to flag accessibility issues. The model surfaces patterns and anomalies that would take a human team weeks to find. Yet the real insight comes when we bring educators and designers together to ask why those patterns matter and how they affect real classrooms. AI sets the table, but we still cook the meal.
There is a subtle but critical difference between using AI to replace thinking and using it to stretch thinking. Replacement narrows our skills over time. Stretching builds new mental flexibility. The partner model forces us to ask better questions, weigh trade-offs, and make calls that only human judgment can resolve.
Protecting critical thinking is not about avoiding AI. It is about building habits that keep our minds active when AI is everywhere.
Here are three I find valuable:
1. Name the fragile assumption
Each time you receive AI output, ask: What is one assumption here that could be wrong? Spend a few minutes digging into that. It forces you to reenter the problem space instead of just editing machine text.2. Run the reverse test
Before you adopt an AI-generated idea, imagine the opposite. If the model suggests that adaptive learning is the key to engagement, ask: What if it is not? Exploring the counter-argument often reveals gaps and deeper insights.3. Slow the first draft
It is tempting to let AI draft emails, reports, or code and just sign off. Instead, start with a rough human outline first. Even if it is just bullet points, you anchor the work in your own reasoning and use the model to enrich–not originate–your thinking.These small practices keep the human at the center of the process and turn AI into a gym for the mind rather than a crutch.
Why this matters for education
For those of us in education technology, the stakes are unusually high. The tools we build help shape how students learn and how teachers teach. If we let critical thinking atrophy inside our companies, we risk passing that weakness to the very people we serve.
Students will increasingly use AI for research, writing, and even tutoring. If the adults designing their digital classrooms accept machine answers without question, we send the message that surface-level synthesis is enough. We would be teaching efficiency at the cost of depth.
By contrast, if we model careful reasoning and thoughtful use of AI, we can help the next generation see these tools for what they are: accelerators of understanding, not replacements for it. AI can help us scale accessibility, personalize instruction, and analyze learning data in ways that were impossible before. But its highest value appears only when it meets human curiosity and judgment.
Building a culture of shared judgment
This is not just an individual challenge. Teams need to build rituals that honor slow thinking in a fast AI environment. Another practice is rotating the role of “critical friend” in meetings. One person’s task is to challenge the group’s AI-assisted conclusions and ask what could go wrong. This simple habit trains everyone to keep their reasoning sharp.
Next time you lean on AI for a key piece of work, pause before you accept the answer. Write down two decisions in that task that only a human can make. It might be about context, ethics, or simple gut judgment. Then share those reflections with your team. Over time this will create a culture where AI supports wisdom rather than diluting it.
The real promise of AI is not that it will think for us, but that it will free us to think at a higher level.
The danger is that we may forget to climb.
The future of education and the integrity of our own work depend on remaining climbers. Let the machines speed the climb, but never let them choose the summit.
Latest posts by Laura Ascione (see all) -

When life is bitter, don’t lose hope
When life takes away your greatest support, it can feel as if the world is falling apart. For me, losing my father as a child was more than heartbreaking. It was a true test of strength. Yet in a world that often seemed bitter, the kindness of strangers and the power of personal dreams helped me rise above my sorrow and shape a future full of hope.
My family and I live in the Eastern province of Rwanda. I was only five years old when one morning, my father packed his bag and left the house. He didn’t say where he was going and he never came back. Days turned into weeks, weeks into years, but there was no sign of him. No call. No letter. Nothing.
At first, I didn’t understand what was happening. I kept asking my mother, “When is Papa coming back?” But she would just smile sadly and say, “One day, maybe.”
In her heart, she knew he was not coming back.
Life changed quickly after that. Without a father and without money, things became hard for the family. My mother, Catherine, had no job. She had never worked outside the home before. Now, she had to take care of me and my four siblings alone.
Struggling with little
We had no house of our own. We moved from one place to another, staying with kind neighbors or sleeping in small, broken huts. During rainy nights, water would leak through the roof and we had to stay awake holding buckets. Sometimes, we didn’t even have enough food to eat. Many nights, we went to bed hungry.
My siblings were in high school at the time, but the family could not afford school fees anymore. One by one, they dropped out and stayed home. It was painful for me to watch them suffer. I loved them deeply and wanted a better life for all of them.
Despite everything, I stayed in school. My mother worked hard doing small jobs washing clothes, digging gardens or selling vegetables in the market. She never gave up. “You are our hope,” she would tell me. “Even if your father left, we must move forward.”
I listened. I promised myself that no matter how hard life became, I would not give up. I wanted to finish school, go to university and one day help my family live a better life.
But it was not easy.
Help can come from surprising places.
I often went to school with old shoes. I had no school bag only an old plastic bag to carry my books. I had no lunch and many times, I sat in class with an empty stomach. But still, I worked hard. I listened carefully, asked questions and always completed my homework, even if it meant studying by candlelight or by the dim light of a kerosene lamp.
Many teachers began to notice me. They saw that even though I had nothing, I had determination and a kind heart. One teacher gave me exercise books. Another helped pay part of my school fees. A neighbor who owned a small shop gave me a few snacks sometimes. A church group gave my mother food and clothes once in a while.
These acts of kindness kept me going.
I studied harder than anyone else and soon became the best performer in my class. Every year, I got top marks. My name was always on the honor list. At school, students looked up to me. But at home, things were still hard. My siblings had lost hope, but I kept believing in a better future.
After many years of struggle, I finally finished high school. I was the first in my family to do so. On the day I received my final results, my mother cried tears of joy. You did it, my son. You made me proud, she said, hugging me tightly.
But my journey wasn’t over.
I had one more goal: to go to university. That meant more fees, laptop, more books, more challenges, but I didn’t stop. I applied for scholarships and after many rejections, I finally got accepted to a university with some financial support.
Now, I’m 22 years old. I’m in university, studying hard every day. I met with a kind person again, who gave me a place to sleep and dinner. Even though I have that support, I’m still facing challenges. I still lack proper shoes, clothes and transport money, but I keep going. My dream is to become a professional, get a good job first, then become self-employed and return home to support my mother and siblings.
I remind myself: “My father left us when I was just a child. We had no house, no food and no money. My siblings could not finish school. But I decided to fight. Kind people helped me and I stayed strong. Now I am at university. I will not stop until I help my family rise again.”
I hope my story will teach young people that even when life feels bitter and people let you down, you must not give up. Strength is not about having everything. It is about standing tall even when you have nothing. This is the reason why I’m writing my story.
Even when life is painful and people walk away from you, never lose hope. With hard work, faith and the help of kind people, you can still rise, succeed and help others do the same.
QUESTIONS TO CONSIDER:
1. What was one thing the author promised himself when things got really hard for his family?
2. In what ways did people help the author succeed?
3. When have people helped you when you were having difficulty?



