by Felicia Mello, The Hechinger Report
December 23, 2025
OAKLAND — In 2020, California led the nation in outlawing transcript-withholding, a debt collection practice that sometimes kept low-income college students from getting jobs or advanced degrees. Five years later, 24 of the state’s 115 community colleges still said on their websites that students with unpaid balances could lose access to their transcripts, according to a recent UC Merced survey.
The communications failure has been misleading, student advocates said, although overall, the state’s students have benefited from the law.
It “raises questions about what actual institutional practices are at colleges and the extent to which colleges know the law and are fully compliant with the law,” said Charlie Eaton, a UC Merced sociology professor who led the research team that conducted the survey in October.
California community colleges say they are following the law, which prohibits them from refusing to release the grades of a student who owes money to the school — anywhere from a $25 library fine to unpaid tuition. The misinformation on some college websites is a clerical problem that campuses have been asked to update, the California Community Colleges chancellor’s office said in an emailed statement.
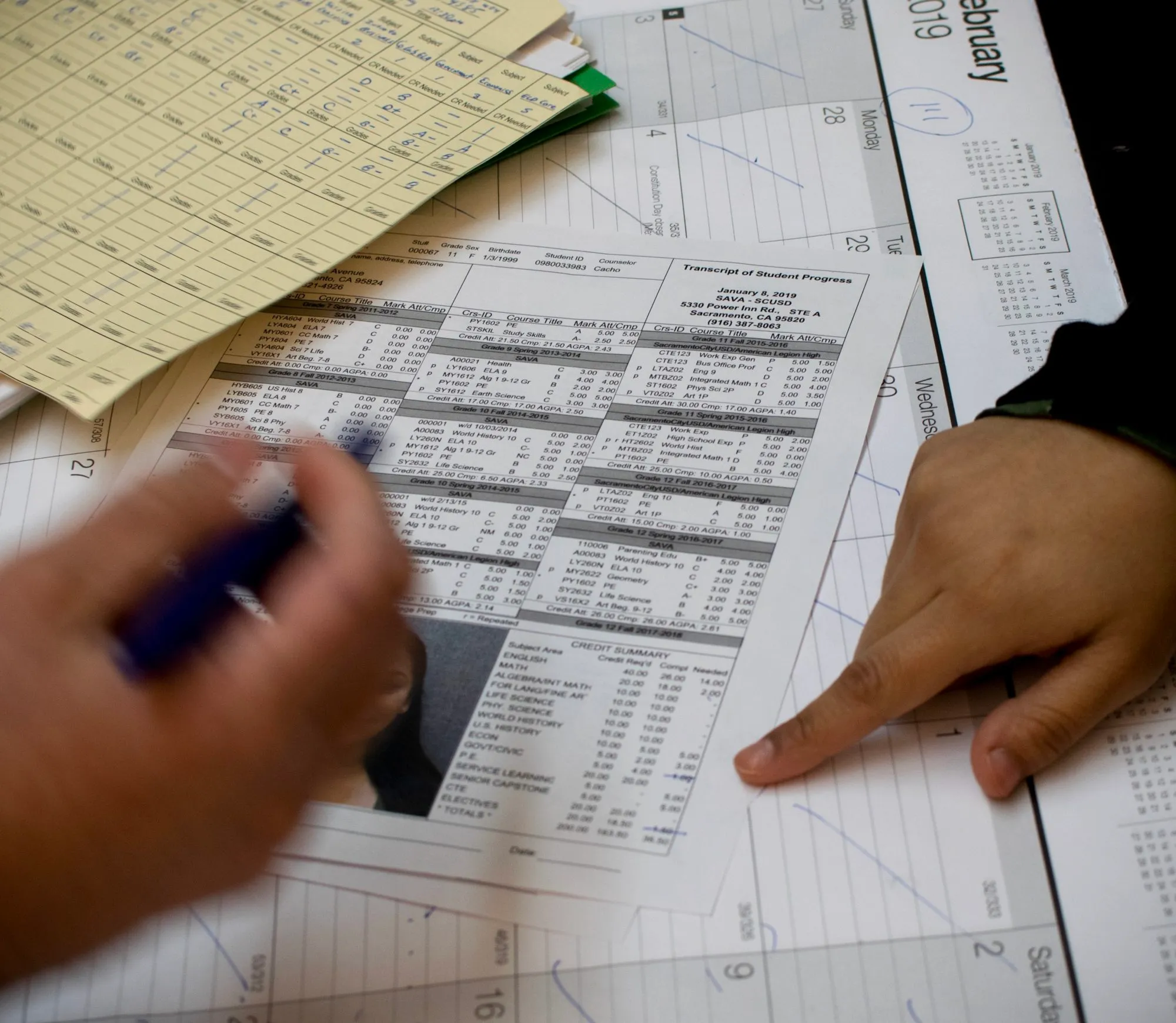
Without an official transcript, students can’t prove they’ve earned college credits to admissions offices elsewhere or to potential employers. Millions of students nationwide have lost access to their transcripts because of unpaid fees, according to estimates from the higher education consulting firm Ithaka S+R.
Student advocates argued that the practice made little money for colleges, while costing graduates opportunities that could help them pay back their debts.
California lawmakers agreed; in 2019, they passed legislation that took effect on Jan. 1 2020, barring colleges from using transcript holds to collect debts.
At least 12 other states have followed California’s lead, passing laws limiting or banning colleges from withholding transcripts.
A similar but less stringent federal rule approved during the Biden administration took effect last year.
The new rules have raised awareness about colleges’ debt collection practices and inspired some to find ways to help their students avoid falling behind on their payments in the first place or to pay off what they owe — including by forgiving their debts.
Related: Interested in innovations in higher education? Subscribe to our free biweekly higher education newsletter.
