Today I’m taking a break from blogging to wish all of you who celebrate a merry Christmas. If you’re in a cold and/or wet climate, be warm and dry. Hug your loved ones and relish some downtime. Be safe and take care.
See you all soon.
Related

Today I’m taking a break from blogging to wish all of you who celebrate a merry Christmas. If you’re in a cold and/or wet climate, be warm and dry. Hug your loved ones and relish some downtime. Be safe and take care.
See you all soon.

This blog was kindly authored by Dr Kate Wicklow, GuildHE Director of Policy and Strategy
The higher education sector is renowned for its innovation and global standing, with diverse providers consistently delivering great work and immense value. However, the sector could also certainly do with some festive cheer at the moment. There are multiple pressures placed upon us which impact our resilience and threaten our energies and resources to continue to be a global powerhouse.
The Post-16 White Paper has offered the sector a new vision, one where it asks higher education institutions to govern themselves differently, with greater collaboration between providers, and therefore less market based ideologies within sector activity. But it places all of the responsibility to fix the sector challenges on individual providers rather than offering systems leadership or policy support.
The recently published new OfS strategy also offers a welcome reset of the regulator-institution relationship to be less combative. However, the actions proposed to underpin the strategic statements seem disconnected from the DfE vision of sector coordination, likely in part due to their unfortunate simultaneous development. The OfS strategy roadmap provides no clarity on how the regulator plans to either reduce the regulatory burden or sustain its current risk-based methodology. Furthermore, it omits measures essential for safeguarding sector diversity, an obligation under the Higher Education and Research Act (HERA), and one that is arguably critical in the current climate.
The missing piece: financial realism
Both documents omit the critical financial realities institutions face, which aren’t solely due to governance failings, but rather mounting pressures that are well rehearsed and have forced the sector to do more with less for the last 13 years – which just isn’t sustainable. At some point, the system breaks, and we are seeing cracks widen now. While the White Paper offered a fee uplift, the unexpected international student levy negates this. We are certainly in a critical moment for the future shape of the sector, which makes the forthcoming review of OfS’s Strategic Priority Grant particularly concerning in its potential to destabilise what additional state funding is received.
GuildHE represents the UK’s most diverse range of higher education providers, varying in size, location, and operational models. Our members, who include small and large, rural and urban, practice-based and online, specialist and more generalist, and both publicly and privately funded institutions, are renowned for delivering practical, industry-relevant education, research, and innovation. Thanks to this unparalleled diversity, GuildHE acts as a crucial gauge for the higher education sector, offering unique insights into the opportunities and challenges affecting the entire landscape.
The white paper rightly highlights the immense value that this diverse range of higher education providers brings to students, local economies, and the nation as a whole. Our member institutions are often pioneers in their fields, offering unique courses and producing highly skilled graduates. Yet, despite this declared commitment to diversity, policy mechanisms and funding models always seem to operate with an inevitable bias towards scale and homogenisation.
The true barrier to sustaining sector excellence and diversity isn’t simply a lack of commitment from institutions, but a contradiction at the heart of policymaking: the very mechanisms of funding and regulation are inadvertently acting as a constraint on the diversity they claim to champion.
The current regulatory framework, built for a typical large-scale, multi-faculty provider, often inadvertently penalises innovative and smaller-scale or specialist institutions. A clear example is how the Teaching Excellence Framework (TEF), with its emphasis on metrics, disadvantages, by design, providers with small student cohorts. The core issue is not just which metrics are used, but the inherent volatility of data when applied to small cohort sizes. Offering providers the opportunity to contextualise their quantitative data with other evidence is therefore vital, but adds additional burden on these institutions.
Funding must recognise the distinctiveness and value of specialist institutions, both in teaching and in research. For research, the White Paper encourages institutions to focus on strengths, specialise, and collaborate, but we must ensure this doesn’t undermine world-leading specialists by overusing the ‘specialist’ term too liberally. Equally, there must be incentives for collaboration, tangible reasons for larger institutions to work with smaller-scale or different partners, and levers pulled to encourage institutions not to simply rinse and repeat the same collaborative arrangements. In addition, innovation funding remains skewed towards larger-scale operations, with thresholds on HEIF remaining a particular barrier for smaller-scale institutions. We need fresh thinking on knowledge exchange and innovation funding to diversify recipients, sustain innovation across all institutions, and enable commercialisation.
In teaching funding, the review of SPG will inevitably create winners and losers. There are worries in the sector that the subject prioritisation will not reflect all of the I8 areas. For example, creative skills are at the top of the Industrial Strategy and are regularly cited as being important to all industries. The creative industries are rife with skills shortages and clearly require graduate skills (75% of the industry have degrees, significantly higher than the UK average of 51%). Yet we are concerned that the forthcoming SPG review will not redress years of creative subject funding cuts to deliver this much-needed pipeline.
Specialist institutions of all types require state-of-the-art equipment, from professional-grade theatres to medical-grade clinics and working farms. These learning environments come with high fixed costs, regardless of student numbers, which themselves need to remain fairly static to ensure the equipment is accessible to all students for a high-quality experience. If funding is driven solely by student volume, without adequate recognition of the fixed costs of this distinctiveness, the business model for specialist institutions becomes perpetually precarious. This is what we’ve seen materialise over the past 10 years and is why the OfS and DfE recognise the additional financial needs through specialist institution funding. This funding is also under review in the new year.
To genuinely champion institutional diversity, the OfS must do more than offer rhetorical support or simply monitor providers. In line with the white paper’s emphasis on protecting and preserving diversity, the OfS has a duty to ensure its funding proposals reflect this goal. If OfS is serious about safeguarding diversity, its conclusions on funding and its response to the white paper must lead to a review of the regulatory policies and processes that currently encourage uniformity. This is essential to create the conditions necessary for all types of institutions to not just survive, but truly thrive. DfE also has a bigger role to play in thinking about diversity within its policy development and vision for the sector. Moving away from market-style regulatory dynamics offers them new levers and ideas for bringing us all together to collectively support our world-class provision to grow and innovate.
GuildHE will continue to push for a regulatory landscape that is proportionate and focused on fostering greater sector collaboration in order to achieve excellence across the widest range of institutions because that is how we deliver for the widest range of students.
So our Christmas wish is simple: that policymakers seize more opportunities to make good on HERA and the white paper’s stated ambition to protect the sector’s diversity.

There’s nothing on the telly this Christmas.
There never is. But if, like me, you have trouble switching off from work but also enjoy being slumped in front of the box with a tub of Heroes (Quality Street are now banned in our house), I have good news.
I’ve picked out films and TV shows released this year that either have something to say about higher education, are set on campus and/or depict contemporary student life.
You’ll laugh, you’ll cry, you’ll shell out for a VPN, you’ll wonder why Disney thinks Nani should abandon her sister for college, and you’ll almost certainly switch off, which is what the break is for – eventually.
Other than the fantastic but final season of Big Boys, it really was slim pickings again this year from a UK perspective – which reminds us that whatever else the BBC, ITV and C4 are doing, it’s not higher education.
Before you take to the comments, I’ve not put in books or podcasts. I do enough reading in this job, and I edit ours, so my appetite for either is fairly thin – but do pop suggestions below if there are any.
