Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
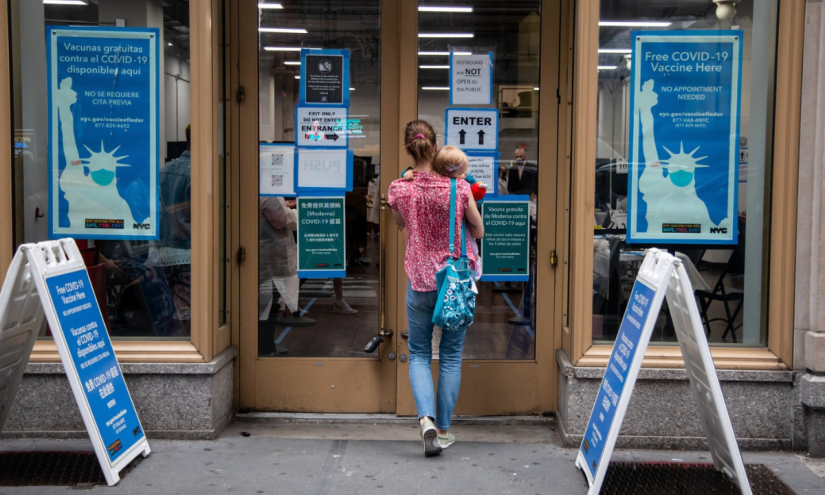
The federal government’s latest guidelines for COVID-19 vaccines make it difficult to know who, exactly, will be able to access shots this fall. While Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. and some of his staff claim anyone will be able to access a shot in consultation with their doctor, medical groups are warning that the new guidance will impact a broad swath of people, including postpartum people and healthy children.
“For children and young adults that I see, there are constraints, and they are significant,” said Dr. Molly O’Shea, a pediatrician in Michigan and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP).
It might also take several more weeks to know who will be able to receive no-cost COVID-19 vaccines covered by health insurance. That decision partly depends on formal recommendations from a vaccine panel that isn’t scheduled to meet until mid-September.
Actions by the Food and Drug Administration last week mean that none of the COVID-19 vaccines that are slated to be on the U.S. market this fall will have an emergency use authorization that had allowed their quick (yet still rigorously tested) approval at the height of the pandemic. The removal of this designation means the drug company Pfizer will no longer offer COVID-19 vaccines to very young children, limiting parents’ brand options and potentially impacting supply.
Moderna, Pfizer and Novavax, the three main COVID-19 vaccine manufacturers, have all shared news releases about what they’ve been approved to offer:
- Moderna, Pfizer or Novavax will offer shots to anyone who is 65 and older, irrespective of medical history.
- Pfizer will offer shots to anyone between the ages of five and 64 if they have at least one underlying condition that puts them at high risk for severe outcomes from COVID-19.
- Moderna will offer shots to anyone between six months and 64 if they have at least one underlying condition that puts them at high risk for severe outcomes from COVID-19.
- Novavax, the only company providing a non-mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, will offer shots to anyone between 12 and 64 if they have at least one underlying condition that puts them at high risk for severe outcomes from COVID-19.
The vaccine panel known as the Advisory Committee for Immunization Practices (ACIP) is expected to make formal recommendations on these FDA-approved vaccines, and those recommendations have historically determined whether insurance providers will cover a vaccine at no cost under insurance.
An HHS spokesperson did not immediately respond to a request for information and comment from The 19th, but in a post on X, Kennedy said: “These vaccines are available for all patients who choose them after consulting with their doctors.” Separately, USA Today reported on a document from HHS stating the FDA’s actions do “not affect access to these vaccines for healthy individuals. These vaccines remain available to those who choose them in consultation with their healthcare provider.”
Dr. Marty Makary, FDA commissioner, added in a separate X post: “100% of adults in this country can still get the vaccine if they choose. We are not limiting availability to anyone.”
But what that means practically for everyday people who want to access a COVID-19 shot — everything from whether their doctor will prescribe it, or if a pharmacy will be able to administer it, and whether there will be an out-of-pocket cost — is unclear for now.
How will it impact postpartum people?
Pregnant people are expected to still have access to the vaccine because the CDC continues to list pregnancy as an underlying condition that puts an individual at high risk for severe outcomes from COVID-19. (The list of at least two dozen conditions also includes chronic health conditions and immunocompromised conditions.)
But Kennedy, who has repeatedly questioned the safety of COVID-19 vaccines despite research that shows their effectiveness, announced in May that the CDC would no longer formally recommend such vaccines to pregnant people and healthy children, a move that seemed to contradict his own department.
