The Union of Jewish Students (UJS) has published a fascinating new episode of “Yalla”, its podcast for Jewish students.
Hosted by Louis Danka, who is the new President of UJS, the September 2025 episode features an extensive interview with Arif Ahmed, OfS’ Director for Freedom of Speech and Academic Freedom.
The conversation comes weeks after the regulator’s new higher education free speech guidance came into force on August 1, 2025, alongside enhanced harassment protections.
What makes the interview especially interesting is what it doesn’t mention – Ahmed’s reversal on the IHRA definition of antisemitism.
In February 2021, Ahmed wrote in a HEPI blog that he was strongly against Gavin Williamson’s requirement that universities adopt the IHRA definition of anti-Semitism, arguing it obstructs perfectly legitimate defence of Palestinian rights and chills free speech:
I hope the Secretary of State reconsiders the need for it; but these new free speech duties ought to rule it out in any case.
We’re all allowed to change our minds on things. The issue is the extent to which the law, or the regulation he’s now in charge of, offers clarity on the volte-face.
And while there’s plenty of helpful material in there on how OfS might approach casework and complaints, it does raise all sorts of questions about expectations – and OfS’ strategy for communicating what in some cases amounts to significant additions and clarifications to its guidance.
What the podcast says
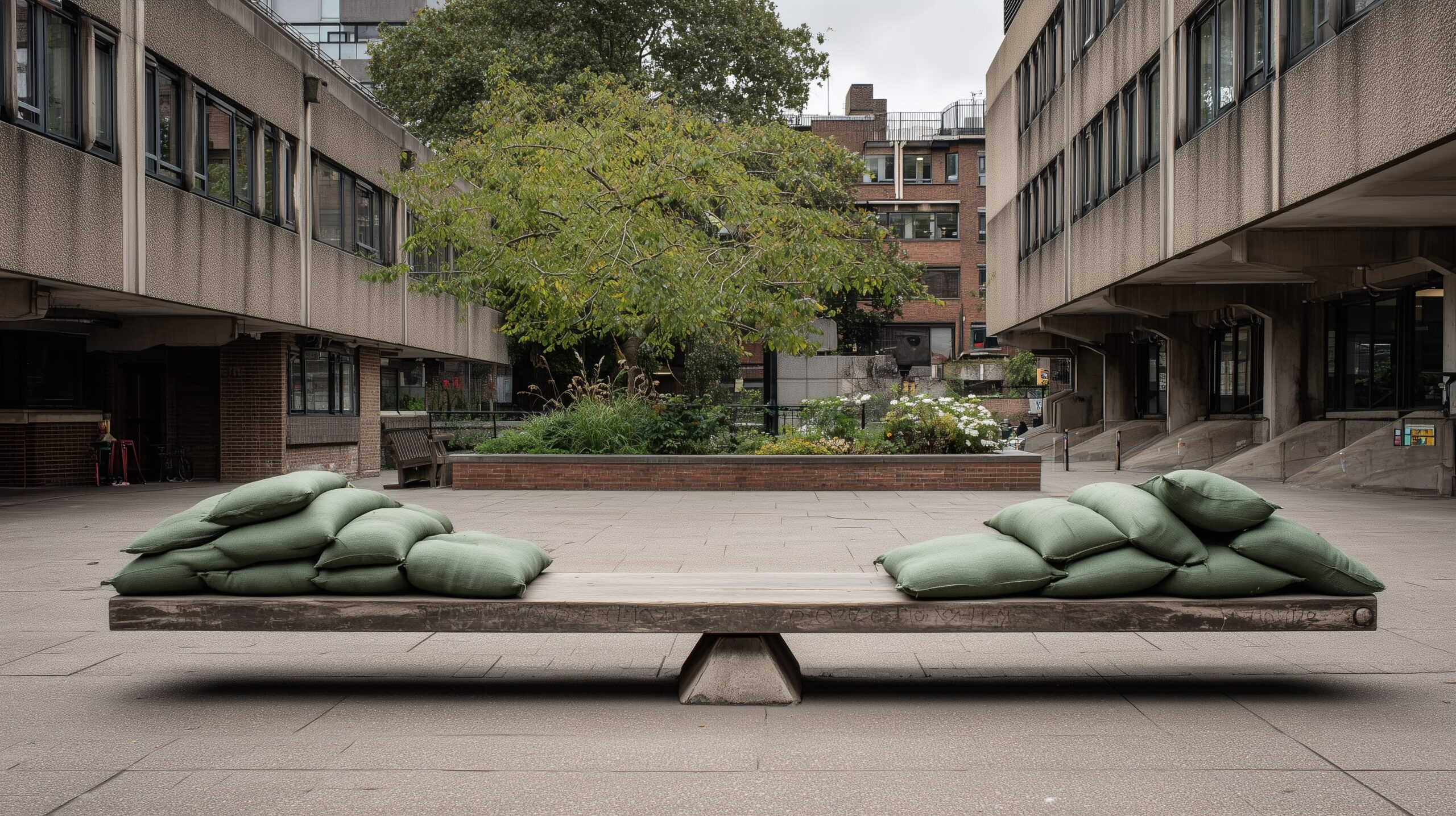
The interview centres on what I’ve previously described as the twin sandbags on the regulatory see-saw – the Higher Education (Freedom of Speech) Act 2023 and the E6 condition on harassment and sexual misconduct.
A central theme throughout is UJS’ contention of a deteriorating campus environment for Jewish students. Ahmed acknowledges there has been “a big rise in antisemitic incidents in recent years, on campus, in the country more generally” and describes this as a source of “grave concern” for OfS.
The discussion then considers how this manifests practically on campuses. Ahmed describes, for example, scenarios where Jewish students may feel unable to attend lectures due to protest activity, or where “protests outside Jewish accommodation” create hostile environments.
