This story was produced in partnership with Teen Vogue and reprinted with permission.
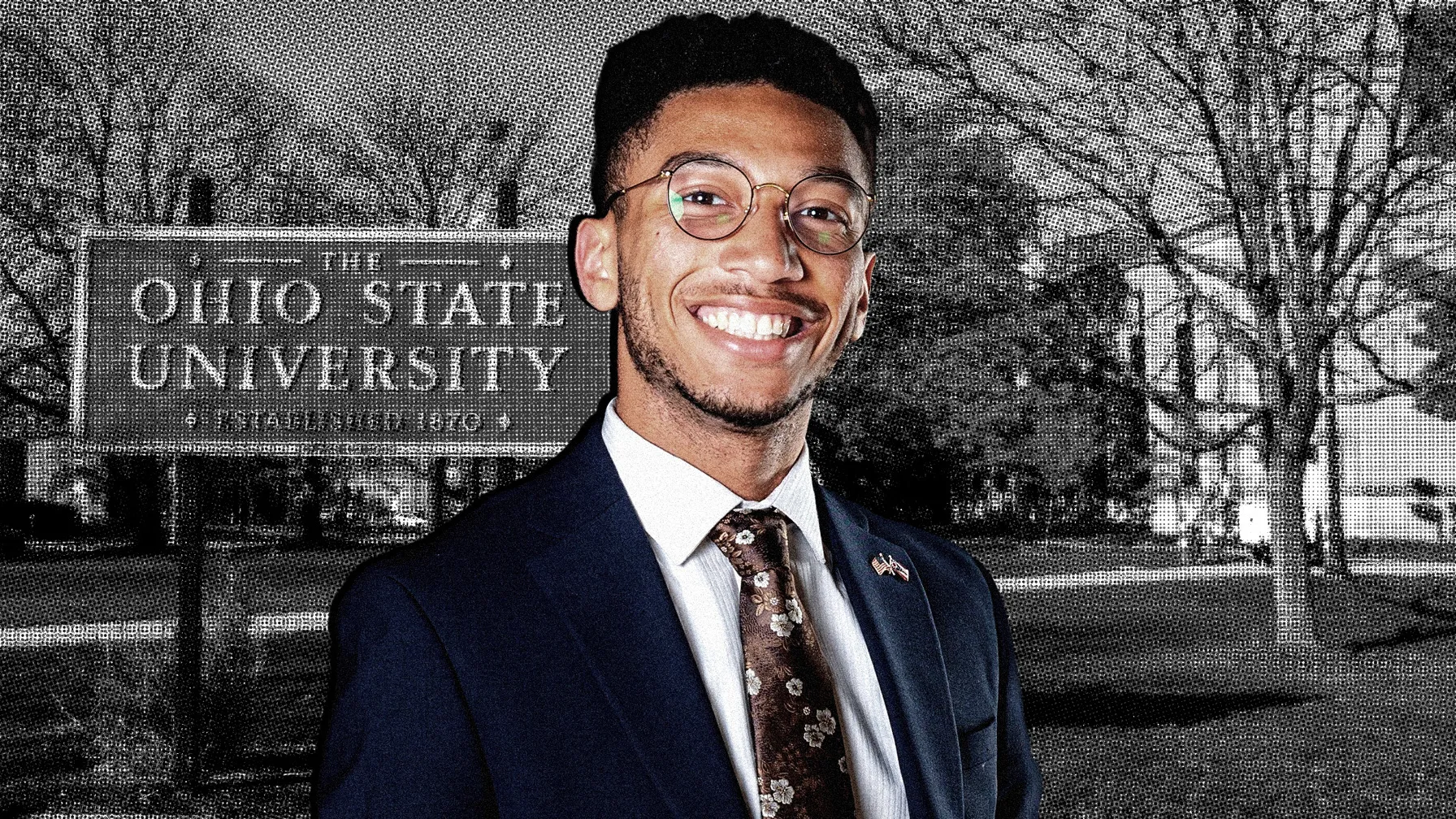
Christopher Cade wants to be president someday. His inspiration largely comes from family members, who have been involved in local politics and activism since long before he was born. But policies from the Trump administration and the Ohio Legislature are complicating his college experience — and his plans to become a politician.
Cade is a student at Ohio State University double-majoring in public policy analysis and political science with a focus on American political theory. He recalls his maternal grandmother, Maude Hill — who had a large hand in raising him — talking to him about her involvement in the Civil Rights Movement. She also worked at Columbus, Ohio-based affordable housing development nonprofit, Homeport, and has gone to Capitol Hill to speak with the state delegation multiple times. His dad is the senior vice president of the housing choice voucher program at the Columbus Metropolitan Housing Authority, and his older brother has a degree in political science and is interested in social justice advocacy work, Cade said. Last fall, his first on campus, Cade began applying to opportunities to bolster his resume for a future career in politics.
