Universities Australia has signed a deal with China that will encourage research collaboration and student exchanges between the two countries.
Please login below to view content or subscribe now.
Membership Login

Universities Australia has signed a deal with China that will encourage research collaboration and student exchanges between the two countries.
Please login below to view content or subscribe now.

Ian Oppermann is in charge of digital ID for the federal government and an Associate Industry Professor of engineering and IT at the University of Technology Sydney.
Please login below to view content or subscribe now.

Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
Members of Gov. Josh Stein’s bipartisan Task Force on Child Care and Early Education got an update on licensed child care closures during their most recent meeting.
“Just in the month of August, we had more than twice as many programs close as open,” said Candace Witherspoon, director of the Division of Child Development and Early Education (DCDEE).
Her statement is evidence that — despite a small uptick in the number of centers last quarter — the overall trend of licensed child care losses has continued since the end of pandemic-era stabilization grants earlier this year.
Based on data provided by the N.C. Child Care Resource and Referral (CCR&R) Council in partnership with DCDEE, EdNC previously found that North Carolina lost 5.8% of licensed child care programs during the five years when stabilization grants were used to supplement teacher wages.
That net loss has increased to 6.1% since the end of stabilization grants. Family child care homes (FCCHs) make up 97% of that net loss.
Since February 2020, the last month of data before the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of licensed FCCHs has decreased by 23%. The number of licensed child care centers has decreased by 0.3%.
The trend for licensed FCCHs since EdNC began tracking the data in June 2023 has been one of consistent net loss, decreasing each quarter.
There were 1,363 FCCHs in February 2020. That number was down to 1,096 in March 2025, the last data before the end of stabilization grants. Now there are 1,052 FCCHs across the state.
While licensed child care centers have also experienced a net loss since February 2020, the trend has been less linear.
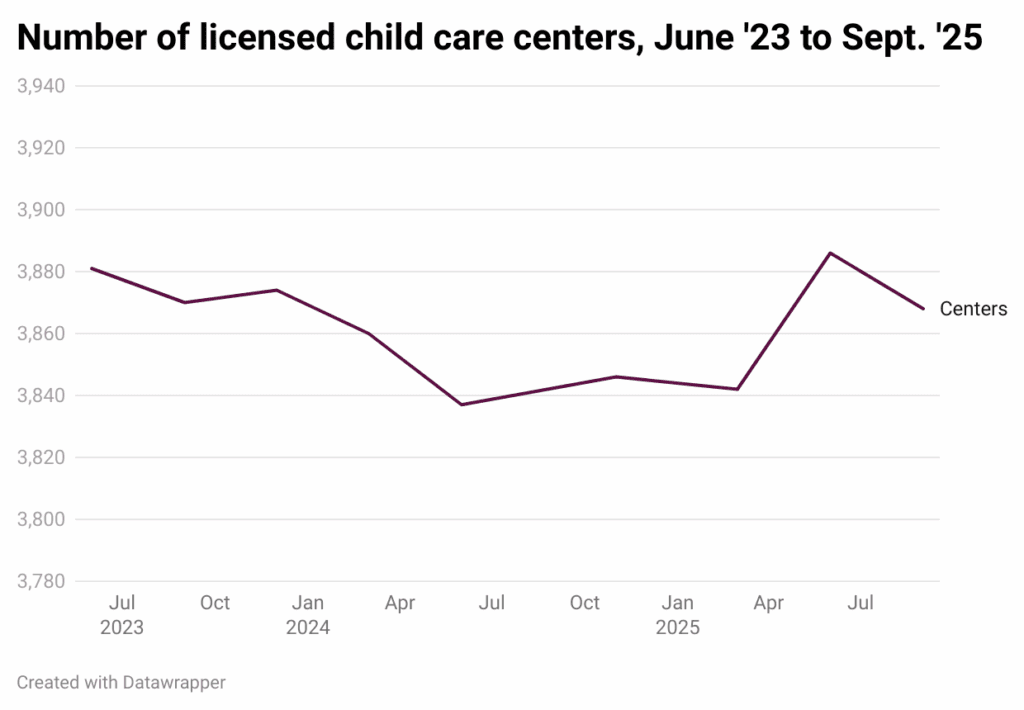
There were 3,879 licensed centers in February 2020. When EdNC began tracking in June 2023, the number was slightly higher at 3,881. From then on it fluctuated, with net gains in some quarters and net losses in others. There are now 3,868 licensed centers statewide.
