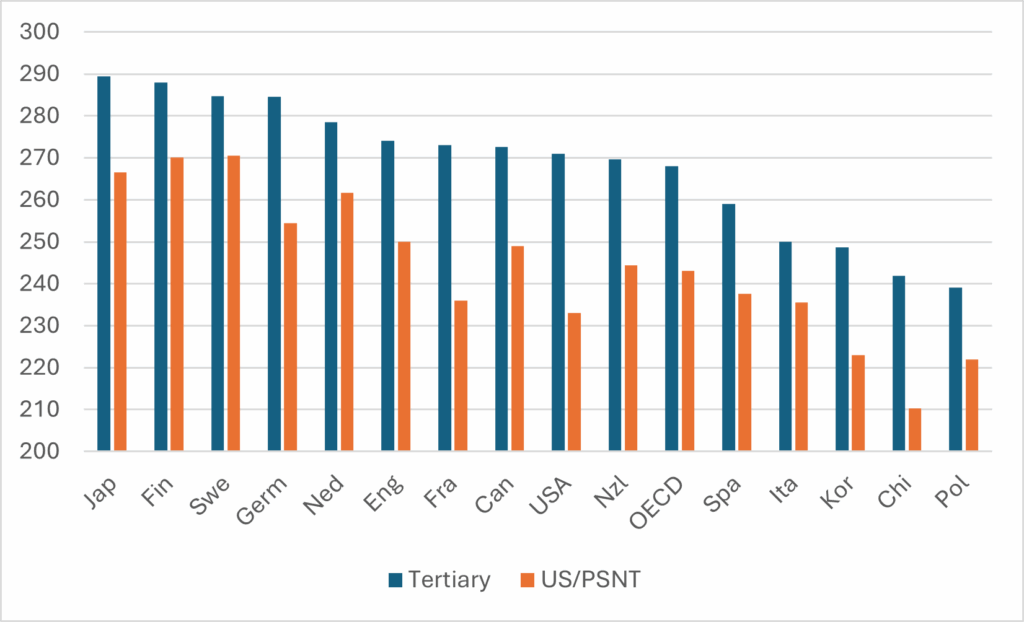
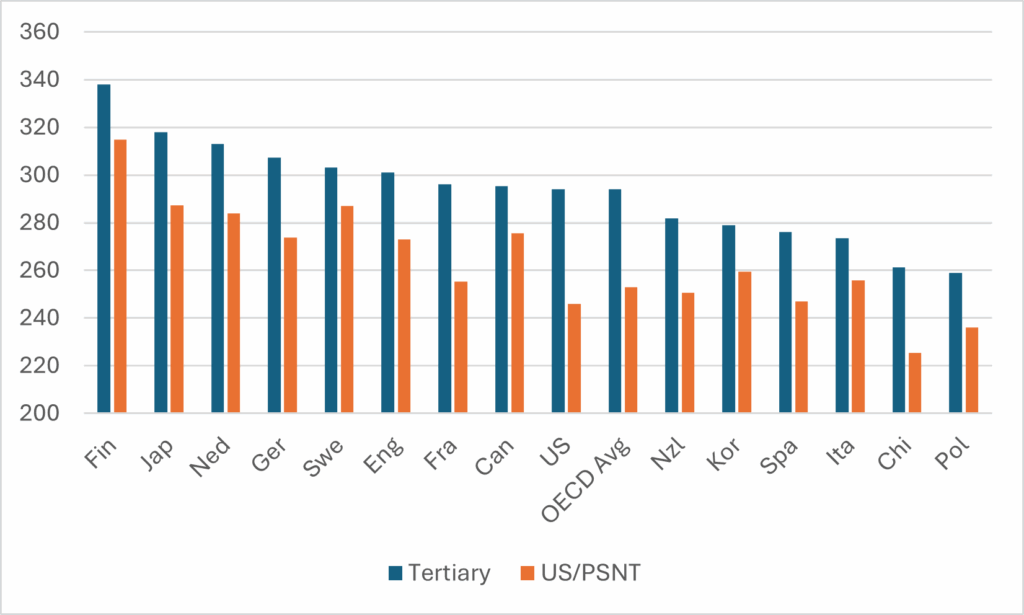
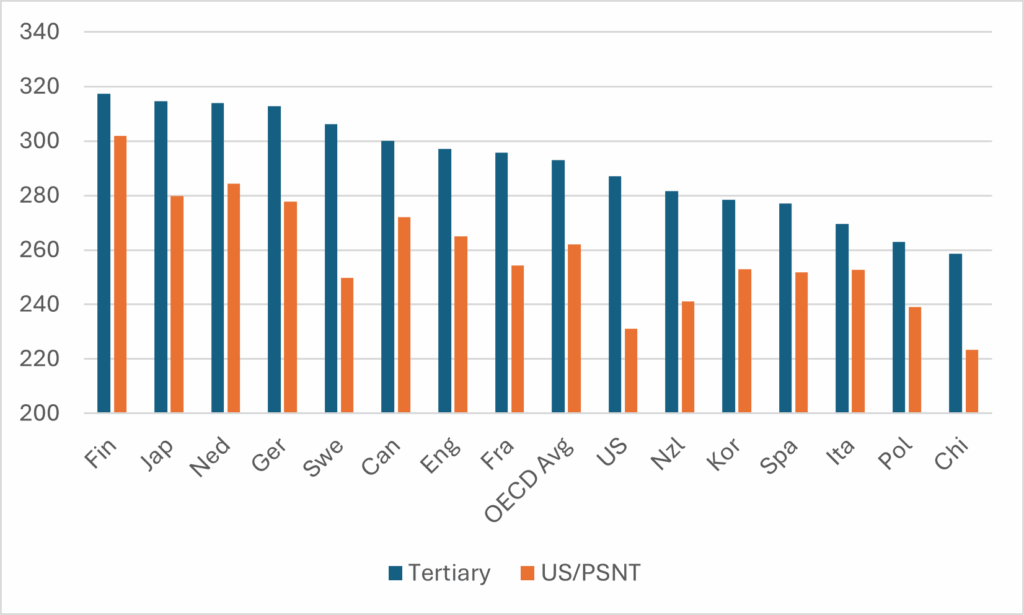
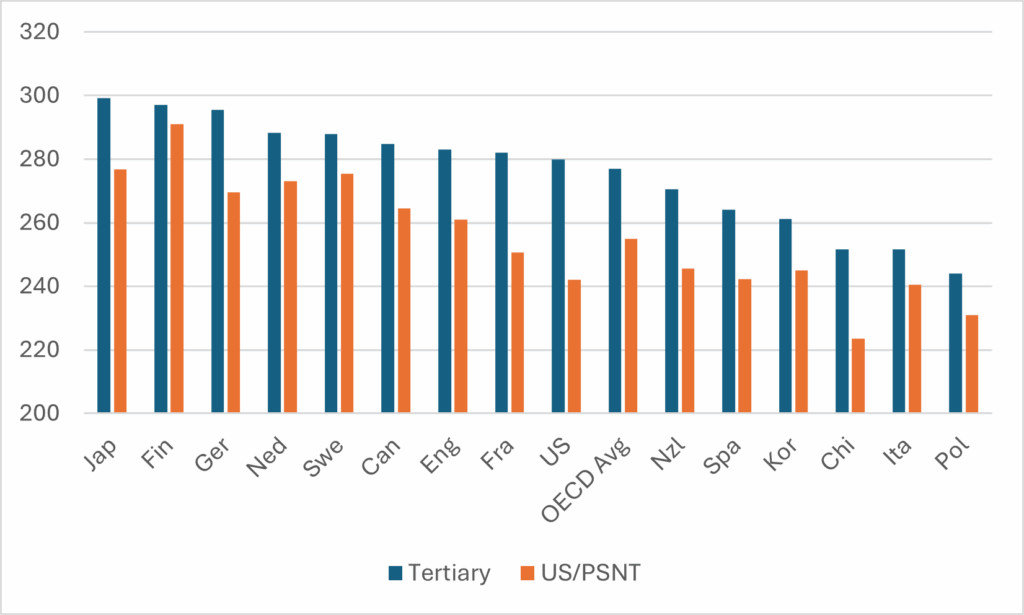
Speaking at the Labour Party conference, Secretary of State for Education Bridget Phillipson announced the (limited) return of student maintenance grants by the end of this Parliament:
I am announcing that this Labour government will introduce new targeted maintenance grants for students who need them most. Their time at college or university should be spent learning or training, not working every hour god sends.
As further details emerged, it became clear that these would be specifically targeted to students from low-income households who were studying courses within the same list of “government priority” subject areas mentioned in plans for the lifelong learning entitlement. As a reminder these are:
- computing
- engineering
- architecture, building & planning (excluding landscape gardening)
- physics & astronomy
- mathematical sciences
- nursing & midwifery
- allied health
- chemistry
- economics
- health & social care
These additional grants will be funded with income from the proposed levy on international student fees, of which little is known outside of the fact that the immigration white paper’s annex contained modelling of its effects were it to be set at six per cent of international student fee income. The international student levy will apply to England only.
There will be further details on the way the new grants will work, and on the detail of the levy, in the Autumn Statement on 26 November. This is what we know so far – everything else is based on speculation.
Eligibility
A whole range of questions surround the announcement.
How disadvantaged will a student have to be – and will it be based on family income in the same way that the current system is? Imagine if entitlement was set at below the current threshold for the maximum loan – disadvantaged enough to get the full loan, not enough for a grant.
If it’s set anywhere near the current threshold – £25,000 residual family income since 2007 – there’s a lot of “disadvantage” going on above that figure. If it’s set above that figure, that will beg the question – why assume a parental contribution in the main loan part of the scheme?
