Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
Nearly 9,000 children across 16 states and Puerto Rico remained locked out of Head Start programming as of Friday evening, according to the National Head Start Association, despite the federal government’s reopening on Wednesday night.
For some programs, the promise of incoming funding will be enough to restart operations. But many won’t be able to open their doors until they receive their federal dollars, which could take up to two weeks, said Tommy Sheridan, deputy director at the NHSA.
Sheridan said the Trump administration understands the urgency and is “moving as fast as they possibly can.”
That said, this interruption had an opportunity cost, and it’s led to instability for families and providers, he said, adding that the shutdown caused staff to focus on issues they “should not be worried about,” such as fundraising and contingency planning.
Some providers fear greater delays since the Trump administration shuttered half of the Head Start regional offices earlier this year.
“They’re going to be working as hard as they can, but they’re going to be doing it with half the capacity,” said Katie Hamm, former deputy assistant secretary for early childhood development under President Joe Biden.
And even once the funding comes through, closed centers will need to go through a series of logistical hurdles, including reaching out to families who may have found alternative child care arrangements and calling back furloughed staff, some of whom have found employment elsewhere.
“Head Start is not a light switch,” Hamm said. “You can’t just turn it back on.”
This interruption has also further eroded trust between grantees and the federal government that was already shaky, she added.
The Administration for Children and Families did not respond to a request for comment on when programs can anticipate communication from the office or their funding.
Since Nov. 1, approximately 65,000 kids and their families — close to 10% of all of those served by Head Start — have been at risk of losing their seats because their programs had not received their awarded funding during the longest government shutdown in history. The early care and education program delivers a range of resources to low-income families including medical screenings, parenting courses and connections to community resources for job, food and housing assistance.
At the peak of the Head Start closures, roughly 10,000 kids across 22 programs lost access to services, according to Sheridan. A number of the remaining programs were able to stay open through private donations, loans, alternative funding streams and staff’s willingness to go without pay.
Valerie Williams, who runs a Head Start program with two facilities in Appalachian Ohio, was excited to tell parents that classrooms would be reopening soon. Her centers have been closed since Nov. 3, impacting 177 kids and 45 staff, many of whom already live paycheck to paycheck, she said.
A number of families were doubly impacted, losing access to Head Start’s resources as well as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, also known as SNAP, simultaneously. In the days leading up to the closure, Williams and her staff prepared families as best they could, sharing information about resources for food, assistance for utilities and heating and guidance on child care options.
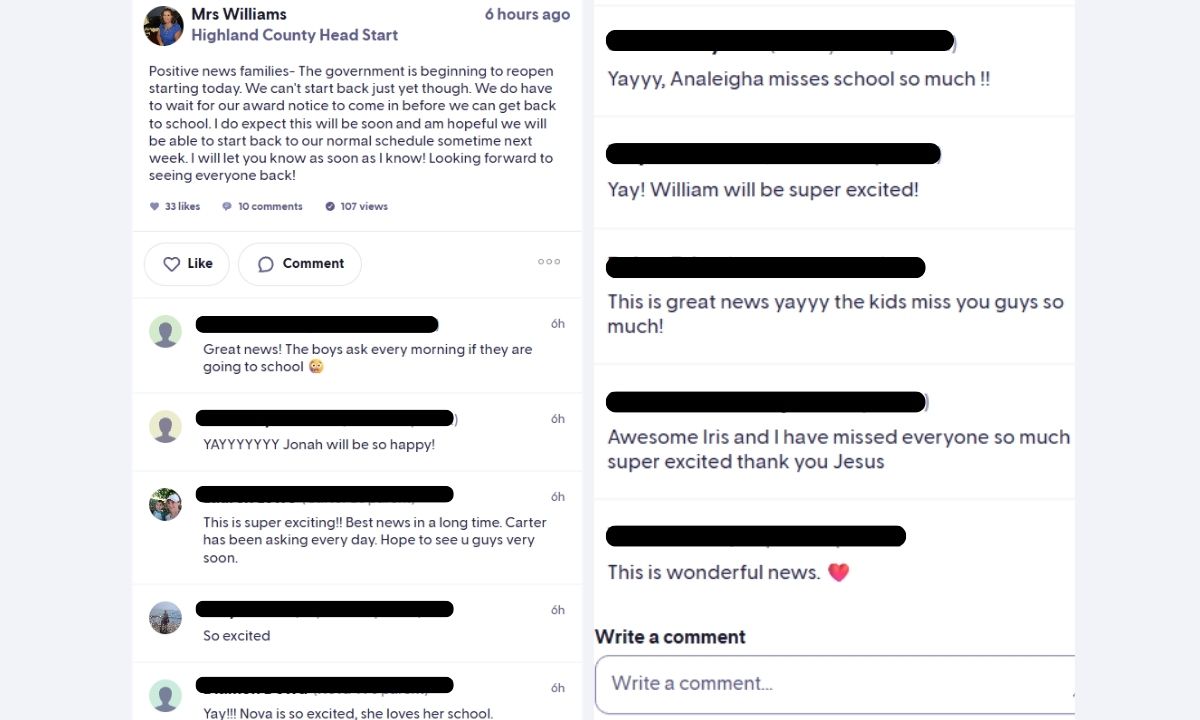
On Thursday, Williams wrote to parents via an online portal that she hopes to restart the normal school schedule sometime next week. The post was quickly flooded with comments.
