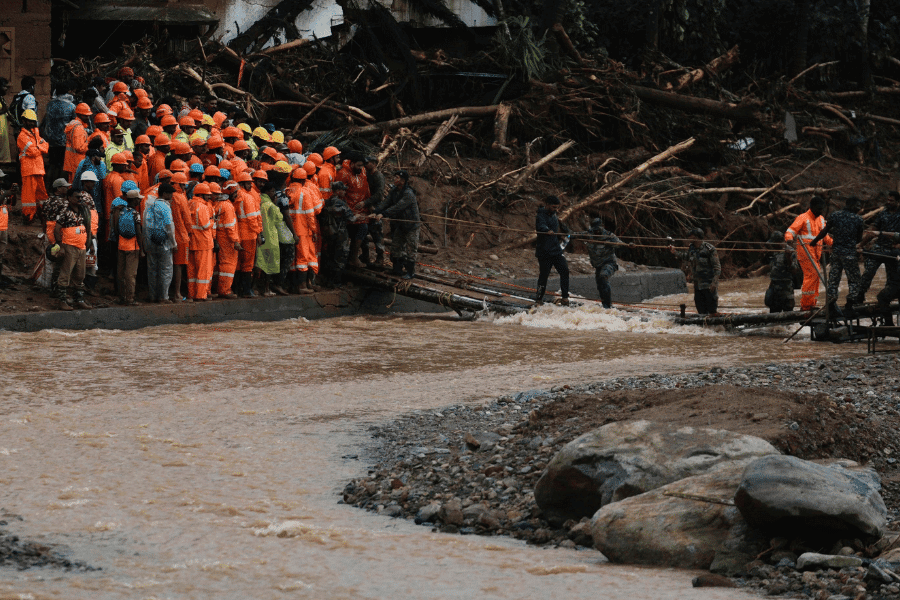
In July 2024, the state of Kerala in southern India was struck by a massive landslide that devastated several villages, including Punchirimattam, Chooralmala and Mundakkai. The impact was catastrophic: nearly 300 people died and hundreds more injured.
This tragedy, triggered by unprecedented rainfall during the monsoon season, drew attention to a stark and growing concern: India’s ability to manage and mitigate the increasing frequency of natural disasters effectively.
Over the past few years, India has witnessed an alarming rise in the intensity and frequency of natural disasters, be it floods, heatwaves, cyclones or landslides.
This surge is being driven by the changing climate. With global warming altering weather patterns, India finds itself vulnerable to an array of disasters that threaten its people, infrastructure and economy. In response, there are calls for legislative reform, particularly an overhaul of the Disaster Management Act of 2005, so that the country will be better prepared to respond to natural disasters.
India’s experience can serve as a lesson for other nations in the region and globally.
Breathtaking landscapes become landslides.
Kerala, located in southwest India on the Malabar Coast, is renowned for its lush landscapes, tranquil backwaters and tea plantations. The state is no stranger to monsoon rains, but in July 2024 it faced a sudden, violent landslide that wreaked havoc in the hilly region of Wayanad.
These areas, often prone to landslides, were overwhelmed by incessant rainfall, which led to soil erosion and a massive collapse of hillsides.
The villages of Punchirimattam, Chooralmala and Mundakkai were hit the hardest, with homes and buildings buried under tons of mud. Most residents were asleep when the disaster struck before dawn, leaving little time for evacuation. The landslides not only caused a tremendous loss of life but also rendered thousands homeless, further deepening the crisis.
In the aftermath, rescue operations were launched swiftly by the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), the Indian Army and the Air Force, along with local government authorities and communities.
Ramakrishnan, a tea estate employee in Mundakkayam, said that emergency relief included immediate financial assistance of Rs. 3,000 per individual. To put that into context 3,000 rupees is about U.S. $35 and the average person in Kerala earns the equivalent of about U.S $23,000 per year. They also received food and medical supplies.
Helping people after a disaster
Affected families were relocated to temporary shelters, and school-going children were enrolled in nearby schools to continue their education. The National Disaster Response Force and state disaster funds provided crucial support for these efforts.
Yet, despite these swift actions, the Kerala government’s request for additional federal support, under the provisions of the Disaster Management Act, was delayed.
By October 2024, the High Court of Kerala had raised concerns about the delay in the disbursement of relief funds. This incident highlights some of the systemic flaws in India’s current disaster management framework — flaws that have become increasingly apparent as natural disasters grow in scale and frequency.
While the Wayanad landslide is one of the deadliest in recent memory, it is far from an isolated event. Over the last few years, India has experienced a disturbing rise in natural disasters, exacerbated by climate change.
