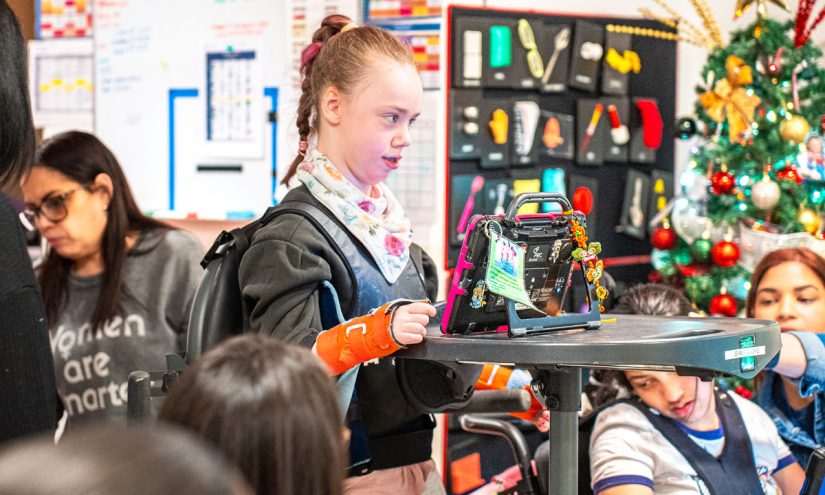
Sitting in his wheelchair at a highly specialized private school in Manhattan designed for students with severe and multiple disabilities, Joshua Omoloju, 17, uses assistive technology to activate his Spotify playlist, sharing snippets of his favorite songs in class — tracks even his parents were unaware he loved.
It’s a role this deejay is thrilled to fill at a school that encourages him to express himself any way he can. The magnetic and jovial Omoloju, a student at The International Academy of Hope, is legally blind, hearing impaired and nonverbal. But none of that stopped him from playing Peanut Butter Jelly Time by Buckwheat Boyz mid-lesson on a recent morning.