While the net loss of centers remains small, the effect of a single center closing is huge — especially in rural communities.
Families on Hatteras Island are learning this firsthand. The only licensed child care program on the island is scheduled to close at the end of the year. With no licensed FCCHs and no clear way to save the sole licensed center, families are trying to figure out how to keep their businesses open and remain in their communities without access to child care.
Access to high-quality, affordable early care and learning is crucial to child and family freedom and well-being. It enables parents to participate in the workforce or continue their education without concern for the safety of their children. It also puts North Carolina’s youngest residents on a path to future success.

In addition to monitoring overall licensed child care trends, EdNC zooms in on trends among three subgroups of counties each quarter.
In the counties that make up the area covered by the Dogwood Health Trust (Avery, Buncombe, Burke, Cherokee, Clay, Graham, Haywood, Henderson, Jackson, Macon, Madison, McDowell, Mitchell, Polk, Rutherford, Swain, Transylvania, and Yancey), the number of licensed child care sites is 5% lower than before the pandemic. These counties had a net loss of eight programs from July through September 2025, the largest single-quarter decrease since EdNC began tracking.
In the majority-Black counties (Bertie, Edgecombe, Halifax, Hertford, Northampton, Vance, Warren, and Washington), the number of licensed child care sites remained relatively stable during and after the pandemic. But in the most recent quarter, these counties had a net loss of nine programs, putting them 4% lower than before the pandemic, a sudden and dramatic shift in circumstance. As with the Dogwood counties, this represents the largest single-quarter decrease since EdNC began tracking.
In Robeson and Swain, which both have large Indigenous populations, the number of licensed child care sites had also remained relatively stable during and after the pandemic. In the most recent quarter, for the first time since EdNC began tracking, the number of licensed child care programs in these counties has dipped just below pre-pandemic levels.
Editor’s note: The Dogwood Health Trust supports the work of EdNC.
This article first appeared on EdNC and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Did you use this article in your work?
We’d love to hear how The 74’s reporting is helping educators, researchers, and policymakers. Tell us how

November 2, 2025, By Dean Hoke — When Sweet Briar College’s trustees voted to close in 2015, they framed the decision as a financial necessity. Alumnae mounted an extraordinary campaign—raising $28.5 million in 110 days—and, through a state-brokered settlement, the college reopened under new governance. By 2023, donors had contributed well over $133 million since the crisis. What looked like an inevitable failure became one of higher education’s most remarkable turnarounds.
Sweet Briar is not only a story of crisis response; it exposes a recurring miscalculation in today’s merger conversations: the assumption that boardroom consensus equals donor legitimacy. Trustees speak for donors in a fiduciary sense—they hold legal responsibility for institutional assets—but not in the communal sense that captures sentiment, legacy, and trust. When colleges announce merger talks, headlines dwell on enrollment curves and debt ratios. Yet behind every deal stands a quieter, decisive constituency: major donors, family foundations, and planned-giving benefactors whose confidence (or loss of it) can determine whether the combined institution thrives—or limps forward under the weight of broken relationships.
This article reframes mergers as philanthropic integration projects. The legal mechanics matter, but durable success is won in the design phase: early engagement with philanthropic stakeholders, explicit safeguards for identity and donor intent, transparent transition planning, and a mission-first case that invites continued—and new—investment. When leaders bring donors and alumni into the architecture of the merger rather than the press release, they convert anxiety into commitment and preserve the institutional DNA that constituents care about most.
We’ll see this principle in contrasting cases: mission-advancing acquisitions that attracted significant philanthropic support, integrations that prioritized identity and donor intent from the outset, and lessons from failed or contested processes. The throughline is simple: treat philanthropy as a core workstream—not an afterthought—and the odds of a credible, sustainable merger rise dramatically.
The stakes have never been higher. Survey data from Ruffalo Noel Levitz’s 2025 National Alumni Survey, which surveyed more than 50,000 alumni, reveals that donor relationships with higher education are already strained. While 81% of alumni report that being philanthropic is important to them personally and 77% make charitable donations, their connection to their alma mater has weakened dramatically. Only 31% of alumni who donate to any charity gave to their alma mater last year, dropping to just 19% among Millennials and 10% among Gen Z graduates.