In 2020, according to the United Nations Disaster Risk Reduction’s Prevention Web, the northeastern state of Assam faced catastrophic flooding that affected over five million people, leaving much of the region submerged. Back in 2018, the Indian Express newspaper reported that dust storms in Rajasthan not only caused widespread destruction but also revealed significant gaps in the country’s disaster management infrastructure, such as the lack of effective early warning systems and inadequate public awareness campaigns.
Similarly, heatwaves, which have always been a concern in India, are becoming more extreme and frequent, leading to an increase in deaths and health crises.
Inequity in disaster management
Some weather events seem to get more attention than others, said Prathiksha Ullal, an advocate whose interests lie primarily at the intersection of environmental law and feminist perspectives.
“Despite heat waves being a major concern, they receive little attention, whereas cold waves are highlighted in discussions in the Lok Sabha [lower house of India’s Parliament],” Ullal said.
These disasters, which are often compounded by inadequate infrastructure and preparation, point to the urgent need for a restructured disaster management framework that can adapt to the growing threats posed by climate change.
The Disaster Management Act of 2005 was enacted to provide a comprehensive framework for disaster preparedness, response and recovery In response to India’s vulnerability to natural disasters. The act established the NDMA to coordinate disaster management efforts at the national level, as well as State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs) to manage disasters within individual states.
The 2005 Act was an important step forward, but under it, there is confusion over the roles of national, state and local authorities in response to disasters; it doesn’t allocate enough money for disaster preparedness or response; and it doesn’t address climate-induced disasters such as heatwaves, droughts and extreme rainfall events.
This has made the framework less relevant in an era where climate change is increasingly contributing to the frequency and severity of disasters.
Improving how a government responds to disasters
Recognizing the shortcomings of the 2005 Act, the Indian government has proposed amendments to strengthen the country’s disaster management framework. The Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill of 2024 seeks to address many of these issues and build a more robust system to tackle the growing threat of natural disasters.
One of the central features of the bill is the strengthening and increased funding of the NDMA and the establishment of state disaster response forces.
The amendment aims to improve response times and coordination during disasters by providing state governments with more autonomy and resources. The bill also emphasizes disaster risk reduction, which focuses on preventing and mitigating the impact of disasters before they occur. This is a shift away from the previous focus solely on response and recovery.
Critics argue that the bill still centralizes too much power in the hands of the central government, limiting the autonomy of local authorities. Additionally, the bill’s failure to explicitly include climate-induced disasters, such as heatwaves and droughts, means that it may not fully address the risks posed by climate change.
India’s vulnerability to natural disasters is closely linked to the impacts of climate change. Rising temperatures, unpredictable monsoons and increased frequency of extreme weather events are all exacerbating the country’s disaster risk.
State-specific disasters
The 2024 Amendment Bill does begin to address climate change by incorporating disaster risk reduction as a key component, but it does not go far enough. For instance, heatwaves — which have become a major concern in India — are not adequately covered.
The DT Next newspaper reported that the South Indian state of Tamil Nadu has taken the initiative to declare heatwaves a state-specific disaster, enabling them to provide relief and take preventive measures. However, this is a localized response, and a more comprehensive national approach is needed.
The bill also does not fully address the role of technology in disaster management. Experts suggest that incorporating artificial intelligence and real-time data monitoring systems could significantly improve India’s ability to predict, track and respond to disasters. According to the AI company Ultralytics, AI models can be trained to provide early warning systems and help reduce the impacts of natural disasters.
For example, predictive modeling and vulnerability mapping could help authorities better prepare for floods, landslides or heatwaves by identifying high-risk areas and populations.
India’s disaster management struggles are not unique. Bangladesh, Nepal, the Philippines and other countries in the region face similar challenges, with frequent floods, cyclones and landslides causing significant loss of life and economic damage.
India’s evolving approach to disaster management, particularly through the Amendment Bill, could serve as a model for these countries, helping them build more resilient systems for managing climate-related disasters.
The tragic landslide in Wayanad serves as a poignant reminder of the increasing vulnerability of India’s communities to natural disasters. While immediate relief efforts were swift and commendable, they also underscored the need for deeper, systemic changes in how India manages its disaster response.
In the face of escalating natural disasters, India has the opportunity to lead the way in developing disaster management policies that are not only reactive but proactive.
Questions to consider:
1. What can cause a landslide in parts of India?
2. What was wrong with the Disaster Management Act of 2005?
3. What are some dangers climate change poses in your area?