by Jill Barshay, The Hechinger Report
October 27, 2025
Timothy Shanahan, a professor emeritus at the University of Illinois at Chicago, has spent his career evaluating education research and helping teachers figure out what works best in the classroom. A leader of the National Reading Panel, whose 2000 report helped shape what’s now known as the “science of reading,” Shanahan has long influenced literacy instruction in the United States. He also served on the National Institute for Literacy’s advisory board in both the George W. Bush and Barack Obama administrations.
Shanahan is a scholar whom I regularly consult when I come across a reading study, and so I was eager to interview him about his new book, “Leveled Reading, Leveled Lives.” (Harvard Education Press, September 2025). In it, Shanahan takes aim at one of the most common teaching practices in American classrooms: matching students with “just-right” books.
He argues that the approach — where students read different texts depending on their assessed reading level — is holding many children back. Teachers spend too much time testing students and assigning leveled books, he says, instead of helping all students learn how to understand challenging texts.
“American children are being prevented from doing better in reading by a longstanding commitment to a pedagogical theory that insists students are best taught with books they can already read,” Shanahan writes in his book. “Reading is so often taught in small groups — not so teachers can guide efforts to negotiate difficult books, but to ensure the books are easy enough that not much guidance is needed.”
Comprehension, he says, doesn’t grow that way.
The trouble with leveled reading
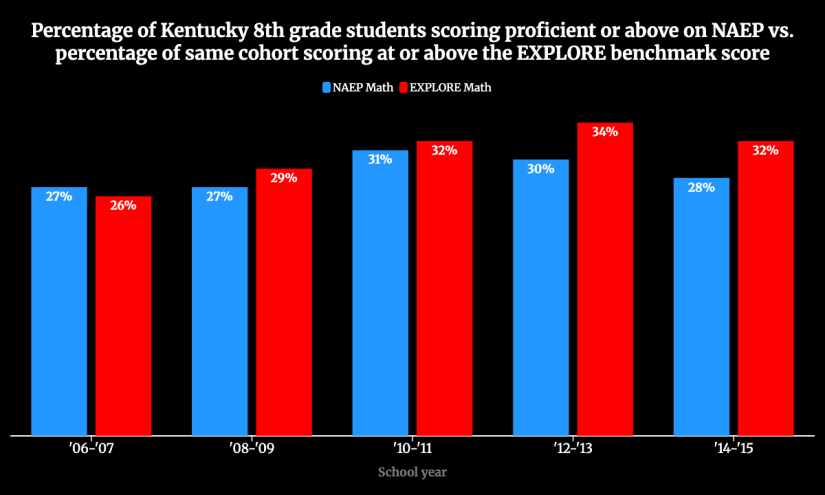
Grouping students by ability and assigning easier or harder books — a practice known as leveled reading — remains deeply embedded in U.S. schools. A 2018 Thomas B. Fordham Institute survey found that 62 percent of upper elementary teachers and more than half of middle school teachers teach at students’ reading level rather than at grade level.
That may sound sensible, but Shanahan says it’s not helping anyone and is even leading teachers to dispense with reading altogether. “In social studies and science, and these days, even in English classes,” he said in an interview, “teachers either don’t assign any readings or they read the texts to the students.” Struggling readers aren’t being given the chance — or the tools — to tackle complex material on their own.
Instead, Shanahan believes all students should read grade-level texts together, with teachers providing more support for those who need it.
Related: Our free weekly newsletter alerts you to what research says about schools and classrooms.
“What I’m recommending is instructional differentiation,” he said in our interview. “Everyone will have the same instructional goal — we’re all going to learn to read the fourth-grade text. I might teach a whole-class lesson and then let some kids move on to independent work while others get more help. Maybe the ones who didn’t get it, read the text again with my support. By the end, more students will have reached the learning goal — and tomorrow the whole class can take on another text.”
27 different ways
Shanahan’s approach doesn’t mean throwing kids into the deep end without help. His book outlines a toolbox of strategies for tackling difficult texts, such as looking up unfamiliar vocabulary, rereading confusing passages, or breaking down long sentences. “You can tip over into successful reading 27 different ways,” he said, and he hopes future researchers discover many more.
He is skeptical of drilling students on skills like identifying the main idea or making inferences. “We’ve treated test questions as the skill,” he said. “That doesn’t work.”