He first emphasises that while “political ideas expressed in the protests may be perfectly awful and expressible,” universities can still regulate their “time, place and manner” – such that core functions can keep going.
Hence on protest regulation, Ahmed says:
…if you have protests that take place in such a way that Jewish students don’t feel able to attend lectures … it may also be right for the university say, well, you can’t do it here, and you can’t do it in this place, and you can’t have it every day outside a lecture theatre.
He also points to protests outside Jewish accommodation as another context where restrictions could be justified.
Ahmed’s contemporary position on IHRA is explained as follows:
…we ourselves have adopted the IHRA definition, and we do think it can be a very useful tool for understanding modern antisemitism.
He adds that there is “no obstacle, in principle” for universities adopting a particular definition, and “certainly not” the IHRA working definition.
He clarifies that it is “absolutely compatible” with the guidance, provided it’s being used properly as a way to understand antisemitism rather than to suppress lawful and legitimate debate. That latter caveat may represent the only vestige of his previous concerns about IHRA chilling Palestinian rights advocacy.
The published guidance takes an uncompromising stance on Holocaust denial, where Ahmed explains this was made explicit after consultation feedback seeking clarity:
…we will not under any circumstances protect Holocaust denial, so nothing that we do in our complaint scheme or otherwise will protect that speech.
With the more obvious stuff out of the way, the subsequent nuanced discussion involves distinguishing between legitimate political discourse and antisemitic harassment, particularly around coded language.
Ahmed addresses scenarios like “Zionists off our campus” signs, explaining that context is crucial. On coded antisemitism, Ahmed explains:
…very often when people use the expression “Zionist”, for instance, it can actually be used as a kind of euphemistic expression meaning Jewish people, and in the circumstances where that’s so it seems very much more likely to be something that’s targeted at individuals because of their race, because of their religion.
He then distinguishes between attacking ideas versus targeting individuals, noting that speech “directed at ideas” differs from speech that makes individuals feel excluded because of their protected characteristic.