You’re welcome – and apologies in advance if you’re at work over the next couple of weeks.
Julia Roberts heads to Yale (sort of – it’s actually filmed in Cambridge but set in New Haven) as a philosophy professor whose star student accuses her colleague of sexual misconduct. If you enjoyed the discomfort of Cate Blanchett in “Tár” but wished it had more Ivy League networking and dialogue about whether university should be a “safe space” or not, this is your Boxing Day sorted. Roberts delivers a line about education being meant to make you uncomfortable, not a “lukewarm bath”. Arif Ahmed will be thrilled.
Guillermo del Toro got his passion project made, and it’s a meditation on academic hubris. Oscar Isaac plays Victor as the ultimate postdoc gone wrong – brilliant, egotistical, and convinced his research will change the world. The university scenes feature actual professors listed in the credits, though they don’t seem to have undertaken that optional supervisor training. Jacob Elordi brings surprising depth to the Creature, who arguably just needed better student support services.
This documentary about the 1988 Gallaudet University protests is the year’s essential viewing for anyone who thinks student activism doesn’t achieve anything. Directed by Nyle DiMarco and Davis Guggenheim, it shows how four students shut down their campus and changed history, forcing the appointment of the university’s first deaf president. The board chair who supposedly said “Deaf people are not ready to function in a hearing world” will have you chanting “Deaf Power!” from your sofa.
If you’ve ever wondered what would happen if someone tried to remake The Sopranos but set it in a Turkish university’s literature department, Bir Zamanlar İstanbul will be right up your street. Ali and Seher – a final-year Turkish Literature student and journalism student respectively – meet during a campus debate on whether crime is driven by society or personal choice, and the series quickly turns into a mafia thriller. It’s another one of those shows that casts 35-year-olds as undergraduates, but at least the debate scene offers a rare glimpse of Turkish academic culture before everyone starts shooting at each other. And just under the surface there’s some fascinating “western culture” v traditional Islamic values themes to get into too.
Where did all the campus high-jinks go? It’s sign of the time that so many titles on this list are bleak – this Spanish show follows 18-year-old Javi as he navigates university after personal tragedy, and shows students dealing with grief, anxiety, and the pressure to experience the perfect university experience. The six half-hour episodes are eminently bingeable and capture the forced intimacy that comes from being thrown together with strangers who you’re told will be friends for life, but in reality are barely friends for the whole of freshers.
Leo Woodall plays Edward Brooks, a Cambridge PhD student whose work on prime numbers could apparently unlock every computer in the world, which would be quite the REF impact if true. The eight-episode thriller sees him team up with an NSA agent after his supervisor dies under suspicious circumstances, and it’s very much The Imitation Game meets Good Will Hunting but with added paranoia about research security. Shot on location in Cambridge, critics moaned about its “uneven pacing” and “leaden dialogue,” which does suggest the writers have captured the authentic Cambridge tutorial experience.
French singer Nolwenn Leroy stars as Fanny, a biologist who returns to teach at the University of Rennes’s biological field station at Paimpont (fictionalised as the “University of Brocéliande”) twenty years after her best friend disappeared and she was the prime suspect. When history repeats itself with another disappearance, we get six episodes of Gallic noir. The series was shot entirely on location at the real university and in the mystical Brocéliande forest, giving us gorgeous establishing shots of campus buildings. It’s particularly refreshing to see academic staff portrayed as accomplished professionals rather than the usual depiction of hapless eccentrics, though the murder rate does suggest their risk assessments need work.
This is a reboot of the cult Russian sitcom “Univer” that brings five freshmen to Moscow State University’s legendary 510th dormitory block, where returning characters like rector Pavel Zuev try to make MVGU “the best university in the country”. The new students are proper Gen Z types who understand TikTok but not why they need to attend lectures, while dealing with the usual comedy of errors that comes from communal living. It’s basically Fresh Meat for the Soviet education system, and comes with the side plot dish of a wealthy student sponsor opening a dumpling restaurant on campus.
Muriel Robin plays Louise Arbus, a psycho-criminology professor who solves murders with the help of four carefully selected students. Now in its second full season with new episodes in 2025, it’s like How to Get Away with Murder but only with more wine and fewer actual murders. The students function as a kind of Greek chorus explaining criminology concepts while their professor employs what I’ll describe here as questionable methods. Lots of vintage Volkswagens to look at too.
It’s a Disney remake nobody wanted, but it puts Nani’s dilemma into policy reality. Her marine biology scholarship becomes the story of care work squeezing out opportunity. The ending has her heading off to university, while Lilo stays with Tūtū as her guardian. Higher education only looks like a choice when someone else is there to pick up the unpaid labour.
If you’ve been missing the “American discovers themselves at Oxbridge” genre since Saltburn, here’s Sofia Carson learning about poetry and terminal illness. Her performance has been universally panned as “stiff” – one reviewer called her and her co-star “beautiful looking puppets going through motions” – but the film does feature that hidden church in Amsterdam if you’re planning a European city break. The student-supervisor romance is romanticised in ways that feel quite dated these days, and the idea that American students would be treated like a novelty at Oxford suggests the writers have never visited.
The superhero university returns with our protagonists now framed as terrorists while the actual villain becomes dean. For me at least, it’s a fun satire of how university leaders someone chuck their own students under the bus. The handling of actor Chance Perdomo’s death (his character dies from the neurological toll of his powers) is genuinely moving, and the new villain Dean Cipher is basically every smooth talking university manager you’ve ever met, but with better hair.
Eva Victor off of TikTok makes her directorial debut with this fractured narrative about a professor dealing with trauma. Shot in Ipswich, Massachusetts, it’s been doing the festival circuit and dividing audiences who either find it “nuanced and brilliant” or “self-pitying mumblecore.” I just thought it was boring.
The final season of Jack Rooke’s masterpiece begins with the gang on holiday in Faliraki before returning to Brent Uni for their terrifying final year. It’s easily both the funniest and most devastating thing on television, dealing with Danny’s mental health crisis and Jack’s Princess Diana poetry with equal sincerity. If you don’t cry at the ending, you will need to check you still have a pulse. Jon Pointing deserves awards for his portrayal of male depression, and the show remains the gold standard for depicting that specific third-year feeling of everything ending before it’s begun.
Odessa A’zion (who’s apparently going to be massive) plays a scholarship student facing expulsion after her father’s death, who deals with it by pool-hopping through Chicago’s wealthy suburbs instead of attending her make-or-break meeting. It’s “The Breakfast Club” meets “Booksmart” meets class warfare, with a healthy dose of Malort (if you know, you know). The film captures the emptiness of a campus over the summer – no catering open and the wrong kind of quiet…
A French philosophy student navigates her Muslim faith, her emerging lesbian identity, and the commute between the Parisian banlieue and the Sorbonne. Based on Fatima Daas’s autobiographical novel, it’s been doing the festival circuit to acclaim, though reviews get it right when they say the pacing is “deliberately contemplative” (nothing happens for ages). Stick with it for some thoughtful A&P parallels – the university serves as both escape and alienation, a place where she can be herself but never quite belong.
