

“No American President has ever before issued executive orders like the one at issue in this lawsuit . . . The instant case presents an unprecedented attack on . . . foundational principles. . . . Here, deciding what process was due to plaintiff is unnecessary, because no process was provided.” — Perkins Coie LLP v. Department of Justice (Dist. Ct., D.C., May 2)
“[T]he Court found that Ms. Rumeysa Ozturk has demonstrated a substantial claim of a violation of due process.” — Ozturk v. Hyde (Dist. Ct., VT, May 16)
“[T]his directive has a breathtaking sweep . . .” — Jenner & Block v. U.S. Dept. of Justice (Dist. Ct., D.C., May 23)
Maxim: #1: Vagueness and due process cannot coexist, at least not in any system of constitutional justice worthy of the name.
Maxim #2: The broader the law’s sweep, the greater the likelihood that it was designed to be arbitrarily punitive.
It is undeniable: Many of Donald Trump’s executive orders run wildly afoul of basic tenets of fairness. Time and again, he has ordered his subordinates to enforce orders that are shockingly vague and disturbingly broad. Both in their conception and execution, such orders patently violate the commands of the First, Fifth, and Fourteenth Amendments. And yet, the public and the courts are asked to countenance such abridgments of law in the name of unfettered executive prerogative.
Clarity and precision in lawmaking are fundamental to any system of justice. That call for clarity, which traces back at least to Roman law, finds expression in Montesquieu’s “Spirit of Laws” and William Blackstone’s “Commentaries on the Laws of England.” Laws must be “plainly and perspicuously penned,” is how Blackstone tagged it.
In “Federalist No. 62,” James Madison condemned those laws that were “incoherent that they cannot be understood.” The idea is rooted in basic fairness, in due process of law. Such a process is especially important in the First Amendment context.
Whether it be in executive orders directed at DEI practices, law firms, universities, libraries, or immigrants, among others, the basic problem of vagueness is the constitutional cancer present in all of them.
As Justice Thurgood Marshall made clear in 1972’s Grayned v. City of Rockford, vagueness offends fairness because (i) it provides no meaningful warning to ordinary persons as to “what is prohibited,” (ii) it provides no “explicit standards” to law enforcement officials, judges, and juries necessary to avoid “arbitrary and discriminatory application,” and (iii) vague laws chill protected speech insofar as the “boundaries of the forbidden areas [are not] clearly marked.”
Justice William Brennan explained the First Amendment importance of that principle in 1963’s NAACP v. Button: “Standards of permissible . . . vagueness are strict in the area of free expression. . . [I]n the area of First Amendment freedoms, the existence of a [vague mandate is] susceptible of sweeping and improper application.”
In the unconstitutional process, lawyers, scientists, librarians, universities, law firms and others are chilled into silence — and that is precisely the point.
The evils of vagueness, among other constitutional wrongs, were thoughtfully identified by federal district court Judge Adam B. Abelson in the recent Maryland District Court case National Association of Diversity Officers in Higher Education v. Trump. In relevant part, Judge Abelson began:
This Court remains of the view that Plaintiffs have shown a strong likelihood of success on the merits of their facial free speech and vagueness claims . . . The Challenged Provisions forbid government contractors and grantees from engaging in “equity-related” work and from “promoting DEI” in ways the administration may consider to violate antidiscrimination laws; they demand that the “private sector” “end . . . DEI” and threaten “strategic enforcement” to effectuate the “end[ing]” of “DEI”; and they threaten contractors and grantees with enforcement actions with the explicit purpose of “deter[ring]” such “programs or principles.”
Thereafter, he emphasized that the Court was
…deeply troubled that the Challenged Provisions, which constitute content-based, viewpoint-discriminatory restrictions on speech (in addition to conduct), have the inherent and ineluctable effect of silencing speech that has long been, and remains, protected by the First Amendment. And they do so through impermissibly vague directives that exacerbate the speech-chilling aspects of the Challenged Provisions.
To elucidate that point, he added:
Historically, the metaphor used to describe the effect of laws that restrict speech is “chill.” The more apt metaphor here is “extinguish.” Part of the explicit purpose and effect of the Challenged Provisions is to stifle debate — to silence selected viewpoints, selected discourse — on matters of public concern. They forbid government contractors and grantees from engaging in discourse — including speech such as teaching, conferences, writing, speaking, etc. — if that discourse is “related” to “equity. ” And they direct the “private sector” to “end” diversity, to “end” equity, and to “end” inclusion. See J21 Order § 4(b) (directing agencies to “encourage the private sector to end . . . DEI”). “End” is not a mere “chill.” “Deter[rence]” is not a side-effect of the Challenged Provisions; their explicit goal is to “deter” not only “programs” but “principles” — i.e. ideas, concepts, and values. After all, the opposite of inclusion is exclusion; the opposite of equity is inequity; and, at least in some forms, the opposite of diversity is segregation.
Such are but some of the evils rooted in many of Trump’s executive orders. Those affronts to due process and First Amendment principles are so obvious as to render their design intentional (see “Trump’s ‘So what?’ stratagem,” FAN 470).
Trump’s Justice Department defends such lawlessness by procedural obfuscation coupled with political rhetoric and claims of unrestrained executive prerogative. When that fails they take cover by being evasive, as revealed in oral arguments in the Second Circuit case of Ozturk v. Hyde:
The appeals court judges pushed . . . [Department of Justice attorney Drew] Ensign on whether or not the Trump administration believed that both students’ speech was lawful speech.
“We have not taken a position on that,” Ensign told the panel of three judges, saying concerns over where the students’ cases should be heard were more important.
“Help my thinking along,” Judge Barrington D. Parker then said. “Take a position.”
“Your honor, I don’t have authority to take a position on that right now,” Ensign replied.

