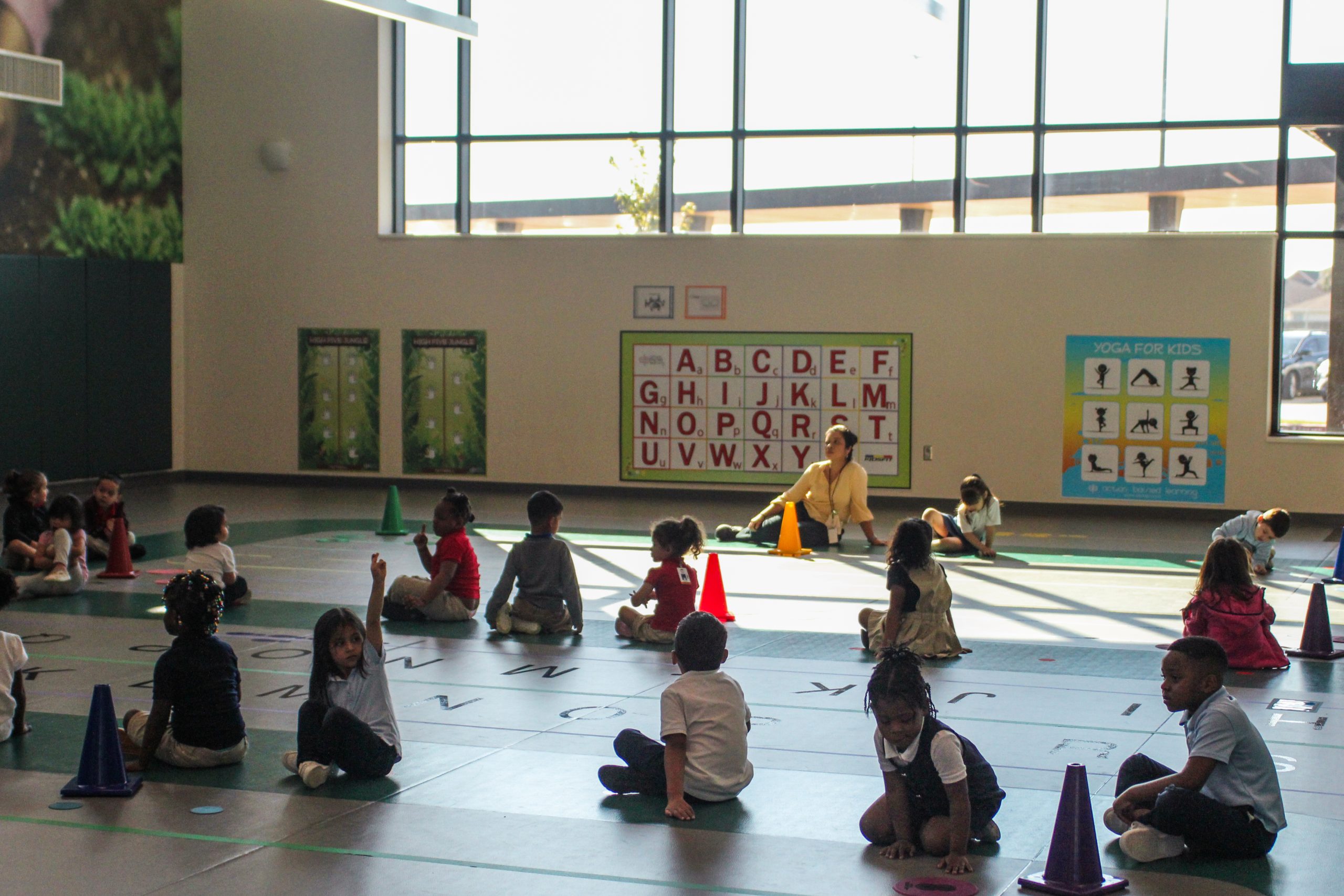
HOUSTON — Jefferson Early Learning Center bears little resemblance to elementary schools many adults recall attending in their earliest years. The classrooms have child-sized boats and construction vehicles children can play on, and ceilings painted to resemble outer space. There are no desks — all space is devoted to learning through play. Windows are low to the ground so children can easily look outside. The gym floor is made of “pre-K friendly” layered vinyl, rather than hardwood, to cushion inevitable trips and falls. Hallways are lined with a corrugated plastic for wiggly fingers to touch as children transition to other locations.
