In February, we launched our commuter student series, seeking to uncover how universities are responding to the increasing numbers of commuter students – students who continue to live at home whilst studying, rather than relocating to attend university, in contrast to “traditional” residential students.
We sought to increase the visibility of commuters and share best practice, responding to demand for thought leadership and evidence-based interventions, with the aim of influencing pedagogy, practice and policy, within institutions and nationally.
The series also followed the inclusion of commuter students on the Office for Students’ Equality of Opportunity Risk Register in England as a distinct group who experience inequality of opportunity.
In our final article we look back at the series, reflecting on key learnings, before looking forward, setting out a change agenda for commuters that will make higher education more accessible, attractive and available to all.
Commuter students are everywhere yet invisible
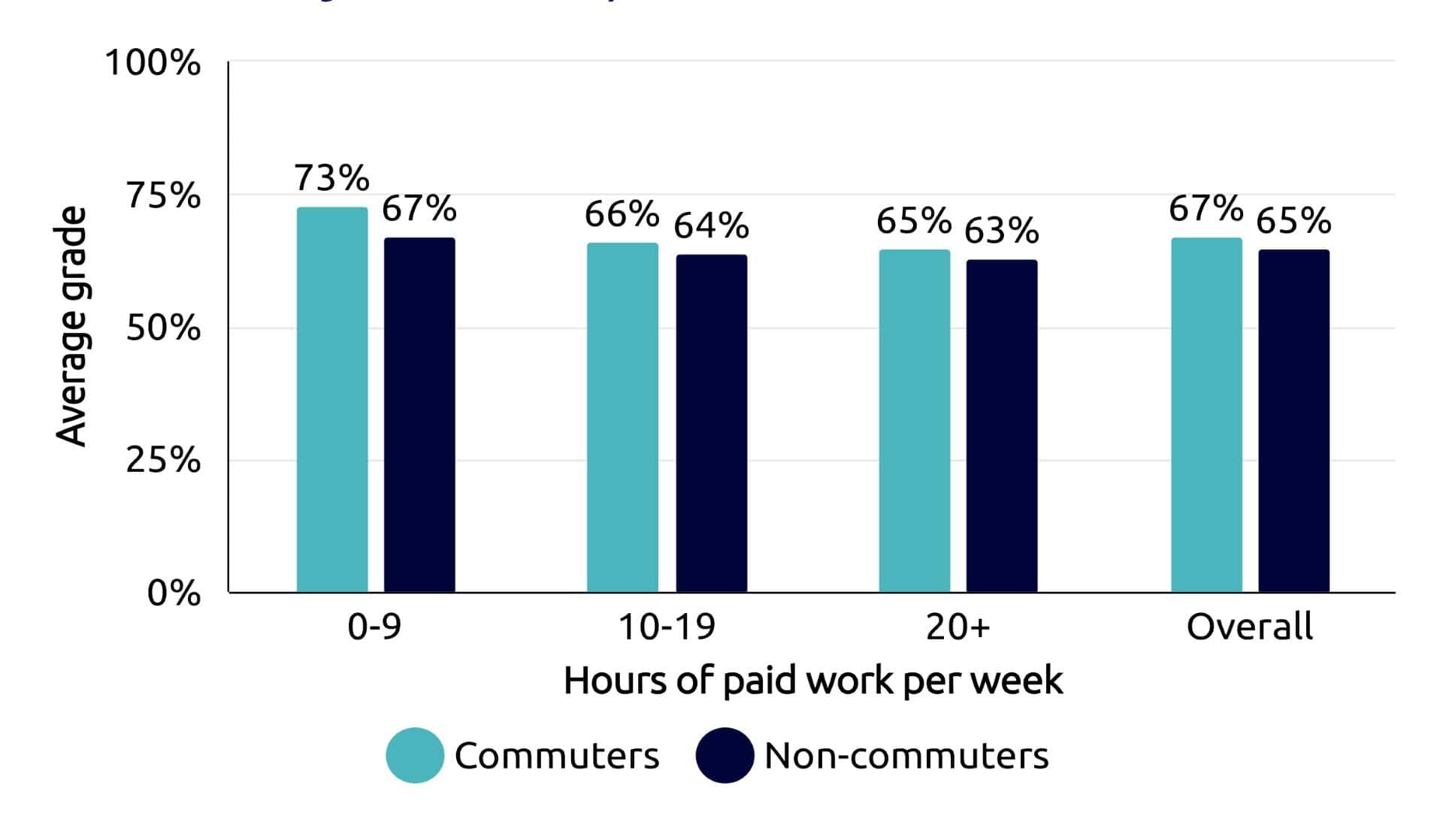
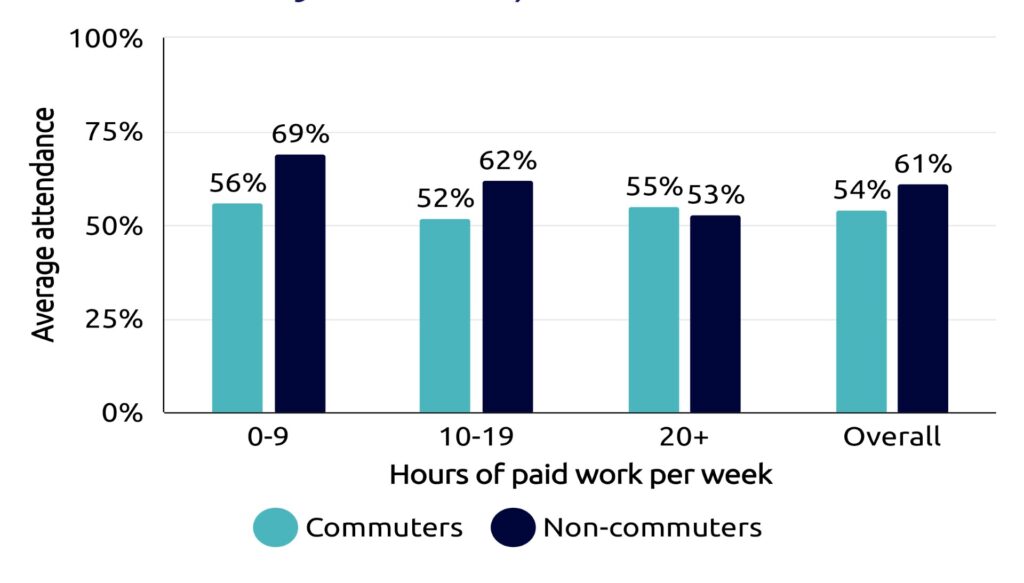
Commuter students are part of every UK university.
The proportion of commuters varies by institution – research by Susan Kenyon using 2022 HESA data, shows a range from 12 to 85 per cent.
As such commuters need to be counted and made visible, acknowledged in pedagogy, policy and processes and, where necessary, considered as communities at risk in Access and Participation Plans (APPs) in England.
And despite being everywhere, commuters can often be invisible and underserved.
Earlier in the series Val Yates and Carolyn Oulton discussed how to build an institutional agenda for change by making commuters visible. Their agenda was one where commuters are embedded across the institution. Commuters don’t interact only with their lecturers – supporting commuters lies with academics, across professional services and into teams like IT and sustainability.
We explored the diverse definitions of commuters in APPs, which often makes measuring progress difficult. In supporting commuters, it’s important we know we’re talking about the same group of students. Expanded definitions have considered those who live locally, use transport, have the same term time and home address but also those who relocate but live further away due to cost and housing pressures.
Commuters need to be visible to their institution first before making them visible to each other through access programmes, networks and student societies.
Commuter students are valuable
Our series also reveals the cultural, educational and social value of commuters to our learning community.