In the unconstitutional process, lawyers, scientists, librarians, universities, law firms and others are chilled into silence — and that is precisely the point.
Consider as well this from an article in The New York Times by Stephanie Saul:
The Trump administration is set to cancel the federal government’s remaining federal contracts with Harvard University — worth an estimated $100 million, according to a letter that is being sent to federal agencies on Tuesday. The May 27 letter [from the U.S. General Services Administration] also instructs agencies to “find alternative vendors” for future services.
The additional planned cuts, outlined in a draft of the letter obtained by The New York Times, represented what an administration official called a complete severance of the government’s longstanding business relationship with Harvard.
The letter is the latest example of the Trump administration’s determination to bring Harvard — arguably the country’s most elite and culturally dominant university — to its knees, by undermining its financial health and global influence. Since last month, the administration has frozen about $3.2 billion in grants and contracts with Harvard. And it has tried to halt the university’s ability to enroll international students.
Related
A new episode of the Academic Freedom Podcast has been released. The podcast is sponsored by the Academic Freedom Alliance and the Center for Academic Freedom and Free Speech at Yale Law School.
This episode features a conversation with Cass Sunstein, the Robert Walmsley University Professor at Harvard Law School and former administrator of the White House Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs. His recent working paper, ‘Our Money or Your Life!’ Higher Education and the First Amendment,’ explores the First Amendment constraints on federal funding to American universities.
In the last few weeks, the Trump administration has made several announcements that it is withholding a significant amount of federal funds from specific universities, notably Columbia University and Harvard University, and that those funds will not be released until those universities comply with a set of demands. Harvard received a letter on April 11 demanding changes in Harvard’s governance, faculty hiring practices, student admissions practices, viewpoint diversity among the faculty, and student disciplinary policies, among other things. On May 5, the Secretary of Education sent a letter to Harvard informing the university that the federal government will award it no grants for scholarly research in the future. Reportedly, there is more than $2 billion dollars at stake.
On the podcast we talk through what the Trump administration is doing, what the consequences are for Harvard and other affected universities, and what constitutional issues are raised by the administration’s actions in denying Harvard access to federal research funds. In the process, we get a short course on First Amendment doctrine relating to viewpoint discrimination and unconstitutional conditions.

“He has . . . abandoned the FCC’s posture as an independent regulator in favor of an openly personal embrace of Trump.”
Four months into his tenure as head of America’s top communications regulator, Brendan Carr appears to be running a Trumpian playbook to transform a long-independent agency.
Immediately after being promoted by President Donald Trump to chair the Federal Communications Commission, on Jan. 20, Carr launched investigations into top media companies, including NPR, PBS and Comcast.
Related
This past Monday the Supreme Court denied review (7-2) in L.M. v. Town of Middleborough. The issue raised in that case was whether school officials may presume substantial disruption or a violation of the rights of others from a student’s silent, passive, and untargeted ideological speech simply because that speech relates to matters of personal identity, even when the speech responds to the school’s opposing views, actions, or policies.
Summary of facts: “In this case, L.M.’s [middle] school prohibited him from wearing a non-obscene, non-vulgar shirt stating, ‘There Are Only Two Genders,’ because the message ‘would cause students in the LGBTQ+ community to feel unsafe.’. The school even banned him from wearing the same shirt on which he covered the words ‘Only Two’ with a piece of tape on which he wrote “CENSORED” so that the message read, ‘There Are [CENSORED] Genders.’”
The petition had been distributed for conference twelve times.
Justice Clarence Thomas wrote a dissent. Justice Samuel Alito also wrote a separate dissent, which in part read:
This case presents an issue of great importance for our Nation’s youth: whether public schools may suppress student speech either because it expresses a viewpoint that the school disfavors or because of vague concerns about the likely effect of the speech on the school atmosphere or on students who find the speech offensive. In this case, a middle school permitted and indeed encouraged student expression endorsing the view that there are many genders. But when L. M., a seventh grader, wore a t-shirt that said “There Are Only Two Genders,” he was barred from attending class. And when he protested this censorship by blocking out the words “Only Two” and substituting “CENSORED,” the school prohibited that shirt as well.
The First Circuit held that the school did not violate L. M.’s free-speech rights. It held that the general prohibition against viewpoint-based censorship does not apply to public schools. And it employed a vague, permissive, and jargon-laden rule that departed from the standard this Court adopted in Tinker v. Des Moines Independent Community School Dist., 393 U. S. 503 (1969).
The FBI will launch new probes into the 2023 discovery of cocaine at the White House during President Joe Biden’s term and the 2022 leak of the Supreme Court’s draft opinion overturning Roe v. Wade, a top official announced on Monday. Dan Bongino, a rightwing podcaster-turned-FBI deputy director, made the announcement on X, saying that he had requested weekly briefings on the cases’ progress. . . .

“[M]y reaction to everything that Trump is doing, and I agree almost across the board with his substantive aims whether it’s with regards to the universities, whether it’s regards to immigration, is what would we feel if the democratic administrations were doing this exact same thing in favor of their values? Everything we’re doing sets a precedent. Again, I acknowledge the precedent has already been set. . . . I’m still very nervous about the government using power because even though I’m not deeply libertarian, I do think that the hope of a neutral arbiter of a government that is restrained by rules that are content-free that are politics-free is one of the biggest yearnings of humanity, at least in the west.” — Heather Mac Donald
Heather Mac Donald discusses the Trump administration’s free speech record amidst its battles with higher ed, mainstream media, law firms, and more.
Mac Donald is a Thomas W. Smith Fellow at the Manhattan Institute. Her most recent book is “When race trumps merit: How the pursuit of equity sacrifices excellence, destroys beauty, and threatens lives.”
Related
Cases decided
Review granted
Pending petitions
Petitions denied
Emergency Applications
Free speech related
Last scheduled FAN
This article is part of First Amendment News, an editorially independent publication edited by Ronald K. L. Collins and hosted by FIRE as part of our mission to educate the public about First Amendment issues. The opinions expressed are those of the article’s author(s) and may not reflect the opinions of FIRE.