Children love coming to the building, said teacher Cathy Delamore. “They feel like they own it.”
Alief Independent School District, which serves about 40,000 children in west Houston, is one of a growing number of districts across the country to pump money into creating a building that is tailor-made for pre-kindergarteners. Its new facility cost about $21 million and enrolls nearly 400 4- and 5-year-olds. By making the investment, school leaders are trying to avoid some of the pitfalls of placing young children in buildings designed for older students, including lost learning time when tiny feet have to meander down long hallways to bathrooms and cafeterias. Research suggests that when designed well, buildings can contribute to better outcomes for children. Creators of the Reggio Emilia approach to early learning, an educational philosophy that emphasizes child-led learning, even refer to the environment as the “third teacher” in a classroom.

Over the past few years, educators have grown aware of the benefits of a personalized pre-K environment, said Melissa Turnbaugh, a senior principal at the architecture firm PBK, which has designed more than 240 elementary schools nationwide, including Jefferson and several others in Texas. “There’s an openness and willingness to rethink these sites,” Turnbaugh said.
Related: Young children have unique needs and providing the right care can be a challenge. Our free early childhood education newsletter tracks the issues.
Similar pre-K renovations and investments have been made in both high- and low-income Texas districts, including the nearby Houston Independent School District, Willis Independent School District north of Houston, the Mansfield Independent School District south of Fort Worth, the Harlingen Consolidated Independent School District in the Rio Grande Valley and Leander Independent School District, just northwest of Austin.
Nationally, districts of all sizes have embraced the trend over the past few years, including the Troy School District in Michigan and New York City Public Schools. In some cases, building a specialized facility helps a district with limited resources get “the biggest bang for their buck,” while meeting enrollment needs, said Turnbaugh. Some states and cities are also dedicating money to the efforts, including Illinois, Detroit and San Mateo, California.
That embrace is in part because of a growing recognition nationwide of the importance of play for young children, as well as reports that play time has been increasingly squeezed out of the early grades. States are also seeing record high enrollment in state-funded preschool programs. During the 2022-23 school year, investment in state-funded preschool reached an all-time high. Spending on the programs increased in 29 states, buoyed in part by Covid relief funds. Between 2022 and 2023, for example, Texas saw more than 21,000 additional 3- and 4-year-olds enroll. The state also slightly increased pre-K funding and, beginning in 2019, started requiring districts to offer full-day pre-K programs. The full-day programs have been rolling out in districts since 2020.
Scores of districts are “adding this new grade of 4-year-olds,” said Shelly Masur, vice president of advisory and state policy for the Low Income Investment Fund, which runs an initiative focused on creating and improving high-quality facilities for early learning programs. “They have to figure out where those kids are going to go.”
A facility built for their needs, like Jefferson, is exactly where young children should go, some experts say. The children seem to agree.
On a sunny fall morning, joyful screams could be heard as children chased each other up and down gentle hills on a large playground with natural-looking features meant to replicate the highlands and lowlands of Texas. Pre-K students in elementary schools don’t always have age-appropriate playgrounds, and structures are often designed for children who are older. But Jefferson has multiple large playgrounds and play courtyards, all designed for pre kindergarteners, featuring natural structures and textures, like logs and grass.