“OK, Josh!” his teachers said, swiveling their hips and smiling. “Let’s go!”
iHOPE, as it’s known, was established in Harlem in 2013 for just six children and moved to its current location blocks from Rockefeller Center in 2022. It now serves 150 students ages 5 through 21 and is currently at capacity with 27 people on its waitlist, according to its principal.
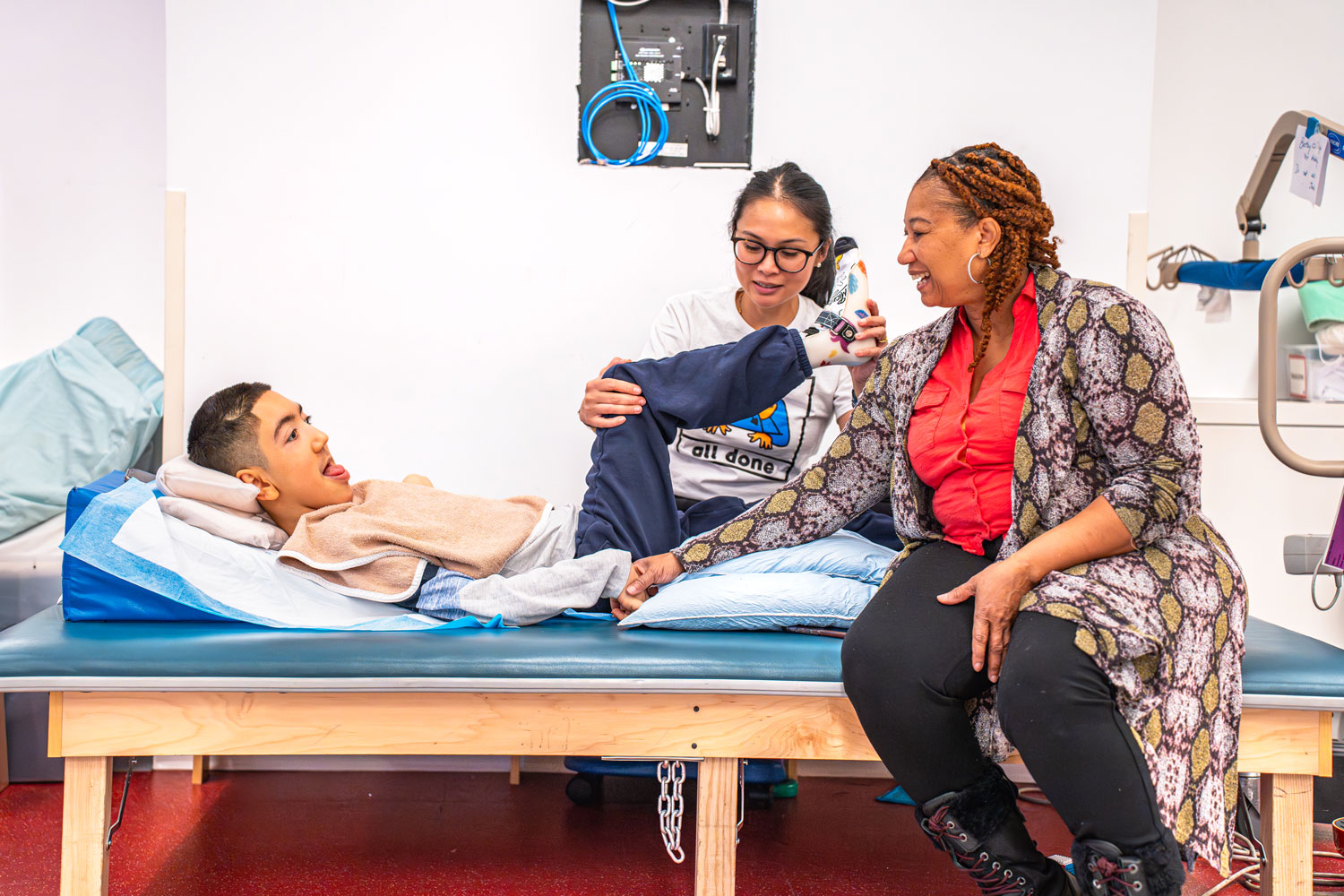
The four-story, nonprofit school offers age-appropriate academics alongside physical, occupational and speech therapy in addition to vision and hearing services. Every student at iHOPE has a full-time paraprofessional, who works with them throughout the day, and at least half participate in aquatic therapy in a heated cellar pool.