Will it be on top of, or simply displace some of the existing loan? If it’s the latter, that won’t help with day to day costs, and as the Augar review noted – those from the most disadvantaged backgrounds are least likely to pay back in full anyway, which would make the “grant” more of a debt-relief scam.
The distribution in the apparent hypothecation will be fascinating. It does mean that international students studying at English universities will be funding grants for English domiciled students wherever they are studying. Will devolved nations now follow suit?
If international student recruitment falls, will that mean that the amount of money available for disadvantaged student grants falls too or is the Treasury willing to agree a fixed amount for the grants that doesn’t change?
Restricting grants to those on the lowest incomes does mean that the government intends to relieve student poverty for some but not others, based on course choice. Will that shift behaviour – on the part of students and universities – in problematic ways?
With the LLE on the way, will grants be chunked up and down by credit? See Jim’s piece from the weekend on the problematic incentives that this would create.
The hypothecation also raises real moral questions about international student hardship being exacerbated to fund home student hardship relief – if, as many will do, universities put fees up to cover the cost of the levy. The possibility of real resentment from international students, who already know they’re propping up the costs of lower and subsidised fees, is significant.
For LLE modular tuition fee funding, under OfS quality proposals Bronze/Requires improvement universities will have to apply for their students to access it – they will need to demonstrate that there is a rationale for them doing IS-8 courses. Will that apply for these grants too?
Phillipson’s speech also referenced work– students’ time at college or university should be “spent learning or training, not working every hour god sends”. By coincidence, Jim worked up some numbers on how much “work” the current loan scheme funds earlier. Whether we’ll get numbers from Phillipson on what she thinks “every hour god sends” means in practice, and how many hours she thinks students should be learning or training for, remains to be seen.
We might also assume that the grant won’t be increased for those in London, and reduced for studying at home in the way that the maintenance loan is now. And if this is all we’re going to get in the way of student finance reform, all of the other myriad problems with the system may not get touched either.
The levy
There’s a certain redistributive logic in using tuition fee income from very prestigious universities to support learners at FE colleges or local providers, though it is unlikely that university senior managers will see it in quite those terms.
A six per cent levy on international fee income in England for the 2023–24 financial year would have yielded around £620m, with half of that coming from the 20 English providers in the Russell Group. Of course, this doesn’t mean that half of all international students are at the Russell Group – it means that they are able to charge higher tuition fees to the international students they do recruit.
[Full screen]
Of course, the levy applies to all providers – and, as we saw back when the idea was first floated there are some outside of the Russell Group that see significant parts of their income come from international fees, and would see their overall financial sustainability adversely affected by the levy. In the main these tend to be smaller specialist providers, but there are some larger modern universities too. Some universities don’t even have undergraduate students, but will still see their fees top-sliced to fund undergraduate-level grants elsewhere.
[Full screen]
There has been a concerted lobbying effort by various university groups aimed at getting the government to abandon the levy plan – as it appears that this effort has failed you would expect the conversations to turn to ensuring the levy is not introduced at six per cent as the Home Office previously modelled, or mitigating its impact for some or all providers. Certainly, as Phillipson chose the same speech to remind us she had taken “the decisive steps we needed on university finances” it would feel like it is not her intention to add to the woes of higher education providers that are genuinely struggling.
DfE has said that the new grants will be “fully funded” by an international student levy. It’s worth noting that this is not the same as saying that all the levy money will go towards the grants.The tie between the grants and the levy is politically rather astute – it will be very difficult for Labour backbenchers to argue against grants for students on low income, even if they are committed to making arguments in the interests of their local university. But legislatively, establishing a ring fence that ensures the levy only pays for these grants will be very difficult – other parts of government will have their eye on this new income, and the Treasury is famously very resistant to ringfencing money that comes in.
It also opens up the idea of the government specifically taxing higher education with targeted levies. It is notable that there has been no indication that the levy will be charged on private school fees, or fees paid to English language colleges, where these are paid by non-resident students. DfE itself suggests that £980m of international fees go to schools, and a further £850m goes to English language training – why leave a certain percentage of that on the table when it can be used to support disadvantaged young people in skills training?
What would it achieve?
In the end, even grants at the maximum level of £3,000 a year that were recommended by the Augar review wouldn’t have made much difference to student poverty, and there’s been a lot of inflation since.
And a part of the idea of the levy was to reduce (albeit slightly) the number of study visas granted – if you recall, the Home Office report emerged in a month that everyone became concerned about students claiming asylum. If that part of the plan works (if that was ever really the plan, rather than a fortunate coincidence) then surely there would be less money to play with for maintenance – and any future government that attempts to reduce international higher education recruitment would be accused of taking the grants away from working class students on priority courses?
The real value in the reintroduction of the grant is that it is politically totemic for Labour. But if it encourages more disadvantaged students to go into HE because of a perception of better affordability when they will still struggle, there will be both a financial and political cost in the long term.