Netflix threw a lot of money at this Japanese series about a college drummer recruited by the “Amadeus of Rock” for his new band. Takeru Satoh learned to actually sing and play guitar for the role, the campus (actually a private management uni in Tokyo) looks amazing and the music slaps. The romance subplot is however dire, not least because the male band members have better chemistry with each other than with the female lead.
Amazon’s take on the 2022 University of Idaho murders focuses on the victims rather than the killer (still on trial when released) – which is fine, but makes for an oddly unfinished documentary. The interviews with the Dean of Students show a management completely overwhelmed by the media circus, while the exploration of how TikTok sleuths made everything worse should be mandatory viewing for anyone teaching crisis communications.
George Clooney produced this documentary about decades of sexual abuse by team doctor Richard Strauss and the wrestling coaches who allegedly knew. It’s harrowing viewing – a real lesson in how institutional harbouring works – and multiple reviewers single out current congressman Jim Jordan’s alleged complicity, making this essential context for American politics watchers.
Season 2 of South Africa’s answer to “Euphoria” has more chaos in the Pantera residence. Four young women navigate koshuis culture, drug dealing to pay fees, and the casual trauma of South African university life. It’s dedicated to the late rapper Angie Oeh and features enough Afrikaans slang to make subtitles essential even for Dutch speakers. The show’s frank depiction of everything from abortion to assault has made it a massive hit on Showmax while horrifying conservative viewers, which is usually a good sign.
It’s a merger! Due to budget cuts, a university merges its engineering department with its modelling department, forcing computer science students to share space with fashion students. The protagonist, Ju Yeon San, is a brilliant coder who treats human emotion like buggy software that needs fixing. When campus celebrity Kang Min Hak – famous from a dating show but unable to operate a laptop – accidentally destroys her computer, he becomes the test subject for her new AI dating programme, LOVE.exe. A cautionary tale for those engaged in wedging modules together to create “interdisciplinary” programmes.
The Dutch have made a #MeToo university drama, focusing on a young lawyer forced to re-examine her “consensual” relationship with her thesis supervisor when he’s accused of abuse by current students. Based loosely on real University of Amsterdam scandals, it features a charismatic predator (Fedja van Huêt is terrifyingly good) and asks uncomfortable questions about power and consent.
Benito Skinner (of TikTok fame) created this series about a closeted freshman football player desperately trying to maintain his facade. Filmed in Toronto pretending to be America, featuring actors who are clearly 30 pretending to be 18, it nonetheless captures something real about the exhausting performance of identity that university demands. Reviews praise its “chaotic energy” and “intentionally unlikeable characters” – it certainly reminded me of those lads lads in the sports clubs that roam around in jackets.
A mockumentary that follows a struggling junior college cheerleading team in Oklahoma. Kristin Chenoweth plays an assistant coach with aggressively toxic positivity, while the rest of the cast nail a specific community college/clearing energy of “we’re all here because we couldn’t get in anywhere else.” Wholesome chaos.
Kristen Stewart’s directorial debut adapts the memoir of a competitive swimmer turned writer navigating trauma through a non-linear narrative. Jim Belushi plays Ken Kesey running a writing workshop, and reviews are divided between “visionary” and “pretentious,” with one critic comparing it to “watching someone’s therapy session through a kaleidoscope.” It took them 10 years to finish it, and it very much felt like a decade watching it.
A soapy “vertical” (watch it on your phone Grandad) mini-series that dives into the high-stakes, exclusionary world of elite university Greek Life. The plot follows a student at a top-tier university who becomes entangled in a volatile love triangle, struggling to balance a relationship with her boyfriend while maintaining a secret affair with a fraternity president. Starring K-Ledani, Amalie Vein, and Ellen Dadasyan, the show explores the social stratification of campus culture, where maintaining one’s reputation in the “elite social scene” often comes at the cost of personal integrity. Ideal for a hangover.
Fees! An Indonesian student accepts a polygamous marriage to fund her Korean study abroad dreams. It’s based on a hit novel and was the first Indonesian film shot on location in Korea, combining K-drama aesthetics with conservative Islamic values. The student finance crisis that drives the plot feels painfully real even if the solution doesn’t.
This documentary follows tech millionaire Bryan Johnson as he spends $2 million a year trying to reverse aging. The contrast between his son preparing for university naturally while Bryan frantically tries to reclaim his youth through supplements and plasma exchanges is weirdly poignant. Academics from Harvard and Birmingham pop up to point out the obvious flaws in his methodology while he ignores them, making this basically a film about the dangers of having too much money and not enough peer review.
If you’re in the mood for student protest cinema, 2025 has a clutch. As Quatro Estações da Juventude (Four seasons of youth) spent a decade documenting Brazilian students fighting to keep their university funded while completing their degrees, creating an archive of a generation that refused to give up. Inner blooming springs captures Georgian students at Tbilisi State University moving between lecture halls and tear gas during the Foreign Agents law protests, with the director as part of the friend group being filmed, blurring the line between documentation and participation.
And Wake up, Serbia! gains exclusive access inside Belgrade’s University of Dramatic Arts during the student uprising, showing how the campus became the nerve centre of resistance against authoritarianism. All three refuse to romanticise protest – they show the exhaustion, the infighting, the way movements fragment when the cameras leave, and the specific courage required when your education becomes inseparable from your politics.
This Finnish documentary deserves more attention than it’s getting. An Australian neurodivergent man called Andrew Clutterbuck appears in Helsinki and somehow becomes the darling of Aalto University’s innovation ecosystem. They love him when he’s being disruptive and bringing that “entrepreneurial energy” that the strategic plan talks about. Then something tragic happens (the film’s coy about what), and suddenly Mr Innovation is yesterday’s news. Nine psychiatric diagnoses later, the “happiest country in the world” can’t find a bed for him.
I’ve not had time to catch everything, obviously. Tiny Toons Looniversity finished with the characters getting degrees in “Toonery” from ACME Looniversity [insert Mickey Mouse degrees joke here]. Night of the dead sorority babes exists and features cannibal witches running a sorority and some nudity. There’s also Shutter, where past university crimes return as literal ghosts, The family plan 2, where Mark Wahlberg’s daughter studying in London kicks off an European heist (you’ll not be hankering for Family Plan 1), and College of the dead does exactly what it says on the tin.
Happy viewing, and if you’re struggling to stream any of these, HMU and I’ll put you in touch with Firestick Dave down the road from me 😉

Mass surveillance is no longer a marginal concern in American life. It is the silent architecture of a society managed from above and distrusted from below. The cameras aimed at students, workers, and the precarious class reflect a deeper spiritual, political, and moral crisis among the elites who designed the systems now monitoring the rest of us.
Universities, corporations, city governments, and federal agencies increasingly rely on surveillance tools to manage populations whose economic security has been gutted by the same leaders who now demand behavioral compliance. Cameras proliferate, keystrokes are tracked, movement is logged, and predictive algorithms follow people across campuses, workplaces, and public spaces. Yet those responsible for creating the conditions that justify surveillance—politicians, corporate boards, university trustees, executive donors, and policy consultants—operate in near total opacity. Their meetings take place behind closed doors, their decisions shielded from public scrutiny, their influence networks essentially invisible.