Ahmed is at pains to point out that freedom of speech encompasses religious expression, making Jewish students’ ability to practice their faith a free speech issue. He also describes scenarios where Jewish students might hide religious symbols like Stars of David due to campus hostility. He then explains the religious expression dimension:
…if you have an atmosphere on campus which is allowed to grow, which grew, Jewish students are intimidated out of expressing their own religion, that’s that’s an affront to their freedom of speech.
The interview also explores “chilling effects” – where students self-censor rather than face consequences. Ahmed describes situations where students with pro-Israel views or Jewish religious expression might “decide not to say it in the first place” due to fears about academic consequences or social ostracism.
Nevertheless, he repeatedly stresses that harassment determinations require objective analysis, not just subjective feelings. He explains that the legal test involves whether:
…a reasonable person would think that was… creating an intimidating atmosphere for people because of their race, because of their religion.
And on that point:
…it’s not enough, for speech to count as harassment, that the person at the receiving end feels offended; what’s important is that a reasonable person would think that was so.
He concludes by stressing that freedom of speech “historically… most protects minorities and those… for whom their voice and their words are the only things that they have.”
What the papers say
The Jewish News coverage of Ahmed’s podcast exemplifies how the reassuring rhetoric translates into heightened community expectations.
The headline itself – “Free speech tsar tells universities: stop intimidation of Jewish students” – frames Ahmed’s nuanced legal discussion as a clear directive for immediate action.
The article’s language amplifies Ahmed’s confidence, presenting his tentative statements (“it may also be right for the university to say”) as firm commitments (“universities must take firm steps”) and his regulatory expectations (“we would expect universities to take action”) as binding obligations.
The coverage also amps up specific protections – Jewish students’ ability to attend lectures, enter accommodation, and express their religion – without conveying the complex legal determinations universities might need to navigate to provide that protection.
Ahmed’s discussion of “coded language” becomes a promise that universities can identify and restrict antisemitic euphemisms, while his IHRA compatibility statements are presented as resolving rather than acknowledging ongoing tensions between free speech and antisemitism prevention.
Most tellingly, UJS President Louis Danker’s response reveals both the raised expectations and their fragility. While expressing satisfaction that “the Office for Students shares our concerns,” he acknowledges that “the ambiguity of the guidance will be challenged by crucial test cases in the coming months.”
This tension, between reassurance about shared concerns and worry about guidance ambiguity, captures the potential problem that OfS has created – confident promises built on uncertain legal foundations that will inevitably face testing in precisely the complex scenarios that the framework struggles to address.
What the podcast doesn’t say
The central question is whether the reassuring statements to Jewish students align with what universities can actually deliver under existing legal frameworks.
If we take holocaust denial, for example, Ahmed demonstrates clear understanding:
Article 17 says that none of these rights can be used, essentially to destroy other people’s rights. So speech that aims to destroy others rights… the courts have found, for instance, that many instances of Holocaust denial they’ve looked at, fall under it.
That explanation appears to be legally accurate. Article 17 is sometimes called the “abuse clause” of the European Convention – it strips protection from speech that aims to destroy the rights of others, such as Holocaust denial.
But the guidance leaves the explanation out, simply declaring Holocaust denial unprotected without explaining why – or when. That omission matters, because Article 17 normally operates alongside Article 10(2) – another part of the Convention that allows restrictions on speech if they are necessary and proportionate to protect others.
As a reminder, the OfS guidance’s three-step framework treats human rights considerations as sequential rather than integrated:
Step 1 asks simply whether speech is “within the law” – defined as speech not prohibited by primary legislation, legal precedent, or secondary legislation. Crucially, university regulations and contracts don’t count as “law” here. If not, don’t allow it. If it is, move to Step 2.