The now 19-year-old secured an internship with the U.S. Department of Transportation and a work-study job on campus in the university’s Office of Diversity and Inclusion. But the federal opportunity was scrapped when the Trump administration imposed a hiring freeze and budget cuts. His campus job ended when the university announced it would “sunset” the diversity office in response to federal and state anti-diversity, equity and inclusion orders and actions, according to Cade.
Related: Become a lifelong learner. Subscribe to our free weekly newsletter featuring the most important stories in education.
The work-study position was with the university’s Bell National Resource Center on the African American Male, which was founded to support Black men to stay in college. It’s a cause he was excited about.
“I would help order food or speak with students or do interviews,” said Cade. “I developed a good 20 different programs for the next year.”
In February, when the university announced it was closing the office, “I was like, ‘Well, so six months of work just for no reason,’” he said.
OSU President Ted Carter released a statement on Feb. 27 saying the closure of the Office of Diversity and Inclusion was a response to both state and federal actions regarding DEI in public education. The move eliminated 17 staff positions, not including student roles, the university said. Programming and services provided by the Office of Student Life’s Center for Belonging and Social Change were also scrapped.
The change came before the Trump administration’s initial deadline for complying with a memo that threatened to cut funding for public colleges and universities, as well as K-12 schools, that offer DEI programs and initiatives. In March, the administration announced that OSU was one of roughly 50 universities under federal investigation for allegedly discriminating against white and Asian students in graduate admissions. Additionally, Ohio Gov. Mike DeWine signed legislation in March banning DEI programs in the state’s public colleges and universities. The legislation went into effect in June.
Before the DEI office closed, Cade said, “I felt so heard and seen.” He’d attended a private, predominantly white, Catholic high school, he said. “It was not a place that supported me culturally and helped me understand more about who I am and my Blackness,” he recalled. At the university, though, “the programming we had throughout the year [was] about how to change the narrative on who a Black man is and what it means when you go out here and interact with people.
“And then for them to close down all these programs, that essentially told me that I wasn’t cared about.”
After the February announcement, students pushed back, organizing protests and a sit-in at the student union. But eventually, those efforts quieted.
Cade says students felt like there was a “cloud of darkness” hanging over them. But he also thought of his Office of Diversity and Inclusion coworkers, some of whom had spent decades working there, helping students. In particular he thought of his former colleague Chila Thomas, who celebrated her fifth anniversary last year as the executive director of the Young Scholars Program. That program, which helps low-income aspiring first-generation college students get to and through college, was one of several of the office’s programs that will continue. The day after Carter’s announcement, she and others in the office spent time giving students space to talk through their feelings, despite the uncertainties surrounding their own employment, Cade said.
Since the university crackdown on DEI, Cade said he’s experienced more discomfort on campus, even outright racism. He says he was approached by a white person who said, “I’m so glad they’re getting rid of DEI” and spit on his shoe and used a racial slur.
“I don’t know how that could ever be acceptable to anyone, but that was [when] a flip switched in my head,” Cade said. “I couldn’t sit down and be sad and silent. I had to stand up and make change.”
In March, he traveled with other students to Washington, D.C., as part of the Undergraduate Student Government’s Governmental Relations Committee. They met with Ohio Rep. Troy Balderson and an aide, along with staffers from the offices of fellow Ohio lawmakers Sen. Bernie Moreno and Rep. Joyce Beatty, to discuss college affordability, DEI policies and the federal hiring freeze. Cade says he described how he was affected by the U.S. Department of Transportation canceling his internship.
In Carter’s announcement, he stated that all student employees would be “offered alternative jobs at the university,” but Cade said during a meeting with Office of Diversity and Inclusion student employees, an OSU dean clarified that they would have to apply for new opportunities. With the policy changes meaning there were fewer work-study roles and more students in need of jobs, Cade saw the market as increasingly competitive, and he began to job hunt elsewhere. This summer he secured work with the Ohio Department of Transportation as a communications and policy intern. In October he began an intake assistant role in the Office of Civil Rights Compliance at the university. (Ohio State Director of Media and PR Chris Booker told Teen Vogue that the school could not comment on the experiences of individual students but that “all student employees and graduate associates impacted by these program changes were offered the opportunity to pursue transitioning into alternative positions at the university, as well as support in navigating that change.”)
Although he was drawn to OSU for the John Glenn College of Public Affairs’ master’s program, Cade says he might have reconsidered schools had he known that the university would bend to lawmakers’ anti-DEI efforts. While he’s concerned about how education-related legislation and policies may continue to affect his college experience, he worries most about some of his peers. College is already so hard to navigate for so many young people, said Cade. “And this is just another thing that says, ‘Oh yeah, this isn’t for me.’”
This story was published in partnership with Teen Vogue.