This is not a coincidence. It is the logical extension of a neoliberal elite culture that elevates market logic above moral obligation. As the Higher Education Inquirer documented in “How Educated Neoliberals Built the Homelessness Crisis,” the architects of modern austerity—professionalized, credentialed, and trained in elite universities—constructed social systems that demand accountability from the poor while providing impunity for the powerful. Their policy models treat human beings as units to be managed, scored, nudged, and surveilled. Surveillance fits seamlessly into this worldview. It is the managerial substitute for solidarity.
The moral void of this elite class is perhaps most visible in the realm of healthcare. The Affordable Care Act, whatever its limitations, represented a modest attempt to affirm that healthcare is a public good and that access should not depend entirely on wealth. But the undermining of Obamacare under Donald Trump laid bare how deeply the nation’s policy culture had descended into nihilism. Trump’s efforts to gut the ACA were not about ideology or fiscal prudence; they were an expression of power for its own sake. Funding for enrollment outreach was slashed. Navigator programs were dismantled. Work requirements for Medicaid were encouraged, despite overwhelming evidence that they punished the sick and disabled. The administration promoted junk insurance plans that offered no real protection, while lawsuits were advanced to overturn the ACA entirely, even if doing so meant millions would lose coverage.
This assault revealed the moral collapse of a political and economic elite that had grown comfortable with cruelty. It was cruelty performed as policy, sanctioned by corporate donors, embraced by right-wing media, and tolerated by the broader professional class that rarely speaks out unless its own interests are threatened. Even many of the centrist neoliberal policymakers who originally shaped the ACA’s cost-sharing structure responded with timidity, reluctant to confront the underlying truth: that the American healthcare system had become an arena where profit mattered more than survival, and where surveillance of the poor replaced accountability for the rich.
As traditional moral frameworks lose their authority—whether organized religion, civic duty, or shared ethical narratives—many Americans have drifted into agnosticism or atheism not enriched by humanist values, but hollowed out by a sense of futility. Without a shared moral anchor, people retreat into private meaning or abandon meaning altogether. In this void, conspiracy theories flourish. People know they are lied to. They sense power operating behind closed doors. They see elite institutions fail repeatedly without consequence. When institutions offer no transparency, alternatives emerge in the shadows.
The elite response is predictable: condemn conspiracies, scold the public for irrationality, invoke the language of “misinformation.” But this reaction deepens the divide. The same elites who created opaque systems—financial, academic, political, and technological—now fault ordinary people for trying to make sense of the opacity. In a society where truth is managed, measured, branded, and optimized, conspiracy becomes a form of folk epistemology. It is not always correct, but it is often understandable.
Mass surveillance is therefore not the root of the crisis but its mirror. It reflects a ruling class that no longer commands moral authority and a public that no longer trusts the institutions governing it. It reflects a society that treats the vulnerable as suspects and the powerful as untouchable. It reflects a political order in which the dismantling of healthcare protections is permissible while the monitoring of poor people’s bodies, behaviors, and spending is normalized.
If the United States is to escape this downward spiral, the cameras must eventually be turned upward. Transparency must apply not only to individuals but to corporations, boards, agencies, foundations, and the political donors who shape public life. Higher education must cease functioning as a credentialing arm of elite impunity and reclaim its role as a defender of democratic inquiry and human dignity. Public institutions must anchor themselves in ethical commitments that do not depend on religious dogma but arise from the basic principle that every human being deserves respect, security, and care.
Until that reconstruction begins, the nation will remain trapped. The elites will continue to rule through metrics and surveillance rather than legitimacy. The public will continue to oscillate between nihilism and suspicion. And the moral void at the center of American life will continue to widen, one camera at a time.
Sources
Shoshana Zuboff, The Age of Surveillance Capitalism
David Lyon, Surveillance Studies
Higher Education Inquirer, How Educated Neoliberals Built the Homelessness Crisis
Wendy Brown, Undoing the Demos
Christopher Lasch, The Revolt of the Elites
Sarah Brayne, Predict and Surveil
Elisabeth Rosenthal, An American Sickness

It feels like Christmas has come early for policy nerds. At 6.01am this morning, we finally got sight of Building a world-class curriculum for all, the long-awaited report from the Government’s independent Curriculum and Assessment Review (CAR).
Overseen by Professor Becky Francis, who is an experienced educational leader and researcher and someone who also has a background in policy, it was commissioned when the Labour Government was facing brighter days back in their first flush.
The first thing to note about the report is that, in truth, independent reports commissioned by governments are only half independent. For example, the lead reviewer is usually keen to ensure their report lands on fertile soil (and, indeed, is usually chosen because they have some affinity to the people in charge). In addition, independent reviews are supported by established civil servants inside the machine and there is usually a conversation behind the scenes between the independent review team and those closest to ministers as the work progresses. (In higher education, for example, both the Browne and Augar reviews fit this model.) So it is no great surprise that the Government has accepted most of what Becky’s largely evidence-led team has said.
Yet anyone reading the press coverage of the CAR while it has been underway, or anyone who has seen the front page of today’s Daily Mail, which screams ‘LABOUR DUMBS DOWN SCHOOLS’, may wonder if the report that has landed today is the nightmare before Christmas rather than a welcome festive present. There is lots to like but the document also feels incomplete, especially – for example – for people with an interest in higher education. So it is perhaps best thought of as a present for which the batteries have yet to arrive.
Nonetheless, this morning I spoke at the always excellent University Admissions Conference hosted annually by the Headmasters’ and Headmistresses’ Conference (HMC) and the Girls’ School Association (GSA) and I could not help wondering aloud whether any new restraints on state-maintained schools might give our leading independent schools, who are much freer to teach what they like, an additional edge – especially as academy schools are already, even before today, having freedoms ripped from them.
But what does the review, which had a team of 11 beneath Becky (including one Vice-Chancellor in Professor Nic Beech and also Jo-Anne Baird from the Oxford University Centre for Educational Assessment) actually say?
The first thing to note is that it is much better than the Interim Report, which said little, sought to be all things to all people and read like it had been written by one of the better generative AI tools.
In terms of hard proposals, the Final Report starts and ends with older pupils, those aged 16 to 19, for whom we are told there should be ’a new third pathway at level 3 to sit alongside A-Levels and T Levels.’ If this feels familiar, it is because the Curriculum and Assessment Review’s emerging findings helped shape the recent Post-16 Education and Skills white paper and, more importantly, because there is already such a pathway populated by qualifications like BTECs.
So there is a sense of reinventing the wheel here, with (to mix my metaphors) politicians putting a new coat of paint on the current system. In many respects, the material on 16-to-19 pupils is the least interesting part of the report – especially as there is next to nothing at all on A-Levels. The review team starkly states, ‘we heard very little concern regarding A Levels in our Call for Evidence and our sector engagement’, so they basically ignore them – in a world of change, A Levels continue to sail steadfastly on.
As trailed in the newspapers, there is a recommendation for new ‘diagnostic Maths and English tests to be taken in Year 8.’ This would obviously help track progress between the tests taken at the end of primary school (in Year 6) and the public exams taken at age 16. But the idea has already prompted anger from trade unionists, almost guaranteeing that the benefits and downsides will be overegged in the inevitable political rows to come.