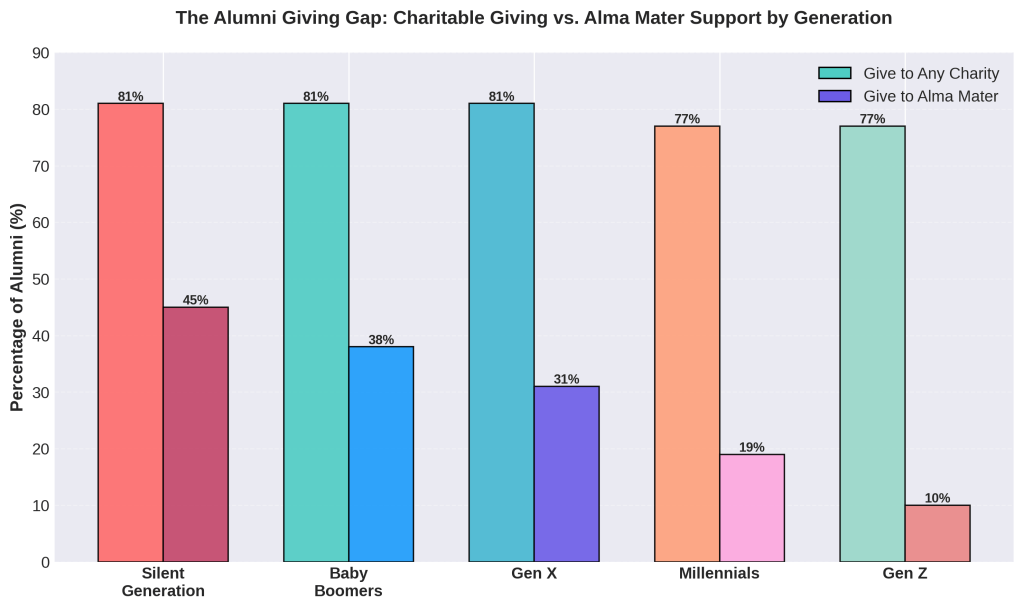
Even more troubling: 59% of alumni who never donate to their alma mater actively support other causes, as do 83% of lapsed donors. They have not stopped giving—they have simply redirected their philanthropy elsewhere. This suggests that alumni disengagement reflects institutional failure rather than generational selfishness.
Satisfaction drives everything. Alumni who report being ‘very satisfied’ with their student experience are 18 times more likely to donate than neutral respondents and 73 times more likely than dissatisfied graduates. Yet only 42% of Gen Z alumni report feeling ‘very satisfied’ with their experience, compared to 72% of Silent Generation graduates.
Mergers test already-fragile relationships. When institutions announce consolidation, donors who felt lukewarm about their undergraduate experience see confirmation that their alma mater is failing. A merger framed solely as a financial necessity will not inspire them. But a merger presented as advancing mission-driven impact—expanding access, strengthening programs that address social challenges, or preserving an educational model under threat—can mobilize support from the very alumni who have drifted away.
As Millett (1976) noted, successful integrations often ‘show structure, not just sentiment’—for example, Case Western Reserve kept a distinct Case Institute identity, and Carnegie Mellon created a Carnegie Institute of Engineering and a Mellon Institute of Science to carry legacies forward.
A half-century ago, John D. Millett’s 1976 analysis of U.S. college mergers examined a range of cases—from research institutes to liberal arts colleges—and distilled lessons that remain strikingly current. Four observations deserve renewed attention today:
1. Endowments transfer; relationships do not. In many mergers, endowments and restricted funds move to successor institutions through standard legal pathways. The mechanics are manageable. The harder work is relational: ensuring donors can see how their original intent will be honored in the new configuration, and that the program or ethos they loved will not be erased.
2. Alumni skepticism is predictable—and manageable. Leaders should not assume alumni approval, especially when the smaller institution is absorbed. Visible steps to cultivate and retain legacy alumni—keeping familiar staff contacts for a transitional period, acknowledging a distinct identity, and offering tangible ways to shape the merged future—go a long way.
3. Governance approval is not donor legitimacy. Even when boards vote, state bodies concur, and presidents sign, philanthropic legitimacy remains a separate test. Communities expect to be consulted; they often oppose mergers if they learn about them too late. Participation must be planned early, not added later.
4. Language and structure matter more than sentiment. Labels and explanations—federation versus absorption, mission expansion versus rescue—shape how alumni and donors interpret the outcome. Leaders who explain clear educational benefits and who visibly protect identity through formal structures earn trust faster.
After the Case Institute of Technology and Western Reserve University merger, the successor Case Western Reserve University continued the designation of Case Institute of Technology as an organizational component. At Carnegie Mellon University, leaders created a Carnegie Institute of Engineering and a Mellon Institute of Science—formal structures that carried legacy identities forward within the new entity.
