This is the first edition of Retrenchment Watch, a new initiative tracking how Canadian post-secondary institutions are reacting to current financial challenges. The Retrenchment Watch monitors the most recent developments, highlighting key trends and institutional responses across the country. Future editions will provide ongoing updates, analysis, and institutional case studies to help sector leaders navigate this challenging period. Updates to the website will be made weekly with summary emails flowing in a biweekly schedule.
The Impact of Declining International Enrollments
International students have played a critical role in the financial stability of Canadian post-secondary institutions. Over the past decade, many universities and colleges have relied heavily on international tuition revenue, amidst rising costs, frozen domestic tuition, and stagnant funding from provincial governments.
The federal immigration policy changes of 2024—including caps on the number of applications for international study permits that will be processed by IRCC—have caused a steep drop in new international student enrollments across the country.
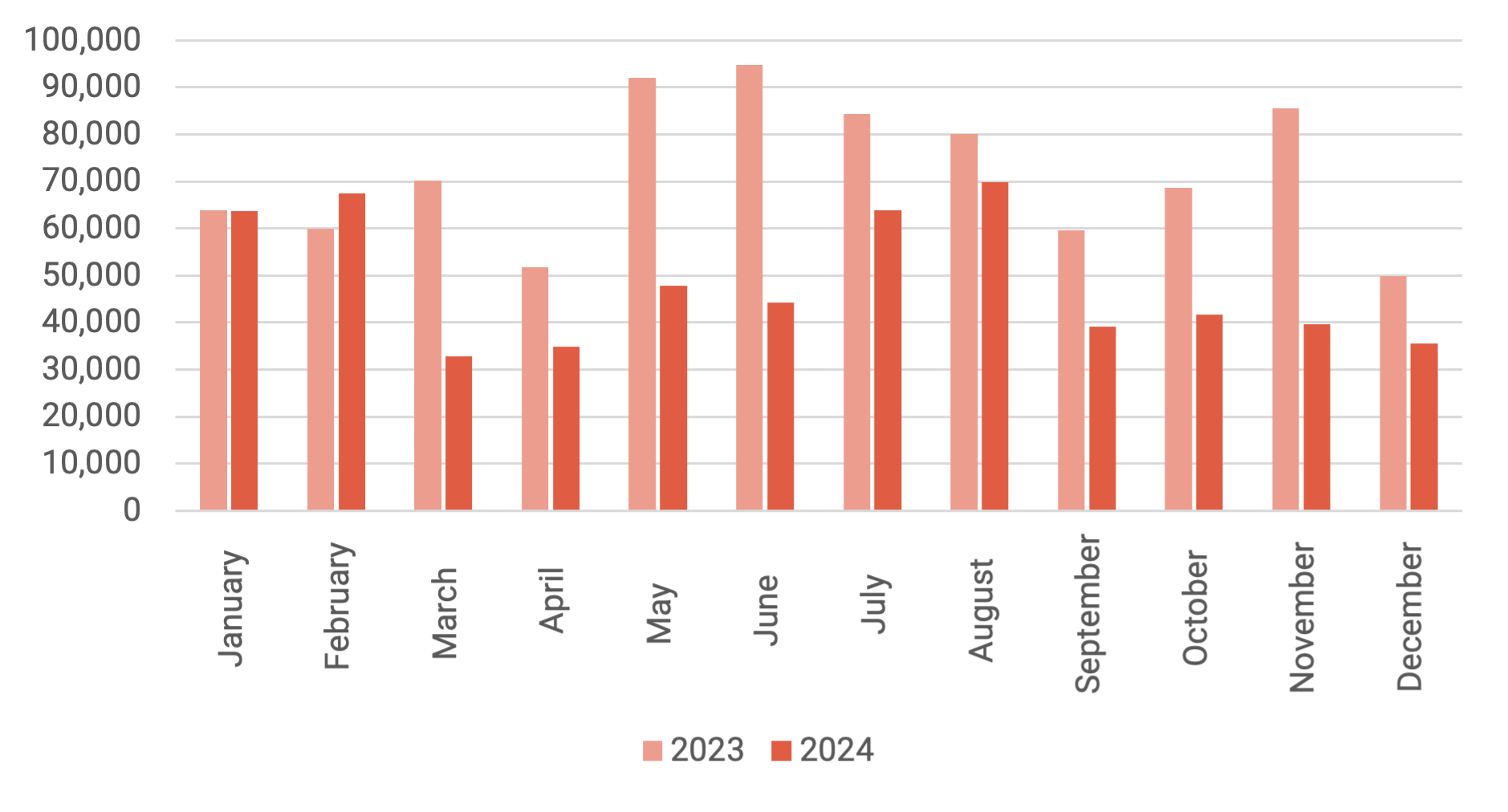
Comparison of Study Permit Applications Processed by IRCC, by Month (2023 vs. 2024)
Source: IRCC Data, “Source Countries – Applications Processed by IRCC for New Study Permit Applications (in Persons) by Month, from January 2022 to December 2024”
However, the impact of the government’s announcements has reduced the numbers of international students who are actually being enrolled much further than the caps themselves would imply. ApplyBoard is projecting that only 280,000 study permits were approved in 2024, as opposed to 515,880 in 2023, a 45% drop in international student numbers.