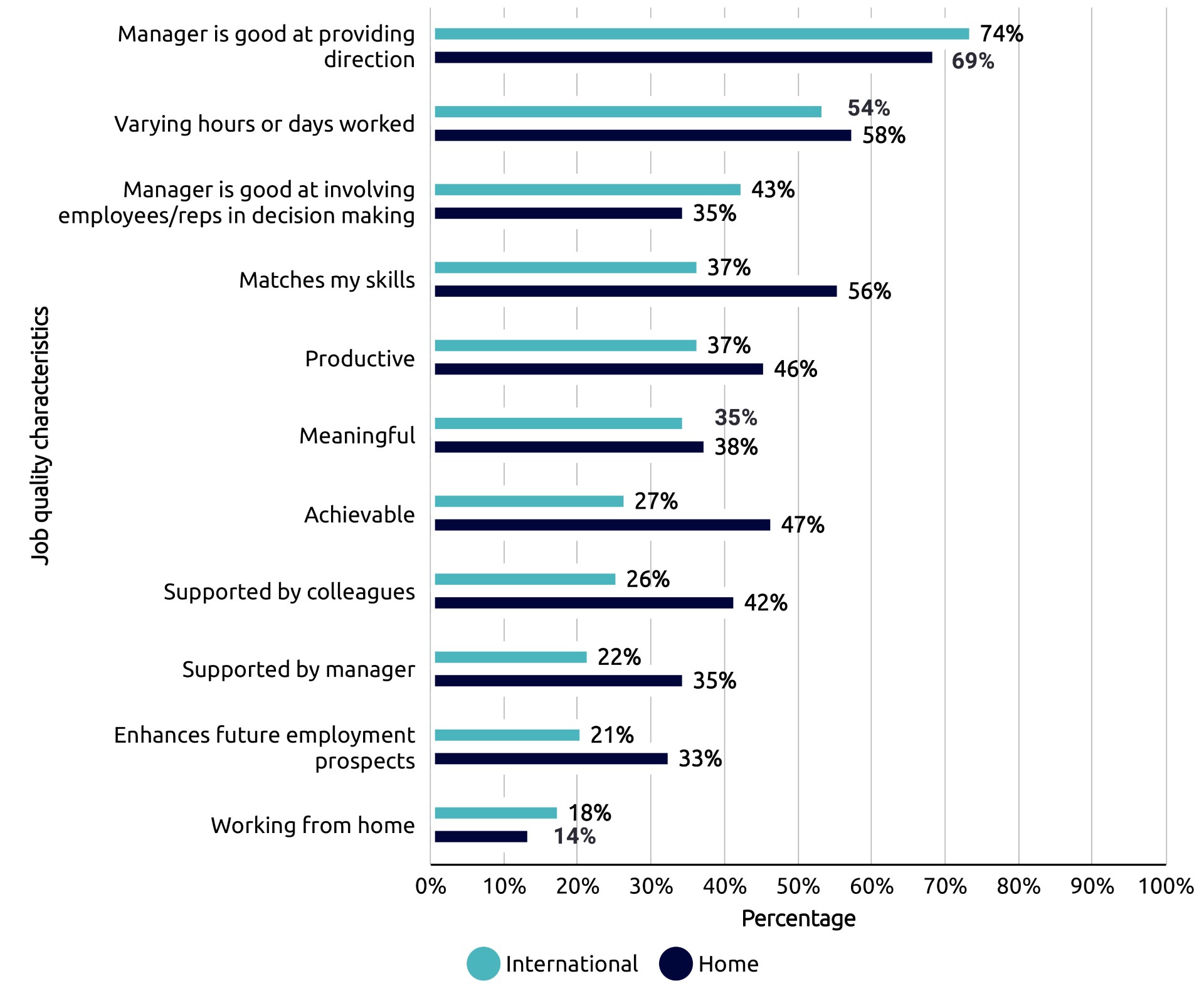
Commuters are passionate, engaged and committed. They bring diverse perspectives, experience and expertise to the classroom. As Martin Lowe, Adrian Wright and Mark Wilding write, they “are not just students, they are employees, caregivers, and active members of their communities,” bringing skills such as time management and the ability to balance multiple responsibilities, alongside discipline and an internal motivation to learn that can inspire and influence other students.
And as Emma Maslin highlighted, there is a tendency to see commuters from a deficit perspective, as a disadvantaged group, whose experience needs to be “fixed.”
Our authors don’t deny the academic, financial and social difficulties of being a commuter in a world designed for residential students, particularly when, as Elise Thornton discusses, commuting is often a financial necessity, rather than an active choice.
But the opportunity to attend university as a commuter student can allow students to maintain community, employment and relationships that they value, whilst learning.
Articles by Molly Pemberton and Susan Preston emphasise how valuable commuter students are to the wider student community. Commuters are campaigning for changes in policy, practice and spaces that reshape the university experience and bring benefits to all students.
