Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
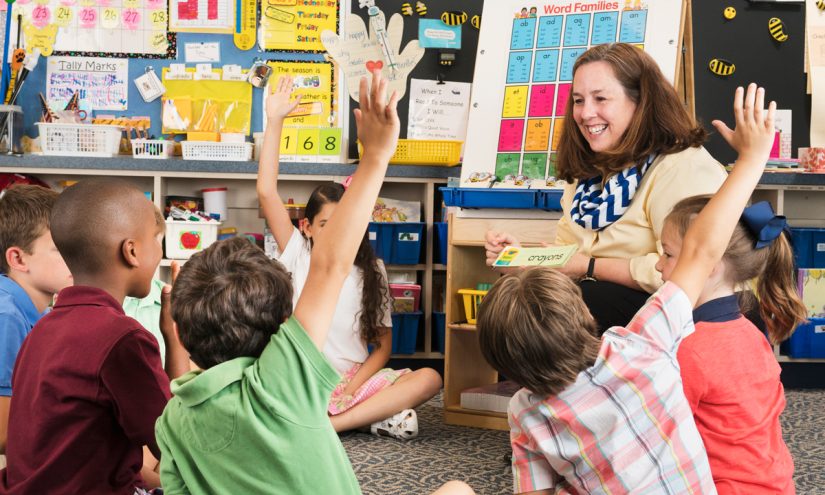
As reading scores remain a top concern for schools nationwide, many districts are experimenting with ability-based grouping in the early grades. The idea is to group students in multiple grade levels by their current reading level — not their grade level. A classroom could have seven kindergartners, 10 first graders, and three second graders grouped together for reading because they all read at the same level.
While this may work for some schools, in our district, Rockwood School District in Missouri, we’ve chosen a different path. We keep students together in their class during whole-class instruction — regardless of ability level — and provide support or enrichment by creating flexible groups based on instructional needs within their grade level.
We’re building skilled, confident readers not by separating them, but by growing them together.
Children, like adults, learn and grow in diverse groups. In a Rockwood classroom, every student contributes to the shared learning environment — and every student benefits from being part of it.
Our approach starts with whole-class instruction. All students, including English multilingual learners and those working toward grade-level benchmarks, participate in daily, grade-level phonics and comprehension lessons. We believe these shared experiences are foundational — not just for building literacy, but for fostering community and academic confidence.
After our explicit, whole-group lessons, students move into flexible, needs-based small groups informed by real-time data and observations. Some students receive reteaching, while others take on enrichment activities. During these blocks, differentiation is fluid: A student may need decoding help one day and vocabulary enrichment the next. No one is locked into a static tier. Every day is a new opportunity.
Students also engage in daily independent and partner reading. In addition, reading specialists provide targeted, research-based interventions for striving readers who need additional instruction.
We build movement into our instruction, as well — not as a brain break, but as a learning tool. We use gestures for phonemes, tapping for spelling and jumping to count syllables. These are “brain boosts,” helping young learners stay focused and engaged.
We challenge all students, regardless of skill level. During phonics and word work, advanced readers work with more complex texts and tasks. Emerging readers receive the time and scaffolded support they need — such as visual cues and pre-teaching or exposing students to a concept or skill before it’s formally taught during a whole-class lesson. That can help them fully participate in every class. A student might not yet be able to decode or encode every word, but they are exposed to the grade-level standards and are challenged to meet the high expectations we have for all students.
During shared and interactive reading lessons, all students are able to practice fluency and build their comprehension skills and vocabulary knowledge. Through these shared experiences, every child experiences success.
There’s a common misconception that mixed-ability classrooms hold back high achievers or overwhelm striving readers. But in practice, engagement depends more on how we teach rather than who is in the room. With well-paced, multimodal lessons grounded in grade-level content, every learner finds an entry point.
You’ll see joy, movement, and mutual respect in our classrooms — because when we treat students as capable, they rise. And when we give them the right tools, not labels, they use them.
While ability grouping may seem like a practical solution, research suggests it can have a lasting downside. A Northwestern University study of nearly 12,000 students found that those placed in the lowest kindergarten reading groups rarely caught up to their peers. For example, when you group a third grader with first graders, when does the older child get caught up? Even if he learns and progresses with his ability group, he’s still two grade levels behind his third-grade peers.
This study echoes what researchers refer to as the Matthew Effect in reading: The rich get richer, and the poor get poorer. Lower-track students are exposed to less complex vocabulary and fewer comprehension strategies. Once placed on that path, it’s hard to catch up. Once a student is assigned a label, it’s difficult to change it — for both the student and educators.
In Rockwood, we’re confident in what we’re doing. We have effective, evidence-based curricula for Tier I phonics and comprehension, and every student receives the same whole-class instruction as every other student in their grade. Then, students receive intervention or enrichment as needed.
At the end of the 2024–25 school year, our data affirmed what we see every day. Our kindergarteners outperformed national proficiency averages in every skill group — in some cases by more than 17 percentage points, according to our Reading Horizons data. Our first and second graders outpaced national averages across nearly every domain. We don’t claim to have solved the literacy crisis — or know that our model will work for every district, school, classroom or student — but we’re building readers before gaps emerge.
We’ve learned that when every student receives strong Tier I instruction, no one gets left behind. The key isn’t separating kids by ability. It’s designing instruction that’s universally strong and strategically supported.
We recognize that every community faces distinct challenges. If you’re a district leader weighing the trade-offs of ability grouping, consider this: When you pull students out of the room during critical learning moments, the rich vocabulary, the shared texts and the academic conversation, you are not closing the learning gap, but creating a bigger one. Those critical moments build more than skills; they build readers.
In Rockwood, our data confirms what we see every day: students growing not only in skills, but also in confidence, stamina and joy. We’re proving that inclusive, grade-level-first instruction can work — and work well — for all learners.
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter












![Building an Internal OPM [Workbook]](https://blog.college-counseling.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/1759786546_Building-an-Internal-OPM-Workbook.jpg)