In early June, the governing board of Florida’s university system surprised the higher education sector when it rejected Santa Ono as the sole finalist for the presidency of the University of Florida. Ono had faced backlash — led by conservative activist Christopher Rufo — over his past embrace of diversity, equity and inclusion efforts while head of the University of Michigan.
Later that month, University of Virginia President Jim Ryan abruptly stepped down after the U.S. Department of Justice pressured him to resign over the institution’s diversity efforts. Ryan said he wouldn’t fight to keep his job when staying would have cost the institution research funding and student aid and hurt international students.
The duties of the modern college president extend far beyond keeping their institutions viable. For decades, how the head of a college is selected and who fills the position has been steadily shifting. Now, whoever assumes the role will likely take vitriol from both the public and policymakers.
James Finkelstein, professor emeritus at George Mason University’s public policy school, researches leadership in higher education. We spoke with him about the changing role of the college president, the increased influence a presidency faces from both the political and private sectors and what that means for higher ed in the long run.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
HIGHER ED DIVE: How does one become a college president? And has that changed in recent decades?
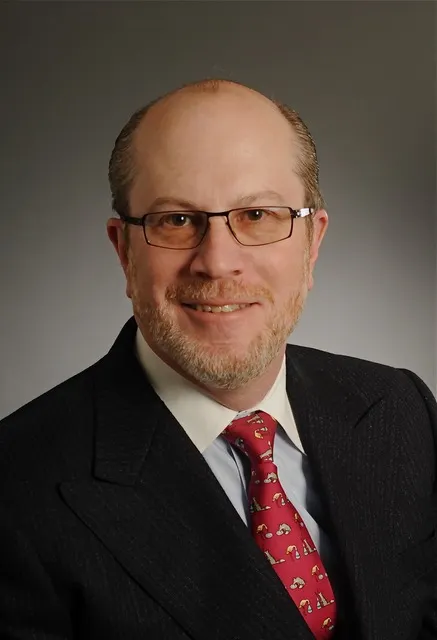

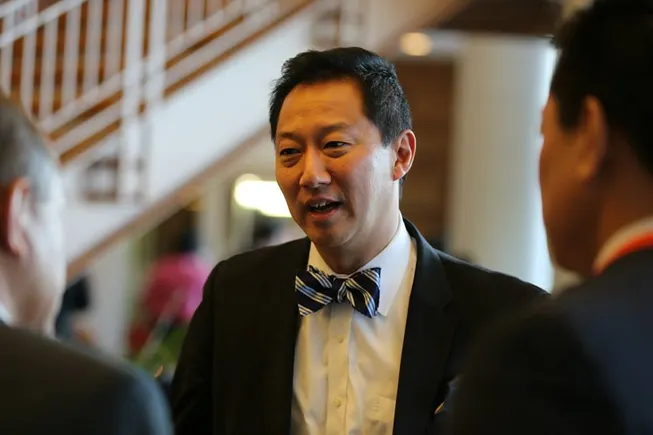
James Finkelstein, professor emeritus at George Mason University
Permission granted by Judith Wilde
JAMES FINKELSTEIN: The traditional route would start with becoming an assistant professor. You get tenure next, and then you may start to move up the administrative ranks. The most common path was to go from provost to president. For now, that’s still the most common path, but it’s on the decline.
The problem is, provosts don’t fundraise. Deans do. And the No. 1 qualification that a board now looks for in a university president is their ability to raise money.
Given that shift in priorities, how do college boards pick their institution’s next presidents?
My colleague, Judith Wilde, and I have studied this process extensively, and boards are increasingly relying on executive search firms.
We found that only 2% or 3% of presidential classified ads mentioned a search firm in 1975. Today, it’s almost 100%. And based on the data, that change has also correlated with the beginning of the decline in the length of university presidents’ tenure.
Search firms do the initial screening and determine for the board which candidates are really viable. But very few of the search firm senior executives have any real experience in higher education and their No. 1 responsibility as fiduciaries is to return profit to investors.
From there, the board picks from the candidates highlighted by the search firm? What do they look for?
Yes. People tend to look for candidates who look like them. And boards are not primarily made up of academics — the only thing most board members know about a university is that they got a degree from one. You’re seeing a lot more political types on the boards, as is the case in Virginia, or corporate types.
It’s interesting, corporations don’t turn to universities for their leadership. They don’t select a college president to run them. The former president of TIAA [Clifton Wharton Jr.] was the only university president to become a CEO of a Fortune 500 company — and he led a company designed to serve universities.
But many universities, at least 10% or so, will select a corporate executive to lead them.
If boards expect university presidents to behave more like corporate executives than leaders of an educational, social and cultural institution — someone who serves the public — then the next generation of university leadership is going to look very different. You’re going to see a different kind of person be not only sought after but interested in these jobs because they think they can take their private sector skill set directly into higher ed.