The Bellarmine-Ursuline (Louisville) merger (1968-1971) offers another instructive example. The combined institution briefly used the Bellarmine-Ursuline name before reverting to Bellarmine College in 1971, but Bellarmine has continued to honor Ursuline identity through durable structures—explicitly including Ursuline alumnae in alumni awards and honors and recognizing the Ursuline legacy through commemorations and alumni programming. These are structural signals that preserve identity even when the combined name does not persist.
Millett also notes that successor institutions often made special effort to cultivate and retain alumni of the absorbed college, including keeping an alumni-relations officer from the legacy institution and providing a special alumni designation or status—practical ways to keep traditions and community intact during transition.
Planning is done privately, the announcement is abrupt, and donors are asked to accept a fait accompli. Mills College’s merger with Northeastern University proceeded despite alumni resistance, prompting legal challenges over donor intent. The Alumnae Association spent hundreds of thousands in legal fees opposing the merger, and a class action lawsuit resulted in a $1.25 million settlement. The litigation divided alumnae and consumed resources that could have been invested in the merged institution’s success.
Even when the legal mechanics are sound, the community verdict is that identity has been erased. The result: backlash, donor-intent disputes, and years of costly trust repair.
Teams carefully inventory restricted funds, ensure transfers align with donor intent, and communicate the basics. This prevents disasters but rarely generates enthusiasm or new investment. Survey data reveals that 70% of alumni need to believe their gift amount matters, and 66% rate the ability to see how their gift is used as critical. When a college merges, donors worry their legacy has been erased—regardless of legal assurances that funds will be protected.
The compliance model maintains existing donors but does not mobilize new support for the merged institution’s expanded mission. The message is ‘We will comply,’ not ‘Here is a better future you can help build.’
Donors and foundations are treated as co-creators from Day 0. Leaders conduct quiet briefings with major benefactors pre-announcement, frame the merger as mission expansion, and embed structural commitments to legacy preservation. This model doesn’t eliminate hard feelings, but it channels energy toward shared outcomes.
Delaware State University–Wesley College (2020–21). DSU—an HBCU—acquired Wesley and framed the move as mission advancement, launching the Wesley College of Health & Behavioral Sciences to expand pathways in nursing and allied health for underserved students. Financing combined philanthropy and prudence: a $20M unrestricted gift from MacKenzie Scott (with a portion—reported as roughly one-third of the $15M total—applied to transition costs) and a $1M Longwood Foundation grant for the acquisition. The case shows how a mission-first narrative can catalyze major-donor and foundation support.
By tying dollars to a new health‑workforce pipeline—rather than balance‑sheet triage—leaders converted donor anxiety into visible, restricted impact.
Ursuline College–Gannon University (ongoing). From the outset, both institutions engaged stakeholders publicly and affirmed philanthropy principles: “Honoring donor intent is important to Gannon University,” and donors will be able to designate gifts to the Pepper Pike campus. Ursuline will retain its identity as the Ursuline College Campus of Gannon University after the transition, and the Ursuline Sisters of Cleveland have voiced support for the merger—signals aimed at preserving community trust and legacy while the integration proceeds through 2026. These commitments, paired with the HLC’s Change-of-Control approval, frame the merger as continuity-minded rather than absorptive.
University of Tennessee Southern (formerly Martin Methodist College).
University of Tennessee Southern (formerly Martin Methodist College)
When Martin Methodist joined the University of Tennessee System in 2021, leaders prioritized transparent, compassionate communication—“a liminal space” requiring a strong plan, as President Mark La Branche put it. They also set aside portions of the legacy endowment (via the Martin Methodist College Foundation) to protect signature programs, showing that integration need not erase institutional identity.
Public commitments to donor intent and the campus naming convention did early legitimacy work that legal filings can’t.
When a stronger institution absorbs a struggling one, leaders often assume donor concerns belong primarily to the acquired institution. This is a strategic error. The acquiring institution’s donors also have a stake in the outcome—and their continued support is essential to merger success.
Major donors to the acquiring institution may question why resources should be directed toward absorbing another college. They may worry that the acquired institution’s struggles will tarnish their alma mater’s reputation, or that merger costs will compete with planned campus improvements. These concerns are legitimate and require proactive engagement.
The narrative for acquiring institution donors must emphasize strategic opportunity rather than charitable rescue. Several frames can be effective:
Geographic expansion: The merger creates a presence in a new market, expanding the institution’s reach and visibility.