Transcript withholding was never an especially effective collection tool, researchers have found. One 2018 study estimated that Ohio’s public colleges only netted only $127 for each transcript they withheld.
Colleges and universities, however, argued that withholding transcripts was one of the few ways they had to prevent students from bouncing among institutions and leaving unpaid bills in their wake. Some use another tactic, blocking them from registering for new courses until bills are paid.
When colleges choose to withhold transcripts, the burden falls more heavily on low-income students and students of color, according to the American Association of Collegiate Registrars and Admissions Officers. Often those students accrue debts when they withdraw partway through a course, leading the college to return part of their financial aid to the federal government and charge the bill to the student.
In states with laws limiting transcript withholding, many colleges have begun communicating earlier and more often with students about their debts and offering flexible payment plans, said Elizabeth Looker, a senior program manager at Ithaka S+R. Some have added financial literacy training or required students with unpaid bills to meet with counselors.
Eight public colleges and universities in Ohio went further, offering a deal to former students with unpaid balances: Reenroll at any of the eight, and get up to $5,000 of the outstanding debt forgiven. Called the Ohio College Comeback Compact, the program, which began in 2002 and concludes this fall, was open to former students who had at least a 2.0 GPA and had been out of school a year or more.
The program was designed to give a second chance to students whose educations stalled because of events outside their control, such as losing a job in the middle of the semester, said Steve McKellips, vice president for enrollment management at the University of Akron.
Since the Ohio College Compact’s inception, 79 students have returned to the university under the program, at a cost to the state of $54,174 in debt forgiven. The university netted five times that, or $271,924, in additional tuition, McKellips said. More than 700 students have used the compact to reenroll, according to Ithaka S+R, which helped coordinate the program and is studying the results.
“I think sometimes people have this image of somebody walking away from a tuition bill because they just don’t care,” McKellips said. “But sometimes there’s just a boulder in the way and somebody needs to move it. Once the boulder was moved and they could move forward, we’re finding them continuing happily along the way they always intended to.”