There are also numerous scattergun subject-by-subject recommendations. These are largely sensible (see, for example, the iideas on improving English GCSEs or the section on Science) but also a little unsatisfying. Some of the subject-specific changes are a little trite or inconsequential (like tweaks to the name of individual GCSEs) while others need much more detail than a general review of everything that happens between the ages of 11 and 19 is able to offer. Any material changes will need to be at a wholly different level of detail to what we have got today, and they will be some years away, so may make no difference to anyone already at secondary school.
Other points to note include that the Review is Gove-ian in its love of exams, which it stresses are a protection against the negatives of AI, over coursework. (I suspect Dennis Sherwood, the campaigner against grading inaccuracy will be incandescent about how the report appears to skate over some of the imperfections of how exams currently operate.) However, despite the support for exams, one of the crunchiest recommendations in the review is the proposal of a 10% reduction in ‘overall GCSE exam volume’, which we are told can happen without any significant downsides, though the tricky details are palmed off to Ofqual and others.
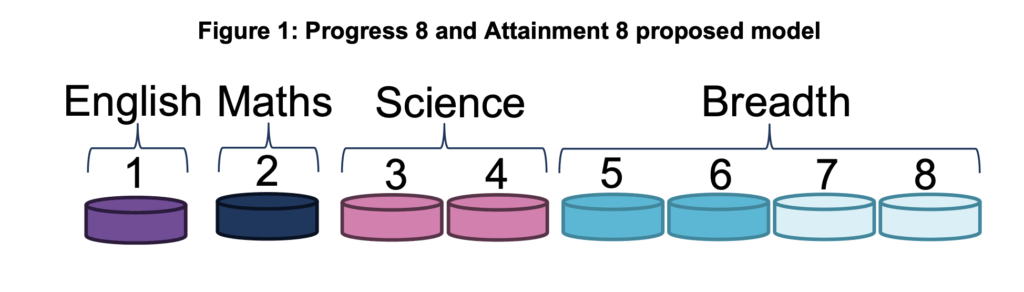
The one really clear place where Professor Francis’s review team and the Government, who have generally accepted the recommendations, are out of kilter with one another is on Progress 8.
Progress 8 is a school accountability measure that assesses how much ‘value-added’ progress occurs between primary school (SATs) and GCSEs. It is such a favoured measure that the Government has recently proposed a new Progress 8 measure for universities (which is a mad idea that wrongly assumes universities are just big schools – in reality, it is a defining feature of universities that they set their own curricula and are their own awarding body).
Becky Francis opposes the EBacc, which is a metric related to, but separate, from Progress 8, yet she wishes to maintain some vestiges of the EBacc within Progress 8. While the EBacc focuses specifically on how many students achieve qualifications in a list of specially favoured subject areas (English Lang and Lit, Maths, Sciences, Geography or History plus a language), the CAR recommends ‘the removal of the EBacc measures but the retention of the EBacc “bucket” in Progress 8 under the new title of “Academic Breadth”.’
This is something the Government is not running with, favouring less restrictions on Progress 8 instead, which may or may not reinvigorate some creative subjects. Yes, it is all exceptionally complicated but Schools Week have an excellent guide and the two pictures below (from Government sources) might help: the first shows the status quo on Progress 8 and is what Becky Francis wishes to maintain (though pillars 3, 4 and 5 would be renamed if she got her way); the second shows the Government’s proposal.
Call me simple, but I was always going to judge the Curriculum and Assessment Review partly on the extent to which it tackled specific challenges that we have looked at closely at HEPI In recent years. Here the CAR is a mixed bag. On the positive side of the ledger, the review recommends more financial education, reflecting the polling we conducted to help inform the CAR’s work: when we asked undergraduates how well prepared they felt for higher education, 59% said they felt they should have had more education on finances and budgeting.
The most obvious problem that the CAR insufficiently addresses is the huge underperformance of boys. This issue usually gets a namecheck in Bridget Phillipson’s interviews but it was entirely ignored in the recent Post-16 white paper; in the CAR, it does at least receive a quick nod and just maybe some of the proposed curriculum changes will benefit boys more than girls. But there is more focus on class and other personal characteristics than sex and in the end the brief acknowledgement of boys’ underperformance does not lead to anything properly focused on the problem.
This is very strange for we simply cannot fix the inequalities in outcomes until we give the gaps in the attainment of boys and girls the attention they deserve. I am beginning to think I was wrong to be so hopeful that a female Secretary of State was more likely to focus on this issue than a male one (on the grounds that it would be less sensitive politically).
Another area where we at HEPI have been mildly obsessed is the catastrophic decline in language learning, as tracked for us by the Oxonian Megan Bowler. Here, as with boys, the new review is disappointing. In the section looking at welcome subject-by-subject changes, the recommendations on languages are both relatively tentative and relatively weak. As one linguist emailed me first thing this morning, ‘It is pretty remarkable that the CAR’s decision on languages runs exactly contrary to the best and consistent advice of the key language advisers on the issue’. However, the Government’s response goes a little further and Ministers promise to ‘explore the feasibility of developing a new qualification for languages that enables all pupils to have their achievements acknowledged when they are ready rather than at fixed points.’ We might not want languages always to be treated so differently from other subjects but I am still chalking that up as a win.
The CAR also ignores entirely one issue that is currently filling some MPs’ postbags – the defunding of the International Baccalaureate (IB). The IB delivers a broad curriculum for sixth-formers, is liked by highly selective universities and tackles the early specialisation which marks out our education system from those in many competitor nations. Back in the heady Blair years, Labour politicians loved the qualification and promised to bring it within touching distance of most young people.
As HEPI is a higher education body, it also feels incumbent upon me to point out that higher education is largely notable by its absence in the CAR, with universities being mentioned just nine times across the (almost) 200 pages and despite schools and colleges obviously being the main pipeline for new students. It is rather different from the days when universities were regarded as having a key direct role to play in designing what goes on in schools. Indeed, our exam boards tended to originate within universities.
The odd references to universities that do make it in to the CAR report are not especially illuminating. For example, more selective universities appear as part of the rationale for killing the EBacc ‘the evidence does not suggest that taking the EBacc combination of subjects increases the likelihood that students attend Russell Group universities.’ Universities also appear in the section on bolstering T Levels, with the review proposing ‘The Government should continue to promote awareness and understanding of T Levels to the HE sector.’ But that is about it.
Incidentally, there is also less in the report on extracurricular activities than the pre-publication press coverage might have led you to believe, even if the Government’s response to the review does focus on improving the offer here.
Becky Francis used to head up the UCL Institute of Education (IoE), which is an institution that has always wrestled with excellence versus opportunity. Years ago, I sat in a learnèd IoE seminar on why university league tables are supposedly pernicious – but I had to walk past multiple banners boasting that the IoE was ‘Number 1’ in the world for studying education to get to the seminar and, while I was in the room, news came through that the IoE was going to cement its reputation and position by merging with UCL.
Such tension is a reminder that educational changes generally have trade-offs and the Executive Summary of the main CAR document admits: ‘All potential reforms to curriculum and assessment come with trade-offs’. Abolishing the EBacc as the CAR team want and watering down Progress 8 as the Department for Education want, might help some pupils and some disciplines while making the numbers we produce about ourselves look better – though the numbers produced by others about us (at places like the OECD) could come to tell a different story in time.