Program complementarity: The acquired institution brings academic strengths that fill gaps in the acquiring institution’s portfolio.
Mission advancement: The merger expands capacity to serve students and fulfill the educational mission on a greater scale.
Competitive positioning: In an era of consolidation, the merger strengthens the institution’s competitive position and long-term sustainability.
Rather than waiting for resistance to emerge, acquiring institution leaders should brief major donors before public announcement. These confidential conversations acknowledge donors’ legitimate interest in institutional strategy, allow leaders to address concerns directly, and create opportunities for donors to become merger advocates.
Legal clarity: When restricted funds cannot be used as originally intended post‑merger, pursue a cy‑près modification early—advancement and counsel should partner on donor communication before any filing to preserve trust.
You can brief a small set of major donors pre‑announcement under strict NDAs without privileging them over faculty governance or regulators. Use a defined rubric for who is briefed (e.g., top 10% of lifetime commitments and active pledgors), disclose no nonpublic counterparties’ terms, and limit to mission rationale, identity safeguards, and timeline. Record each briefing in counsel’s log.
Philanthropic due diligence—parallel to financial. Inventory endowed and restricted funds, bequests in the pipeline, and active foundation grants. Identify potential cy-près risks and draft stewardship language now. Treat this as a distinct workstream with advancement, finance, and counsel at the table from the start.
Quiet briefings with top donors and foundations on both sides. Under confidentiality, preview the rationale, surface donor-intent questions, and invite advice. Ask for early champions willing to speak publicly when the time comes.
Identity protections by design, not promise. Prepare a naming plan (e.g., ‘[Legacy] College at [Acquirer]’), preserve scholarship and reporting lines, and keep alumni-relations continuity for 12-24 months. Publish a short ‘Identity & Intent’ brief on day one that shows, in plain language, how donor purposes are carried forward.
Mission-driven case for support. Lead with the educational value only possible together: new academic pathways, access expansions, regional partnerships, research synergies. Avoid rescue framing. Make the case specific and concrete, tied to programs and outcomes donors care about.
Dedicated ‘Legacy to Impact’ funds with challenge matches. Create visible vehicles that convert anxiety into investment—restricted funds for scholarships, program launches, and student success tied to the integrated entity.
Community-benefit specificity. Spell out local benefits and stakeholder wins (clinics, teacher pipelines, innovation hubs). When people can ‘see’ the upside, they are likelier to invest in it.
Quarterly transparency. Report enrollment in merged programs, first scholarship cohorts, renewed or new foundation grants, and capital milestones. Transparency reduces rumors and builds credibility.
Recognition symmetry. Offer parity for legacy and acquirer donors—naming walls, digital honor rolls, endowed-fund dashboards, and joint stewardship events.
Two-sided cultivation. Brief the acquirer’s major donors so they see strategic growth rather than a charitable drain. Ask two or three to seed a matching pool restricted to merger priorities; matches signal confidence and reduce perceived risk.
Because reliable analytics on donor behavior in mergers are sparse, leaders should build their own lightweight evidence base. For each merger, track three years pre- and post-integration for: total private support; alumni participation (where available); number of $1M+ gifts; and the mix of restricted versus unrestricted giving.
Pair quantitative metrics with a qualitative log: Was identity preserved in naming? Did a Legacy Alumni structure exist? Were there donor-intent disputes? Did the acquirer launch dedicated legacy funds? How soon were KPIs reported?
Even a simple dashboard, updated quarterly, changes the conversation with trustees and donors. It shows momentum (or lack thereof), prompts targeted stewardship, and gives leaders permission to make mid-course corrections. It also validates the core claim of this article: philanthropy works best when it is built into planning, not bolted on after the fact.
The most fundamental error in merger planning is treating donors as communications targets rather than strategic partners. Donors are not merely sources of revenue to be managed; they are partners whose investments reflect belief in institutional mission and values.
Mergers that succeed treat donors, foundations, and alumni as planning inputs, not a downstream audience for PR. Millett’s 1976 study reminds us that while the legal mechanics of endowment transfers are straightforward, the human mechanics are not. Alumni skepticism is predictable; identity needs visible protection through formal structures, not just promises; language and framing carry unusual weight.
When leaders internalize those lessons—and create structures that honor donor intent, invite co-creation, and make the mission upside measurable—legacy becomes leverage rather than liability. Higher education’s financial pressures are real, but so is the reservoir of goodwill that donors and alumni hold for institutions that respect them.