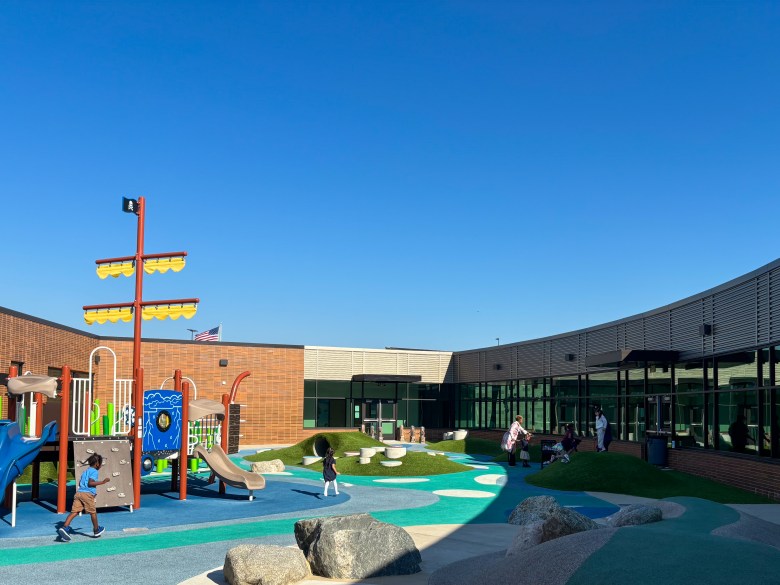

In Alief, where more than 83 percent of children qualify as economically disadvantaged, more than 20 percentage points higher than the state average, residents voted in 2015 to approve a property tax increase to help pay for full-day pre-K programs in the district. After touring the Mansfield Independent School District’s early learning facility, Alief’s district leaders decided they wanted to invest in an early learning building with immersive, themed classrooms, instead of simply adding on or repurposing classrooms in elementary schools around the district. Jefferson opened in 2022 as one of two new early learning facilities in the district. About 6 miles away, the second, Maria Del Carmen Martinez Early Learning Center, which has a similar design, serves around 400 students.
A growing body of research shows that not all pre-K classrooms, or the facilities they’re housed in, are appropriate for young kids. Early learning settings in particular should have a warm, homelike environment with ample natural light, research shows. There should be spacious classrooms that allow children to move their bodies and play in a variety of spaces around the room. Facilities should have playgrounds that are appropriate for the littlest learners, and provide ample opportunities to experience and explore nature.
Related: How play is making a comeback in kindergarten
There are also practical details to keep in mind for preschoolers, like having bathrooms adjacent to classrooms, child-sized furniture, tiny toilets, and sinks low to the ground so children can practice routines like hand washing independently. “When we make things more accessible to them, they start to learn the independence that we need them to develop over time,” said Masur. This type of setting isn’t always present in elementary schools, which are built to accommodate a much wider age range of children and are typically designed for instruction rather than play.
Facilities can have a surprisingly large impact on the experiences of teachers and young children. A study of a preschool program in West Hartford, Connecticut, for example, found the amount of children’s time spent interacting with an adult caregiver increased from 3 percent to 22 percent after the program moved from a crowded basement room to a larger classroom with bathrooms, sinks, storage space and phones inside the classroom. Although all other factors remained the same, the teachers reported their students had fewer tantrums, something they attributed to having a larger, brighter and more organized space.
A facility can even affect how satisfied early educators are with their jobs. Delamore, the Jefferson teacher, who has worked in the district for 18 years, said the bright, spacious rooms and hallways help keep her from feeling “confined” during the day. While aimed at 4-year-olds, the building’s “calming atmosphere” helps her enjoy being at work, she said.