This matches what we are hearing about dramatic falls in international student numbers across the country. However, the drops are much greater at certain institutions. For example, Okanagan College has seen a 50% decline in new international student enrollment, with expectations of a further 70% in the winter term. Thompson Rivers University reported a 50% drop in new undergraduate international enrollments and a 75% drop in post-baccalaureate diploma students. These declines are forcing institutions to make difficult financial decisions to remain operational.
Budget Deficits
The enrollment shortfall has translated into substantial budget deficits at many institutions. Universities and colleges across Canada are now facing difficult financial realities, with some implementing drastic cost-cutting measures.
- York University has the largest projected deficit, at $142 million, and is implementing cost-cutting measures to reduce spending by $130 million over three years.
- Sheridan College is projecting a $112 million loss in revenue due to falling international student numbers.
- University of Waterloo estimates a $75 million deficit.
- Algonquin College is projecting a $32 million deficit for 2024-25, which is expected to rise to nearly $100 million by 2026-27.
- Carleton University is projecting a $38 million deficit for 2024-25, expected to reach $70 million by 2025-26.
- Memorial University reported a $9.5 million revenue loss.
While these numbers may seem alarming, they don’t tell the full story. Public details on institutional budgets and cuts remain limited and inconsistent. Some institutions report projected deficits, others focus on lost revenue, and many omit details on where cuts will actually fall. Job loss estimates vary widely, and program cuts are often announced without specifying which programs are affected.
In the coming weeks, we’ll be diving deeper into institutional budgets to provide a clearer picture of what these figures really mean and how they will shape the sector in the years ahead.
Program Suspensions and Faculty/Staff Layoffs
To manage financial constraints, many institutions are suspending programs and reducing staff. The impact is particularly severe for smaller colleges and those heavily reliant on international students.
- Sheridan College is suspending 40 programs and reviewing 27 others, with an estimated 700 layoffs.
- Fleming College has suspended 29 programs, possibly increasing to 42, due to a $38 million revenue shortfall.
- Centennial College is suspending 49 programs after experiencing a 43% drop in international student enrollment.
- St. Lawrence College is cutting 55 programs—approximately 40% of its offerings.
- Seneca Polytechnic has temporarily closed its Markham campus, which primarily served international students.
- Fanshawe College is cutting 18 programs this semester.
- Public-private partnership campuses, set up primarily by Ontario colleges in the Greater Toronto Area, are being wound down.
Hiring freezes have become common, with institutions like McGill University, Dalhousie University, the University of Waterloo and the University of Alberta pausing recruitment efforts to manage budget shortfalls. A number of institutions, such as Conestoga College and Carleton University, have introduced programs to incentivize voluntary retirement, in the hope that they can reduce salary expenditures without widespread compulsory layoffs.
However, layoffs are occurring across the sector. Mohawk College has cut 65 full-time administrative staff, amounting to 20% of its administrative workforce. Simon Fraser University has eliminated 85 staff and faculty positions. University of Windsor has already issued layoff notices to 15 employees and is warning of further cuts.
We know that large, but so far uncounted, numbers of contract instructors are not being rehired as their contracts expire. For example, Okanagan College has canceled 11 part-time term faculty contracts, with up to 80 more positions at risk. Western University is introducing enrollment thresholds to determine whether a course will be offered, with minimum class sizes ranging from 50 for first-year courses to 15 for fourth-year courses. These thresholds imply that contract instructors teaching courses which do not meet the cap are unlikely to have their contracts renewed.
We will be updating a list of institutional responses on the Retrenchment Watch as they are announced.
The Recovery Project
In response to the widespread retrenchment across Canadian higher education, HESA has launched the Recovery Project.
The financial challenges facing Canadian higher education are unprecedented, but they are not insurmountable. Most institutions have survived similar experiences in the past. The HESA Recovery Project helps Canadian colleges, polytechnics, and universities navigate financial challenges by providing insights and facilitating peer learning and collaborative action. Through monthly reports and virtual meetings, leaders gain evidence-based strategies on budget decisions, maintaining morale, and academic redesign. Drawing from interviews with veterans of past periods of retrenchment and case studies of institutions that have successfully come through major cuts, the project delivers actionable guidance. Reports and discussions begin this month, with future topics shaped by member needs to ensure timely, relevant support for institutions adapting to financial pressures. For more information, contact Tiffany MacLennan at [email protected].
Looking Ahead
The Retrenchment Watch will continue to monitor and analyze developments across the sector, providing timely updates and insights. The next editions will cover new announcements, policy shifts, and institutional adaptations that arise in response to ongoing financial pressures.
For more details, you can visit the Retrenchment Watch webpage. Have something you want to share with us about cuts at your institution? Reach out to us.