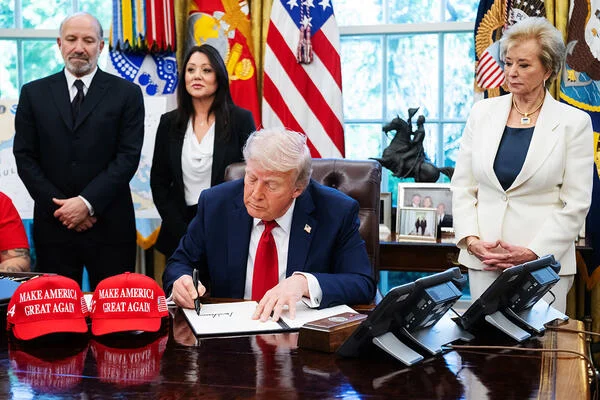
President Trump signed an executive order in April to reform accreditation.
Saul Loeb/AFP/Getty Images
Reforming the accreditation process has been a key focus for the Trump administration. Officials from the Education Department reinforced that Wednesday when they announced a request for information to solicit public feedback on updating the accreditation handbook.
The aim, the department said in a news release, is to reduce “unduly burdensome and bureaucratic requirements” and increase “transparency and efficiency.”
“Instead of driving high-quality programs that better serve students, the antiquated accreditation system has led to inflated tuition costs and fees, administrative bloat, and ideology-driven initiatives at colleges across the country,” Assistant Secretary for Postsecondary Education David Barker said. “We are excited to receive feedback on how best to update the Handbook, streamline guidance, and eliminate bureaucratic headaches for accrediting agencies and associations.”
The request falls in line with an April executive order to “reform and strengthen” the accreditation system. It also comes less than a week before the next meeting of the National Advisory Committee on Institutional Quality and Integrity, the group that weighs in on accreditation issues and reviews accrediting agencies.
The department is planning to draft new rules and regulations for accreditors sometime next year.
Commenters will have 45 days to provide feedback on the following questions:
- What policies or standards are encouraging innovation or reducing college costs within the postsecondary education sector and should be retained in or added to the new version of the handbook?
- How can the handbook be designed to be less burdensome?
- Is the handbook serving its intended purpose?
- How can it better assist accrediting agencies and associations in evaluating the quality of educational institutions and programs or in applying for federal recognition?
- How could accreditation standards be updated to incentivize intellectual diversity on campus?
- What guidance or standards, if any, can the handbook provide to institutions and programs to help achieve this goal?
- What methods should be incorporated into the handbook to determine appropriate assessment benchmarks, and what data sources or validation methods could be used to ensure those benchmarks reflect student competency?