The school has three gymnasiums fitted with equipment to increase students’ mobility, helping many walk or stand, something they rarely do because of their physical limitations.
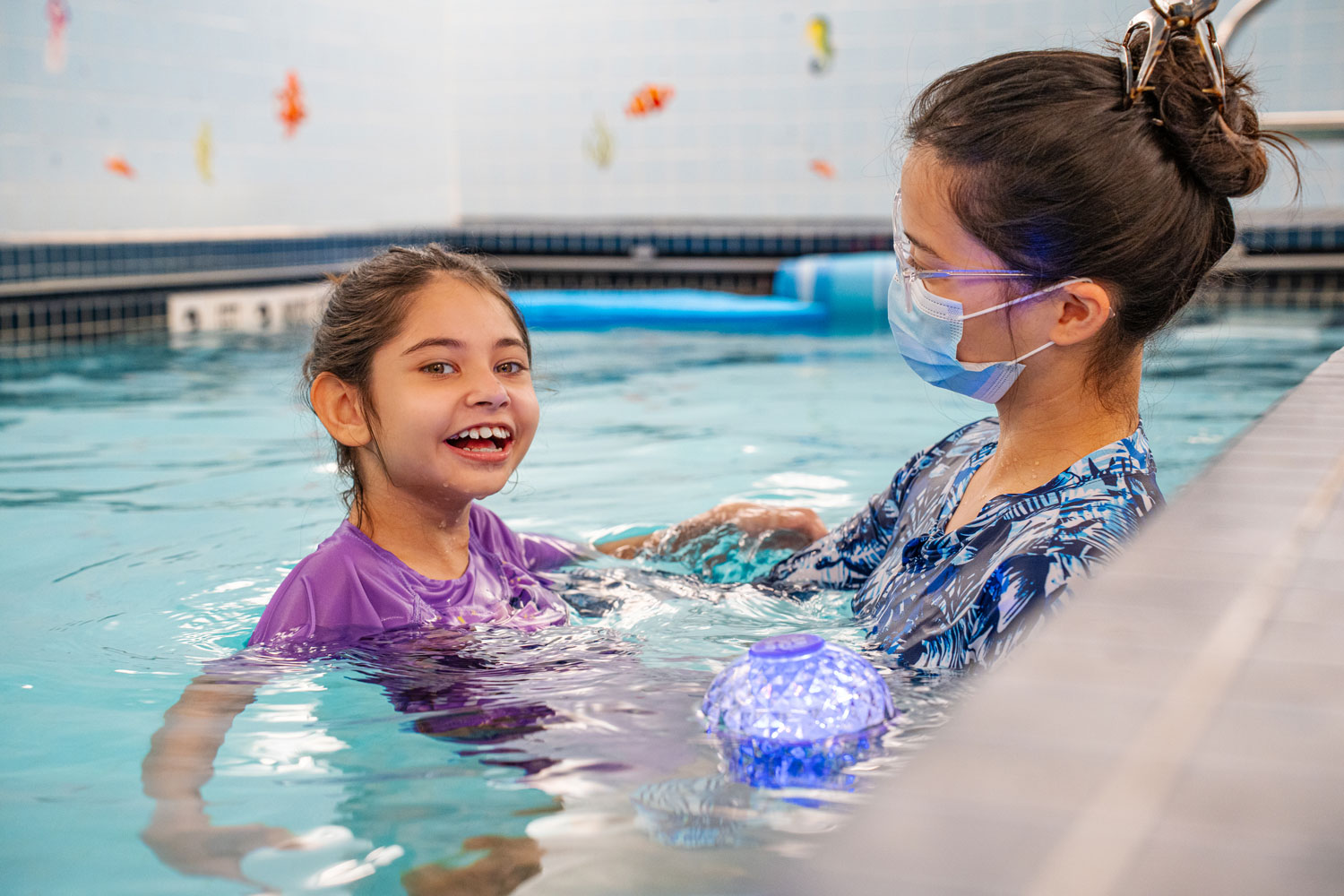
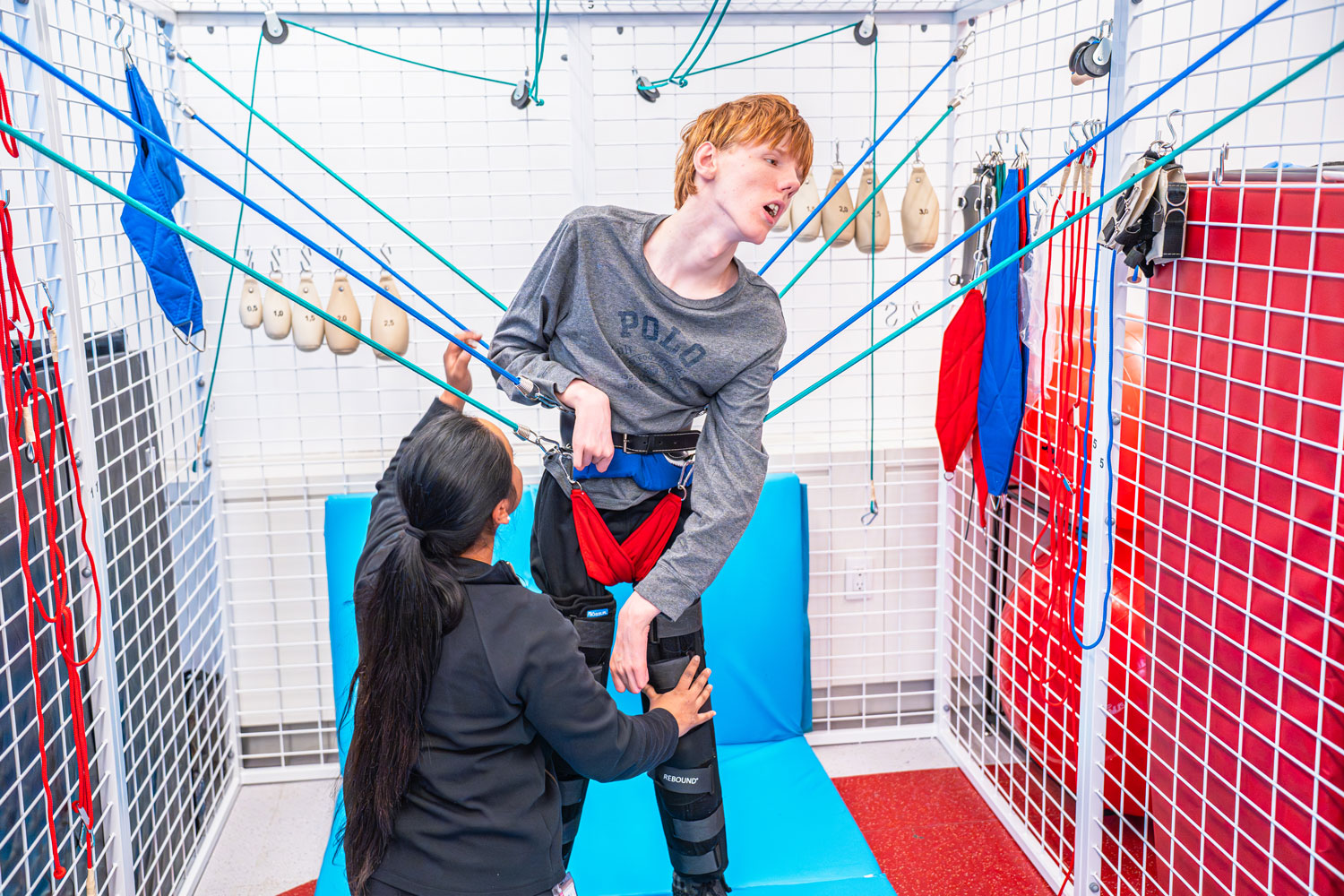


Its 300-member staff includes four full-time nurses and its six-figure cost averages $200,000 annually depending on each child’s needs. Parents can seek tuition reimbursement from the New York City Department of Education through legal processes set out by the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, arguing that the public school cannot adequately meet their child’s needs.
iHOPE focused primarily on rehabilitation in its early years but is now centered on academics and assistive technology, particularly augmentative and alternative communication devices that improve students’ access to learning. Mastery means users can take greater control of their lives. Shani Chill, the school’s principal and executive director, said working at iHOPE allows her to witness this transformational magic each day.
“Every student who comes here is a gift that is locked away inside and the staff come together to figure that out, saying, ‘I can give you this device, this tool, these tactiles’ and suddenly the student breaks through and shows us something amazing about themselves,” she said. “You see their personality, their humor, and the true wisdom that comes from students who would otherwise be sitting there in a wheelchair with everything being done for them — or to them.”