Related: City University of New York reverses its policy on withholding transcripts over unpaid bills
Another California bill, introduced this year, would have given students a one-time pass to register for courses, even if they owed a debt. It failed after the University of California, Cal State and many private colleges and universities opposed it.
The University of California cited expected cuts to federal and state funding as one reason it opposed the bill. “UC believes that maintaining the ability to hold registration is essential for its ability to reasonably secure unpaid student debt,” UC legislative director Jessica Duong wrote to lawmakers.
Cal State spokesperson Amy Bentley-Smith said that Cal State wanted a flexible approach to debt collection and that campuses had started eliminating registration holds for minor debts such as parking tickets and lost library books.
“Students are able to move forward with their enrollment even with institutional debts in the low hundreds to the low thousands of dollars, depending upon the university,” she said.
Supporters of the failed bill — which also would have barred colleges from reporting a student’s institutional debt to credit agencies — said curbing aggressive debt collection doesn’t just help low-income students; it speeds up the training of workers in industries crucial to the state’s economy.
“Schools think about these institutional debts in a way that is very penny-wise and pound-foolish, and it’s preventing people from participating in the economy,” said Mike Pierce, executive director of Protect Borrowers.
Related: Colleges fight attempts to stop them from withholding transcripts over unpaid bills
Annette Ayala of Simi Valley, hoping to become a registered nurse, took her for-profit college to court to force it to comply with California’s debt collection law.
She had earned her vocational nursing license from the school, the Professional Medical Careers Institute, and wanted to continue her studies to become a registered nurse. But the college refused to release her transcript — citing a $7,500 debt that Ayala argued in court records she did not owe — and without the transcript she could not apply to other colleges.
In her case, California’s Bureau for Private Postsecondary Education, which regulates for-profit colleges under the state’s Department of Consumer Affairs, cited her former school for violating the state’s transcript-withholding law.
The college was fined $1,000 and ordered to update its enrollment agreement. The school forgave the debt it said Ayala owed. It’s the only case in which a school has been cited for withholding a transcript since the bureau started monitoring compliance with the law more closely two years ago, said Monica Vargas, a spokesperson for consumer affairs.
School officials had been unaware of the California law at the time Ayala sued, the school’s controller, Joshua Taylor, said, and have since updated their catalog to comply with it.
With her vocational nursing license, Ayala has been working in home health care. Now that she has her transcript, she’s applying for RN programs, and said her salary would roughly double once she has the new degree, allowing her to save for the future and help her son pay for college.
“You’ve got to give people the chance to get through their program and pay their debts as they’re working,” she said. “You can’t hold them back from being able to make top dollar with their abilities to pay back these loans.”
Contact editor Lawrie Mifflin at 212-678-4078 or [email protected]
This story about student debt and transcript withholding was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for our higher education newsletter. Listen to ourhigher education podcast.
This <a target=”_blank” href=”https://hechingerreport.org/5-years-after-california-banned-holding-college-students-transcripts-hostage-for-unpaid-debt-some-colleges-neglect-the-law/”>article</a> first appeared on <a target=”_blank” href=”https://hechingerreport.org”>The Hechinger Report</a> and is republished here under a <a target=”_blank” href=”https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/”>Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License</a>.<img src=”https://i0.wp.com/hechingerreport.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/cropped-favicon.jpg?fit=150%2C150&ssl=1″ style=”width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;”>
<img id=”republication-tracker-tool-source” src=”https://hechingerreport.org/?republication-pixel=true&post=114067&ga4=G-03KPHXDF3H” style=”width:1px;height:1px;”><script> PARSELY = { autotrack: false, onload: function() { PARSELY.beacon.trackPageView({ url: “https://hechingerreport.org/5-years-after-california-banned-holding-college-students-transcripts-hostage-for-unpaid-debt-some-colleges-neglect-the-law/”, urlref: window.location.href }); } } </script> <script id=”parsely-cfg” src=”//cdn.parsely.com/keys/hechingerreport.org/p.js”></script>