In a world obsessed with TikTok trends and digital ad spends, it’s easy to overlook the humble email. Yet, email marketing for universities and other higher educational institutions isn’t just surviving, it’s thriving.
While newer platforms grab headlines, email continues to deliver results where it matters most: student recruitment. In fact, email engagement has surged by a staggering 78% in recent years. That’s a clear signal: email is not just relevant, it’s essential.
Email remains one of the most powerful channels in higher education marketing, and for good reason. By the end of 2025, global email users are projected to reach 4.6 billion, with over 376 billion emails sent daily.
The ROI speaks for itself: email marketing returns around $36 for every $1 spent, outshining many other channels. Here’s the surprising part. Students want your emails. In a recent survey, more than 68% of students prefer to receive content via email from higher-ed institutions.
But many schools are still doing it wrong. They send the same message to every contact, ignore personalization, and fail to align emails with the student journey. The result? Missed opportunities and low conversions.
This guide will walk you through how to craft student-first, high-converting email campaigns, from audience research to measuring real impact. Ready to turn your inbox into an enrollment engine? Let’s dive in.
Let’s start from the very beginning. What is educational marketing? Educational marketing refers to the strategies and tactics used by schools, colleges, and universities to attract, engage, and enroll students. It includes campaigns across digital channels like email, social media, SEO, and paid ads to promote programs and build institutional brand awareness.
From there, we move on to the big question: Is email still relevant in 2025? Absolutely. In fact, 69% of education marketers say email provides a good to excellent ROI, outperforming heavy hitters like social media (55%), display ads (19%), and even SEO (46%).
Why is that?
Because email does three things exceptionally well. It provides a direct line to decision-makers, allows for scalable personalization, and supports long-term engagement without burning through your budget.
But, and this is key, many schools still aren’t tapping into its full potential. Too often, the same message is sent to everyone, without clearly defined audience profiles to guide the way. That’s where opportunity lives, for those willing to do it right.
Let’s talk about what separates forgettable campaigns from unforgettable ones.
It starts with understanding your audience, not just broadly, but deeply. This is where student personas come into play.
Meet Sophie.
She’s a 30-something international career professional with 3–7 years of experience. Sophie is exploring MBA programs and micro-credentials, driven by career advancement and global networking opportunities. She’s ROI-conscious, skeptical about short courses, and likely found your school via Instagram or Google.
See the difference?
When you write with Sophie in mind, you’re not just blasting content, you’re building trust. She wants to know your credentials are legit. She’s inspired by student success stories. She’s curious about cultural experiences.
So instead of saying, “Join our business program,” try, “Boost your global career with accredited micro-credentials and a community that spans five continents.” Now that’s an email that connects. Now that we’ve seen what a well-developed persona looks like, let’s explore how to apply this kind of insight through segmentation.
Example: McMaster University’s Continuing Education division’s persona-based email drip campaigns for lead nurturing show how each email is tailored to a persona (e.g. career changers in Project Management or Applied Clinical Research) with personalized greetings (“Hi {{FirstName}}”) and program-specific content.


Source: McMaster University
Different students have different interests and needs, so your university email campaign should too.
By dividing your email list into meaningful groups (or “segments”), you can send each group content that truly matters to them. The result? Dramatically better performance.
For instance, marketers have seen a staggering 760% increase in email revenue from segmented campaigns. Campaign Monitor also found that segmented education campaigns can achieve open rates around 18%, far above the industry average. Clearly, segmentation isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s a game-changer.
How to segment effectively? Think about the factors that distinguish your prospective students. Common segmentation angles in higher ed include:
Segmenting your list by criteria like these ensures each student gets content that speaks to their specific situation. As a result, your emails feel more relevant, and relevance drives results.
Example: The Cut Design Academy launched a promotional recruitment email targeting prospective students for its January 2025 Makeup Artistry Certificate intake. The campaign focused on driving immediate applications from students close to the decision stage, offering a limited-time tuition discount to accelerate conversions. Framed around an exclusive offer, the email used urgency, clear benefits, and student-focused messaging to stand out. The campaign leveraged personalization through tone (“Dear creative mind”) and clear calls to action, guiding prospects from interest to enrollment with stage-aligned messaging.
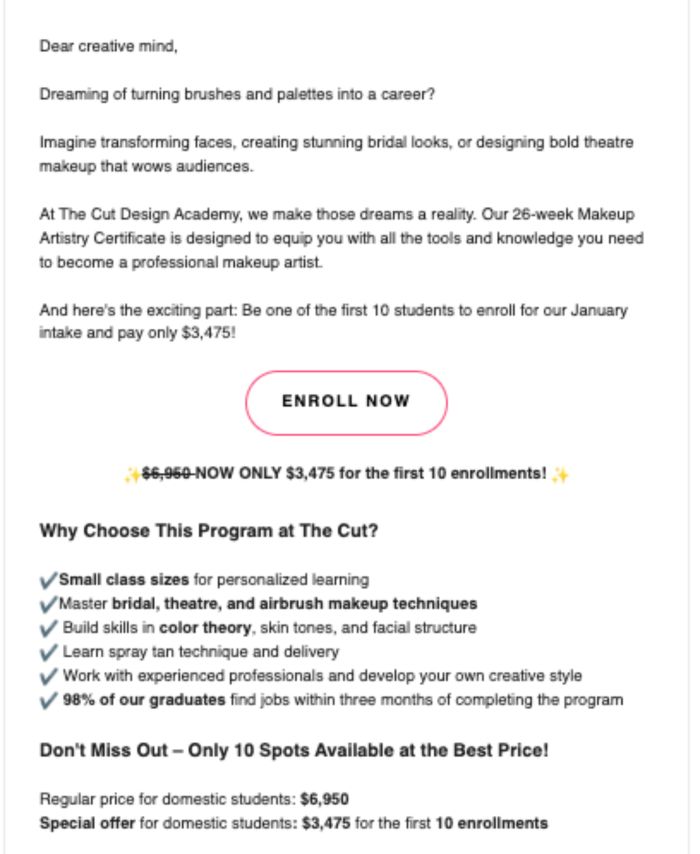

Source: The Cut Design Academy
Segmented emails consistently outperform generic blasts, leading to stronger engagement, greater relevance, and improved results across the board. Marketers find that tailoring messages to specific audience groups makes campaigns more effective and impactful. The bottom line? When you embrace the diversity of your audience and tailor your messaging accordingly, they’ll reward you with higher engagement.
Let’s say you have a student interested in your Executive MBA. They’ve clicked on emails but haven’t registered for an event. You wouldn’t send them the same message as a high school student in Colombia interested in ESL.
Now add personalization on top. If segmentation is about who you’re writing to, personalization is about what and how you communicate to each person. Today’s prospective students expect a personalized touch, and they respond when they get it.
Here’s why: Research shows that emails with personalized content have a 29% higher open rate and a 41% higher click-through rate than non-personalized emails. Simply put, personalization grabs attention. It signals to the student that “this is about you,” cutting through the clutter of impersonal mass communications.
Personalization can be as simple as using the student’s first name in the greeting or subject line – emails with a personalized subject are 29% more likely to be opened, according to Experian. But it goes much deeper than that. Effective enrollment emails often incorporate personal details like the student’s intended major, specific interests, or past interactions.
An EAB survey in 2024 found that 93% of students said receiving a personalized message from a college would encourage them to explore that school further.
That’s an overwhelming majority who are more likely to engage simply because your email spoke directly to their interests or concerns. 71% of students expect personalized interactions from brands (including universities), and 76% get frustrated when they don’t get them. The message is clear: personalization isn’t just a nice touch; it’s expected.
Example: This email from London Business School (LBS), addressed personally to the recipient (“Conor, come and meet some of the people that make LBS unique”), exemplifies effective personalization (using the student’s name and regional relevance) and event-based drip sequencing, reinforcing LBS’s presence and availability as the student prepares to make a decision.