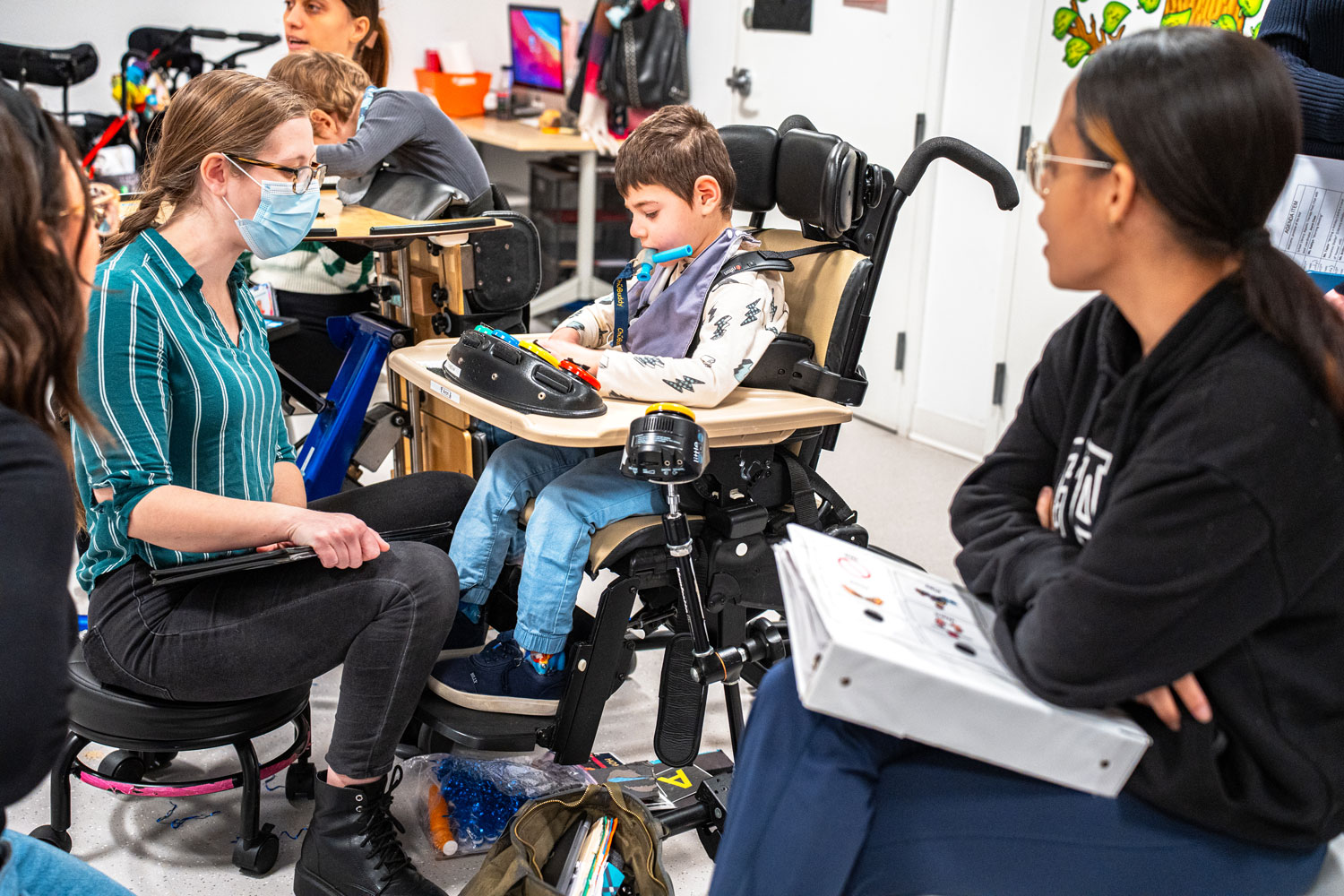

Some devices, like the one Omoloju uses in his impromptu deejay booth, track students’ pupils, allowing them to answer questions and express, for example, joy or discomfort, prompting staff to make needed modifications.
Because he’s unable to speak, Omoloju’s parents, teachers and friends assess his mood through other means, including his laughter, which arrives with ease and frequency at iHOPE. It’s a welcome contrast to what came before it at a different school, when a sudden eruption of tears would prompt a call to his mother, who would rush down to the campus, often too late to glean what upset him.
“One of the things we saw when we first visited (iHOPE) was that they knew exactly how to work with him,” Terra Omoloju said earlier this week. “That was so impressive to me. I don’t feel anxious anymore about getting those calls.”
Yosef Travis, father to 8-year-old Juliette, said iHOPE embodies the idea that children with multiple disabilities and complex syndromes can grow with the right support.
Juliette has a rare genetic disorder that impacts brain development and is also visually impaired. She squeals with joy with one-on-one attention and often taps her feet in excitement, Chill said.
“Juliette has grown in leaps and bounds over the past three and a half years and the dedication and creativity of the staff played a significant role,” her father said. “When she is out sick or on school vacation, we can tell that she misses them.”
Travis said his family considered many options, both public and private, before choosing iHOPE.
