We’ve all seen the endless lists of study apps and productivity
hacks floating around the internet. They’re useful—sometimes. But
they rarely acknowledge what staying motivated actually feels
like when you’re balancing classes, work, personal obligations,
and the inevitable end-of-semester whirlwind.
Being in my first semester and experiencing the online learning
environment, I’ve taken some time to reflect on the tools and
strategies that have actually helped me stay grounded, organized
and on track this semester. In this post, I reflect on various
tools I’ve explored to help me meet deadlines and produce the
best work, even when classes began ramping up in intensity. I
hope some of these tools will help you, too.
Productivity Apps
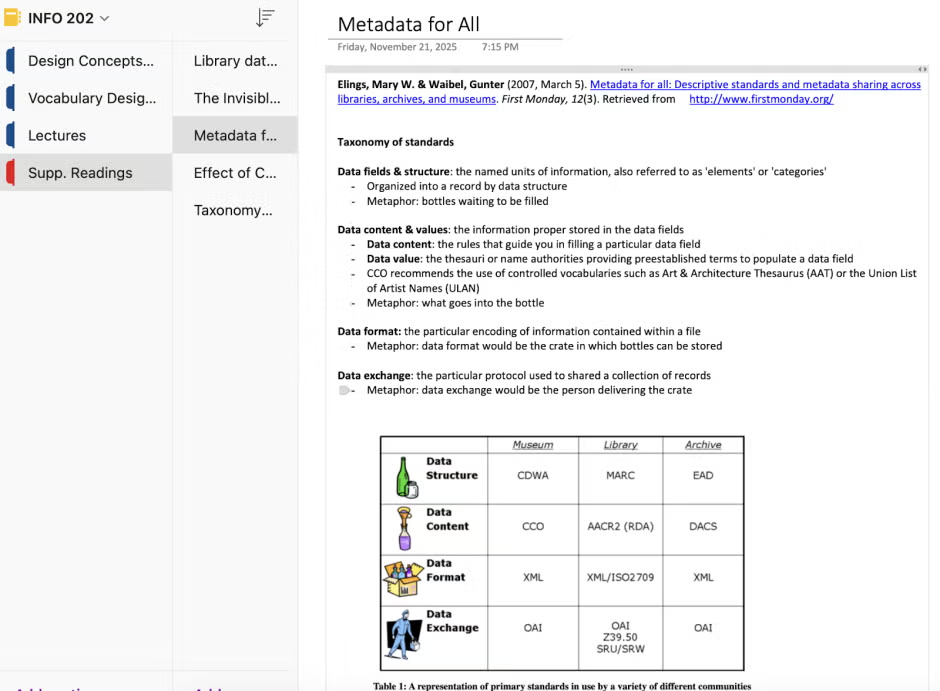
Notion
Endlessly versatile and aesthetically pleasing, Notion has been a mainstay
of mine for years to manage time across various aspects of my
life. Beyond the myriads of templates to choose from, it’s easy
to tailor a page to your own liking and make it what you want it
to be.
Most effective usages:
-
To-do lists: Creating sections within Notion
dedicated to weekly or daily checklists is one of the easiest
ways to track progress visually. You can format tasks with
toggles, color-coded tags or even embed due dates so they
automatically appear in your calendar view. -
Dashboards: Design a personal “home base”
where all your semester essentials live—links to syllabi,
assignment databases, reading trackers and a calendar of
upcoming deadlines. Having everything gathered in one place
reduces tab-hopping and makes it easier to orient yourself
at the start of each study session. -
Databases: This is where Notion really shines.
Whether you create a master assignment tracker, a reading log
or a project board with statuses like “Not Started,” “In
Progress” and “Done,” database views make it easy to sort,
filter and see exactly what needs attention each week.
OneNote
One of many note-taking apps out there, OneNote is clean and
simple to use, and available for free for all iSchool students as
a part of the Microsoft Office Suite offered by SJSU.
Most effective usages
-
Separate notebooks for each class: This keeps
everything tidy and minimizes the scramble of
remembering where you saved something. You can also create
sections inside each notebook (e.g., lectures, readings,
assignments and discussion posts) for smoother organization. -
Layered notetaking: Whether you prefer typing,
highlighting PDFs directly or handwriting on a tablet, OneNote
is flexible. Having your notes, embedded articles and
screenshots all in one place makes studying for finals so much
easier. -
ePortfolio prep: Since OneNote is built for
long-term organization, it’s a great place to collect artifacts
and reflections for your ePortfolio as the semester goes on.
Keeping everything in a designated notebook means you’ll
already have the pieces you need when it’s time to put it
together.
Time Management Apps
Google Calendar
Sometimes overlooked, GCal is an easy-to-use and handy tool for
scheduling weekly and monthly workflows. Offered free, it’s an
incredibly accessible way to streamline your weekly commitments.
If you’re more of a visual learner, like me, the colorful blocks
representing events are a useful way to visually structure time.
Messing around with the various features yourself will give you a
feel for what helps you stay organized.