A common theme running throughout the series is that changes made to pedagogy, policy and processes, which initially aim to create a more inclusive environment for commuter students, benefit all students. And a lot of the time, they’re changes driven by students themselves.
In designing services and learning for commuters, we’ve seen Tom Perou discusses the universal benefits of podcasts, which provide bite-sized learning in an alternative format; Kulvinder Singh described the importance of enhancing belonging in the classroom; and Susan Kenyon and Flic Lindo stressed the importance of improving information on the “rules of the game” and demystifying the “hidden curriculum.”
Commuters are in the city
In the traditional residential model, students remain largely in their defined area. But commuter students are integrated into the wider fabric of communities.
Finding out where commuters are is often a good first step. David Kernohan analysed HESA data to help us understand what constitutes a local student and if local students aren’t going to your provider, where are they going?
It’s common that local authorities don’t know how many students live locally, have relocated or are registered to vote, all of which inhibits the design of services to meet students’ needs. In the context of transport providers, bus fares and transport routes often don’t serve commuters because they don’t first understand that population.
Joel Dowson’s article takes this further, outlining how universities and their students’ unions can leverage the financial value of students to transport providers, in terms of revenue and potential gains from reduced road congestion. At the Greater Manchester Student Partnership they have been lobbying for an improved commuter student experience, influencing the affordability and availability of transport services, to the benefit of all students.
A commuter change agenda
The aim of this series was to empower everyone in HE, whatever their role, to have a better understanding of the needs of commuter students.
And as our contributions have evidenced, work happens everywhere – in professional services, in the classroom, in regional advocacy and with students.
When thinking about where the work starts, it might be at your desk. There’s four categories to our change agenda, drawing on contributions from authors across the series: in the classroom, at the institution, with students and in national policy.
In the classroom
Supporting commuters in the classroom is about making them feel seen and making them visible to each other. Active pedagogies develop belonging and on-commute learning options such as podcasts, pre-recorded lectures or flipped learning are examples of inclusive learning delivery. Creating a reason to attend and articulating the benefits to students is important to sustain engagement.
At the institution
Institutions need to count commuters, then research, listen and review policies to ensure they work for all students. Practical steps include things like student-centric timetabling, consistent and empathetic attendance policies, providing clear information to commuters on application and offering accommodation options so that students can engage beyond the classroom. Institutions have influence with local governments and transport authorities and can be an effective conduit for making the city more commuter student friendly. And institutions can work towards building institutional empathy so colleagues understand that a lack of engagement may not be laziness, it may be a delayed bus or a train fare hike.
With students
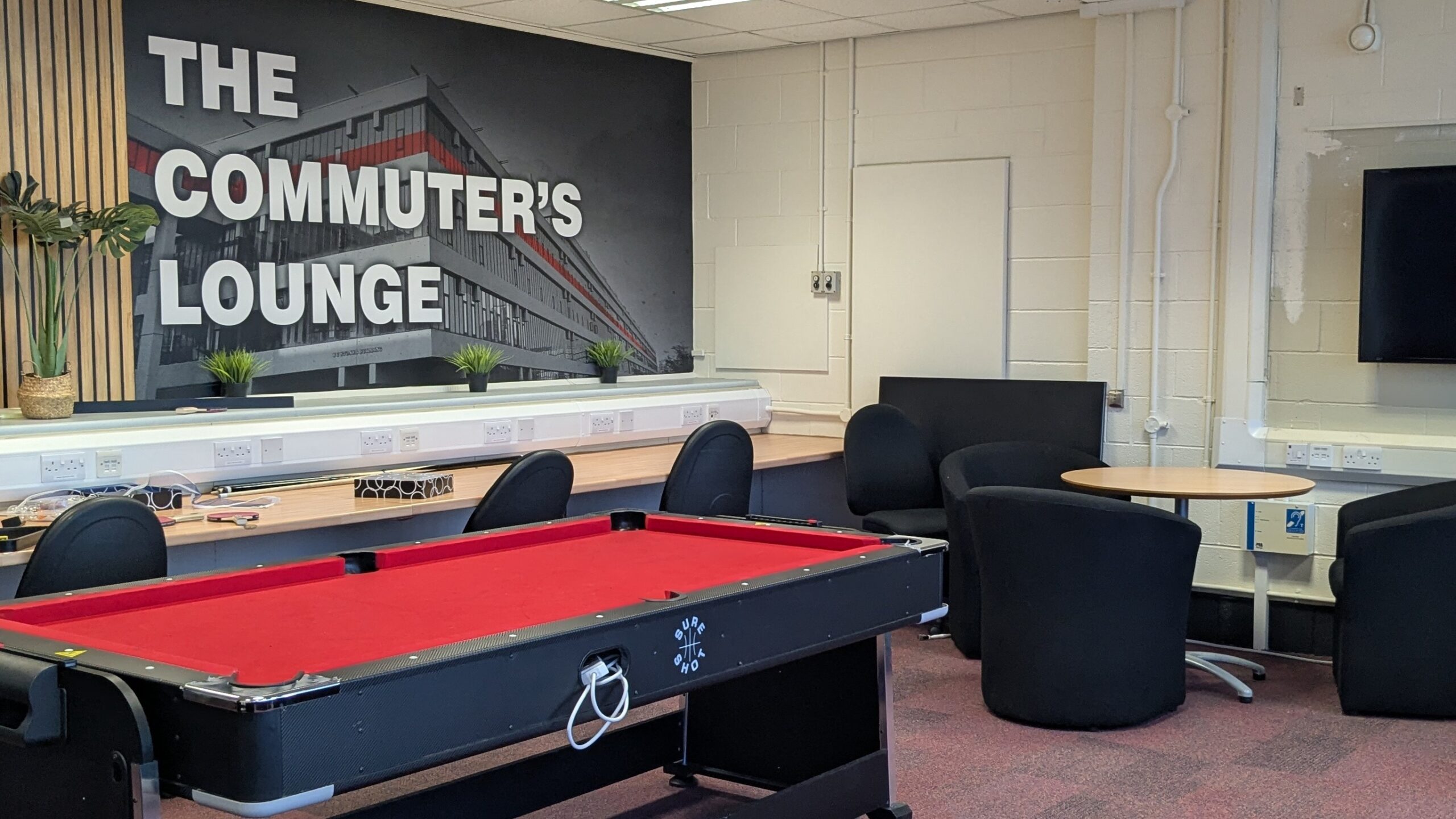
Many APP interventions included co-creating solutions with students rather than for them which is undoubtedly the best step forward. It was students who led the way to making a commuter student lounge at Leeds University through the sharing of university rooms, giving them ownership, space and agency. In any project, involving commuters beyond consultation leads to successful interventions and outcomes.
On a national level
Measuring progress is difficult with different and diverse definitions, the sector needs to start with a shared agreement of who this student group is and how to measure them.
The engagement barriers universities face are often tied to the cost of living crisis. Transport fares are expensive, so commuters make tactical, tough decisions about when and how to engage. Responding to consultations and calls for evidence on key transport policy with commuters helps shift transport service design in favour of students. And institutions are key agents in making change on a national level – at Sheffield Hallam SU, it was their VC support that got students in the room with their mayor to discuss bus prices.
Whether it’s student-centric timetables, creating a commuter student lounge or working with the local transport authority, individuals across institutions want to feel empowered to enhance the commuter student experience themselves. So as institutions better understand, count and make visible the commuter student experience, the next step is for the work to start. And small things make a difference, simply talking about commuters in the classroom helps build community. Students experience enough delays on public transport, they don’t want to see the same delays happening with support at their institutions.
Since publication, John Blake, Director for Fair Access and Participation at the Office for Students told us:
Commuter students can sometimes get forgotten in the discourse around higher education. Yet they make up a significant proportion of the student body at all institutions, and at some comprise over three quarters of students. That’s why I really welcome Wonkhe’s focus on this issue. This series has helped identify who commuter students are, the enormous amount they add to the institutions where they study, and the work institutions are doing to support commuter students to get the most from their studies. The OfS has included commuter students in our equality of opportunity risk register, and a number of institutions are working with these students to develop creative solutions to some of the challenges they might face to access and succeed in higher education.
Thank you to all the contributors to the series, if you would like to discuss supporting commuters in more detail, please do reach out to Susan Kenyon.
Click here to read the rest of our commuter student series.