Source: London Business School
So, how can you infuse personalization into your campaigns? Here are a few proven tactics (think of these as the “little things” that yield big results):
In a nutshell, how do you develop a marketing strategy for a university? Start by defining clear goals (e.g., increase applications or improve yield), identify target audiences using personas, choose the right channels (email, social, SEO), create tailored content for each stage of the student journey, and measure results regularly to optimize performance.
A student’s path from curiosity to commitment isn’t linear. Your email marketing strategy shouldn’t be either.
This is your digital handshake. Send welcome emails that reflect your institution’s voice: professional, warm, and resourceful. Keep it brief and include CTAs to helpful blog posts, reports, or program videos. The goal here? Spark interest and build trust.
Example: Algonquin College initiated a welcome email campaign targeting newly inquiring students, aimed at supporting the awareness stage of the enrollment funnel. This automated email is sent immediately after a student checks out a program or completes an inquiry form, making it a textbook example of an early-stage drip campaign designed to keep the college top-of-mind and help prospects begin their research journey.


Source: Algonquin College
Now that they’re paying attention, it’s time to educate. Share program benefits, tuition details, and testimonials. Even better, offer personalized interaction, like a Q&A session with advisors. Emails at this stage become your student’s research partner.
Example: Miami Ad School implemented a direct and informative follow-up email targeting prospective students who had expressed prior interest in one of its portfolio programs. The message used light personalization and concise formatting to clearly lay out the next steps for engagement. This email served as an early-stage consideration touchpoint designed to convert inquiry-stage leads into applicants.


Source: Miami Ad School
Here’s where the magic happens, or it doesn’t. Use emails to overcome last-minute doubts, emphasize application deadlines, and make it ridiculously easy to act. Offer a call with an advisor. Include direct application links. This is where you close the loop.
Don’t stop now. Once students say “yes,” keep the momentum going. Celebrate with a warm welcome, then guide them through the next steps: registration links, orientation videos, and community invites. Make them feel like part of something exciting.
So what does a high-converting email actually look like?
Example:
[Alex], Your Journey to an International Career Starts Here
Even the best content won’t help if it lands in the junk folder. Avoid spam triggers (like “FREE!!!”). Keep your database clean, and follow laws like CAN-SPAM (US), CASL (Canada), and PECR (UK). And yes, always include that unsubscribe link; it builds trust.
Fun fact: The average inbox placement rate is 83%, so there’s room to optimize.
Think of a drip campaign as a well-timed sequence of nudges. It starts with a thank-you or auto-response after form submission.
Then, over days or weeks, you send emails that deepen interest, event invites, alumni success stories, or a reminder to complete an application. Every email has a purpose. Every message moves the needle.
If you’re only looking at open rates, you’re missing the bigger picture.
Here’s a smarter approach:
The data doesn’t lie. HEM’s insights show that most student bookings happen only after a lead is nurtured, sometimes weeks after their first touchpoint.
We’ve covered a lot of ground, and you might be thinking, “How do I implement all of this?” The key is to view these strategies not as isolated tactics, but as complementary pieces of a holistic email marketing plan.
Segmentation gives you the framework (who gets what), personalization adds the special sauce (making content relevant to each individual), drip campaigns provide the delivery engine (timing and automation), mobile optimization ensures your efforts actually get seen on students’ preferred devices, and enrollment-stage alignment keeps your messaging strategy coherent from start to finish.
Each strategy is powerful on its own, but together they truly transform your email marketing from a simple broadcast tool into an engaging, research-backed recruitment machine.
You’ll be speaking to the right student with the right message at the right time – and that’s a recipe for higher open rates, click-throughs, and conversion to applications and enrollments. Just ask the institutions we discussed: they’ve seen application surges, increased yield, and record enrollments by putting these principles into practice.
To recap, how can colleges increase enrollment? Colleges can boost enrollment by improving lead nurturing (e.g., drip email campaigns), enhancing website conversion, offering personalized communication, streamlining the application process, and using data to better target and engage prospective students.
Done right, email isn’t just part of your marketing mix. It’s the glue that holds your enrollment strategy together.
Question: What is educational marketing?
Answer: Educational marketing refers to the strategies and tactics used by schools, colleges, and universities to attract, engage, and enroll students. It includes campaigns across digital channels like email, social media, SEO, and paid ads to promote programs and build institutional brand awareness.
Question: How do you develop a marketing strategy for a university?
Answer: Start by defining clear goals (e.g., increase applications or improve yield), identify target audiences using personas, choose the right channels (email, social, SEO), create tailored content for each stage of the student journey, and measure results regularly to optimize performance.
Question: How can colleges increase enrollment?
Answer: Colleges can boost enrollment by improving lead nurturing (e.g., drip email campaigns), enhancing website conversion, offering personalized communication, streamlining the application process, and using data to better target and engage prospective students.

