The HEPI blog was kindly authored by Fiona Ellison, Co-Director, Unite Foundation
University is often described as a transformative experience, full of growth, challenge, and discovery. But for care-experienced and estranged students, the journey through higher education is often shaped by the absence of family support, financial insecurity, and a lack of belonging. The Unite Foundation has taken a deep dive into the latest findings from the HEPI and Advance HE Student Academic Experience Survey 2025 (SAES), offering a clear picture of these students’ realities and developing a call to action.
The cost of insecurity
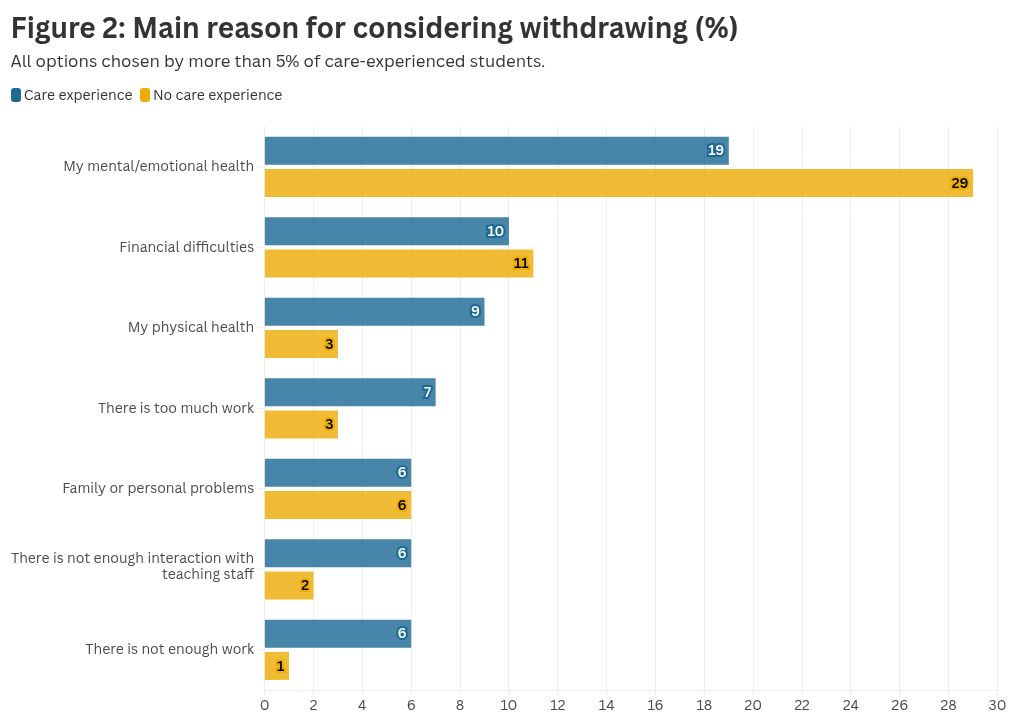
Care-experienced & estranged students are much more likely to drop out of university but we also know from the findings from the SAES that they’re much more likely to consider dropping out as well:
- 43% of care–experienced students and 44% of estranged students have considered withdrawing from university, compared to 28% of their peers.
Whilst the survey doesn’t give us insight into the reasons why, it does provide clues. For example, care-experienced students are experienced and estranged students work significantly more hours in paid employment:
- Care–experienced students work on average 11.3 hours/week, and estranged students work 11.1 hours/week, compared to 8.8 hours/week for other students.
This extra workload often stems from limited access to family financial support and a student finance system that doesn’t fully meet the needs of independent students. As HEPI highlighted in their work on minimum income standards those studying without financial support, even with the full maintenance loan, would still need to work over 20 hours at minimum wage to achieve the minimum income standard needed to survive at university.
We see this increased workload play out in students’ ability to attend lectures and complete academic work:
- 44% of care experienced students requested deadline extensions, compared to 29% of non-care experienced students.
It’s no wonder that only 79% of care-experienced students complete their undergraduate degrees compared to 89% of non-care-experienced students, and just 64% achieve a good honours degree compared to 77% of their non-care-experienced peers. We don’t have reliable data on estranged students – but that’s for another blog! If students are having to work longer hours just to afford to live, then it’s no wonder academic studies will often take a back seat.
