Depending on the era in which we began learning, formally or informally, we all have a diverse range of valuable definitions and perspectives about artificial intelligence pertaining to teaching and learning.
Teaching and learning with AI
When I was a student in elementary school during the 1980s, AI was using a calculator rather than longhand or a traditional adding machine for arithmetic. Additionally, the entire school only had six computers for student use, which were housed in the library. Only students acting responsibly earned access to time on these devices to play The Oregon Trail, “an educational game that simulates the hardships of [1848] …”
With all of this in mind, AI has been teaching us, and we’ve been learning from it, for quite some time, in and out of school.
However, with the advancement of generative AI, the implications for teaching and learning now have to do more with academic integrity. And academic dishonesty policies about original work vs. AI in education have come into the conversation. This is where MindTap features like Turnitin can be applied to help monitor students’ acceptable and ethical use of AI in English composition courses.
My conversation with students
My students may engage in conversations about acceptable, ethical uses of GenAI and academic integrity before they even enroll in my courses. This is because I post the policies in my syllabus. Students learn that there is a monitoring system in place in MindTap for English by Turnitin. Once enrolled in MindTap, there are discussions, in both online and face-to-face modalities, about these policies at length. Policies are also copied into each of the writing assignments in MindTap. Our focus is on ethics, or academic integrity, to ensure students’ coursework is original. Valuable feedback, information and resources can be provided for students to learn and progress rather than to get a grade.
Since students cannot prove learning and mastery of learning outcomes without work being original, I discuss with them and copy in their assignments that they should not use any words that are not original. MindTap provides me with access to Turnitin to monitor academic integrity.
Suggestions for monitoring
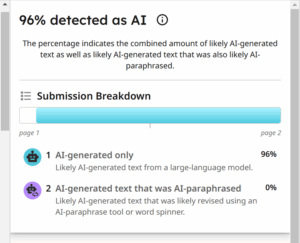
To help monitor students’ use of AI, parameters in MindTap for English with Turnitin should be set. For example, students need to submit more than 300 words for the detector to perform. Once students submit work, the detector generates an originality report. This can be downloaded to provide the instructor and learner with feedback about the percentage amount of acceptable and ethical usage of AI or plagiarism.
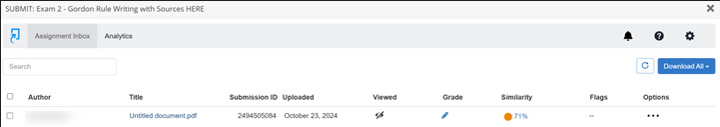
The report highlights where originality is in question directly on the student’s document. Some instructors will set percentage parameters as well, instructing students that there cannot be more than 15% flagged by the detector in MindTap. Clicking on what the detector has highlighted shows the possible source where information may have been taken or just generally that AI has been used. Note: this is just a monitoring system. So, please be mindful that the report is a tool instructors can use to have conversations with their students. We cannot accuse academic dishonesty based on a report alone.

MindTap’s monitoring system has always been correct for me, but conversations are still beneficial for assurance. I use this monitoring document for every submission in MindTap.
The big picture to consider
AI can be used ethically as a tool for teaching and learning, bridging student learning gaps and strengthening their mastery of skills. However, when it comes to academic integrity, the concern is that GenAI is being used not as an aid, but as a tool devoid of the values of teaching and learning. According to Cengage’s recent research, 82% of instructors expressed concern specifically about AI and academic integrity. Setting policies and parameters with clear definitions and having conversations with students is essential to my ability to monitor my students’ acceptable use of AI.
Do you use AI in your English composition classroom? Reach out to discuss the ways you’re utilizing AI as an ethical tool to advance teaching and learning.
Written by Faye Pelosi, Professor in the Communications Department at Palm Beach State College and Cengage Faculty Partner.
Stay tuned for Professor Pelosi’s upcoming video demo of how she uses the MindTap Turnitin feature in her English course.