This essay was originally published in The Hill on May 8, 2025.
From free speech rights and desegregation to gun rights and religious freedoms, civil rights litigation has long been a cornerstone of personal liberty in America. But in February, the Supreme Court issued an opinion that will make it harder for us as Americans to vindicate our constitutional rights when the government violates them.
In Lackey v. Stinnie, a group of Virginia drivers challenged a state law that punished people for failing to pay court fees by automatically suspending their driver’s licenses. The plaintiffs secured a preliminary injunction — a court order issued early in a case to prevent potential harm while it is litigated in full — allowing them to keep their licenses. Virginia did not appeal that ruling, and before the case went to trial, the legislature changed the law and reinstated any licenses that had been suspended under it.
In cases alleging violations of constitutional rights, a federal statute preempts the general rule that litigants pay their own fees and costs by allowing “prevailing” parties to recover attorney’s fees from the government actor who violated their rights. But in this case, the federal district court held the drivers had not in fact “prevailed” given that the case did not progress to a final conclusion, making them ineligible to recover attorney’s fees. This flew in the face of what courts and litigators had understood the law to be for decades.
The case eventually made its way to the Supreme Court to determine what “prevailing” meant in federal law and whether the drivers were entitled to reimbursement. The court, to the disappointment of advocates for civil rights and liberties, held that plaintiffs who do not obtain a final judgment on the merits do not qualify as “prevailing” even if, as with the Virginia drivers, they prevail in getting the government to change the law.
Unlike corporate litigation, civil rights cases rarely involve large financial recoveries. In any event, plaintiffs often seek changes to laws or policies rather than monetary gain. Yet these are vital cases, not just for the individuals involved but for the communities they represent, even if they rarely provide enough financial incentive to make private representation feasible — unless attorneys receive compensation after winning the case.
Congress intended to encourage civil rights litigation by tying fee awards to success, whether through final judgments or preliminary relief. The House Judiciary Committee report on the legislation enacting the attorney’s fees provision noted, “a defendant might voluntarily cease the unlawful practice. A court should still award fees even though it might conclude … that no formal relief, such as an injunction, is needed.” Despite this clear evidence of congressional intent, the court held otherwise.
Importantly, as the court pointed out, Congress has the power to clarify in the statute that attorney’s fees can be awarded before a final judgement on the merits. Congress must do so.
The breadth of amicus briefs submitted in this case — from the ACLU to the Alliance Defending Freedom to the Firearms Policy Coalition — demonstrates that across the ideological spectrum, organizations recognize the critical role awarding attorney’s fees plays in civil rights litigation.
As FIRE noted in its amicus brief to the Supreme Court, “Withholding attorney’s fees from victims of these First Amendment violations would be devastating — not just for them individually, but for access to justice more broadly.”
Congress must enact a simple, clarifying change that will have broad support and ensure all Americans can vindicate their constitutional rights. Justice isn’t free, but we can ensure it remains accessible to all.

The focus of these articles was corruption, fraud and scandal in the Los Angeles Community College District, primarily at Los Angeles Valley College’s Media Arts Department.
A few of these articles summarized.
Erika Endrijonas faces new questions in LACCD fraud | May 2, 2023 |
Pasadena City College President-Superintendent Erika Endrijonas being fired from the institution and trying to get a job at Santa Barbara City College, Mt. SAC, and Los Angeles City College. Endrijonas had been subjected to a vote of no confidence by the Pasadena Academic Senate, Pasadena Full-Time Faculty Union, protests by Part-Time Faculty, and finally the vote to reduce her contract by the newly elected board of trustees.
The article dived into Endrijonas’s tenure at her previous institution – Los Angeles Valley College. Endrijonas was announced in her new role at PCC in December 2018, the same week that a jury in Van Nuys awarded a former LAVC employee $2.9 million jury award for illegal retaliation and abuse. A few months earlier, the Los Angeles Times published a major story about the Valley Academic and Cultural Center – a project meant to be Endrijonas’s crowning achievement – being an alleged massive racketeering scheme.
Further it documented the Media Arts Department the VACC would house had a lengthy history of lawsuits and accreditation complaints against the faculty for not providing the education and training advertised – negating the need for the new building. The building’s approval vote happened in August 2016, the lawsuit happened in 2009, and the Accreditation Complaints happened in June 2016.
Dozen LAVC Cinema Students Narratives challenge Erika Endrijonas’s LACCD Success Story | May 5, 2023 |
This article covered a release of an email thread from a dozen students in 2016 that was ultimately sent to the Accreditation Commission for Junior and Community Colleges in 2016, substantiating that there was widespread fraud in the department. Classes were not scheduled by Department Chair Eric Swelstad, training was not provided, labs were not held, etc . . .
Van Nuys/Los Angeles College Screenwriting Professor Faked Writer’s Guild Membership | May 17, 2023 |
Revealed that LAVC Media Arts Department Chair Eric Swelstad faked his membership in the Writer’s Guild of America – West, and then used it in multiple professional bios.
Los Angeles Valley College perpetuated wage theft against students on Julie Su’s watch | May 19, 2023 |
Documented how Grant Director Dan Watanabe engaged in wage theft against students for two years from 2013 – 2016.
Two Los Angeles Film Professors Bilked Taxpayers Over $3.5 Million Dollars | May 21, 2023 |
Described how LAVC Media Arts Department Founder Joseph Dacursso’s retirement first as Department Chair, then as a full-time faculty in 2012, left Department Chair Eric Swelstad and Arantxa Rodriguez to engage in petty infighting and squabbling that spilled over into scheduling decisions. In short, two faculty members collected six-figure-salaries while putting students in the middle of department in-fighting.
LAVC Omsbudsman Stalked Whistleblowers | August 8, 2023 |
Described how LAVC’s Dean of Students, Annie G. Reed (Goldman) retaliated and stalked students that went to Accreditation, going as far as running a smear campaign that one of them was a potential school shooter. Worse, she began stalking him after he left school – including on social media.
[Image: Annie G. Reed Goldman, Dean of Labor and HR at LACCD]
The scrubbing of these articles coincided with the formal appointment of Alberto J. Roman as the new Chancellor of the Los Angeles Community College District, following the retirement of disgraced administrator Francisco Rodriguez.
It also came with the publication of two final articles. One about Annie G. Reed’s being named as a Defendant in a lawsuit by former faculty at Los Angeles City College, who came to her about an administrator engaging in illegal behavior – including planting drugs on employees to get them fired.
The second article, probed Los Angeles Valley College Department Chair, Eric Swelstad’s professional bio again and provided evidence that he repeatedly lied and engaged in deceptive advertising and practices for two decades. It provided students who held loans with information about student borrower defenses.
The censorship also came months after Jo Ann Rivas aka AuditLA, herself probed by the articles, launched a barrage of attacks for about a week in January about a former student who had grievance’s against the school. Rivas had previously engaged in a similar barrage in July 2020.
This was not the first time that an attempt was made to censor this news stream.
In 2020, an attempt was made to hack the community news feed account on Twitter/X.com @LACCDW. Then a week before the LACCD Board of Trustees election in November 2020, Twitter suspended the community newsfeed altogether. It was only restored two years later after Twitter’s sale and the re-evaluation of previous suspended accounts.
In a final update – The Valley Academic and Cultural Center, despite having a 2018 completion date, remains unfinished. According to minutes of the LAVC Work Environment Committee Minutes from 2025-05-08;
“The Valley Academic and Cultural Center (VACC) is as of Friday, May 8th, about 80% complete. They are still patching the roof. There are still some critical items like stage protection net.”