“iHOPE was the only one that could provide a sound education without sacrificing the necessary supports and related services she needs for her educational journey,” he said.
iHOPE currently serves one child from Westchester but all the others are from New York City. Parents are not referred there by their local district: They learn about it from social workers, therapists, doctors or through their own research, the principal said.
Those seeking enrollment complete an intake process to ensure their child would be adequately served there. Parents typically make partial payments or deposits upfront — the amount varies depending on income — while seeking tuition reimbursement from the NYC DOE.
iHOPE does not receive state or federal funding but some organizations that aid its students saw their budgets slashed by the Trump administration, reducing the amount of support they can provide to families in the form of services and equipment.
You can have classrooms that feel like a babysitting facility with kids in wheelchairs given colored paper and crayons, which makes no sense. Or you have a place like iHOPE, which takes advantage of the age in which we are.
Shani Chill, iHope principal and executive director
Principal Chill said her school is devoted to giving children the tools they need, even if it means absorbing added costs.
“We’ll get it from somewhere,” she said, noting iHOPE can turn to partner organization YAI and to its own fundraising efforts to pay those expenses so that every child, no matter their challenges, can learn.
‘He knows he is in the right place’
Omoloju’ symptoms mimic cerebral palsy and he also has scoliosis. He’s prone to viruses and other ailments, is frequently hospitalized and has undergone surgeries for his hip and back.
“He is also very charming,” his mother said. “He likes to have fun. He loves people. I feel very blessed that he is so joyous — even when he’s sick. He is very resilient. I love that about him. He teaches me so much.”

This is Omoloju’s fourth year at iHOPE. He’s in the upper school program — iHOPE does not use grade levels — which serves students ages 14 through 21.
He has made marked improvements in his mobility and communication since his enrollment. And his parents know he loves it there: Josh’s father, Wale, saw that firsthand after he dropped his son off at campus after a recent off-site appointment.
“I wish I had a video for when Keith [his son’s paraprofessional] came out of the elevator,” his father said. “[Josh] was beside himself laughing and was so excited to see him. He absolutely loves being there. I know he is in the right place and we love that.”