Step 2 considers whether there are “reasonably practicable steps” to enable the speech. Universities should consider factors like legal requirements (including any formal duties), maintaining essential functions, and physical safety – but explicitly cannot consider the viewpoint expressed, whether it’s controversial, or reputational impact. If steps can be taken, take them. If not, move to Step 3.
Step 3 – which is only reached if no reasonably practicable steps exist – then asks whether any restrictions are “prescribed by law” and proportionate under the European Convention. This involves checking if there’s a specific legal rule authorising the restriction, and runs through a four-part proportionality test weighing the importance of the objective against the severity of limiting the right.
That proportionality test looks something like this:
- Is the objective important enough? – The reason for restricting speech must be sufficiently weighty to justify limiting a fundamental right.
- Is the restriction rationally connected? – The measure must actually help achieve the objective, not just be vaguely related to it.
- Is this the least restrictive option? – Could you achieve the same goal with less impact on free speech? If yes, you must use the less intrusive approach.
- Does the benefit outweigh the harm? – Even if the first three tests are met, you must still balance the severity of restricting speech against how much the restriction actually helps achieve your objective. The restriction fails if the damage to free expression outweighs the benefit gained.
As I’ve noted before on here, the published approach seems to conflict with Minasyan v Armenia (2019), where the European Court of Human Rights struck down Armenia’s handling of a protest case. The Armenian courts had first checked whether protesters broke domestic criminal law, and only afterwards asked whether their free speech rights were engaged.
Strasbourg was clear – you can’t separate those steps. The balancing of rights under Article 10(2) has to be done at the outset. So when the guidance asks universities to check domestic criminal law first and only consider broader human rights implications as an afterthought, the sequential framework seems to repeat the flaw that Strasbourg condemned.
Meanwhile, Ahmed seems to correctly state the objective harassment test:
…it’s not enough. Speech to count as harassment, that the person at the receiving end feels offended… what’s important is that a reasonable person would think that was so.
But his practical applications consistently reference subjective experiences without clear frameworks for objective assessment. He discusses Jewish students feeling “unable to attend lectures” or “intimidated out of expressing their own religion” – but then offers up little on how universities should distinguish between justified concerns and unfounded complaints.
The “reasonable person” test sounds simple, but in practice it is one of the hardest questions courts face. Would an average observer see this as harassment, taking into account context, repetition, and effect?
Judges often split over the answer, even with days of evidence. Expecting university or SU staff to make that call in real time, during a protest or at a room-booking stage, is asking staff to perform complex human rights analyses on the fly. Clarity on what he might expect is reasonable in those scenarios would help.
Ahmed’s discussion of antisemitic language also illustrates the analytical burden placed on those enforcing or explaining rules day to day:
…very often when people use the expression Zionist, for instance, they can actually, can actually be used as a kind of euphemistic expression meaning Jewish people.
Determining when “Zionist” functions as coded antisemitism requires careful analysis of speaker intent, contextual factors, and impact on targeted individuals. These are determinations that typically require evidence about speaker’s background and previous statements, analysis of the specific context and setting, an assessment of audience understanding and reaction, and an evaluation of the targeting effects on specific individuals.
Day to day, staff may well lack both the investigative capacity and legal expertise to perform those sorts of analyses reliably. Ahmed acknowledges the complexity – “it might depend on context” – but doesn’t offer anything like a practical methodology for making the determinations.
The UK Supreme Court in Elan-Cane (2021) stressed that domestic bodies should not push human rights analysis beyond what the European Court of Human Rights has already recognised. Lord Reed warned against overstepping into areas Strasbourg had not yet endorsed.
Ahmed’s framework arguably asks universities to do exactly that – making human rights calls (on protests, coded language, or harassment) that even the courts approach with extreme caution.
If legally trained judges with full procedural protections must be cautious about extending human rights analysis, how can staff be expected to perform similar determinations through internal processes? Is OfS fit to do so when it gets a complaint in? And what are the penalties for getting it wrong?