Higher education is designed to prepare students for their future lives and careers by imparting technical and soft skills, but what about practical, hands-on tasks, like managing a home or vehicle?
A 2023 survey found that young adults lack practical life skills, with two-thirds (68 percent) of millennials and Gen Z unable to change their car oil, nearly half (48 percent) unable to change a tire and 46 percent unable to tie a tie. Eighty percent of Gen Z respondents said they do not feel like they have figured out adulting.
A workshop series at George Mason University in Virginia, titled Now What?, helps build students’ practical knowledge and well-being by giving them life advice and skills, such as how to change a tire.
In this episode of Voices of Student Success, host Ashley Mowreader spoke with Ethan Carter, associate director of programs, well-being and assessment, and graduate student assistant Dianna Philipps, to learn more about the program offerings and how it supports student success.
An edited version of the podcast appears below.
Inside Higher Ed: I wonder if we can just start by talking about the inspiration for this program. Where did the idea come from?
Ethan Carter: I came up with the idea, because as a [student activities] programmer, it is difficult to replicate things. When I thought a lot about being a college student—which was several years ago—I was like, “Man, what were the things that I wish I had known back then?” And so I kind of tried to think about something catchy, and I said, “Well, there were lots of things— I would do something, and then I’d be like, ‘So now what?’’ And so I was like, “Oh, that would be a really good little catchy phrase.”
Also, from a programming standpoint, it is very adaptable to what we want to do. I don’t have to replicate my programs, but we can have the theme of Now What?, and seeking what students would want to know more about in their lives. Not that what I wanted to learn was bad. It was just, things change.
Inside Higher Ed: When you address that question of Now What?, what are some of the themes you all have talked about? What has programming looked like practically?
Dianna Philipps: One of our main ones would be the “how to change a tire” one. I feel like most people on campus have a car, [but] they don’t really think of the things that come with having a car.
So when you see the tire-changing [workshop], you’re like, “Oh, what if I do get a flat tire? Like, maybe I should learn how to handle that if I’m on my own on the road or something.” I feel like things like that really stand out to students when they see it.
Inside Higher Ed: Something I thought was cool is that your roles focus on well-being and recreation and this program is an interesting intersection of those two ideas. I wonder if you can talk about how this contributes to students’ well-being and thriving on campus.
Carter: When you work on a college campus, and the big theme behind the campus is about well-being, you try and find out, where do you fit? And for us, it wasn’t just in the fitness realm. We wanted to think about something that was what we would consider our niche.
I settled on practical well-being because it is adaptable and relatable. Recreation is usually seen as something that does provide movement, but I wanted to capitalize on that and build off of the aspect of, just, living in general can be tough. It also opens the door for us to be able to partner, because a lot of our programs within themselves are not things that we run, and it’s not our expertise, but it is a place where we can be a hub and connect individuals, which kind of ties in with the well-being aspect, like, you need to find your own well-being.
Inside Higher Ed: Who are those partners across campus, and how do they participate in this?
Carter: Anyone and everyone is actually who we get to partner with. The [change a] tire one is done with our facilities group and specifically the auto shop—they help us with any vehicle-based activities that we have going on.
We’ve also connected with Student Health Services for ones that are related to health insurance, with anything about self-care. And then we did another [event] with academics for a little bit, talking about preparing for exams and test-taking and things like that.
One of my other favorite [events] is intercollaboration within a department. So like, how to do a hike, how to change a flat tire on a bike.
I think we had one more connection, oh, with dining. Dining teaches us how to cook, and so we’ve done a Super Bowl one where we made a special dip and some other little fun delicacies.
Inside Higher Ed: What have you learned from students and their feedback as you’ve done the events over the past year or so? What did they enjoy about it?
Philipps: I would say the main feedback is that it was very helpful for them. I think most of the people who have come to one event, they’re the ones who continue going to each of the events. I think it just helps them learn the things that they don’t know, because they’re like, you don’t know what you don’t know until you, I guess, go to the event. So that kind of helps them a lot.
Inside Higher Ed: There are knowledge gaps for all students as they come on college campuses—whether that’s academic preparedness or just life skills that you might not know. If you’ve never owned a car before, you might not know how to jump your car or change a tire, or if you’ve never had a full-size kitchen before, you might not know how to cook a Super Bowl dish. So I think it’s really cool that you all give them the opportunity to identify what they don’t know, but then also just close those gaps and help them feel like they’re not left behind or unsure of what they do next.
Carter: I would also add that they’ve enjoyed putting their hands on the tools that help them.
We do one [workshop] on how to use hand tools, and sometimes the power drill is the [tool] that we get to play around with. Other times it’s a hammer and nail. Sometimes we play around with a tape measure. And I’ve appreciated the vulnerability of the students and admitting like, “Hey, this is what I don’t know,” and it provides an opportunity for me to talk more about like, “Hey, this is what I was feeling when I was a college student.”
When you are thinking about all the resources that are available to you on campus, it’s important that you’re able to admit that you don’t know how to do something, and then go out and ask someone, because most of the time, most of those tools are readily available for you on campus. You just have to be pointed in the right direction, and people can’t give you what they don’t know you need. So that would be something else that I would say has been a great benefit for me in connecting with other campus partners and connecting with those students.
Inside Higher Ed: I remember when I was a college student, I was really afraid of the makers’ studio, where the VR lab and the 3-D printing are. It just felt so intimidating to go in and actually try things out. But once you have an experience like this, where it’s a little more hands-on and assisted, you feel like you have the skills to do it.
I bet there’s also an element of introduction to staff on campus. Maybe students have never met a facilities manager before, and now, after changing a tire with them, they can ask for help in other ways. Or if you’ve never talked to the Student Health Center, now you feel more comfortable talking about health insurance or other things like that.
If you had to give advice or insight to another college or university that was looking to replicate your idea, what would you say you’ve learned? Or what are some best practices for people to know?
Carter: First one is, what I actually tell the students all the time, is to be yourself within your organization. You maybe have a limited budget, and you only have certain resources available to you, so it’s important for you to not try and go and do what everybody else is doing. It’s important for you to do what you’re able to do, and then to connect with your students and allow them to be part of the construction of what your program is going to be.
It may start out as just being something where you’re looking at budgets, and then another student comes in—because you are making this for the students. So if you don’t have the student audience that is available for what you’re providing, like, it isn’t super helpful.
So do that, and then the adaptability aspect: Be OK with something not working. Because when you hear “no” or no one comes, that is good information; you know not to do that anymore. A lot of people get offended by that and are like, “Oh, I’m a horrible programmer” or whatnot.
It could be that you’re doing it at the wrong time, or it’s just that students are not available for that. Why would we do something that’s related to budget and all the students that need to do the budget stuff are in class in the a.m., so maybe I should try it in the evening. Things of that nature. So be OK not always having everything get hit out of the ballpark. And then if you do find something, you try and make it better as you go.
Inside Higher Ed: You mentioned that this is a different sort of programming and something that you all can adapt to reflect student needs. I’ve heard a lot from people who work on college campuses that post-COVID, it’s just been harder to get students to show up for things or feel like you’re being responsive to their needs. Have you felt like this has accomplished that goal in being adaptable, but also engaging students?
Carter: I would say it depends, and it really depends on what’s going on and what the particular group you’re working with is all about. So, Dianna, if you don’t mind sharing some of your ideas to try and help us get some people coming.
Philipps: One of the main ones would be changing locations. Especially if you’re on a bigger campus, trying to make it more central so it can target different types of people, either coming from class or coming from the dining hall or things like that.
Just back to what Ethan had said about being creative with it, and if something doesn’t work, look at what did work, keep that and then change what didn’t work. You can learn from that. See what things people are actually going to, what they actually need help with. So, again, being adaptable to things.
Inside Higher Ed: You mentioned earlier that students who come to one event might come to multiple—like, they really appreciate the skills that they’re building. Have you seen that that’s true of a handful of students or more?
Carter: It makes you feel good when you see somebody that you’ve seen before; it kind of increases your self-esteem. You’re like, “Oh, I did something, right?”
I think the bonus is that they invite their friends and they make them aware. I think that a lot of times, even as an adjunct professor, I’ve had to change my perspective of it isn’t what the student looks like, because most of the time when I’ve talked to my students, they look like they don’t care about my class. But then I mentioned that to them, and they’re like, “No, you’re one of the coolest professors that I’ve ever had.” I’m like, “I can’t tell from looking at your face.”
So when we’re doing our programming, it may not be that the students don’t like it, they just may not be aware, which is why we’ve tried really, really hard to go to the students to make the things available—not just putting a flier in front of their face, but providing them an opportunity where they can go and do something.
I would say we’ve gotten the greatest number of students coming to things when we went to another class with content that was in line with what we were doing; we were complimenting what an instructor was teaching. And then the students are like, “We had no idea that this was going on; what other programming do you have available?”
So I would say that that has been super, super helpful, going to the students and just becoming more and more visible, shaking hands and getting to know people, which, again, it seems like it’s common sense, but you do have to become visible in a way that is helpful and not harmful.
Inside Higher Ed: You mentioned working with other staff on campus; have faculty been a partner in this work as well?
Carter: We have gotten to work with them. And like I said, when we invite ourselves to their class, it doesn’t work out so well. When we are paying attention to what it is that they’re teaching and ask them, “Hey, this is something that we’re offering. Is there, maybe, 15 or 20 minutes that we can come and complement some of the stuff that you’re teaching?” That actually ends up being a two-way thing, because usually that instructor is willing to come over to our workshops and provide some informational knowledge, and so that has been super, super helpful with that. So having a crossover is good.
Inside Higher Ed: This series is all about helping Gen Z prepare for unknown futures and navigate their world after college. When we talk about the role of higher education, I think we talk a lot about careers, about students building life skills like critical thinking and things like that. But there’s also this idea of helping students just be people, having that practical wellness. I wonder if you can tie this all together—why this is important for colleges and universities to do, and how this is foundational to not only the students’ success, but also just being responsive to their needs?
Carter: We have a saying in our well-being practices—our goal is to help students to live just as they breathe.
When you think about well-being and the holistic aspect of it, it’s important that people realize that eating well can be tied into you, just coming and sitting in a facility, being around people. It can also be exercise. It can also be yoga. It can also be about you being able to get the job done, or even going through a bout of anxiety and finding out you know how to be resilient in that space, or how to ask for help.
When it comes to our programming, we want to do what’s going to help people to be the best version of themselves. And that’s a journey that students have to take, and we’re on that journey with them.
We want to walk alongside the student and provide the things that they need, to help them to feel like, “Hey, you know, I feel like I’m a better adult,” and at the end of the day, want to come back and give to other students. So being a human being is what we’re all about, and we want to support that in the best way possible, through our programming. And if we don’t have the programming, we can point them to other services and other individuals on a college campus, because that’s what universities are here for.
In higher education, the more that we acknowledge the humanity of others, I think the better off that we’ll be, as opposed to trying to figure out things in a box. We’re not people built in boxes; we’re people with unique qualities and differences.
Philipps: I would add that these events also teach us how to ask for help. Because I feel like that’s a big thing, especially when we’ll have actual careers and stuff, you don’t know everything as much as you may think you do. So just having that skill of asking for help, or just even getting assistance collaborating with others, is really important, and I think we get that from these events.
Get more content like this directly to your inbox. Subscribe here.

