Digital transformation has become essential for educational institutions navigating budget pressures, evolving compliance demands, and rising expectations from students and staff. But for many universities and TAFEs, ERP projects have been slow, costly, and difficult to deliver.
This article explores how the SaaS+ delivery model from TechnologyOne is helping education providers unlock faster and better results with a delivery approach designed for the sector, not just the software.
The sector needs change and certainty
Why education providers can’t afford risk
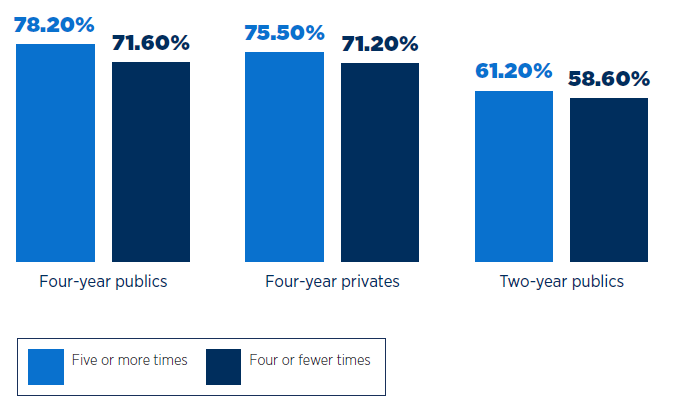
Australian universities and TAFEs face growing pressure to modernise outdated systems while maintaining tight budgets and resource control. Finance, HR, and administrative teams are expected to do more with less, managing complex funding models and ensuring seamless student and staff experiences, all while staying compliant with evolving regulations.
Yet, many ERP projects still fall short. Long timelines, shifting scopes, and many other challenges have led to cost blowouts, underwhelming outcomes, and internal fatigue from staff caught in the crossfire.
Uncertainty isn’t just inconvenient in a sector where every dollar and every hour matters. It’s unsustainable.
For transformation to succeed, education providers need more than a product. They need a clear path to results: one that simplifies complexity and removes unnecessary risk from the equation.
Enter SaaS+: One platform. One price. One trusted partner.
What is SaaS+ and why is it different?
SaaS+ is TechnologyOne’s delivery model for enterprise software, and it turns the traditional ERP experience on its head.
Instead of relying on multiple vendors, consultants, and unpredictable timelines, SaaS+ delivers everything under one roof: software, implementation, support, and ongoing success – all covered by a single annual fee.
It’s a complete, end-to-end model that takes the risk out of transformation and puts control back in the hands of the institution.
SaaS+ is also underpinned by preconfigured solutions built specifically for education. That means less time spent reinventing the wheel and more time focusing on the outcomes that matter – better student experiences, smarter financial decisions, and more efficient operations across the board.
Education outcomes, not IT projects
Proven success from sector leaders
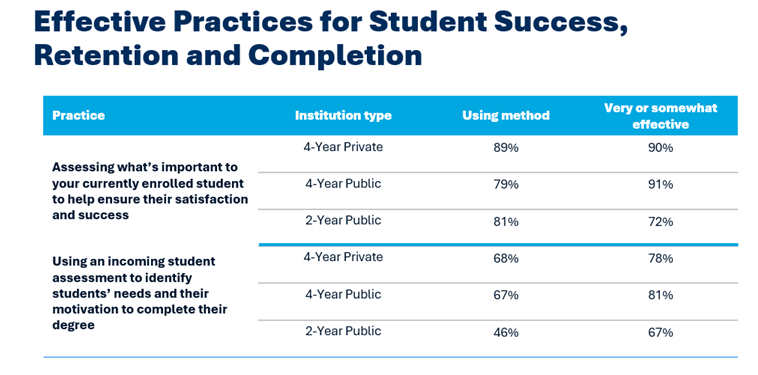
For many institutions, traditional ERP projects have become more about navigating implementation than achieving real change. SaaS+ shifts the focus back to what matters: delivering better outcomes for students, staff, and the broader education community.
Institutions like Victoria University and TasTAFE, for example, have recently embraced TechnologyOne’s SaaS+ model to modernise systems, streamline administration, and refocus their resources on delivering better student outcomes.
These institutions aren’t just upgrading software. They’re improving how they operate, how they serve their students, and how they plan for what’s next.
With SaaS+, success isn’t measured by go-live dates. It’s measured by the outcomes it enables.
Why buying Australian matters
When it comes to ERP, local knowledge isn’t a nice-to-have – it’s essential. From sector-specific compliance to the nuances of funding models, education providers in Australia operate in a unique regulatory and operational environment. Generic, global systems often fall short.
TechnologyOne is Australia’s only homegrown ERP provider, with more than 37 years of experience working alongside the country’s universities, TAFEs, and education departments. Our solutions are built, hosted, and supported locally, with a deep understanding of the sector’s needs embedded from day one.
Today, our software supports more than 6.5 million students across 150+ education institutions in Australia, New Zealand and the UK. That reach is built on local trust, not on a global scale.
Beyond the product itself, this local presence means faster support, tighter alignment with government and education standards, and a genuine partnership model. It also means every dollar invested stays in the region, supporting local jobs, innovation, and long-term capability in the sector.
Time to value, time to lead
A smarter path forward for transformation
SaaS+ is designed to accelerate results. With a preconfigured approach and a single point of accountability, it removes the friction and uncertainty that often slow traditional ERP rollouts. Faster implementations mean faster benefits, and more time to focus on the strategic goals that matter.
Whether it’s enabling more responsive finance and HR teams, supporting hybrid workforces, or improving how students interact with institutional services, SaaS+ helps education providers act with confidence and clarity.
Because when your systems work better, your people can too.
Explore how TechnologyOne’s OneEducation SaaS+ model is helping institutions across Australia lead the future of education.
Do you have an idea for a story?
Email [email protected]