The Sweet Briar alumnae who raised $133 million did not do so because they were told the college would comply with donor intent. They did so because they were invited to co-create a future worth investing in. That is the lesson for every merger: bring philanthropic stakeholders into the room early, build identity protections into the design, launch vehicles that convert anxiety into investment, and report steadily and transparently on what their support makes possible.
That is how two proud legacies become one stronger future—and how the ‘silent stakeholders’ find their voice in shaping it.
Sources (selected): institutional FAQs and press releases (Ursuline–Gannon; DSU–Wesley; UT Southern), RNL Alumni Giving Data 2025 (for participation/attitudes), and Millett, J.D. (1976) ED134105 on college mergers.
Dean Hoke is Managing Partner of Edu Alliance Group, a higher education consultancy. He formerly served as President/CEO of the American Association of University Administrators (AAUA). Dean has worked with higher education institutions worldwide. With decades of experience in higher education leadership, consulting, and institutional strategy, he brings a wealth of knowledge on colleges’ challenges and opportunities. Dean is the Executive Producer and co-host for the podcast series Small College America.

The three-day gathering in Aurora, Colorado, opened with a sense of urgency as attendees acknowledged both the progress made in Hispanic higher education and the mounting challenges facing students and institutions.
“The attacks on immigrants and higher education by the Trump administration is reason for why we need organizations like HACU to stand up for students like me,” said Maria Valasquez, 21, a college junior who attended the conference for the first time. “The threats are real and these are scary times for many first-generation college students.”
The conference began with four specialized pre-conference events on October 31 and November 1, drawing approximately 200 participants total. These included the 14th Annual Deans’ Forum, focused on “Shaping Visionary Leaders for a Thriving and Democratic Future”; the Third Women’s Leadership Symposium; the 24th Annual Latino Higher Education Leadership Institute, themed “Building Transformational Leaders at All Levels to Strengthen Democracy and Prosperity”; and the 11th Annual PreK-12/Higher Education Collaboration Symposium, addressing “Bridging Education for Lifelong Success: Innovation, Collaboration, and Life Readiness.”
The main conference kicked off with an Opening Plenary convened by Dr. Juan Sanchez Muñoz, HACU’s Governing Board chair and chancellor of the University of California, Merced. HACU Interim CEO Dr. John Moder delivered the Annual Address, followed by the induction of Dr. Félix V. Matos Rodriguez, chancellor of The City University of New York, into HACU’s Hall of Champions 2025.
 Dr. Mordecai Brownlee, President of The Community College of Aurora, and Dr. Christopher Reber, President of Hudson County Community College at the HACU conference.
Dr. Mordecai Brownlee, President of The Community College of Aurora, and Dr. Christopher Reber, President of Hudson County Community College at the HACU conference.
A regional focus emerged through the Illinois Hispanic-Serving Institution Summit, also held November 1. After welcoming remarks from Moder and virtual comments from Illinois State Representative La Shawn Ford, a panel discussion addressed the midwestern region’s legislative agenda. The panel featured Dr. Susana Rivera-Mills, president of Aurora University; Dr. Lisa Freeman, president of Northern Illinois University; and Juan Salgado, chancellor of City Colleges of Chicago.
The summit provided a platform for discussing HACU’s policy and legislative priorities in Illinois, including the critical role college and university presidents play in advancing and sustaining Hispanic-Serving Institutions across the state. Participants shared promising practices and explored collaborative approaches to strengthen institutional capacity.
Seven honorees are being recognized throughout the conference for their contributions to improving opportunities for college students, with awards presented during various events over the three days.
“As a president of a Hispanic-Serving Institution and member of HACU’s Board of Directors, I witness firsthand how these colleges and universities transform lives, strengthen families, and fortify our economy,” said Dr. Mordecai I. Brownlee, President of The Community College of Aurora. “The mission of HACU is not a moment — it’s a movement. Despite the challenges of our times, our collective commitment to equity, opportunity, and excellence is just getting started.”
In an interview, Brownlee said that Hispanic-Serving Institutions are not just essential to higher education — they are essential to America’s economic growth and democratic future.
“By investing in HSIs, our nation invests in innovation, workforce readiness, and prosperity for all,” he said. “The mission of HACU is not simply about serving Hispanic students; it’s about strengthening the very foundation of America’s competitiveness and civic vitality.”
The conference continues through November 3, as higher education leaders work to chart a path forward for Hispanic student success amid an increasingly complex political landscape.
Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
Politicians love to say, “We must protect our children. They are our future.” But looking at what’s happening in Congress right now, children are not being protected. Families are not being prioritized. Instead, lawmakers are locked in a standoff, waiting to see who blinks first as they fight over who gets the last word and how big of a tax break they can give the wealthiest Americans.
Meanwhile, families — especially families of color and low-income families — are left to hold their breath and wonder what this shutdown means for them. As members of Congress keep making their rounds on television, babies still need formula, toddlers still need health screenings, children still need breakfast and lunch at school and in their child care programs, and parents still need child care so they can work. Amid extreme stress, families are left, wondering how they will be able to take care of their children.
The demands of children and their families do not stop just because Congress is at a standstill.
According to Kids’ Share 2024, an annual report published by the Urban Institute about federal expenditures, children received only about 9% of all federal spending in 2023, while about 43% of federal spending went toward health and retirement benefits for adults 18 years and older. That’s a very small percentage for a nation in which politicians on both sides of the aisle have expressed interest in increased government investment in children. These numbers contradict the narrative that claims children matter because they are our future.
That 9% starts to feel even smaller during a government shutdown. Some programs, like Social Security, Medicaid and Medicare, are mandatory, meaning they don’t require annual congressional approval. But others, including a number of crucial children’s programs, such as the Special Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC), are funded through the annual appropriations process, which Congress must approve. This means when lawmakers can’t agree on a budget, these critical programs are left in limbo.
The fallout on the horizon from this needless dysfunction is becoming clearer.
In September, the National WIC Association reminded the public that WIC only had enough funds to temporarily remain open during a government shutdown. Now, according to Reuters, at least two dozen state websites warn there could be an unprecedented benefit gap for more than 41 million people in America who get aid from the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) and the nearly 7 million people who rely on WIC.
Georgia Machell, president and chief executive officer of the National WIC Association, delivered this sobering news last week.
“Without additional support, State WIC Agencies face another looming crisis,” she said. “Several are set to run out of funds to pay for WIC benefits on November 1 and may need to start making contingency plans.”
Many families in historically marginalized communities, who already face greater barriers to health care, housing and early education, will feel this impact even more sharply. For example, we know that tens of thousands of young children and families rely on vital support received through Head Start, a service that promotes early learning and development, health and well-being. The shutdown is already in its fourth week, and, according to a statement issued on Oct. 16 from the National Head Start Association, if the government shutdown doesn’t end by Nov. 1, more than 65,000 children and families will be at risk of losing critical services.
A missed doctor’s appointment, a delay in SNAP benefits or a gap in child care isn’t just inconvenient. It can destabilize a family and hinder a child’s development, especially in the classroom.
A research brief published by The Food Research & Action Center highlighted the links between hunger and learning, stating that “behavioral, emotional, mental health, and academic problems are more prevalent among children and adolescents struggling with hunger” and that young people experiencing hunger have lower math scores and poorer grades. The shutdown will have real and lasting consequences on the learning, development and well-being of America’s children because these programs are being impacted.
It’s frustrating to watch lawmakers stand at podiums and declare how much they care about children while their actions — or inaction — puts children at risk.
Words don’t put food on the table. Words don’t pay rent. But actions do.
And right now, the actions coming out of Congress are sending an unfortunate message to families: protecting children is not the priority.
If children truly are our future, then they cannot be treated as bargaining chips. Children deserve more than 9% of America’s federal spending budget. We need federal budgets that reflect children’s needs and protection for essential services. Critical programs that protect child health and well-being should never be disrupted by a government shutdown.
Finally, Americans deserve government accountability. Policymakers should be held responsible for their words and actions, especially when they fail to deliver on the promises they make about protecting children.
Children cannot wait. They are growing, learning and developing right now. The choices we make as a country today will shape their tomorrow.
Did you use this article in your work?
We’d love to hear how The 74’s reporting is helping educators, researchers, and policymakers. Tell us how

This blog was kindly authored by Richard Markham, Chief Executive Officer of the IB Schools and Colleges Association (IBSCA).
At International Baccalaureate (IB) schools and colleges, we have always been ambitious for our students. We know what they can achieve and support them to reach their goals. Through its broad curriculum – including Maths, English, a humanities, science, arts and language subject – the IB Diploma Programme (DP) provides stretch and challenge, developing a thirst for lifelong learning in our 16 to 19-year-olds. And, through extended essays, theory of knowledge and service in the community, it produces confident, well-rounded citizens who thrive in life and work. Year after year, we join our students and their families in celebrating their outstanding destinations at top universities and apprenticeships.