Rights collision
Another silence in the interview is how to handle the collision of rights. He clearly anchors harassment to protected characteristics like race and religion, and he treats Zionism as an idea that can be lawfully discussed – while warning it is sometimes used as a euphemism for “Jew” in context. He doesn’t quite say “Zionism is a protected belief” in terms, though that would be the likely legal position under Equality Act case law. The same goes for anti-Zionism.
Under UK equality law, political and philosophical beliefs qualify for protection if they meet what’s known as the Grainger criteria – that is, the belief must be genuinely held, relate to a weighty aspect of human life, attain a certain level of seriousness and cogency, and be worthy of respect in a democratic society.
Courts have already recognised beliefs such as environmentalism, gender-critical feminism, and ethical veganism under this test. Anti-Zionism looks like it would qualify on the same basis, provided it is expressed as a coherent political or philosophical position rather than as a proxy for antisemitism.
What he does not explain is what universities should do when the protections appear to come into direct conflict or quite how a university is supposed to differentiate between the political or philosophical position and the proxy.
Let’s imagine a student holding a placard reading “Zionism is racism” and another responding that “anti-Zionism is antisemitism.” Both statements can amount to the expression of protected beliefs under the Equality Act. Both students might also claim they are being harassed by the other.
Courts take weeks to sift through context, intent, and impact in such cases – weighing not just Article 10 free speech but also Article 9 (religion), Article 8 (private life) and Article 11 (assembly).
On balance, “Zionists off campus” feels like it targets a group of people. Those banned from painting it on a banner may feel their speech is being chilled. “Zionism off campus” feels more like a protected piece of political expression. Some reading that may feel harassed. Complaints in either event are likely.
Recent cases show how fraught these clashes can be. In Forstater v CGD Europe, the tribunal upheld that gender-critical beliefs were protected, even though many found them offensive – but also emphasised that protection for a belief does not mean protection for every manifestation of it.
In Mackereth v DWP, the tribunal held that a doctor’s refusal to use trans patients’ pronouns could lawfully be limited, despite his Christian beliefs being protected. The principle is clear – both Zionism and anti-Zionism can be protected, but the way they are expressed may still lawfully be restricted if it harasses others.
What’s missing from Ahmed’s account is the extent to which universities are expected to perform that fine distinction in real time, and at which stage of a process they’re expected to do so.
What now?
The danger in all of this is a form of regulatory false advertising – promising protection through frameworks that universities cannot properly execute without risking legal challenge or practical failure.
The focus on context is welcome, but it doesn’t solve the core problem – the absence of a practical framework for when and how to balance competing rights. Without it, institutions risk inconsistency, overreach, or paralysis – either censoring lawful political expression or failing to protect students from harassment.
The reassuring tone also suggests clearer legal boundaries than actually exist. When he says that universities “would expect to take action” about intimidatory speech, he presents complex, fact-specific determinations as straightforward administrative decisions.
It’s a false certainty that may mislead universities into thinking they have clear authority to restrict speech, and could simultaneously raise student expectations about protection that may prove impossible to deliver.
Then the style compounds the problem. In the podcast and coverage of it, Jewish students hear confident reassurances; in the consultation response annex, Article 17 is quietly acknowledged; in public guidance, proportionality is all but absent from the “within the law” test.
The impression is of a regulator telling each audience what it wants to hear by pointing at one end of the see-saw, rather than grappling with the hard edges of the case law in ways that may temper expectations rather than raise them.
And given both the free speech guidance and the E6 guidance drives home the need to get these messages into the heads of students themselves, there’s certainly nothing in there on how universities are supposed to explain all of this to students.
It leaves universities (and by proxy their SUs) stuck in the impossible position that they have been for months.
They remain caught between those heavy sandbags without mechanisms to resolve them, having expectations raised on both ends in ways that may not be as simple in practice, and offering little confidence that a good stab at making the calls, carried out in good faith, will result in anything other than Kafka’s regulator appearing with a fine either way.