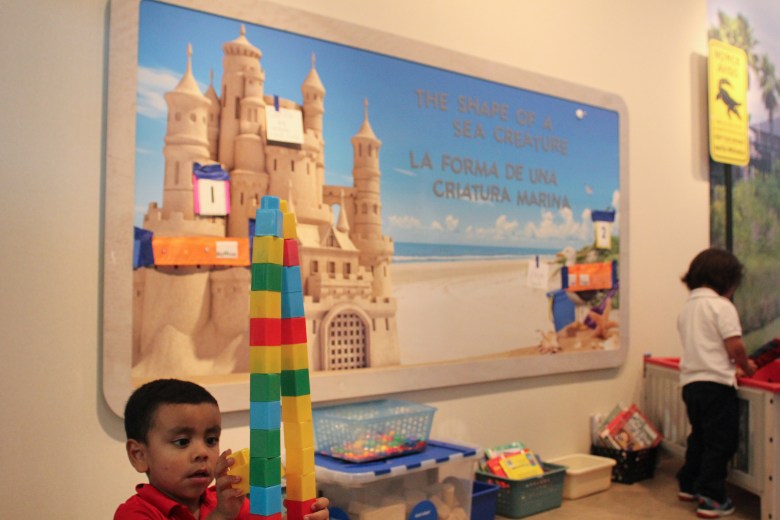

Certain aspects make more sense for children at this age, she added, like the spiral shape of the building, which makes it easier to keep students together as they transition. Students eat family-style meals around circular tables, creating a sense of community, Delamore said, a contrast to the long, rectangular tables often seen in elementary school cafeterias.
Buildings that are not designed to meet childrens’ needs, or that are cramped and outdated, can impede development and learning, experts say.
One of the most recent examples of this comes from a 2016 study of Tennessee’s public preschool classrooms, which are mostly housed in existing elementary schools. That study, conducted by researchers at Vanderbilt University, found 25 percent of each school day was lost transitioning children to another activity, including walking to bathrooms and lining up to go to lunch.
Related: The complex world of pre-K play
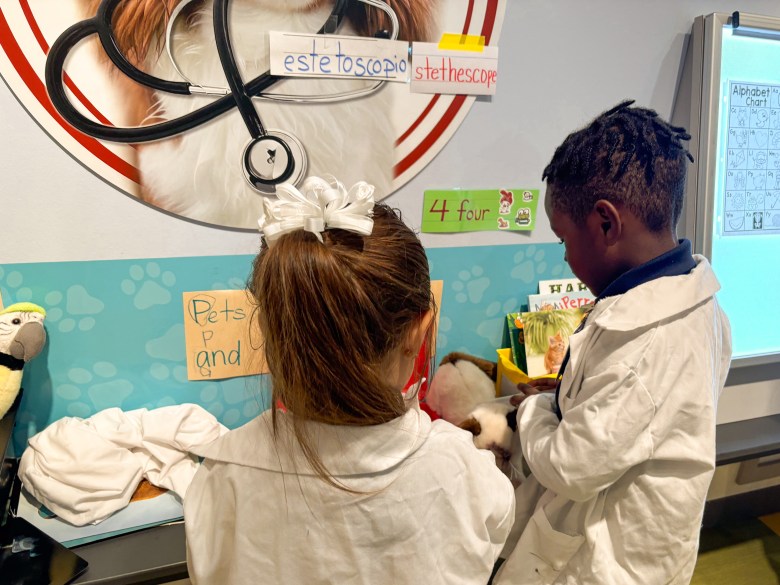
When designing Jefferson, Turnbaugh and her team tried to “think of the campus through the eyes of a 4-year-old.” Delamore, at Jefferson, said the intricately-designed classrooms motivate students to go deeper in their play. On a recent morning in the “veterinary” classroom, a dozen 4- and 5-year-olds busied themselves around the room, immersed in play or small group work with a teacher. Children drew pictures of animals, read books and played animal-themed card games beneath large, colorful pictures of dogs and cats painted on the walls.
On one side of the room, 4-year-old Jaycyon had donned a white lab coat and was inspecting a fluffy gray and white toy cat lying on the counter in front of him. The cat was hurt, Jaycyon announced, likely from a sharp corner of the cage he was kept in.
“I have to give him a shot,” he said bravely. Jaycyon dipped a clear, plastic syringe into an orange medication bottle and confidently injected invisible medication into the cat.