“This is super exciting!!” wrote one parent. “Best news in a long time. Carter has been asking every day. Hope to see u guys very soon.”
“Yayyy,” wrote another. “The kids miss you guys so much!”
Still, Williams knows reopening won’t be seamless. Along with program leaders across the country, she’ll need to call back furloughed staff, place food orders and handle a number of other operational challenges.
And despite the excitement, the transition back may also prove tricky for some kids.
“I do think that it will feel like starting school again for a lot of our classrooms,” Williams said. “They’ve been out for two weeks … You’re going to work on separation anxiety issues, you’re going to have to get into that routine again and the structure of a classroom environment. So I think that will be a big issue for a lot of our teachers.”
As of Friday afternoon, Williams was still awaiting communication from the federal Office of Head Start with information about the anticipated timeline for next steps.
“As soon as we get that notice of award, [I want to] start our staff and kids back immediately,” she said. “The very next day.”
Now that the shutdown has ended, what’s next for Head Start?
Funding for Head Start is complex. Some 80% comes from federal grants that are released to local providers on a staggered schedule throughout the year. This year, grant recipients with funding deadlines on the first of October and November were left scrambling, as the federal shutdown dragged on.
The government began to resume operations late Wednesday night after President Donald Trump signed a bill, funding most federal agencies through Jan. 30 and allowing programs that didn’t receive their funding on time, including Head Start, to use forthcoming dollars to backpay expenses incurred over the past month and a half.
Here’s what Hamm predicts will happen next: The Office of Head Start will recall all staff to resume, including those who were furloughed during the shutdown. The employees will review grant applications, a process which now requires them to flag any language that might be reflective of diversity, equity and inclusion practices. Next, money will be sent along to the remaining regional offices, and eventually dispersed to individual grantees. The NHSA is hopeful that this process will be completed by Thanksgiving for all grantees.
There are two things the federal government can do to help centers open faster, according to Hamm. First, they could waive a typical protocol that leads to a period of seven days between when a member of Congress is notified that their state will be receiving funding and when the funding actually goes out, Hamm explained.
Officials could also notify grantees, in writing, about how much money they’ll get and when it’s expected to come through, so they can begin planning.
Unlike SNAP, which received guaranteed funding through the budget year, money for Head Start remains uncertain beyond Jan. 30. While the fear of another shutdown has caused “quite a bit of worry” among the Head Start community, Sheridan said it would likely lead to fewer program disruptions, since it wouldn’t fall at the start of the fiscal year.

To prevent similar chaos moving forward, Democratic Sen. Tammy Baldwin of Wisconsin introduced a bill in the final days of the shutdown that would guarantee uninterrupted service for fiscal year 2026.
“The 750,000 children and their families who use Head Start shouldn’t pay the price for Washington dysfunction,” Baldwin, the ranking member of the Senate Appropriations Subcommittee for Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, and Related Agencies, wrote in a statement to The 74.
Multiple funding threats and deep staffing cuts by the Trump administration over the past year have plunged programs across the country into uncertainty. In the wake of that recent upheaval, a leadership change is also underway. The acting director of the Office of Head Start, Tala Hooban, accepted a new role within the Office of Administration for Children and Families and will be replaced by political appointee Laurie Todd-Smith, according to an email statement from ACF. Todd-Smith currently leads the Office of Early Childhood Development, which oversees the Office of Head Start.
Sheridan described this move as anticipated and not particularly concerning, though others were less sure. Joel Ryan, the executive director of the Washington State Association of Head Start, noted that Hooban was a longtime civil servant and strong supporter of the Head Start program. Without her, he fears “there’s nobody internally with any kind of power that will push back,” on future threats to the program.
Another worry plaguing providers: current funding for Head Start has remained stagnant since the end of 2024, meaning that through at least Jan. 30, programs will be operating under the same budget amid rising costs across the board.
In previous years, the program’s grant recipients typically got a cost-of-living adjustment, such as the 2.35% bump ($275 million) for fiscal year 2024. In May, a group of almost 200 members of Congress signed a letter to a House Appropriations subcommittee, requesting an adjustment of 3.2% for 2026. A recent statement from NHSA suggested that instead, the proposed Senate bill for next year includes a jump of just 0.6%, or $77 million.
“If we don’t see a funding increase in line with inflation, that means that Head Start will be facing a cut of that degree,” said Sheridan. “It’s just kind of a quiet cut, or a silent cut.”
“I think what will end up happening,” said Ryan, “is you’ll end up seeing a massive reduction in the number of kids being served.”
Did you use this article in your work?
We’d love to hear how The 74’s reporting is helping educators, researchers, and policymakers. Tell us how