Depending on your own personal work style, plan out your workload
for the upcoming week or month, and check it regularly to make
sure nothing slips through the cracks. By having deadlines and
other pertinent information regarding your workload recorded,
GCal will notify you about schedule conflicts when accepting
a meeting invitation or recording events on other calendars.
Most effective usages
-
Layer different calendars: Subscribing to my
school calendar, work calendar and personal calendar allows for
each of my commitments to show up together, which is useful in
for deeper and multi-faceted organization -
Task vs. Event: Using the task option is a
great way to record deadlines for upcoming assignments.
Clicking ‘all day’ allows it to show up at the top of the day,
for easier viewing. And the strikethrough that happens after
submitting an assignment is satisfying. -
Focus time: Use this feature to block off time
in your day for uninterrupted work.
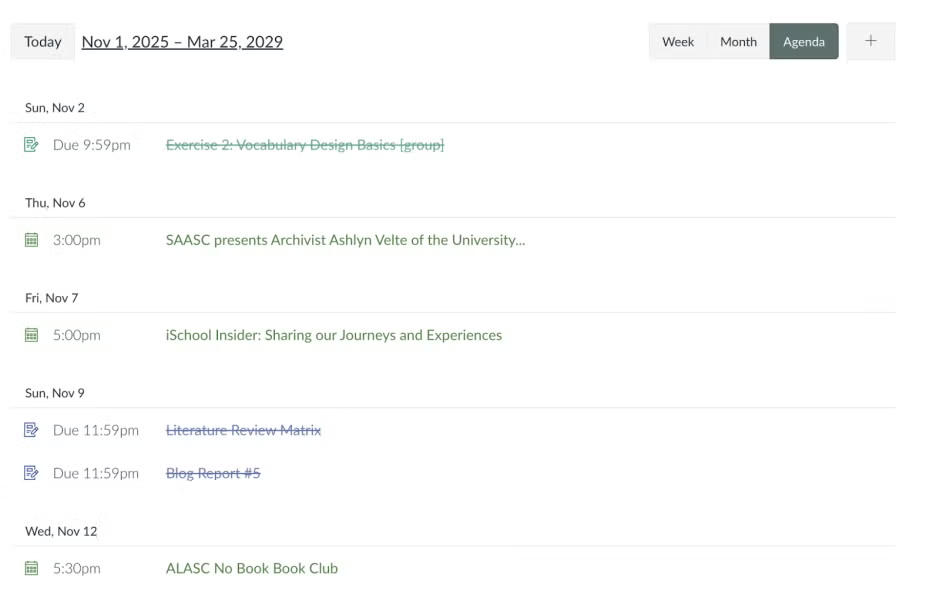
Canvas Calendar
If simplicity is more your thing, using Canvas’ calendar to keep
track of work is a great idea. All assignment due dates will show
in your calendar, along with meetings and events for iSchool
students to join. While it’s a great resource, it’s important to
check your class syllabus and weekly modules yourself to make
sure all assignments are accounted for.
Most effective usages:
-
Agenda: A visually clean list of upcoming
deadlines and events. Using the agenda feature is a good way to
see all upcoming work side by side, and account for deadlines. -
Calendar: A monthly overview of workload. This
is a good way to see what days assignment deadlines fall on, to
let you get into your own groove of anticipated workdays
Study Tips
Along with the aforementioned apps, being a good student is a
skill you learn over time and a muscle you must routinely flex.
You know yourself best, so listen to yourself and reflect on
times you’ve been most successful and what specifically you did
that brought you there.
-
Listen to your energy levels: I am always most
productive first thing in the morning, so by planning a block
of time right when I wake up to knock out assignments and
lectures, I can relax the rest of the day knowing my to-do list
is significantly smaller. If you have the flexibility to move
things around based upon when you’re most equipped to stay
focused, scheduling out other daily commitments around it can
help things fall into place. -
Short bursts vs. Long haul: Study strategies
like the Pomodoro Technique are proven ways for many people to
stay productive. The technique is simple and easy to follow: 25
minutes of active work and 5 minutes of rest. Change the time
to suit the task. This is a great way to manage time, but it’s
okay if it doesn’t work for you. As I mentioned, I do much
better when I complete work in large chunks of time, resulting
in multiple consecutive hours of uninterrupted
focus. -
Rest: Arguably, the most important tip of them
all: If you aren’t getting adequate rest in between
commitments, your fuse for work will be much shorter.
Scheduling your week in advance is a good way to break things
up, in turn freeing up time and ensuring you have a dedicated
rest period and time of day when you set work aside.
Overall Thoughts
As the semester comes to a close, reflect on how things worked
well for you and what could be improved. If you’re like me and
it’s your first semester of graduate school, it’s okay if it took
a little bit to get to where you’d like to be in terms of
effective workload management, or if you didn’t hit that place at
all. Above all, listen to yourself and adjust your strategies and
apps to best suit your unique needs. If you have any tips that
helped you throughout the semester, feel free to share them
below!