That is why it is deeply disappointing that the Government is axing the financial uplift for schools and colleges delivering the IB DP in the state sector, as soon as the next academic year.
Disappointing, but also surprising. By axing the large programme uplift – the top-up funding awarded to schools and colleges to reflect the additional teaching time required to deliver the IB DP – the Government risks tripping over its own hurdles. The post-16 white paper sets “objectives” for the 16-19 sector, with the first being that it “delivers world-leading provision that breaks down the barriers to opportunity”. The imminent final report of the Curriculum and Assessment Review will set out its recommendations to ensure that “every child” has “access to a broad range of subjects”.
On this front, it is vital that we keep the IB alive in the state sector. Far more extensive than A Levels, T Levels and now V Levels, the IB proves that creativity is not the preserve of the arts, nor logic the preserve of science. Both belong together in world-class education. It is a rigorous, aspirational study programme, offering all the advantages of a private school education, accessible to families who couldn’t dream of affording tuition. We should be expanding opportunities to an IB education, not shutting them down.
The second objective set for further education is that it supports the Government’s “ambition for two-thirds of young people to participate in higher-level learning” after they leave school. IB DP students in the UK are three times more likely to enrol in a top-20 higher education institution. Deep thinkers, broad skill sets – they excel at university-level study. DP students are 40% more likely to achieve a first-class or upper second-class honours degree. If the Government does not find a way through, the higher education sector will be poorer for it.
Moreover, UCAS data from the 2021/24 cycles gives us an indication of just how well the IB DP supports progression into courses that closely align with the UK’s Industrial Strategy priority sectors. The greatest proportion of DP students (4,900) accepted university offers in courses related to the life sciences sector, driven by medicine, dentistry and nursing. This was closely followed by professional and business services – with 3,365accepted offers for subjects like economics, law, management and politics – and upwards of 1,000 accepted offers in crucial science and engineering courses.
Evidently, this is a financial decision, not one taken in the best interests of our education and skills system. To dress it up in any other way does our educators a disservice. The large programme uplift given to IB DP schools is worth just £2.5 million a year. That is 0.0025 per cent of the Department for Education’s £100 billion annual budget. A drop in the ocean, and yet the programme delivers true value for money.
On Wednesday, MPs across the House united to fight for the future of the IB in Westminster Hall, calling for an urgent reversal of these cuts to provide certainty for school and college leaders, current and prospective IB students and their families, universities and employers. MPs questioned the very basis for the Department’s decision: “how can the Government can claim to want more students, particularly more girls, on STEM pathways while cutting funding for a qualification that demonstrably helps to achieve exactly that?”
Let us not forget, it was a Labour Government under Prime Minister Tony Blair that pledged an IB school in every local authority, but subsequent Prime Ministers have recognised the value and championed a baccalaureate-style education system. Support for the IB cuts across party lines and nation’s borders – reflecting the shared values of its global community of alumni, prospective students, parents, teachers, and policymakers who see its potential to raise ambition and foster international understanding. That cross-party appeal is no accident: many MPs, former IB teachers and alumni, know first-hand what the programme can do. They recognise its power to develop deeper thinkers, broader skill sets and more adaptable young people – qualities our economy and universities urgently need right now.
Find out more about the ‘Save the IB’ via the IBSCA website: www.ibsca.org.uk/save-the-ib-with-ibsca

A smaller percentage of Americans are drinking alcohol than ever before. For non-drinkers, Lilia Luciano reports, businesses and organizations are ready to serve alternatives.
Source link

One month ago, Republicans chose to shut down the government rather than protect our healthcare. Now, by refusing to process SNAP benefits for November, they’ve put 42 million working families at risk of going hungry or being forced deeper into debt just to put food on the table.
Most of us aren’t in debt because we live beyond our means — we’re in debt because we’ve been denied the means to live. This is especially true for SNAP recipients, most of whom are workers being paid starvation wages by greedy employers, or tenants being squeezed every month by predatory landlords. SNAP is a lifeline for people trapped in an economic system that’s designed to work against us, which is exactly why they’re trying to destroy it.
Authoritarianism thrives on silence and complicity. We refuse to give in. This weekend, organizers across the country are mobilizing a mass effort to connect people with existing mutual aid networks. If you are on SNAP and are not sure where to look for help, get plugged into your local mutual aid network to get your needs met and organize to help others meet theirs.