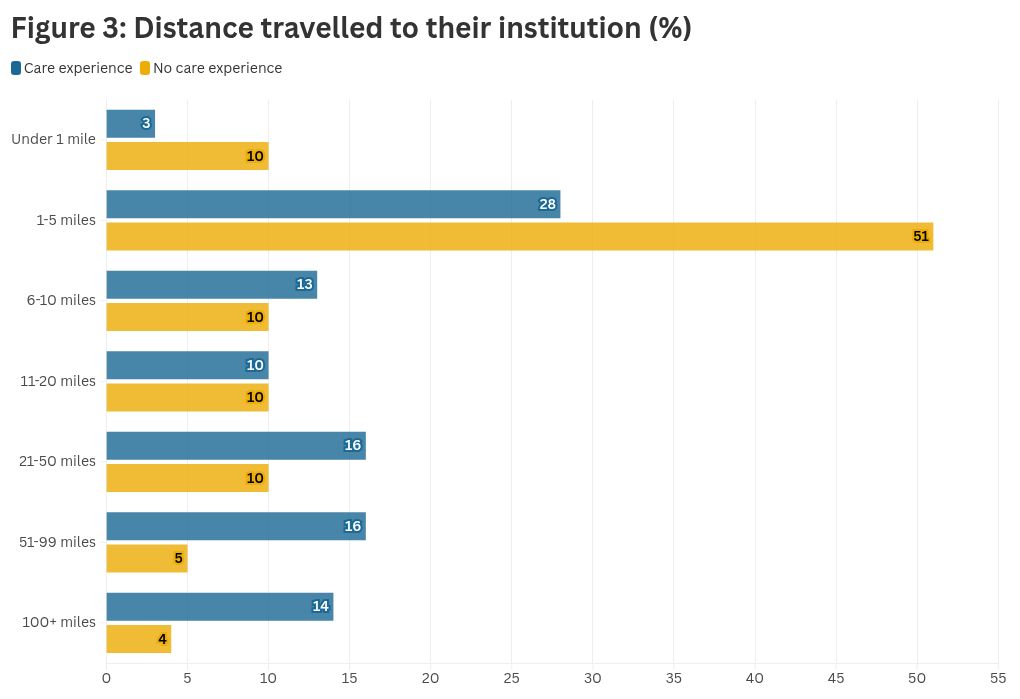
However, there is a shining light. Housing is more than shelter – it’s a foundation for success. The Unite Foundation has, over the last 14 years, provided free, year-round accommodation to care-experienced and estranged students, removing a major barrier to continuity and wellbeing. Data published to celebrate our 10th birthday found that there is ‘strong evidence that the scholarship improves educational outcomes of the students we support, specifically in year-to-year progression and completion’.
These figures highlight how housing insecurity and financial pressure can directly impact academic persistence and performance – but whilst there is a simple answer, not enough institutions are truly looking at the evidence-based solution to address the inequality this group of students face.
Loneliness and the need for community
One of the most striking findings within the report is the prevalence of loneliness:
- 45% of estranged students and 36% of care experienced students feel lonely “all or most of the time,” compared to 27% of other students.
Loneliness affects mental health, engagement, and retention. While it’s encouraging that loneliness among care-experienced students has decreased from 48% in 2023, the rise among estranged students signals a need for targeted support.
For this group of students, studying without the support network of family means the lack of ready-made networks needed when times are hard. The All of Us community was designed by and for care-experienced and estranged students to connect with peers – whether online or in real life. The handy guide #AllOfUsLocal is a practical toolkit that institutions can take to help create a community in your institution to create ways to support care experienced and estranged students to avoid isolation.
A mixed picture on wellbeing
Encouragingly, care-experienced students report similar levels of wellbeing to their non-care-experienced peers:
- Life satisfaction: 6.7 vs. 6.6
- Happiness yesterday: 6.2 for both groups
- Anxiety yesterday: 4.6 for both groups
However, estranged students consistently report lower scores:
- Happiness yesterday: 5.9
These differences underscore the emotional toll of estrangement and the importance of tailored support that ensures estranged students can access at any point – given we know for many students estrangement happens through their academic journey.
What next?
The Student Academic Experience Survey continues gives us the evidence about what this group of students thinks and feels about their time in higher education – it makes for some pretty tough reading. However, there isn’t anything new or surprising in the report for those of us that work in this space.
We now need to move beyond data and turn these insights into action. Universities, policymakers, and sector leaders must work together to ensure that care-experienced and estranged students are a target for activity. To do this, we need:
- Universities to prioritise year-round, affordable accommodation – Institutions should commit to providing or partnering on secure, year-round housing options for care-experienced and estranged students, recognising housing as a foundation for academic success.
- Targeted financial support and flexible funding models – Review and adapt bursary and hardship funding to reflect the true cost of living for independent students, especially those without family support.
- Better data collection and visibility – Universities and sector bodies must improve the identification and tracking of estranged students to ensure their needs are recognised and met.
- Embedding community-building initiatives – Adopt and promote tools like #AllOfUsLocal to reduce loneliness and foster belonging on campus. You can join our HE Peer Professionals network to share your challenges, celebrate successes and learn from others about how to support community-building activities.
At the Unite Foundation, we’ll shortly launch our new strategy, which will include practical steps that higher education institutions can take to ensure a focus on housing plays a key role in driving equality for care-experienced and estranged students. If you want to be the first to know about what we’re up to, do sign up to our newsletter.