In recent years, the presidential compensation packages at some colleges have mirrored those of Fortune 500 CEOs. In 2022, Ben Sasse received a notably lucrative package when he was hired to lead the University of Florida, as you and Judith have discussed. What effect does that shift have on colleges?
When I was an undergraduate, the university president probably wore a tweed sport coat with leather patches on the elbows. And the patches weren’t there to make a style statement; it’s because the elbows were worn out. If he had a car — and it was far and away “he” when I was in school — it was a car from the university’s car pool that was several years old.
And in the past, presidents maintained some academic interests. They taught. They were visible on campus.
Now, university presidents drive expensive cars and are more likely to associate with people outside the university than faculty inside the university.
Our sector does not enjoy the reputation with the public that it used to. There are all sorts of questions now about the value of a college degree. People generally think faculty get paid a lot of money and don’t do very much.
More than anything, presidents today are facing the question of if there is a way to win back that trust.
While college presidents are grappling with that question, though, they are also watching their positions become increasingly precarious. One recent example is Santa Ono, who had been set up as Sasse’s replacement. Traditionally, the vote from the Florida universities’ governing board would have been pro forma. What shifted the tides and left Ono out of a job?
Ono was targeted by the Chris Rufo machine. You can go back and read Rufo’s interview with Politico and listen to his interview with The New York Times — he’s very public about his strategy to delegitimize leaders in higher ed. His team made a decision early on that they wanted one of their own in Florida. And Ono wasn’t it.
Having watched the entire governing board meeting in Florida, my professional assessment is that I’ve never seen a president or someone of Ono’s stature so ill-prepared and give so poor a performance on every level.
Whoever prepared him, didn’t. And if they did, they weren’t preparing him for the right thing. It was much like what happened to the college presidents who testified at congressional committee hearings. Ono wasn’t completely prepared that he was going to be essentially cross-examined by a former state legislator.
By that point, Ono had already announced his departure from the University of Michigan, leaving a highly debated track record on diversity efforts and the handling of student protests in his wake. Does he stand a chance of getting another job heading a university?
About 75% of presidents are what we call one-and-done — they report they’ll hold one presidency, and that’s more than enough. The Gordon Gees of the world are the exception, not the rule.
Ono was, in my view, the modern-day equivalent of [former West Virginia University President] Gordon Gee. He’s the professional president who developed a public persona. He developed it at the University of Cincinnati, refined it at the University of British Columbia, and then brought it to Michigan.
But I’ve talked to people at Cincinnati and Michigan. The truth of the matter is, he wasn’t well-thought of by the faculty. And he burned out very quickly in Michigan.
Ono shouldn’t be the model for the modern university president. Personally, I don’t think that he’s going to get another presidency after the Florida situation, at least not for a while.
Is the role of president still a consequential one? Do the heads of colleges wield influence in the same way they have in the past?
Who the president is makes a difference. They set the tone of the institution in many ways. But presidents today can exercise less independent leadership than they did in the past — they’re being put on a shorter and shorter leash.
There are so many different constituencies that they’re having to serve, and a lot of those constituencies are in conflict with each other.
Some presidents are engaging in what people call anticipatory compliance.
“In order to avoid these conflicts,” the thinking goes, “I’m going to get one step ahead.” Sadly, what that means is that when the board intervenes, they want even more.
Is there a world where that kind of interference becomes so unpleasant that it renders the job unpalatable?
I think for many serious potential candidates, the answer is yes. It doesn’t matter whether you’re being paid $1 million. Or if you have two country club memberships, a big car, a big house and staff, and all of that. These jobs have always been 24/7, 365. And the scrutiny is exponentially worse now.
The real question is: Who’s going to want these jobs? That’s part of the plan of critics of higher education. They want to drive people out so they can replicate what they’re doing in Florida and appoint political loyalists who have no experience in higher education.
Even though conservatives are critical of what they see as judicial activism, they have been extraordinarily active on college boards, working to influence curriculum and promotions and tenure.
The current climate changes things for all trustees, even those who don’t align with this thinking. Regardless of their backgrounds, no board will want to appoint a president who is going to put at risk all of their research funding. And the Trump administration has shown that it is willing to use any lever it has to bring these institutions under its thumb. Look how quickly Jim Ryan was gone from UVA.
As you mentioned, presidents are serving increasingly shorter tenures, instead of holding the position for life, or at least until retirement. Beyond a loss of leadership consistency, does this turnover hurt colleges?
Take Jim Ryan as an example. He’s 58 years old.
I assume the terms of his contract were renegotiated when he left, but based on my analysis of his 2022 contract, the university has a future liability of almost $17 million to him. He would actuarially retire from teaching in 15 years, and in 2038, his base salary would be over $1 million a year for teaching at most two courses a semester.
The people who are actually doing most of the teaching at UVA in 2038 won’t be tenured or tenure track. They will be contingent faculty who are barely able to scrape together a living.
If you put $10 million in a scholarship fund at UVA, would that be a better investment than keeping Ryan on the faculty? The answer is a no-brainer.