In the end, we have to recognise that there are only so many hours in the school day, only so many (ie not enough) teachers and only so much room in pupils’ lives, not to mention huge diversity among pupils, schools and staff, which together ensure there can be no perfect curriculum. More of one subject or more extracurricular activities are likely to mean less of other things because the school day is not infinitely expandable (and there is nothing here to free up teachers’ time or fill in all those teacher vacancies). Yet the school curriculum does need to be revised over time to ensure it remains fit for purpose.
The question now is whether the CAR report matters. Will we still be talking about it in 20 years time? Can a Government buffeted by all sides, facing a huge fiscal crisis and with a Secretary of State for Education who sometimes seems more focused on political battles (like the recent Deputy Leadership election of the Labour Party) than on engaging with the latest educational evidence really deliver Becky Francis’s vision? Or will the CAR’s proposals wilt as quickly as the last really big proposal for curriculum reform: Rishi Sunak’s British Baccalaureate? In all honesty, I am not certain but there are, in theory at least, four years of this Parliament left whereas Rishi Sunak spent more like four months pushing his idea.
My parting thought, however, is different. It is that, while the trade-offs in the CAR report partly just represent the facts of life in education, they do not entirely do so. Trade-offs are much trickier to deal with when you are also seeking to root out diversity of provision. And in the end, if there is one thing that marks this Government’s mixed approach to schooling out above all, it is the desire to make all schools more alike, whether that is reducing academy freedoms, micromanaging the rules on school uniforms, defunding the IB, forcing state schools to stop offering classical languages or pushing independent schools to the wall. Would it be better, and also make politicians’ lives easier, if we stopped pretending that the 700,000 kids in each school year group are more like one another than they really are?
Postscript: While the CAR paper is infinitely more digestible than the interim document, there is still some wonderful eduspeak, my favourite of which is:
A vocational qualification is aligned to a sector and is usually taught and assessed in an applied way. A technical qualification meanwhile has a direct alignment with an occupational standard. Despite the name ‘Technical Awards’, these qualifications are therefore vocational rather than technical.
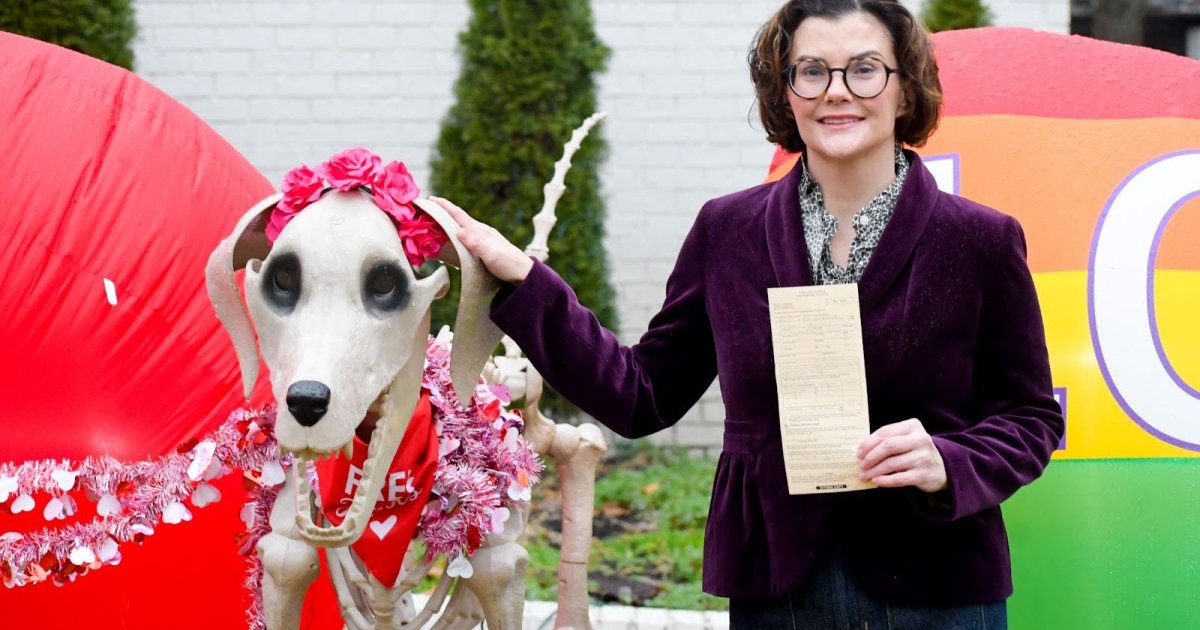

GERMANTOWN, Tenn., March 10, 2025 —Less than a month after the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression filed a First Amendment lawsuit against Germantown, Tennessee, the city has voluntarily dismissed charges against its resident Alexis Luttrell for keeping skeletons in her yard after Halloween.
“We are thrilled that Alexis will no longer have to stand trial because government officials disapproved of her decorative skeletons,” said FIRE attorney Colin McDonell. “Punishing Alexis for her choice of expressing holiday cheer would have been a bone-chilling restriction on her First Amendment rights.”
“I’m beyond pleased that I’m no longer on trial for nothing more than decorating my yard in a way that City Hall didn’t like,” said Alexis. “That these charges were ever brought in the first place was utterly surreal, but I’m glad that they’re dead and buried — and my skeletons aren’t.”
Alexis set up a decorative skeleton and skeleton dog in her front yard to celebrate Halloween last year, and then redressed them for Election Day and Christmas as well. But in December, a Germantown code officer left a notice that said that she had violated Ordinance 11-33, which says that yard decorations “shall not be installed or placed more than 45 days before the date of the holiday” and must be removed within “30 days, following the date of the holiday.”
On Jan. 6, she received a citation from the Memphis suburb saying she was still in violation and that she would have to appear before a local judge. If found guilty, she would have been subject to fines and a court order prohibiting skeletons in her holiday displays.
All this violated Alexis’s First Amendment rights. Americans have the right to put up skeletal decorations in September, October, November, December —- whenever they want. And by refusing to acknowledge Alexis’s Christmas-themed skeletons as Christmas decorations, the city engaged in viewpoint discrimination by enforcing an arbitrary and narrow idea of the “right” way to celebrate Christmas.
COURTESY PHOTOS OF ALEXIS AND HER HOLIDAY DISPLAYS
FIRE jumped into action, agreeing to represent Alexis in Germantown municipal court and filing a federal lawsuit seeking to overturn the Germantown ordinance on First Amendment grounds.
“The Holiday Decorations Ordinance violates the First Amendment,” the civil rights complaint read. “It is a content-based and viewpoint-discriminatory restriction on speech. It is not narrowly tailored to a compelling government interest. And it is unconstitutionally vague, allowing government officials to arbitrarily punish holiday expression based on their subjective beliefs.”
Alexis’s municipal court date was originally scheduled for Feb. 13, but it was postponed for a month after FIRE filed the federal lawsuit. But ahead of the March 13 hearing, the city’s attorneys dropped the charges, meaning Alexis is no longer at immediate risk of being punished for exorcising — er, exercising her rights.
