by CUPA-HR | February 7, 2023
After a month in session, the U.S. House of Representatives and Senate are finalizing their committee and subcommittee membership rosters. Of particular significance are the House Education and the Workforce Committee and Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions (HELP) Committee, which have jurisdiction over higher education and many labor and employment issues, including overtime, paid leave, occupational safety and health and employment-based discrimination.
House Education and the Workforce Committee and Subcommittees
The House Education and the Workforce Committee will be comprised of 25 Republicans and 20 Democrats with Rep. Virginia Foxx (R-NC) serving as chairwoman and Rep. Bobby Scott (D-VA) serving as ranking member of the full committee. Both Foxx and Scott served as their party’s committee leader in the previous Congress when Democrats held the majority, but Foxx was notably able to secure a waiver granting her exemption from House Republican-imposed committee leadership term limits that would have prohibited her from serving a fourth consecutive term as Republican leader on the committee.
Foxx has publicly stated her priorities for the committee, citing oversight of the Biden administration, Department of Labor and Department of Education as a top concern for the committee. Having previously taught at two institutions of higher education and served as president at Mayland Community College, Foxx also has a particular interest in higher education. With divided control of Congress and Democrat control of the Senate, however, it is unlikely that Foxx will be able to pass any meaningful legislation that would garner support from the Senate and the president.
In addition to the full committee roster, the Education and the Workforce Committee has also finalized their subcommittee rosters.
Subcommittee on Workforce Protections
The Subcommittee on Workforce Protections has jurisdiction over issues relating to wages, hours of workers and overtime, including the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA); workers’ compensation, including the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA); issues relating to immigration and employment; and occupational safety and health, including the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
Freshman Rep. Kevin Kiley (R-CA) will serve as chairman of the subcommittee and Rep. Alma Adams (D-NC) will serve as ranking member after serving as chair of the subcommittee last Congress. The subcommittee will made be up of six Republicans, including Glenn Grothman (R-WI), James Comer (R-KY), Mary Miller (R-IL) and Eric Burlison (R-MO), all who did not serve on the subcommittee in the previous Congress; and four Democrats, all who served on the subcommittee in the last Congress.
Subcommittee on Higher Education and Workforce Development
The Subcommittee on Higher Education and Workforce Development has jurisdiction over the following areas: postsecondary student assistance and employment services, and the Higher Education Act; postsecondary career and technical education, apprenticeship programs, and workforce development; and science and technology programs.
Rep. Owen Burgess (R-UT) will serve as chairman of the Subcommittee on Higher Education and Workforce Development, while Rep. Frederica S. Wilson (D-FL) will serve as ranking member of the subcommittee after serving as chair of the subcommittee in the 117th Congress. The makeup of the subcommittee will include 13 Republicans, including Reps. Glenn Thompson (R-PA), Lloyd Smucker (R-PA), Nathaniel Moran (R-TX), John James (R-MI), Lori Chavez-DeRemer (R-OR), Erin Houchin (R-IN) and Brandon Williams (R-NY) as new members; and 11 Democrats, including Reps. Lucy McBath (D-GA), Gregorio Kilili Camacho Sablan (D-Northern Marina Islands) and Alma Adams (D-NC) as new members.
Subcommittee on Health, Employment, Labor and Pensions
The Subcommittee on Health, Employment, Labor and Pensions’ jurisdiction involves “matters dealing with relations between employers and employees,” including to the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) and employment-related health and retirement security, such as pension, health and other employee benefits and the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA).
The subcommittee will see Rep. Bob Good (R-VA) serve as chairman and Rep. Mark DeSaulnier (D-CA) serve as ranking member after previously serving as chair in the 117th Congress. The subcommittee will be composed of 12 Republicans, including Reps. James Comer (R-KY), Lloyd Smucker (R-PA), Michelle Steele (R-C), Aaron Bean (R-FL), Eric Burlison (R-MO), Lori Chavez-DeRemer (R-OR) and Erin Houchin (R-IN) serving as new members; and 10 Democrats, including Reps. Pramila Jayapal (D-WA), Jahana Hayes (D-CT), Ilhan Omar (D-MN) and Kathy Manning (D-NC) serving as new members.
Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee
The Senate HELP Committee is the Senate counterpart to the House Education and the Workforce Committee. Chair Bernie Sanders (I-VT) will be replacing former Chair Patty Murray (D-WA), who is now the chair of the Senate Appropriations Committee, and Ranking Member Bill Cassidy (R-LA) will be replacing former Ranking Member Richard Burr (R-NC), who retired at the end of the 117th Congress. Democrats will have 11 members and Republicans will have 10 members on the committee. Subcommittees have not yet been finalized, though we expect to see membership lists soon.
Sanders staffers have stated that, as chair, he will “focus on universal healthcare, lowering the cost of prescription drugs, increasing access to higher education and protecting workers’ rights on the job.” As previously mentioned, however, the divided Congress and Republican control of the House will likely prevent meaningful legislation from moving to President Biden’s desk for his signature.
CUPA-HR will be monitoring committee activity and will keep members apprised of any major hearings or updates that come out of the committees.
Share This Article:







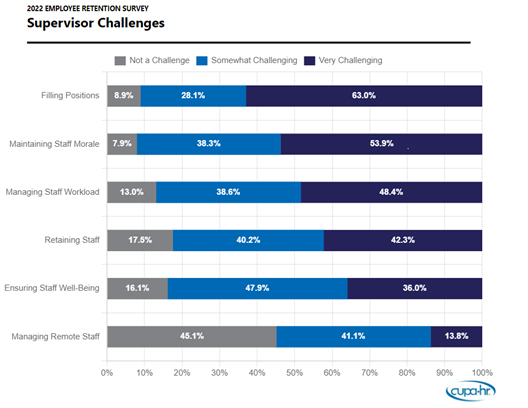
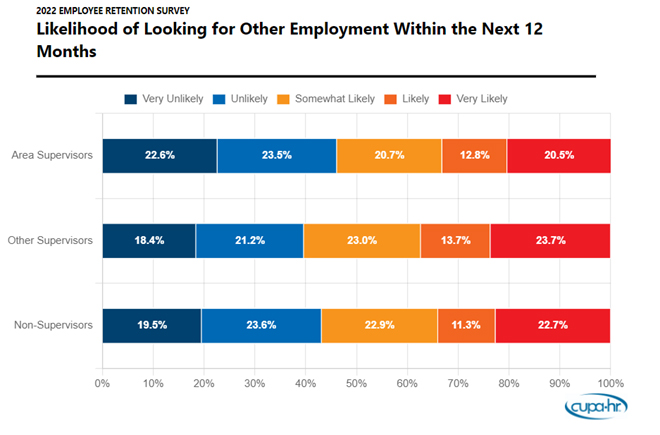 Most higher ed supervisors work long hours and have absorbed more duties since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Data show that supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to work additional hours. Fewer than half (47 percent) of non-supervisors work more hours than what is considered full-time. However, 89 percent of area supervisors and 76 percent of other supervisors work more hours per week than what is considered full-time at their institution. Additionally, supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to agree that they have absorbed additional responsibilities of other staff who have left the institution since the onset of COVID-19. Supervisors are also more likely than non-supervisors to report that they experienced an increase in job expectations since the start of the pandemic.
Most higher ed supervisors work long hours and have absorbed more duties since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Data show that supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to work additional hours. Fewer than half (47 percent) of non-supervisors work more hours than what is considered full-time. However, 89 percent of area supervisors and 76 percent of other supervisors work more hours per week than what is considered full-time at their institution. Additionally, supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to agree that they have absorbed additional responsibilities of other staff who have left the institution since the onset of COVID-19. Supervisors are also more likely than non-supervisors to report that they experienced an increase in job expectations since the start of the pandemic.