Another former Florida lawmaker is stepping into a presidency after the University of West Florida Board of Trustees voted to hire Manny Diaz Jr. in an interim capacity Tuesday.
Diaz, who is currently Florida’s education commissioner, served in Florida’s Senate from 2019 to 2022. The former GOP lawmaker is a close ally of the state’s Republican governor, Ron DeSantis.
The UWF board approved the hire despite the objections of two trustees who raised concerns about transparency and argued that the process of selecting an interim was rushed. UWF’s current president, Martha Saunders, announced her resignation earlier this month after a board member took issue with social media posts from the university dating back several years. Zach Smith, who works for the Heritage Foundation, said he was troubled by actions that included encouraging students to read a book about antiracism and promoting a drag event in 2019.
Both board members and the public questioned Diaz’s qualifications at the meeting.
Trustee Alonzie Scott noted that it was unusual to select an interim without considering internal options and questioned how Diaz was elevated as a sudden candidate without a prior board discussion. He also pressed board chair Rebecca Matthews on whom she spoke with before advancing Diaz as the pick, though she did not offer specifics on those conversations.
“I don’t feel as if I have to run through that list with you today,” Matthews told Scott when he asked whom she had discussed the appointment with before adding it to the board agenda.
Scott also questioned whether the board had violated state sunshine laws.
“I can’t prove that any of us have violated the sunshine guidelines, but I can tell you everything that I read about all the different Florida news outlets, it appears that those decisions were made before this board even had a chance to even discuss. And to me, ma’am, that is a travesty in terms of how we operate,” Scott said, adding the process was “a disservice to the community.”
Matthews defended the hire, noting Diaz’s past work in K-12 education and the State Legislature.
Diaz will formally assume the interim presidency July 14. Despite tapping Diaz as interim, the board will begin a search for its next president, though some trustees argued that naming Diaz instead of an internal candidate to lead UWF would likely suppress the number of applicants.
Of five presidents hired at Florida’s public universities this year (including interim roles), Diaz is one of four who are either former lawmakers or directly connected to the governor’s office. Santa Ono, who was hired as president of the University of Florida on the same day UWF tapped Diaz, is the outlier.