FIRE’s federal lawsuit challenging Germantown’s ordinance is still pending, but with charges dropped, Alexis’s skeletons will stay up and dressed to the nines as the lawsuit progresses through the courts. Alexis has continued dressing the skeletons to celebrate every new holiday season. Last month, it was Valentine’s Day, now they’re dressed for St. Patrick’s Day, and Easter and Pride Month displays are set to follow.
“Holidays come and go, but the First Amendment is here year-round,” said McDonell. “We look forward to seeing all the ways Alexis will express herself for the holidays this year, without government interference.”
The Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression (FIRE) is a nonpartisan, nonprofit organization dedicated to defending and sustaining the individual rights of all Americans to free speech and free thought — the most essential qualities of liberty. FIRE educates Americans about the importance of these inalienable rights, promotes a culture of respect for these rights, and provides the means to preserve them.
CONTACT:
Alex Griswold, Communications Campaign Manager, FIRE: 215-717-3473; [email protected]

GERMANTOWN, Tenn., March 10, 2025 —Less than a month after the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression filed a First Amendment lawsuit against Germantown, Tennessee, the city has voluntarily dismissed charges against its resident Alexis Luttrell for keeping skeletons in her yard after Halloween.
“We are thrilled that Alexis will no longer have to stand trial because government officials disapproved of her decorative skeletons,” said FIRE attorney Colin McDonell. “Punishing Alexis for her choice of expressing holiday cheer would have been a bone-chilling restriction on her First Amendment rights.”
“I’m beyond pleased that I’m no longer on trial for nothing more than decorating my yard in a way that City Hall didn’t like,” said Alexis. “That these charges were ever brought in the first place was utterly surreal, but I’m glad that they’re dead and buried — and my skeletons aren’t.”
Alexis set up a decorative skeleton and skeleton dog in her front yard to celebrate Halloween last year, and then redressed them for Election Day and Christmas as well. But in December, a Germantown code officer left a notice that said that she had violated Ordinance 11-33, which says that yard decorations “shall not be installed or placed more than 45 days before the date of the holiday” and must be removed within “30 days, following the date of the holiday.”
On Jan. 6, she received a citation from the Memphis suburb saying she was still in violation and that she would have to appear before a local judge. If found guilty, she would have been subject to fines and a court order prohibiting skeletons in her holiday displays.
All this violated Alexis’s First Amendment rights. Americans have the right to put up skeletal decorations in September, October, November, December —- whenever they want. And by refusing to acknowledge Alexis’s Christmas-themed skeletons as Christmas decorations, the city engaged in viewpoint discrimination by enforcing an arbitrary and narrow idea of the “right” way to celebrate Christmas.
COURTESY PHOTOS OF ALEXIS AND HER HOLIDAY DISPLAYS
FIRE jumped into action, agreeing to represent Alexis in Germantown municipal court and filing a federal lawsuit seeking to overturn the Germantown ordinance on First Amendment grounds.
“The Holiday Decorations Ordinance violates the First Amendment,” the civil rights complaint read. “It is a content-based and viewpoint-discriminatory restriction on speech. It is not narrowly tailored to a compelling government interest. And it is unconstitutionally vague, allowing government officials to arbitrarily punish holiday expression based on their subjective beliefs.”
Alexis’s municipal court date was originally scheduled for Feb. 13, but it was postponed for a month after FIRE filed the federal lawsuit. But ahead of the March 13 hearing, the city’s attorneys dropped the charges, meaning Alexis is no longer at immediate risk of being punished for exorcising — er, exercising her rights.
FIRE’s federal lawsuit challenging Germantown’s ordinance is still pending, but with charges dropped, Alexis’s skeletons will stay up and dressed to the nines as the lawsuit progresses through the courts. Alexis has continued dressing the skeletons to celebrate every new holiday season. Last month, it was Valentine’s Day, now they’re dressed for St. Patrick’s Day, and Easter and Pride Month displays are set to follow.
“Holidays come and go, but the First Amendment is here year-round,” said McDonell. “We look forward to seeing all the ways Alexis will express herself for the holidays this year, without government interference.”
The Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression (FIRE) is a nonpartisan, nonprofit organization dedicated to defending and sustaining the individual rights of all Americans to free speech and free thought — the most essential qualities of liberty. FIRE educates Americans about the importance of these inalienable rights, promotes a culture of respect for these rights, and provides the means to preserve them.
CONTACT:
Alex Griswold, Communications Campaign Manager, FIRE: 215-717-3473; [email protected]

There’s nothing on the telly this Christmas.
There never is. Unless you’re searching for some hidden nuance in repeats of The Chase.
But if, like me, you have trouble switching off from work but also enjoy being slumped in front of the box with a tub of Quality Street, I have good news.
I’ve picked out ten films and TV shows released this year that either have something to say about higher education, are set on campus and/or depict contemporary student life.
You’ll laugh, you’ll cry, you’ll shell out for a VPN, you’ll get frustrated by torrent ratios, and you’ll almost certainly switch off, which is what the break is for – eventually.
It really was slim pickings this year from a UK perspective. Everyone talks a lot about how universities are portrayed “in the media”, but I think they mean on Newsnight or in the Telegraph. The sector will probably win more hearts and minds on Netflix, if anyone knows anyone that might be able to help.
Before you take to the comments, I’ve not put in books or podcasts. I do enough reading in this job, and I edit ours, so my appetite for either is fairly thin – but do pop suggestions below if there are any.
You’re welcome – and apologies in advance if you’re at work over the next couple of weeks.
If having worked in or around the sector you’ve not quite had your fill of toxic and manipulative relationships this year, the second season of Tell Me Lies is a good bet. Filmed largely on the picturesque campus of Agnes Scott College in Georgia, we’re whisked into a world of 2008 fashions, messy frat parties, tense dorm room interactions and academics’ office hours – all used to illustrate how central character Lucy Albright’s university experiences shaped her later life. It’s all a bit soapy, but the deep discomfort at having to hang out with your exes that campus life can require is very well played.
There are more depictions of dorm life in Sweethearts, a romantic comedy whose set-up centres on two friends breaking up with their girlfriends from home over a holiday weekend. It’s all a bit loaded lads retro – flying urine and a flaccid full-frontal give you a sense of the tone here – but treat it like gazing out of the window on a train, and you’ll take in some lovely interior scenes from Ramapo College in Mahwah, and some lush exterior shots from the Vermont College of Fine Arts.
This is a low-budget “feminist horror thriller” that follows a fraternity pledge who, during a brutal hazing ritual, is pressured to lose his virginity by leading a drugged girl upstairs at a party – something that has unexpected and increasingly disturbing consequences. It’s cleverly filmed, there’s a cracking soundtrack and it’s comically gruesome – until you remember that without the blood and gore of act three, it’s depicting an unsettlingly common scenario.
Yôji Minamimaru, the central character of Land of Tanabata, navigates all the typical challenges of being a student – academic life, social relationships, self-discovery, and a supernatural ability to create small holes in objects, something he shows off as the President of the New Skills Development Research Society. It’s an unlikely hook for a series, and the murder (of a professor) mystery that ensues is a struggle to stick with in this manga adaptation.
Two old friends enroll in an adult university, looking for adventure, love and fun. What could go wrong? Quite a lot, it seems, in this Dominican go at mature student life that drags up some particularly dated caricatures of women and LGBT+ people. I got about 15 minutes in before I was tired of the buffering.