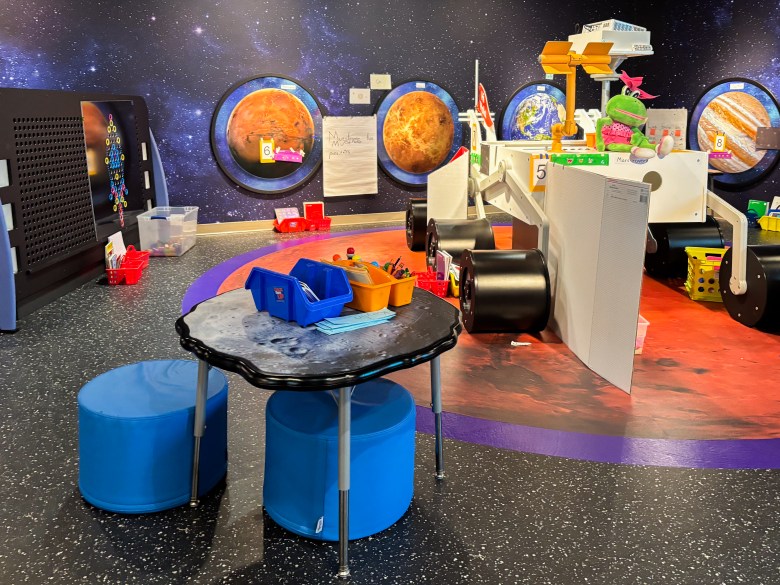
At the end of three weeks, Jaycyon and his classmates will transition to a new classroom, such as “Tinker Town,” where they will learn about construction, or “Space City,” an homage to the nearby NASA space center.
On a daily basis, students have access to one of several outdoor spaces called a “back porch,” where families can also come and eat lunch together. These spaces also act as surrogate back yards for students, many of whom don’t have yards at home or access to parks. Students also have access to a sensory room with toys and soft mats, where they can take a break when they are overstimulated and practice skills to calm down.
Jefferson sits on nearly 20 acres of land, accessible via trails for students to explore with their teachers. (Alief returned the surrounding land back to its natural prairie state to help with climate-change related flooding.)
The educators at Alief say the district’s investment in a facility that encourages play-based learning has paid off. “What I see as a major difference is the children’s self-regulation, but also their confidence,” said the school’s principal, Kim Hammer, now in her 16th year leading an early childhood center. “A traditional pre-K setting is more teacher led and teacher directed,” she said. “Here it’s more teacher facilitated, so you see more of the children taking more initiative,” she added. “Children have autonomy, and children have much more choice.”

There is evidence that the new facility may be helping children progress. During the 2023-24 school year, 49 percent of students came in meeting vocabulary benchmarks. By the end of the year, 73 percent were at that level, Hammer said, a higher rate than previous years when the district’s pre-K programs were in traditional elementary schools. School officials say the themed classrooms help enhance children’s language skills, as children learn the vocabulary specific to that room. Attendance rates are high and holding steady, something that is uncommon in pre-K.
Despite the success and benefits of programs like Jefferson’s, educators agree there are challenges. A pre-K only facility adds an extra transition for students who, in traditional programs, might otherwise attend pre-K at their home elementary school.
Without more funding, revamped pre-K facilities are unlikely to spread fast. Many districts lack the money, partly because state and federal funding for pre-K is often less than for other grades. In Texas, for example, although the state now requires districts to offer full day pre-K, it only provides funding for half a day of pre-K. Alief has to cover the rest from local funds.
Although sustaining the building will be financially challenging in the long run, educators are determined to find a way to make it work for the benefit of the kids.
Back at the veterinary center on that fall morning, Jaycyon finally had a breakthrough. He had discovered something alarming about his patient, or “kitty,” as he had been named by the pre-kindergarteners, that would direct his next veterinary tactics.
“He burned himself in the kitchen!” he exclaimed.
How?
Jaycyon answered somberly: “He was cooking eggs.”
Contact staff writer Jackie Mader at (212) 678-3562 or [email protected].
This story about early learning centers was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education, with support from the Spencer Fellowship at Columbia Journalism School. Sign up for the Early Childhood newsletter.