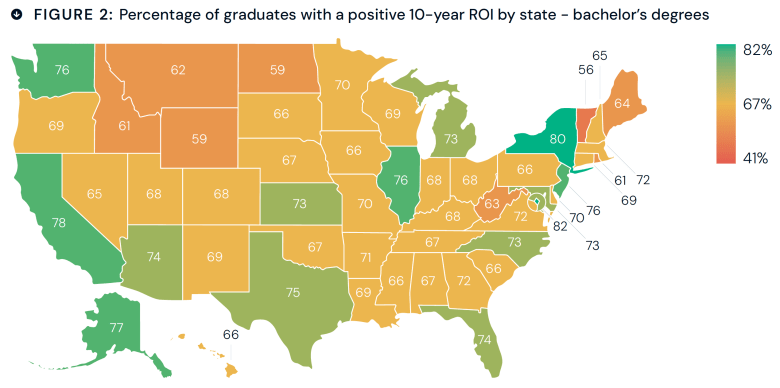
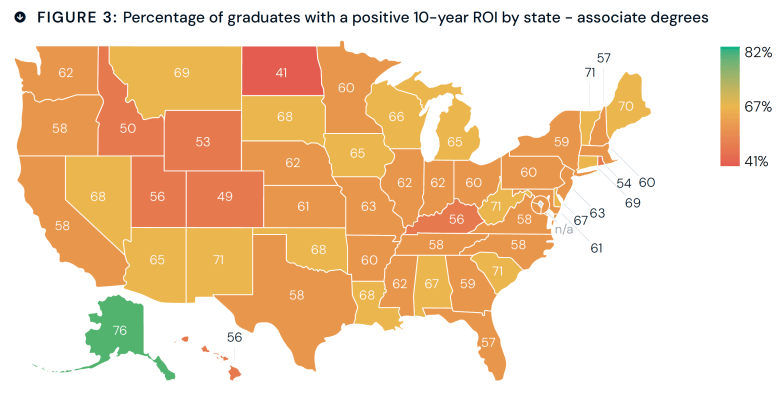
More than three dozen higher education organizations, led by the American Council on Education, are urging the Trump administration to reconsider its plan to require colleges to submit years of new data on applicants and enrolled students, disaggregated by race and sex.
As proposed, the reporting requirements would begin on Dec. 3., giving colleges just 17 weeks to provide extensive new admissions data, ACE President Ted Mitchell wrote in an Oct. 7 public comment. Mitchell argued that isn’t enough time for most colleges to effectively comply and would lead to significant errors.
ACE’s comment came as part of a chorus of higher education groups and colleges panning the proposal. The plan’s public comment period ended Tuesday, drawing over 3,000 responses.
A survey conducted by ACE and the Association for Institutional Research found that 91% of polled college leaders expressed concern about the proposed timeline, and 84% said they didn’t have the resources and staff necessary to collect and process the data.
Delaying new reporting requirements would leave time for necessary trainings and support services to be created, Mitchell said. The Education Department — which has cut about half its staff under President Donald Trump — should also ensure that its help desk is fully crewed to assist colleges during implementation, Mitchell said.
Unreliable and misleading data?
In August, Trump issued a memo requiring colleges to annually report significantly more admissions data to the National Center for Education Statistics, which oversees the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System.
The Education Department’s resulting proposal would require colleges to submit six years’ worth of undergraduate and graduate data in the first year of the IPEDS reporting cycle, including information on standardized test scores, parental education level and GPA.
In a Federal Register notice, the Education Department said this information would increase transparency and “help to expose unlawful practices″ at colleges. The initial multi-year data requirement would “establish a baseline of admissions practices” before the U.S. Supreme Court’s 2023 ruling against race-conscious admissions, it said.
But the department’s proposal and comments have caused unease among colleges, higher ed systems and advocacy groups in the sector.
“While we support better data collection that will help students and families make informed decisions regarding postsecondary education, we fear that the new survey component will instead result in unreliable and misleading data that is intended to be used against institutions of higher education,” Mitchell said in the coalition’s public comment.
The wording of the data collection survey — or lack thereof — also raised some red flags.
Mitchell criticized the Trump administration for introducing the plan without including the text of the proposed questions. Without having the actual survey to examine, “determining whether the Department is using ‘effective and efficient’ statistical survey methodology seems unachievable,” he said.
The Education Department said in the Federal Register notice that the additional reporting requirements will likely apply to four-year colleges with selective admissions processes, contending their admissions and scholarships “have an elevated risk of noncompliance with the civil rights laws.”
During the public comment period, the department specifically sought feedback on which types of colleges should be required to submit the new data.
The strain on institutions ‘cannot be overstated’
Several religious colleges voiced concerns about the feasibility of completing the Education Department’s proposed request without additional manpower.
“Meeting the new requirements would necessitate developing new data extracts, coding structures, validation routines, and quality assurance checks — all while maintaining existing reporting obligations,” Ryon Kaopuiki, vice president for enrollment management at the University of Indianapolis, said in a submitted comment.
The religious college’s Office of Institutional Research has just two staff members, Kaopuiki said. The Education Department would not provide additional funding and did not suggest it would offer technical support.
Vanguard University of Southern California, another religious institution, said in a public comment that the new work would fall on just one staff member.
A majority of the college leaders surveyed by ACE and AIR said it would take their institution between 250 to 499 hours of work to comply with the new reporting requirements. The federal proposal estimated that the changes will create over 740,000 hours of additional work across the higher ed sector.
But the National Association of Independent Colleges and Universities said required labor will be much worse.
“The strain this collection will place on institutions cannot be overstated,” NAICU, which signed on to ACE’s letter, said in a separately submitted comment. “The proposal greatly underestimates both the burden and timeframe, particularly for colleges with limited staff, infrastructure, and resources already stretched thin” by other new reporting requirements.
Vanguard and the University of Indianapolis urged the department to delay implementing the new requirements until the 2027–28 collection cycle and to test them via a pilot with volunteer institutions before rolling them out nationally.
The institutions also proposed an exemption for small colleges, though they suggested different enrollment cut-offs — the University of Indianapolis suggested fewer than 750 full-time students, while Vanguard pitched fewer than 3,000.
Other concerns from colleges
The University of Texas System, along with the University of Alabama System and the ACE coalition, raised concerns about student privacy and the feasibility of collecting graduate-level data.
“Graduate admissions are inherently decentralized and vary by program,” Archie Holmes, the Texas system’s executive vice chancellor for academic affairs, wrote in a public comment. “Required data elements such as program-level GPA and test scores are not uniformly collected and may not be directly comparable.”
He recommended that the Education Department focus on undergraduate data until the process has been standardized.
Holmes also flagged that colleges risk inadvertently sharing private student data by disaggregating it so significantly, especially in smaller programs.
The University of Alabama System likewise warned of “significant legal and privacy risks” if the Education Department did not provide “clear federal guidance” on privacy protections.
The presidents of Capella and Strayer universities, two for-profit institutions owned by the same company, asked that the Education Department exclude noncompetitive scholarships from its reporting requirements for colleges that accept all or a “vast majority” of their applicants.
For example, a scholarship “whose only eligibility requirement is student persistence” does not “bear any connection to race” and reporting data on its recipients “would not advance the Department’s goal of detecting or preventing racial discrimination,” they said in a joint comment. But it would add an unnecessary administrative burden for colleges, they said.