What do you fancy watching. A drama? A rom-com? A thriller? An overdone Indonesian horror film based on a viral Twitter thread from 2016? On the assumption that it’s the latter, Dosen Ghaib: Sudah Malam atau Sudah Tahu (The Ghost Lecturer: Is It Night Already or Do You Already Know) follows four university students who fail the year and are required to enrol onto a catch-up module over the holiday, who pitch up only to get a message that the lecturer can’t make it – so who is the person already in the room? For clarity, it’s a murdery ghost man, not one of his PhD students.
You might remember a story from 2023 that involved an academic specialising in the social impacts of climate change avoiding air travel to minimise his carbon footprint – only to get sacked for doing so. The Researcher chronicles Gianluca Grimalda’s 40-day journey via trains, buses, and ships to reach his research site in Papua New Guinea. Maybe he was sacked for not using Key Travel to book it all.
Decades on from the end of apartheid, Afrikaans media is only just starting to break away from its historically conservative roots. Wyfie – opening up conversations about rape, sexuality and politics – caused quite a stir when it appeared in 2023, and this year’s second season of the show, about four mismatched university roommates at a womens’ residence at the fictional Eike University, takes things up a notch. It’s especially fascinating for the insights into university life – first-year initiation ceremonies, cheating on a test to maintain academic standing and a mother-and-daughter tea event all make it in, as does a whole bunch of drama over an annual photo of those in the halls. It’s especially good on both portraying and dramatising that “you befriend people that aren’t like you” cliche.
If all of these sensitive and revealing portrayals of student life are a bit woke for your liking, and you’ve never got around to reading The Coddling of the American Mind, you’ll be pleased to learn that you watch it now instead. The central conceit of the Lukianoff and Haidt viral article-cum-bestseller gains some visuals, voxpops and dramatic music here – but decent evidence for their claims, which to these eyes and ears is age-old generational indignation dressed up as science – is still in short supply. That said, the idea that pervasive racism, sexism, homophobia and transphobia are merely bad ideas that a good debate will solve is at least in the solid tradition of Christmas TV escapism.
This is set in Kota, Rajasthan – a city known as a hothousing hub for coaching centers that prepare students for India’s highly competitive IIT-JEE entrance exams. Back for a darker yet compelling third season this year, there’s plenty to learn here about the coaching system’s human impact as the focus shifts a little to draw in the coaches themselves and the choices made between the gifted students and everyone else. If there’s a fault with it, it’s the season ending – a crowbarred bit of plotting presumably designed to hang out the prospect of a fourth run.
Admissions were quite a big story in the US in 2023 – the supreme court banned the use of affirmative action policies that had been in place for decades – and Bad Genius plays into the slipstream by overlaying some higher education race politics to a remake of a Thai blockbuster from 2017. The plot centres around a clever student who helps her friends cheat on their entrance exams to reflect the struggles of first-generation Americans pressured to support their immigrant families. If you’re a fan of the original you’ll be wondering why they bothered – but given you’ve not seen the original, this is a fun way to while away an afternoon if you’re into watching the underdog poor outmaneuvering the rich.
Finally, (and no I’m not including One Day), I won’t have a word said against Big Boys, which had a criminally under-celebrated season 2 this year. The search for student housing, mental health, student sex work and plenty of students’ union activity all feature at Brent University, where Jack and Danny’s decidedly uncool struggles with the second year manage to be both laugh-out loud funny, heart-wrenching and revealing often all in the same scene. Set somewhere near Watford (and filmed largely on the Harrow campus of the University of Westminster), it’s the polar opposite of glamorous, and all the better for it.

For the time being, John Cater is the longest-serving Vice-Chancellor in UK higher education, having held his current post for approaching 32 years. He hands over the reins at Edge Hill University at the end of January 2025. In the blog below he finds parallels between what is happening in the high street and in the university sector…
This week Mark Allen, the Chief Executive of Land Securities, announced that his company had paid £490m for a 92% stake in Liverpool One, the shopping centre. In quotes, he explained that the top one per cent of UK retail shopping destinations provide access to 30 per cent of all in-store retail spend, “which is why we continue to see brands focus on fewer but bigger and better stores in the best locations”.
You may well ask, ‘What has this to do with higher education?’ First, there is a tangential link, in that Mark Allen is a former Chief Executive of Unite Students, the sector’s largest housing provider and a company that has, indeed, sought to maximise access to student residential spend and in the ‘best’ locations, typically cities with universities that are part of the perceptual elite.
But are we seeing this in higher education too? Any graph of higher education participation since the removal of the student number cap in 2015 has seen an increasing bifurcation between high-tariff institutions and, initially, low and, more recently, mid-tariff institutions. If you’re in the latter categories and you look at the 2024 intake data, the new cohort is in the sector, just not, in all probability, in your institution.
So, are we seeing Land Securities’ retail revolution, a race to the best locations, a clear focus of demand, in higher education? A decade of ‘spending’ decisions by each new intake, their friends, families and schools and colleges – ‘where do I go to draw down my loan?’ – says so. The UCAS 2024 End of Cycle data, as ever ably summarised by David Kernohan for Wonkhe, makes it clear that “higher tariff providers have been fishing in deeper waters”, with both lower tariff offers and a more flexible approach to clearing. And this is clearly understood by those making ‘purchasing’ decisions, with the exponential growth of self-release highlighting (perceived) trading-up.
With no constraints on an institution’s numbers, this trend appears inexorable, whilst a constraint on numbers would constitute a significant reduction in choice. There may be a middle road, a managed market, with limitations on the pace of growth, possibly determined by discipline, but the howls of protest would reverberate, particularly in elements of the media, constituency postbags and selective schools. And, whilst the Department for Education has indicated that it is no longer using Russell Group entries as a measure of a school’s success, the Treasury has yet to mirror that action.
The crunch is coming. With very few exceptions, university sustainability depends on two variables, number and price. The failure to secure, at least to date, a five-year index-linked settlement has curtailed price, and, with it, investment and forward planning. And a broadly static market, with no signs of an increase in all-age participation, is reflected in curtailed demand and fewer numbers.
From 2030 the age cohort declines by one-sixth. Demand for traditional higher education is broadly static and increasingly differentiated by tariff. Innovation, be it Lifelong Learning or apprenticeships, has yet to grip the market.
In retail investment has headed in two directions, niche providers in up-market ‘village’ style communities, whilst the big city retail brands, such as those in Liverpool One, acquire floor space and greater market penetration. Quoted companies pay nine figure sums for a piece of the big city pie, whilst non-niche players, the poor, the periphery, the ‘red wall’ towns, suffer.
Is this relevant to higher education? I believe so. Demand for higher education is broadly static and increasingly concentrated in a smaller number of providers. In-migration is severely constrained and the number of UK-resident eighteen-year-olds is heading towards a cliff edge.
I have written previously on the possible shape of higher education in the coming decade. Trifurcation: a three-way split. A perceptual elite offering three-year away from home residential degrees. Sub-regional providers closely tied to further education, anchor institutions in their communities. And, a (re-) emergence of global online players in the education marketplace, with strong brands and an almost uncapped resource; providers with the capacity, largely unfettered, to shape opinions and behaviours on whim.