In reflecting on my feelings about the advent of artificial intelligence in our lives, I must report they are mixed. I have the strong sense of the inevitability that this technology will meet and exceed its hype to alter the course of humanity, generally for the better. However, at the same time there is a measure of trepidation in my awe of the potential power and performance of AI.
I am receiving more frequent emails from colleagues reporting renewed intransigence among faculty regarding the push to adapt to AI use by students, to integrate the technology into teaching and to help prepare learners for the AI-enhanced workplace. I see parallels to the 1990s and early 2000s, when faculty also resisted the advent of online and blended learning. That resistance gradually subsided until the pandemic, when remote learning, albeit a less refined use of the technology, came to the rescue of universities.
In both instances, the resistance seems to be prompted by a general lack of understanding and comfort with the technology. This creates an elevated level of anxiety. It also requires a change in pedagogy to adapt to expanded capabilities in the hands of students. This involves reconceiving and rewriting lesson plans and, in some cases, learning outcomes for multiple classes. This can be time-consuming. Yet, this is not the first time that emerging technology has impacted teaching modes and methods.
I am fortunate to remember, as a faculty member, the advent of the personal computer in the late 1970s, graphing calculators in the mid-1980s, the rise of the World Wide Web in the early 1990s, Google Search in 1998 and, in 2001, the launch of Wikipedia. Each one of these technologies demanded changes in the ways we presented and assessed learning. Questions of student integrity were raised in each of these cases. We also were urged to consider the students’ needs to become facile with these tools as they left to commence their careers. Imagine HR’s response to applicants who could not conduct an internet search or use a personal computer. The pressure was on to adapt to the emerging technologies while ensuring integrity.
Each of the technologies has become incrementally more sophisticated and more capable. They have required more and more attention by faculty to maintain a quality learning environment, and to prepare students for the rapidly changing workplace environment. In the case of AI, larger leaps in sophistication are coming on a weekly or monthly basis. The stakes are high. The integrity of the instruction, the relevance of the learning and the future employment of the students hang in the balance. The pressure is on the faculty to maintain quality and security in a rapidly changing environment.
Change in the AI field comes not on the rather pedestrian pace of new releases of the past, when we would see new versions released on annual schedules by just a handful of providers. Now, we must track 10 or 12 of the largest providers, as each of them releases new versions about every three or four months, or more often. Generative models still see improvements while agentic models offering awesome deep research and autonomous agents are flooding the market from around the world.
In a TED talk recorded last month in Vancouver, former Google CEO and chairman Eric Schmidt explained that, if anything, artificial intelligence is wildly underhyped, as near-constant breakthroughs give rise to systems capable of doing even the most complex tasks on their own. He points to the staggering opportunities, sobering challenges and urgent risks of AI. Schmidt asserts that everyone will need to engage with this technology in order to remain relevant. Meanwhile, in an interview this month, the current Alphabet/Google CEO, Sundar Pichai, on the All In podcast, affirms the commitment of the company to developing AI. He describes the evolution from Google search through AI, while it continues on the continuum of a discovery path of quantum computing and pursuing the concept of autonomous robots.
Just as Google is working to further develop and refine their multiple versions of AI, so too are many other major corporations and start-ups. What they come up with over the coming months and years will have a huge impact on higher education, the workplace, job market and society as a whole. The very nature of human jobs will change. Meanwhile, Elon Musk predicts smart robots will proliferate and will outnumber humans. His Optimus robots are to sell under the Tesla label, priced at $20,000 to $30,000. Of course, AI is central to the operation and functioning of such humanoid robots.
So, what might the workplace, or more specifically the individual human work assignment within that workplace, look like? In his recent podcast, Wes Roth reviews “The Age of the Agent Orchestrator” by OpenAI’s Shyamal Hitesh Anadkat. In the article, Anadkat describes the key new role that humans may play in the AI-enhanced workplace, noting that in the future “the scarce thing is no longer ‘who knows how to do that task by hand.’ The scarce thing becomes ‘who can orchestrate resources well’—compute, capital, access to data, and human/expert judgment.” That role he describes as the “agent orchestrator.” In sum, Anadkat writes,
“As always, the most important thing is to build something that users want. In a world where your marginal cost of expertise/knowledge goes to zero, your ability to turn cheap intelligence and expensive resources into valuable products is what will matter. i’m [sic] very excited to see the new companies, the new tools, and the new jobs that come out of this. Welcome to the Age of the Agent Orchestrator!”
The human will orchestrate what may be a very large number of highly capable intelligent AI agents. That may not seem as creative of a job as many of us now hold, such as authors, researchers, graphic designers, Web developers and the diversity of positions in designing and enhancing instructional resources. Yet, there is creativity, and certainly impact, in marshaling the vast resources at hand in the workplace of the future. Implicitly, the job becomes one of orchestrating abundant resources in conducting a symphony of interacting virtual workers to achieve desired goals. Doing so in the very best way calls upon higher-order creative thinking, strategic planning and execution.
All of these developments bring to mind the assertion of the pre-Socratic philosopher, Heraclitus, who is credited with saying 2,500 years ago, “The only constant is change.” We can expect much more change in the field of AI over the coming months and years. It will be far-reaching and long-lasting. It will penetrate the very essence of what it means to be a human in a technological society. We in higher education cannot ignore this change or make it stop simply because it is inconvenient or incompatible to our teaching style. The money, momentum and weight of advantages of AI make it an inevitable advance to civilization. It is not stoppable. We must change our practice to meet the needs of the students and society.
I am left with a less-than-easy feeling to welcome artificial intelligence with all of its sweeping ramifications into our work, lives and future. Yet, at the same time, I know that we must move forward to meet that future, if not so much for ourselves, but rather for our students who will live the greater part of their lives alongside their AI companions.
In the late 1960s, a gifted folk music composer and performer, Joni Mitchell, released an impactful song titled “Both Sides Now.” Within that song is a phrase that has stayed with me through the decades: “Well, something’s lost, but something’s gained in living every day.” I suppose it helps to sum up my feelings about this new technology that is rapidly gaining momentum and promising to change our learning systems, workplaces, lives, identities and society.