What should go on my research lab website? Hi everyone! My name is Jennifer van Alstyne. Welcome to The Social Academic, my blog/podcast about managing your online presence in academia.
Today I want to talk about what is a research lab website? And, why should I have one?
This is a question that I’m asked often. Now that I’ve been doing this for 6 years, I have some new perspectives I’d like to share with you. So the 1st thing you need to know is that a research lab website is kind of a lot of work, and if you’re not willing to listen to this idea that it’s a lot of work, you probably aren’t going to be able to enjoy the benefits, and I promise you that the hard work is worth it.
The conversation today is going to be about structure, like what goes on a website. We’re going to talk about whether you need help, whether you want to hire professional support to make your website happen and what you need to consider before you actually take that step. We’ll get into all of the details.
Before we get into your research lab website, I want to give a shout out to my friend Dr. Sheena Howard, whose new book Academic Branding: A Step-by-Step Guide to Increased Visibility, Authority, and Income for Academics is out February 27, 2024.
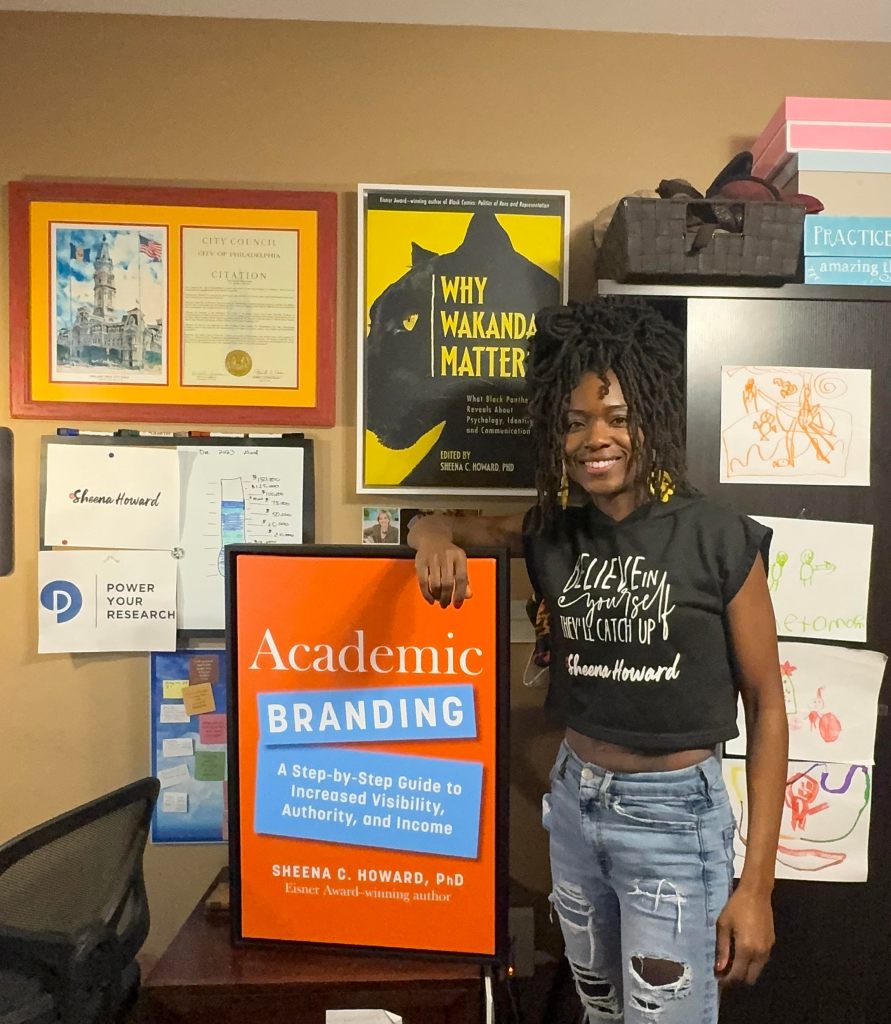

Dr. Howard was a featured interview guest on The Social Academic where we talked about how to get media attention for your research. I highly recommend her and her new book. Get your copy of Academic Branding on the Penguin Random House website.
Page ideas for your research lab website
Let’s talk about the structure of a research lab website. There are so many more pages that you could have on your website than people might expect, so I’m going to go through some ideas today and you can use whatever you find helpful and just not create pages for anything that you don’t.
Jump to the list of page ideas
Everyone needs a Homepage, a main landing page for your research lab website. That’s going to be the only page if you have a one page website, but a lot of people want more.
They want to be able to highlight the people who are involved in their lab, like their team. So you can have a Team page.
You could also have a page that really specifically focuses on your Research Impact and the people who your research is most trying to help: that end user that you’re trying to reach.
Definitely include a page for Publications. Your lab probably has a number of publications that come out every year, and while the individuals who work on those publications, it would be great for them to share them online. Having a research lab share those publications in one place makes it easy for anyone who cares deeply about the research that you’re doing. And helps people, find collaborators.
I love having a News page for research labs because it shows people all of the new things that you have going on, any events, conferences, meetings. This is a great place to curate that for people who are curious.
Speaking Engagements is a page that a lot of research labs don’t think about, to be honest. It’s not a common page on research lab websites, but it’s highly recommended. The people who are in your lab are going out and presenting research. They’re going to conferences. They’re spending money on that travel, whether it’s funded through the lab or self-funded beyond whatever professional development budget there is for that year. I want to make sure that if you have a research lab and the people who are in it are going out and presenting work that they’re doing associated with the lab, that people can still engage and come back and learn about the rest of the research that you’re doing through that Speaking Engagements page. Even though it’s not a common page, I do recommend it.
I love when research labs have a Photo Gallery, something that shows when you get together. Maybe it is just at the annual meeting, but that kind of personal touch makes such a difference for researchers. For students who are considering joining your lab and joining that particular research subject, knowing how personal it is can make a big difference. People are looking to understand the lab culture that you create as a P.I., and I want to make sure that they can see that through different visuals on your website whether you have a Photo Gallery page or just visuals on other pages of the website.
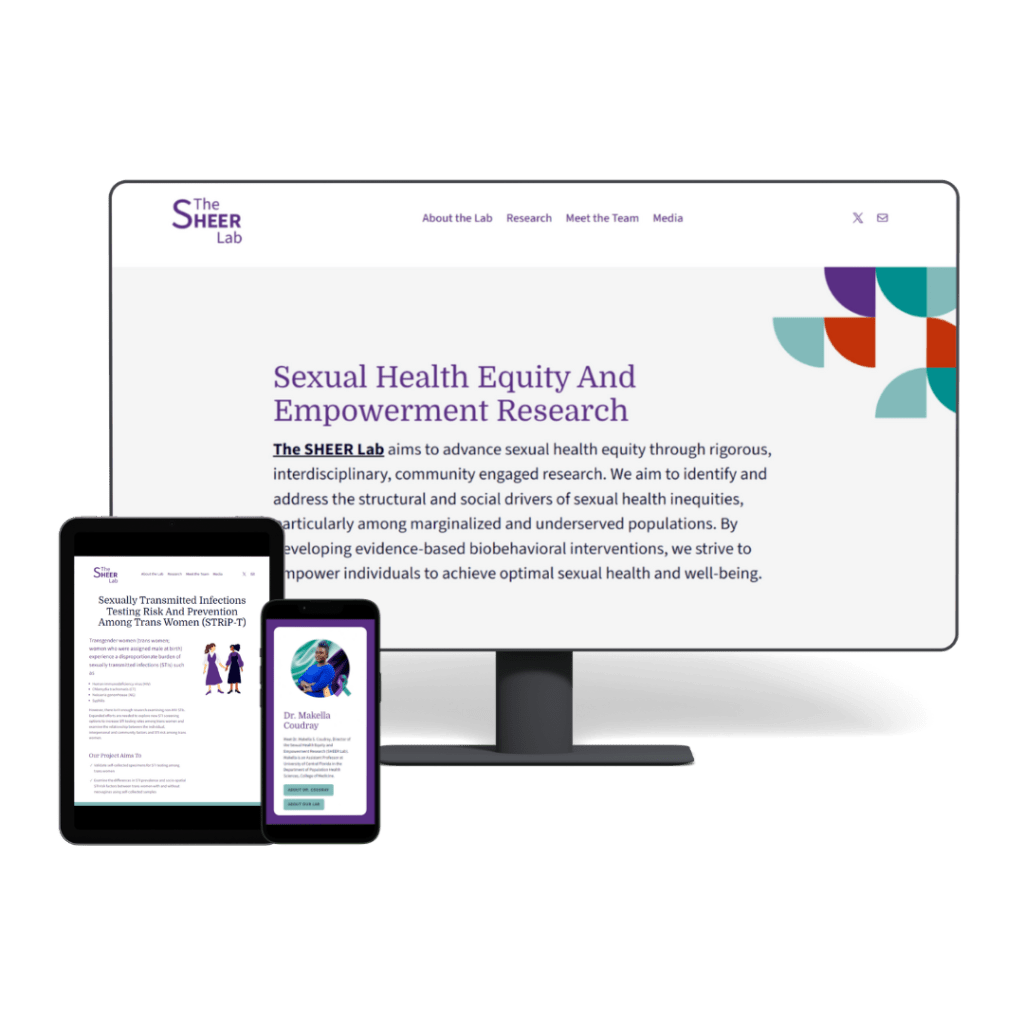
I highly recommend that the P.I., the principal investigator of the lab, has their own page, something that includes a bio, a photo, how people can get in touch with them, and the research topics that they care most about.
If you have a personal academic website that is separate from this page, your research lab should still have this page even if you have your own website. That’s because people really want to understand why you do the work that you do, what kind of impact that you hope to create in the world, and the values that you care about. If you can share that in your bio on your website, it makes a massive difference. Each co-P.I. should get their own page. So if there are multiple P.I.s in your lab, make sure that each person has their own page with their bio, headshot, and any links like contact information that they should have.
Some people really consider whether they want a Team page that has a bunch of bios on it or photos on it. Some people actually like to create an individual Bios pages for each member of their lab, more like a faculty profile. This is more work, but it can really help create an online presence for people who might not have one otherwise. And it’s a wonderful way to highlight staff and other supporters in your lab who may be there more permanently.
I want to make sure that you know that you can have a Team page with a number of bios on it, but each person could also have their own page if you’d find it helpful. This is particularly helpful if you are at a research center or have a larger group with multiple teams of researchers or multiple teams of P.I.s. The more people there are in a research lab, the better it is to have that information out there so people can better understand the person that they’re most closely collaborating with.
Anywhere on the website is a great place to have contact information, whether you’re on an individual bio for someone or on the homepage of the website. You want to make sure that that contact information is easy to find. Some people like having a form on their website, but I found that forms don’t always function correctly across different devices. Sometimes in different areas of the world. Having an email address at minimum is super helpful. Where you include that contact information? Definitely include it on the homepage. Include contact information on any bios. I like to have a contact button or a contact space in the upper menu in the heading. Even having contact information in the site footer. Basically, if you want people to be able to contact your lab, get in touch with you, if you want media to be interested in your research and be able to actually reach out to talk about it, having that contact information easy to find is super important.
Another question you want to consider is, do you want an email list? A lot of labs already have some kind of internal email list of members of the lab, people that they’re already communicating with. Would you like people to be able to subscribe to a larger email list or maybe a newsletter that you’re planning on having? That’s something to consider when you have a website because there are legal permissions and requirements that are involved when making that decision.
You want to make sure that you think about that when you’re starting that website project. So if you work with a developer, they know to make sure that you have all of the permissions correct. Basically, you want to protect people’s privacy and make sure that they’re legally opting in to receiving email from you. You’re not just sending it without permission.
I always recommend having a Research Funders page somewhere where you can thank the people who are helping fund your research and helping it really make an impact. So if you can have a Research Funders page to thank people? That is wonderful.
You might also consider a Partnerships page, especially if you partner with corporations or organizations.
Subscribe to The Social Academic blog.
The form above subscribes you to new posts published on The Social Academic blog.
Want emails from Jennifer about building your online presence? Subscribe to her email list.
Looking for the podcast? Subscribe on Spotify.
Prefer to watch videos? Subscribe on YouTube.
Do-it-yourself research lab website
The next question is with all of these pages in mind…and you don’t need all of these pages! You definitely can start with a 1, 2, or even 3 page website. You can grow it over time. So don’t feel like even though I just listed 15 pages or something that you have to have all of those.
But when you think about the website that you want and dream about for your research lab, or your research group, or your research center, are you like, “Oh yeah, we could do this ourselves! We actually, we have a communications person on staff or at the university who can support this project. I actually think that we can do this in house.”
Well hey, that’s great! Now you have a bunch of page ideas. You can start putting together a document that actually will support that person in making changes to your website.
But if you think about that question, “Can I do this myself?” And your answer is like, “Oh, I don’t think so. I definitely need to hire help with that.”
Let’s talk about what that looks like.
When people ask me questions like, “Can I do this myself?” I often turn that around and say, “Do you want to do this yourself? Is that something you want for yourself? Because the question of can I is of course. I mean you’re a professor, you’re likely a PhD. You can learn this. You can totally learn to build a website and develop those skills if you want to. And now you have a list of website pages that you might consider including on your research lab website. So not only can you develop the skills, you know what to put on the website.”
A question is, do you want to develop those skills? Because a lot of people that I talk to are like, “No, I’m busy doing my research. I’m busy being a mentor and doing these leadership positions on campus. I don’t have time. I don’t have time to develop these skills even if I wanted to.” And to be honest, most people that I talk to, they just don’t want to.
Now, if you want to develop the skills, I promise this is possible. You can create a personal academic website. And if you want a research lab website that doesn’t involve a lot of decision making, you just want to be able to add these pages? I highly recommend Owlstown. It is an academic website builder from my friend Dr. Ian Li. He knows that research labs need websites. He’s created a free service to help you create one yourself. Please know there are options for you if you want to do-it-yourself.
Another question that I typically have for people who come to me and say, “Can I do this myself? Do I need to hire help?” is, “Do you have time to do this?”
Because you might not have the time. You’re already doing a lot. You’re already adding value to the world. You might not have the capacity to build another skillset.
And even though you can create your website yourself, it may not be the best use of your time. You are someone who prioritizes your time very well. That’s why you’re in academia and being successful at it. But that also means knowing when to say no. So if you don’t want to do it yourself, but you want a website, hire help. If you don’t have the time or capacity to do it yourself, but you want a website, hire help. I mean, that is my goal, is to help you get help whether it’s working with me or whether I can direct you to someone else who’s better suited to help you.
“The truth is you either have to invest the time. Or you have to invest the money. To get it done in the best way possible, it often takes both.”
Hiring professional support for your research group website
Let’s talk about how to hire help. Most developers don’t know how to make a research lab website unless you know what you’re looking for, like the pages you want and the content that you want to share on those pages. These are also things that you need to build yourself. If you want to D.I.Y., your research lab website, so know what pages that you want to have and what you’d like to be included on each of those pages. Either way, that’s the step you’re going to need to take.
Actually, that is even a block for people like what to put on your website? You don’t know what goes on the page, what to say. There’s so many things to think about like photos or links or buttons.
Sometimes it becomes hard to communicate with a website developer if you’ve not already thought about some of those things in advance.
I highly recommend that you create a Word Doc or any kind of document processor that you use, something that you can share with your website developer. If you already know your bio and you know what you want to link, like publications, now you have a Publications page. If you want to highlight team members and their bios, you got to gather all of that stuff. Put it into a document. That’s some work that you do have to do upfront. But once you have those things, the developer can make you a great website.
You need the vision and hopes for your website before you start talking to the website developer. That’s something that becomes surprising for a lot of people. And I want to tell you this because I’m trying to save you money.
The cost of a website can range wildly depending on the skill level of the developer, what country they’re located in. It can range from about $1,500 USD to over $65,000. A P.I. reached out to me at the end of 2023 who had been given a quote by a website design agency for their research lab website of $65,000. This is a huge range for professional websites that are specific like a research lab, research group, research center, or other grant-funded initiative.
But if you don’t know what you want on the website, the quote that a developer gives you is not going to be specific to your needs. They’re going to quote you what they think you need. Having things prepared in terms of what you want to be on your website in advance will result in a more accurate quote.
Your website will be launched quicker and you’ll be celebrating your new website. That’s what I want for you.
Doing this work, thinking about this, being a little introspective about what you want on your website upfront? Really helps set expectations for you and the website developer or designer on this project. I want to avoid any miscommunication. Having that information upfront will help you both know what to expect.
Subscribe to The Social Academic blog.
The form above subscribes you to new posts published on The Social Academic blog.
Want emails from Jennifer about building your online presence? Subscribe to her email list.
Looking for the podcast? Subscribe on Spotify.
Prefer to watch videos? Subscribe on YouTube.
How a lab website can be life-changing for researchers

Okay, so what are the benefits now that we’ve gone through all the things you can have on your website, and if you need to hire help. Now you’re really like, “Oh, this is kind of tangible now. How is this going to affect my life?”
Well, a research lab website is great. It highlights the research that your lab does. Research can go on your Homepage, News, Research Impact pages. I mean, it shows visitors how they can actually engage with your research. And, with you, as a researcher and a person to potentially collaborate with in the future.
It really helps people invite you for speaking engagements that are really specific to your topic, because I know that there are things you have to say no to, that aren’t going to fit into your schedule.
I want to make sure that when people are reaching out to you, it’s even closer aligned to what you hope for that relationship in the future. Again, not everyone cares about that Speaking Engagements page, but that’s where you’re out talking with people who are in your research field and who already care about it. That’s why they’re coming to the talk. So having that page is something I highly recommend. I hope that maybe this podcast and blog makes an impact on research centers out there. I think that this is a page more people should have.
The impact of the hard work that you do for your research is apparent on each page of your website, but people can’t really explore that in any way now. When you don’t have a website, people are probably engaging with your research when they come across your publication, if they’re searching for it. When they see you on Twitter or LinkedIn, these are all kind of momentary.
Even meeting at a conference, it’s great to see the people that you care about, but you don’t always catch up on all the cool things that they’re doing. There’s just not time. And oftentimes that’s not the main topic of conversation.
When people can explore that in advance before they even come and meet you at the conference? Your lab website gives something for the conversation to be informed by. And it can really prompt new relationships, new collaborations, and help people better refer you or recommend you to the people who care about your research, whether it’s their students, their research funders, or other potential collaborators for you. I think it’s so great when you can highlight your research, media mentions, publications, collaborators, funders, events, speaking engagements. Gosh, there’s so much you can include on a research lab website, and it’s all really exciting.
Please know that when you do this work, it is really attractive to your research funders. It invites people to understand how they can get involved and how they can reach out to you. I encourage you to check out my interview with Dr. Julia Barzyk, who was featured on The Social Academic in 2023. We talk all about how online presence is awesome for getting your research funded by people who actually care.
Your website works for you even when you’re sleeping, even when you’re traveling, or going to conferences and meeting people in person. Your research lab website is a tool. It’s a boost to every in-person interaction that you’ll have in the future.
When people meet you or consider going to your talk, I mean they Google you, they just do, and they look at your research lab and sometimes they decided if they wanted to go to your panel or they want to go to someone else’s. Your website really helps them make that decision. And gets people excited to be in your audience.
People are already searching for you and the change that you want to see in the world. I want your research lab, your research group, or your research center to be more findable. I want your research lab to be the answer to the question that they’re looking for.
You are a part of your research lab website too

A lot of P.I.s are specifically looking for a research lab website, like, “This isn’t about me, it’s about my research or my team.”
I get it. They want ‘to remove the ego’ from their website. But a good research lab website is direct and clear about how you help people, and it actually helps people because it’s clear. And that includes sharing a bit about yourself as the P.I.
Be a little bit more open than you might be comfortable with.
Be proud of the research that your lab does and your team. Your website can proudly stand behind your work for you.
The labs, research centers, and grant funded initiatives that I work with care deeply about their team and their collaborators. They want their people, their staff, postdoctoral researchers, students, and sometimes the people that their research supports to actually inform the plan for their website. It gets everyone excited about the project.
My strategic website planning service starts with in-depth interviews with the principal investigators and members of your team. It’s my favorite part of the process because I get to discover all the amazing things you do. Especially the things that aren’t being communicated with your online presence. I’d love to help you with your research lab, research center, or grant funded initiative website.
If you want support, and you just want help thinking through what to include on your website before meeting with a local website developer? Let’s do a one hour website consultation to get you started on your website project so that when you approach the project yourself or you approach a developer, you have the next steps.
Schedule a no pressure Zoom call to chat about working with me 1-on-1 on your research lab, research group, or research center website. I promise to help you in the right direction, even if it isn’t working with me.
I’m Jennifer van Alstyne. You can find me on social media @HigherEdPR. Thanks for listening to this episode of The Social Academic podcast. Please share it with a friend or a colleague who might find it helpful.
Subscribe to The Social Academic so you don’t miss the next one.
Subscribe to The Social Academic blog.
The form above subscribes you to new posts published on The Social Academic blog.
Want emails from Jennifer about building your online presence? Subscribe to her email list.
Looking for the podcast? Subscribe on Spotify.
Prefer to watch videos? Subscribe on YouTube.

List of research lab page ideas
Pages in this article
Principal Investigator page(s)
Page ideas not detailed in this article you might consider
About our Lab page
Research Facilities page
Our Story page
Mission page
Research Values page
Methodology page
Research Project pages
Get Involved page
Recruitment page
For Students page
Videos page
In the Media page
Resources page
Email list
Do you want an email list or newsletter?
More resources for lab websites
For more page ideas and tips for your academic lab website, check out this episode of the Beyond Your Science Podcast from my friend Brittany Trinh. I love her tip about updating your website content before recruitment season. Brittany and I love collaborating to create your website for you in as little as a single Team VIP Day.
Get inspired with the award winning lab websites from the 2023 Best Personal Academic Websites Contest which Brittany and I judged along with Dr. Ian Li from free academic website builder, Owlstown.
View examples of lab websites Jennifer has worked on.
Guides and Advice Articles Personal Website How To’s Share Your Research The Social Academic