There is widespread frustration over the deterioration of American reading achievement, especially among middle schoolers. (Thirty-nine percent of eighth graders cannot reach the lowest of three achievement levels, called “basic,” on the National Assessment of Educational Progress.) But there is little agreement among reading advocates on how to fix the problem. Some argue that what children primarily need is more knowledge to grasp unfamiliar ideas in a new reading passage, but Shanahan argues that background knowledge won’t be sufficient or as powerful as explicit comprehension instruction. Other reading experts agree. Nonie Lesaux, dean of the Harvard Graduate School of Education who specializes in literacy in her own academic work, endorsed Shanahan’s argument in an October 2025 online discussion of the new book.
Shanahan is most persuasive in pointing out that there isn’t strong experimental evidence to show that reading achievement goes up more when students read a text at their individual level. By contrast, a 2024 analysis found that the most effective schools are those that keep instruction at grade level. Still, Shanahan acknowledges that more research is needed to pinpoint which comprehension strategies work best for which students and in which circumstances.
Misunderstanding Vygotsky
Teachers often cite the Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky’s “zone of proximal development” to justify giving students books that are neither too easy nor too hard. But Shanahan says that’s a misunderstanding of Vygotsky’s work.
Vygotsky believed teachers should guide students to learn challenging things they cannot yet do on their own, he said.
He offers an analogy: a mother teaching her child to tie their shoes. At first, she demonstrates while narrating the steps aloud. Then the child does one step, and she finishes the rest. Over time, the mother gradually releases control and the child ties a bow on his own. “Leveled reading,” Shanahan said, “is like saying, ‘Why don’t we just get Velcro?’ This is about real teaching. ‘Boys and girls, you don’t know how to ride this bike yet, but I’m going to make sure you do by the time we’re done.’ ”
Related: What happens to reading comprehension when students focus on the main idea
Shanahan’s critique of reading instruction applies mainly from second grade onward, after children learn how to read and are focusing on understanding what they read. In kindergarten and first grade, when children are still learning phonics and how to decode the words on the page, the research evidence against small group instruction with different level texts isn’t as strong, he said.
Learning to read first – decoding – is important. Shanahan says there are rare exceptions to teaching all children at grade level.
“If a fifth grader still can’t read,” Shanahan said, “I wouldn’t make that child read a fifth-grade text.” That child might need separate instruction from a reading specialist.
Advanced readers, meanwhile, can be challenged in other ways, Shanahan suggests, through independent reading time, skipping ahead to higher-grade reading classes, or by exploring complex ideas within grade-level texts.
The role of AI — and parents
Artificial intelligence is increasingly being used to rewrite texts for different difficulty levels. Shanahan is skeptical of that approach. Simpler texts, whether written by humans or generated by AI, don’t teach students to improve their reading ability, he argues.
Still, he’s intrigued by the idea of using AI to help students “climb the stairs” by instantly modifying a single text to a range of reading levels, say, to third-, fifth- and seventh-grade levels, and having students read them in quick succession. Whether that boosts comprehension is still unknown and needs to be studied.
AI might be most helpful to teachers, Shanahan suspects, to help point to a sentence or a passage that tends to confuse students or trip them up. The teacher can then address those common difficulties in class.
Shanahan worries about what happens outside of school: Kids aren’t reading much at all.
He urges parents to let children read whatever they enjoy — regardless if it’s above or below their level — but to set consistent expectations. “Nagging may not be effective,” he said. “But you can be specific: ‘After dinner Thursday, read the first chapter. When you’re done, we’ll talk about it, and then you can play a computer game or go on your phone.’ ”
Too often, he says, parents back down when kids resist. “They are the kids. We are the adults,” Shanahan said. “We’re responsible. Let’s step up and do what’s right for them.”
Contact staff writer Jill Barshay at 212-678-3595, jillbarshay.35 on Signal, or [email protected].
This story about reading levels was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for Proof Points and other Hechinger newsletters.
This <a target=”_blank” href=”https://hechingerreport.org/proof-points-shanahan-leveled-reading/”>article</a> first appeared on <a target=”_blank” href=”https://hechingerreport.org”>The Hechinger Report</a> and is republished here under a <a target=”_blank” href=”https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/”>Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License</a>.<img src=”https://i0.wp.com/hechingerreport.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/cropped-favicon.jpg?fit=150%2C150&ssl=1″ style=”width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;”>
<img id=”republication-tracker-tool-source” src=”https://hechingerreport.org/?republication-pixel=true&post=113055&ga4=G-03KPHXDF3H” style=”width:1px;height:1px;”><script> PARSELY = { autotrack: false, onload: function() { PARSELY.beacon.trackPageView({ url: “https://hechingerreport.org/proof-points-shanahan-leveled-reading/”, urlref: window.location.href }); } } </script> <script id=”parsely-cfg” src=”//cdn.parsely.com/keys/hechingerreport.org/p.js”></script>