Lactating and postpartum individuals must have an underlying medical condition to be eligible for one of the FDA’s approved vaccines, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG)’s understanding of the announcement. ACOG continues to recommend COVID-19 vaccination to people who are contemplating pregnancy, are pregnant, were recently pregnant or are now lactating.
“We recognize that now, disappointingly, only lactating and postpartum individuals with an underlying condition will be eligible for vaccination. Still, it remains critical that pregnant patients receive the vaccines so that they are able to provide passive immunity from COVID-19 to their infants in those first few months of life before they can be vaccinated,” said ACOG President Steven J. Fleischman in an email.
How will it impact healthy children?
Healthy children will likely still be able to access the COVID vaccine, but the cost for a parent or guardian, as well as availability, will be impacted by these decisions.
Charlotte A. Moser, co-director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said parents who want to get their kids the COVID-19 vaccine should still be able to do so through what is called shared clinical decision-making in consultation with their child’s health care provider, according to the CDC’s current vaccine schedule. But it’s unclear whether this will change when ACIP meets again.
But physicians who prescribe a COVID-19 vaccine outside of the parameters of how the FDA approved them would be OKing use of the shot “off-label” — a designation that means a medical product is being used outside of how the FDA approved it. That raises questions about access and cost. Physicians might not be willing to prescribe off-label because of concerns about liability.
“I think that there will be a substantially smaller number of pediatricians, pharmacies, etc., who will be comfortable taking that risk,” O’Shea said.
Dr. Dial Hewlett, medical director of tuberculosis services at Westchester County Department of Health in New York and a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America, said an off-label prescription might also not be covered by insurance.
“A mother or father can go in with their child and say, ‘I’d like for them to have the vaccine,’ but they may be told, ‘Well we’ll give it, but you’re going to have to pay $200,’” he said.
(Joseph Prezioso / AFP / Getty Images)
Depending on the circumstances, pharmacists may also not be able to provide off-label vaccines. Some states tie pharmacist immunization authority to FDA approval,which has the potential to create a hodgepodge of access. The New York Times reported that CVS and Walgreens, the country’s largest pharmacy chains, have begun restricting COVID-19 shots in some states to people with a prescription.
“There may be some variability from state to state, but it’s a big barrier if FDA approval is not there, and the FDA approvals have been pulled back from where they were previously,” Hewlett said.
The FDA announcement is “concerning,” added Moser, who noted that limiting Pfizer’s vaccine will make it more difficult for all children to get a COVID-19 vaccine this year because of anticipated supply limitations.
O’Shea, the pediatrician in Michigan, said her office is currently deciding how many COVID-19 shots to stock, and it’s proving tricky as they weigh the cost vs. demand — the percentage of children under 18 getting the shot is under 15 percent.
“Figuring out how much we want to have at any one time, and how we are going to give it to people — this really makes it a lot more complicated,” she said.
What happens next?
Moser said the announcement adds confusion for providers and families, and noted that the unilateral approach by Kennedy so far when it comes to vaccine policy “removes hundreds of voices of clinicians and scientists that were part of the process.” Moser recently served on ACIP and is among the members that Kennedy removed. He has replaced the panel with people who do not have relevant experience.
“That army of voices ensured a process informed by clinical experience and scientific expertise to which the small group making these decisions now cannot possibly compare,” she said in an email.
The revamped ACIP panel is scheduled to meet over two days beginning on September 18. Republican Sen. Bill Cassidy, a doctor who is chair of the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions (HELP) Committee, is now questioning whether that panel has enough legitimacy to meet, especially amid a leadership shakeup at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Serious allegations have been made about the meeting agenda, membership, and lack of scientific process being followed for the now announced September ACIP meeting,” he said in a statement. “These decisions directly impact children’s health and the meeting should not occur until significant oversight has been conducted. If the meeting proceeds, any recommendations made should be rejected as lacking legitimacy given the seriousness of the allegations and the current turmoil in CDC leadership.”
AAP called Kennedy’s latest COVID guidelines “deeply troubling” and urged COVID vaccine decision-making to remain between medical experts and families.
Dr. Susan J. Kressly, president of AAP, said in a statement that any barrier to COVID-19 vaccination as the nation enters the respiratory virus season creates “a dangerous vulnerability for children and their families.”
“Any parent who wants their child vaccinated should have access to this vaccine,” she said, adding that HHS’ action “not only prevents this option for many families, but adds further confusion and stress for parents trying to make the best choices for their children.”
This story was originally reported by Barbara Rodriguez of The 19th. Meet Barbara and read more of their reporting on gender, politics and policy.

Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter