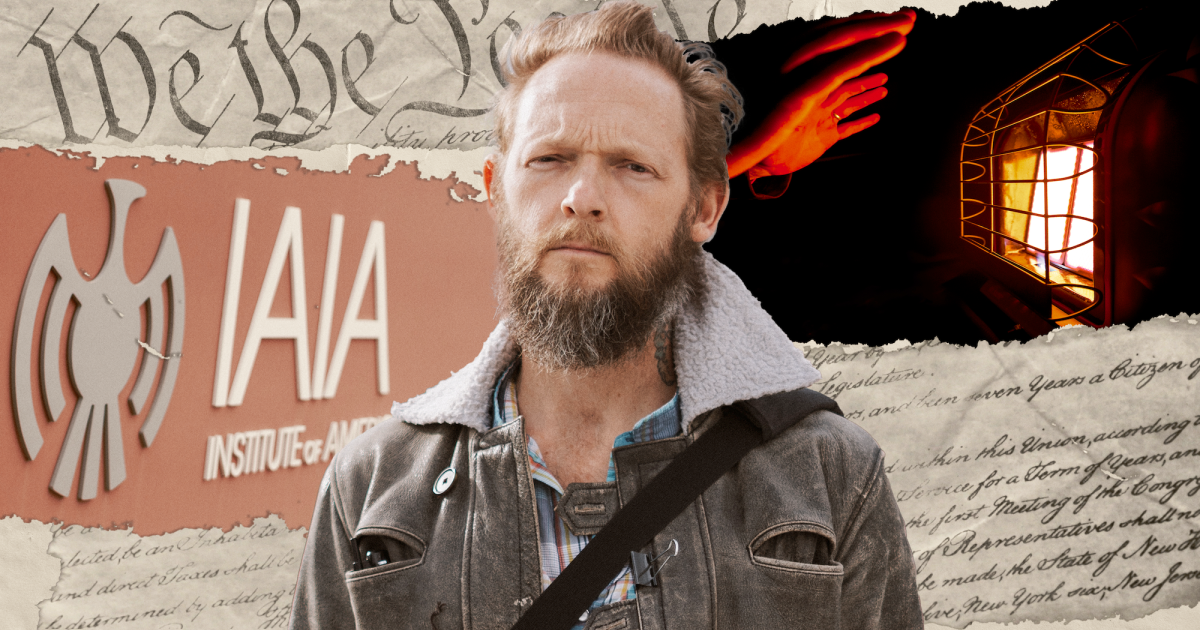
David John Baer McNicholas sleeps every night next to a bomb.
The worst thing about being homeless is the weather, he says. Santa Fe gets so cold that sometimes diesel fuel turns to gel. At those temperatures, frostbite hits in minutes.
In The Martian, Matt Damon’s character Mark Watney uses a radioactive isotope to keep his rover warm. In the Martian landscape of New Mexico’s Chihuahuan Desert, McNicholas keeps his van warm with a rusty five-gallon propane tank hissing beside his bed.
It’s not just the cold of the desert at night, either. Santa Fe is also the highest state capital in America, at 7,000 feet above sea level. That’s higher than the base lodge at most ski resorts. To stay warm, he keeps a pile of old covers and shirts in his van. A top from TJ Maxx. A blanket from a friend. An oversized green-and-black fleece from his sister who died of cancer.
But in the thick of winter, it’s nowhere near enough. So he fires up the heater hooked to the propane tank beside his bed. Burning an open flame inside a flammable structure filled with combustible fuel isn’t exactly safe, so he keeps a carbon-monoxide detector on his pillow. It’s a thin safeguard since these alarms can, and do, fail. But it’s better than nothing. To avoid freezing to death, he has to risk burning alive.
Summer brings no relief either. “The average temperature in the van during summer is about 110 degrees,” he says. “There’s only so much shade in Santa Fe, especially considering most people don’t want you parking near them.”
And if the weather doesn’t get you, there are a hundred other little things about being homeless that surely will. For one, his van is tiny, and he’s tall. Cooking involves a camp stove that makes his clothes stink of grease, increasing the risk of fire, and turning his van into a dripping sweatbox. Not to mention, the constant anxiety of knowing his belongings are not safe. Or that his home could be towed. Or having to move multiple times a day to avoid such an outcome. Or having to pee into a plastic bottle every night. Or having to find a place to dump the bottles every morning.
“I go to bed every night thinking, this could be it,” he says, reflecting on how his propane tank might blow up and kill him in his sleep. “I might not wake up.”
He adds, after a pause, “All my troubles would be over.”
The moment of truth
McNicholas is a student journalist who studies creative writing at the Institute of American Indian Arts (IAIA) in Santa Fe, and he is on track to graduate this spring with a 4.0 GPA. He often writes about life on the road. His poem “Flatbed,” which earned the 2022 Betty and Norman Lockwood Poetry Prize from the Academy of American Poets, captures a cross-country adventure he took with his father when he was 15.
In New Mexico, over half of students face food insecurity. When a whistleblower at IAIA uncovered evidence that school officials might have misused a $50,000 grant meant to support campus food pantries, McNicholas thought it was clearly newsworthy. When students claimed school officials retaliated against the whistleblower who raised the alarm, he published their allegations.
This was groundbreaking journalism. Food scarcity in Native American communities is a dire problem, so a food-pantry scandal at the nation’s top indigenous arts college is a five-alarm fire. Native Americans are twice as likely to face food insecurity compared to white Americans, and sometimes three times higher. In fact, the entire Navajo Nation, which overlaps New Mexico, is considered a food desert.
But instead of being celebrated for such journalistic work, David McNicholas was fired. Put on probation. Evicted. Homeless.
McNicholas’s clash with IAIA leadership began in 2024, after he published two anonymous submissions in his student-run zine The Young Warrior. One piece accused school officials of bullying a beloved student advisor, Karen Redeye, out of her job. Redeye herself later confirmed this, writing:
I resigned from IAIA due to repeated lack of support from my superiors, maltreatment and bullying from my direct supervisors. It elevated to the point of affecting me physically and my workspace did not provide me emotional safety … I loved my job but it became a hostile workplace and I could not continue on with my position.
The second piece accused Dean of Students Nena Martinez of misappropriating the $50,000 food-security grant. After publishing, McNicholas says he received a flood of thanks and support from his fellow students. Many of them, like McNicholas, depended on the food pantry for survival.
But the administration was not so grateful. They hit back hard, claiming McNicholas was “bullying” university staff. They opened a formal investigation with consequences sure to follow.
“Oh shit,” McNicholas remembers thinking at the time. “They’re going to throw everything at me.”
Learning to hide

I grew up in the 1980s near the poverty line, raised by a single mom. The McNicholas residence was a one-car garage with a few rooms tacked on the back in Newington, New Hampshire. Mom was an artist who scraped by doing cleaning jobs. She struggled with alcoholism. Dad was absent until I was 12, but sent $150 a month in child support. Mom didn’t really cook, but she could make a pot of beans. Most nights, we ate TV dinners. It was more than some folks had.
I had undiagnosed autism as a kid, so as you can imagine, school was hell. I learned to keep my mouth shut or get beaten up. Most of the torment from my peers was psychological. I was terrified and lonely. But work was different. In high school, I worked part-time at Market Basket, on the front end. Got hired as a bagger, promoted to keyholder within a day. I found it easier to talk to the cashiers and baggers my age because there, our roles were clearly defined.
Life at school was harder. Blending in became its own kind of hobby. I spent years studying people like an anthropologist, trying to fit in. And I spent years ostracized and harassed for being different. But every year, I got better at hiding myself.
I had traditional hobbies too, you know. I liked computers. I even thought I might study computer science. But I changed my mind at the close of senior year because I knew I had to study people more if I was ever going to have a normal life.
I could only take so much. I started drinking and ended up living in parking lots, storage closets, and couch-surfed for over a decade. But eventually I got sober, bought a house, even started a business. The startup life was too stressful, though. I lost everything — except my sobriety. I entered IAIA to study creative writing. I did my first two years at IAIA while living in my van. In my third year, I moved into the dorms. It was a chance at more stability. And life began to make sense.
I entered at 42, while my peers were mostly 19, so there wasn’t the same pressure to make friends. I contextualize my social life at IAIA as work. Most of my peers are half my age and I am a trusted mentor. These clearly defined roles make me comfortable. Around this time, I was diagnosed with autism, and that helped make sense of things. I also started The Young Warrior, and people liked it. I was part of a community.
When I got into trouble for publishing those pieces, I did what I always do. I tried to study my way out of the problem. I went to the archives and read about old IAIA publications. I read Dean Spade’s “Mutual Aid” and FIRE’s “Guide to Free Speech on Campus.” I studied other undergrad publications and wrote an official proposal and operations manual for what I hoped would be the new Young Warrior.
But overall, life was going well. I haven’t had a drink or drug in 13 years. IAIA has been a huge part of my continued sobriety. And my creative studies have given me the space to unpack the person I hid away so long ago.
Going public
Anticipating housing sanctions barring him from his dorm room, McNicholas left campus before they were formally applied and started living out of his van. But the school’s vicious overreaction in moving to evict him only convinced him it was trying to cover something up. In addition, McNicholas says when Dean of Students Martinez heard the allegations about school officials robbing the food pantry, she simply dismissed the need for food pantries to begin with. According to him, she said, “Students have meal plans. They don’t need food pantries.”
But that explanation didn’t sit right with McNicholas, who lives below the poverty line and depends on food pantries to survive. The situation escalated, he says, when the administration denied that the grant even existed. On March 21, 2024, after McNicholas, acting as press officer for the Associated Student Government (ASG), re-posted an image on Instagram summarizing the scandal, Provost Felipe Colón emailed ASG officers:
It has come to my attention over the last 24 hours that in response to the resignation of Student Success Adviser, Karen Redeye, several students, including members of ASG, have been involved in bullying, defamation, and possibly legally actionable slander and liable [sic] against members of the IAIA staff.
He then suggested that the ASG officers invite him to discuss “Karen’s departure, and particularly to receive information about the pantry grant fund and re-stocking process which has been repeatedly and grossly misrepresented.”
When McNicholas and other ASG members met to discuss the matter with Colón, McNicholas didn’t come empty-handed. An anonymous source had already given him a photocopy of the grant-award letter for $50,000. But when Colón denied the existence of the grant, and McNicholas brandished the proof, Colón tried to explain it away.
Not only that, but university President Robert Martin later threatened to sue them all.
McNicholas was floored. But given the school’s history, he wasn’t surprised. IAIA has a pattern of silencing critics — especially those trying to improve the school’s performance where it falls glaringly short. During a faculty meeting with the Board of Trustees in February 2022, former sculpture professor Matthew Eaton cited an academic paper by a former IAIA department head that showed a staff turnover rate of 30%. According to McNicholas, “They came down on him hard.”
Colón told Eaton he had embarrassed Martinez and demanded that Eaton write a public apology. Eaton wrote the coerced apology and quit the next day. In it, he said citing the high turnover rate was “disparaging” to Martinez as well as “a direct assault” against her.
But McNicholas’ main concern was for his fellow students. The lack of food, coupled with legal threats and the intense stress of having to deal with an administration that appeared to prey on its students rather than support them, had taken an emotional toll on him and his peers. And that toll was beginning to show.

One day, the ASG called yet another meeting to discuss the situation, but this time they only invited ASG members because the students feared they couldn’t trust their own advisors. When the meeting began, the ASG president showed up in tears. She had just come from a one-on-one meeting with President Martin, who had delivered shocking news — the school was seriously considering suing ASG and her over the bad publicity.
“She came to us and said, ‘They told me to fix it,’” McNicholas says. “She was in tears. And that made me mad.”
At the next ASG meeting, now that the existence of the grant was proven, Colón changed his tune. McNicholas says, “He showed up and said, ‘Oh, you know what? I did some looking, I researched it, and I think I found the grant that you guys were talking about. And I’d like to come and explain how it was spent.’”
“I was like, yeah,” says McNicholas, “I bet you do.”
McNicholas was unable to attend the meeting, but he got the sheet Colón handed out, which showed budget-to-actual figures. When pressed to release the ledger, however, Colón claimed bank statements might not go back that far. “We’re talking a year,” says McNicholas, “maybe two at most. I think he thought he could get away with that because he was in a room full of 19-year-olds. If I’d been there, I would’ve pushed back.”
In all this, what got under his skin the most, he says, was how the school treated his fellow students, such as the girl who had posted the original Instagram summary of the scandal. “I can’t stand that they did the same thing [they did to me] to a 19-year-old freshman for making an Instagram post,” he says. “They kicked that person out, kept their money, and made a 19-year-old student homeless. As far as I’m concerned, that’s unconscionable.”

Meanwhile, Colón concluded his investigation, finding McNicholas guilty of violating IAIA’s highly restrictive anti-bullying policy, which broadly bans “unwanted, aggressive behavior” and includes constitutionally-protected expression as examples of prohibited conduct. That is, he accused McNicholas of bullying administrators by publishing claims that those administrators had bullied others. McNicholas later successfully appealed his ban from campus housing and recovered about $2,000 in lost fees, but much of the damage was already done. Given this victory, he could move back into housing this upcoming semester, but continues to live in his van where IAIA can’t kick him out.
The sanctions against him not only sent him back to homelessness, but cost him work too, including a federal work-study opportunity that should have been protected from administrative meddling. “I was hired to be an orientation mentor at the end of last summer,” says McNicholas. “And the day before I was going to start, I got a call from the director of that program who said, ‘Yeah, you can’t participate because you’re on institutional probation.’”
Finding himself ruthlessly targeted by the administration, McNicholas turned to the press. Teaming up with a few peers, they went to the Santa Fe Reporter, and the article that followed made an immediate impact. “When that article came out,” he says, “both the interim director and dean of students were gone within days. Like, they were gone.”
Breaking through
After the Santa Fe Reporter exposé and the ensuing leadership shakeup, the food pantry underwent a striking transformation. The 20-foot-long conference table in the Student Success Center, once a barren surface lined with unused cans of tomatoes, is suddenly overflowing with fresh groceries. McNicholas’s journalistic work, for which he was evicted from campus housing, has not only been vindicated, but has helped make his campus a better place.
As for himself, McNicholas is about to enter his fifth and final year at IAIA. He is applying to MFAs this fall and says he hopes all this doesn’t affect his chances. “But,” he adds, “I chose to stick up for my community — and to incur the costs of doing so.”
That said, he remains shaken by the experience. “The school administration violated my rights and treated me like a criminal, offering no meaningful due process, and protecting themselves over the community at every turn.”
Indeed, IAIA has offered little in the way of accountability. The school has refused FIRE’s demands to clear McNicholas’s disciplinary records or those of any other student punished and threatened for speaking out, including the ASG president. It has also failed to revise its vague and censorial anti-bullying policy, still found in the publicly-available student handbook — leaving open the possibility of IAIA silencing other students the same way they did McNicholas. On top of all this, IAIA leadership has also failed to offer any legal or moral justification for its actions.
Following President Martin’s retirement this July, one can only hope that the newly minted president, Shelly C. Lowe, breaks from his administration’s legacy of censorship and authoritarianism. IAIA’s crackdown on student dissent must be challenged. Oversight from the school’s Board of Trustees and the Bureau of Indian Education is essential to help push IAIA in the right direction. Because no student should ever be left homeless for telling the truth.
Each night, McNicholas returns to his van. On cold nights, the propane tank hisses beside him, threatening him in whispers. On hot nights, he lies there sweating. But he remains unshaken. In one of his poems, McNicholas describes chopping through six feet of ice, the water “fixed like concrete,” his hands burning in the cold “with thin gloves or nothing.” It’s a searing image. McNicholas is nothing if not resilient.
“I want my uncredited legacy to be a small part of the student handbook,” he says, “enshrining the right to free speech that we all fought for.”