Principal Chill notes many of these students would not have been placed in an academic setting in decades past. Instead, she said, they would have been institutionalized, a cruel loss for them, their families and the greater community.
“These kids deserve an education and what that looks like runs the spectrum,” she said. “You can have classrooms that feel like a babysitting facility with kids in wheelchairs given colored paper and crayons, which makes no sense. Or you have a place like iHOPE, which takes advantage of the age in which we are.”
Chill notes that assistive and communication-related devices have improved dramatically in recent years and are only expected to develop further. She’s not sure how AI might transform their lives moving forward, but highly sensitive devices that can be operated with a glance or a light touch could be life changing, for example, allowing students to activate smart devices in their own living space.
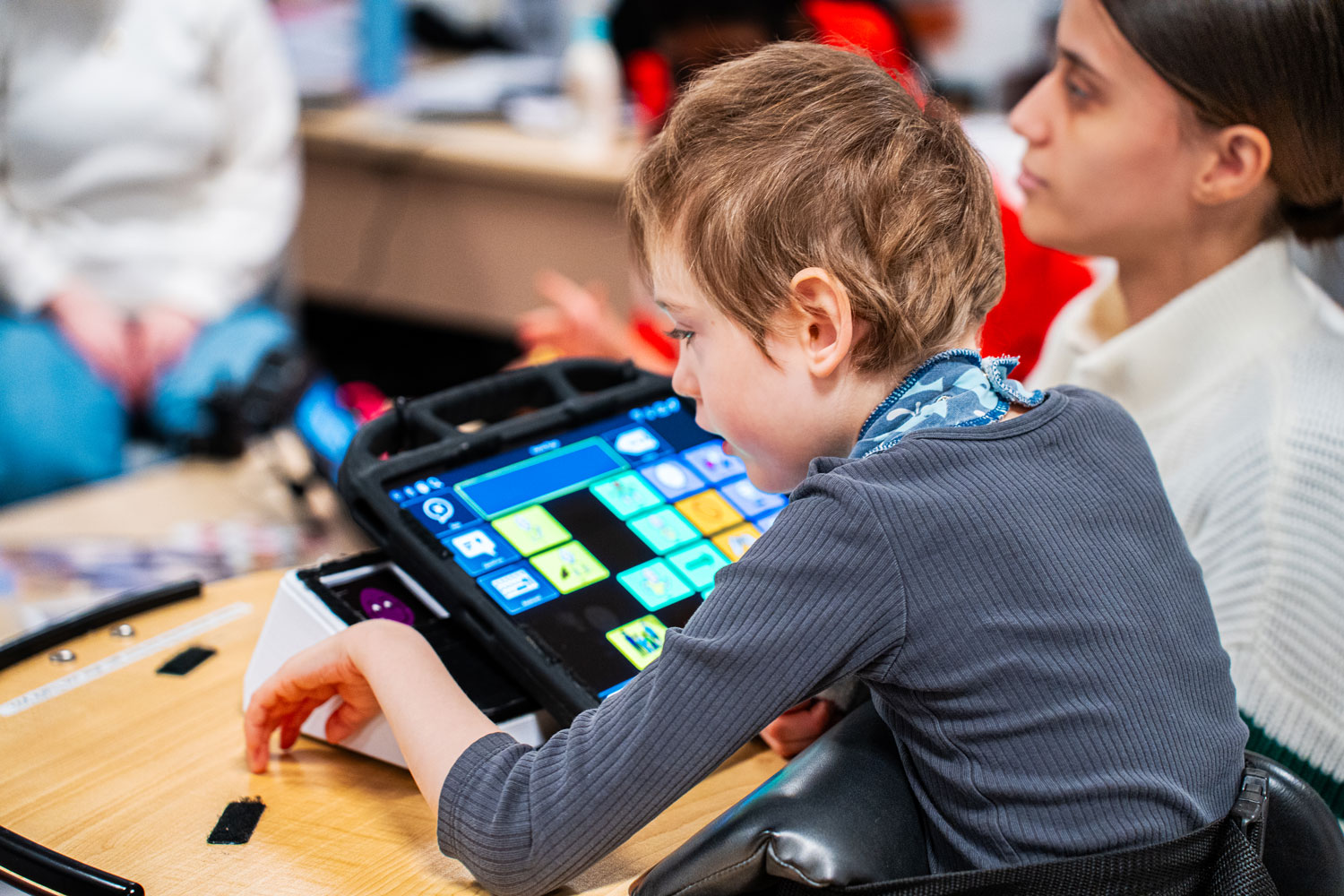

“This is a great time when you look at all of the technology that is available,” she said.
‘Moved to tears’
Miriam Franco was thrilled about the progress her son, Kevin Carmona, 16, made in just his first six months at iHOPE, she said.
Kevin, a high-energy student who thrives on praise from his teachers, is also good at listening: Ever curious, he’ll keep pace with a conversation from across the room if it interests him.
Kevin has cerebral palsy and a rare genetic disorder that affects the brain and immune system. He has seizures, hip dysplasia and is fed with a gastronomy tube.
“He was able to receive a communication device, which opened an entirely new world for him and allowed him to express himself in ways he could not before,” his mother said. “He also became more engaged and independent during his physical therapy and occupational therapy sessions. His attention and focus improved when completing tasks or responding to prompts, leading to greater engagement and participation.”
His enthusiasm for the school shows itself each morning, Franco said.
“You can see how happy he is while waiting for the bus and greeting his travel paraprofessional,” she said. “It starts from the moment he wakes up and continues as he gets ready for school. In every part of his current educational setting, Kevin is given real opportunities to participate, with the support in place to make that possible.”
Principal Chill said she cherishes the moment parents visit the site for the first time, imagining all their child is capable of achieving.
“They are moved to tears, saying, ‘Now I can picture what my child can do someday,” she said.
Did you use this article in your work?
We’d love to hear how The 74’s reporting is helping educators, researchers, and policymakers. Tell us how



