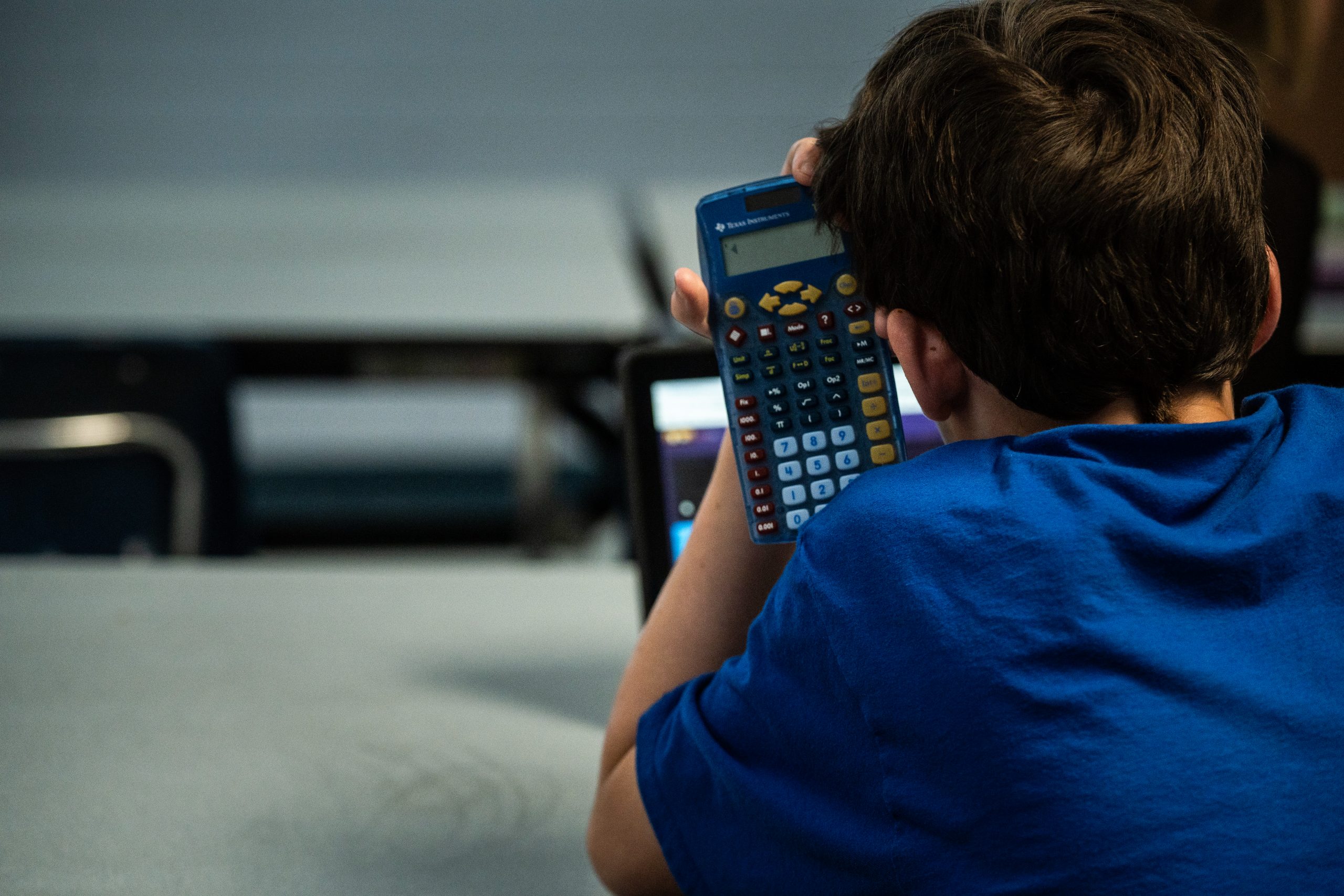
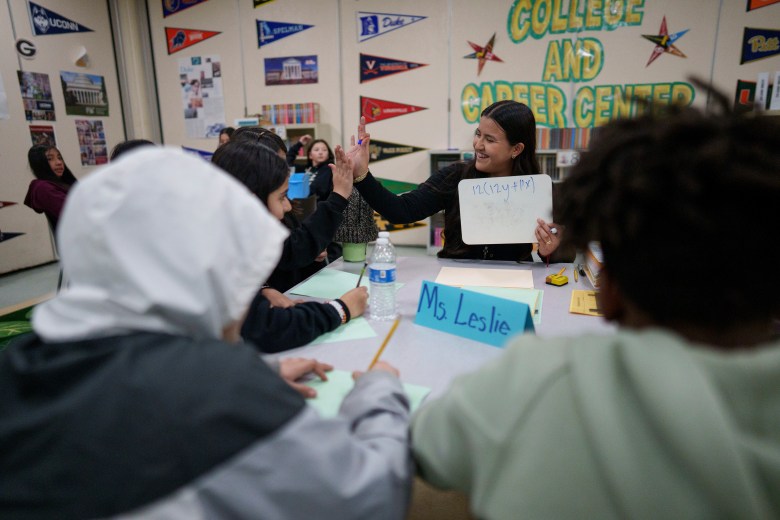
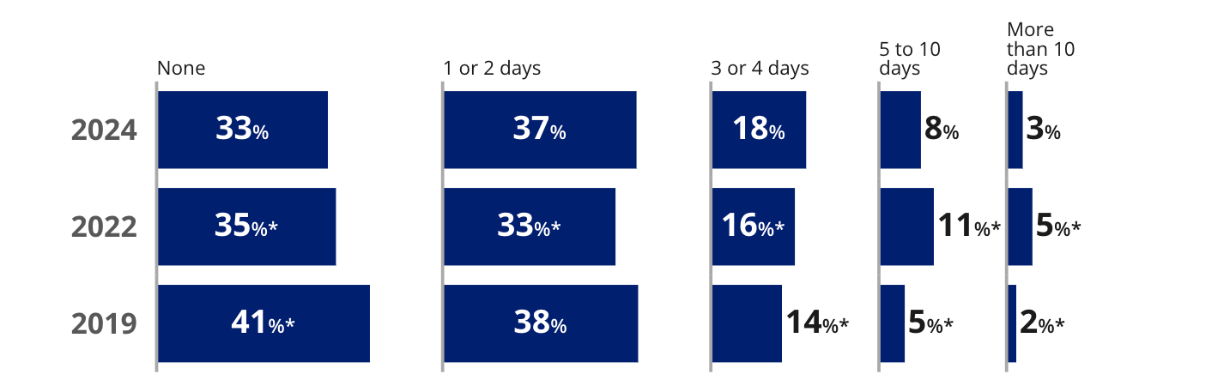
DRESDEN, Tenn. — In early February, seventh grade math teacher Jamie Gallimore tried something new: She watched herself teach class. The idea had come from Ed Baker, district math coach at Tennessee’s Weakley County Schools. Baker set up an iPad on a cabinet in Gallimore’s classroom at Martin Middle School and hit record.
Gallimore watched the videos twice, and she and Baker ran through them together. They dissected the questions she asked during the lesson, looked at how much time she took to work through problems and analyzed how she’d moved around the room. As a veteran teacher, she did a lot right — but the meeting with Baker also made her change a few things.
Instead of throwing out questions to the whole class, now Gallimore more often calls on individuals. When a student answers, she might turn to the other side of the room and ask, “What did they just say?” The tactics, she said, have helped keep her students engaged.
Coaching is one strategy Weakley administrators and teachers credit with boosting middle school math scores after they crashed during the pandemic. Weakley’s third through eighth graders are more than half a grade ahead of where they were at the same time in 2022 and about a third of a grade ahead of 2019, according to a national study of academic recovery released in February. In three of the district’s four middle schools, the percentage of students meeting grade-level expectations on Tennessee’s standardized math test, including among economically disadvantaged students, rose in 2024 above pre-pandemic levels.
Amid a grim landscape nationwide for middle school math, Tennessee fared better than most states. In two districts in the state that bucked the national trend — Weakley and the Putnam County School District — educators point to instructional coaches, a dramatic increase in class time devoted to math and teachers systematically using student performance data to inform their teaching and push students to improve.
How students do in middle school can predict how they do in life. Higher achievement in eighth grade math is associated with a higher income, more education later and with declines in teen motherhood and incarceration and arrest rates, a 2022 study by Harvard’s Center for Education Policy Research found. In addition, middle school grades and attendance are the best indicators of how a student will do in high school and whether they’re ready for college at the end of high school, a 2014 study found.
Related: A lot goes on in classrooms from kindergarten to high school. Keep up with our free weekly newsletter on K-12 education.
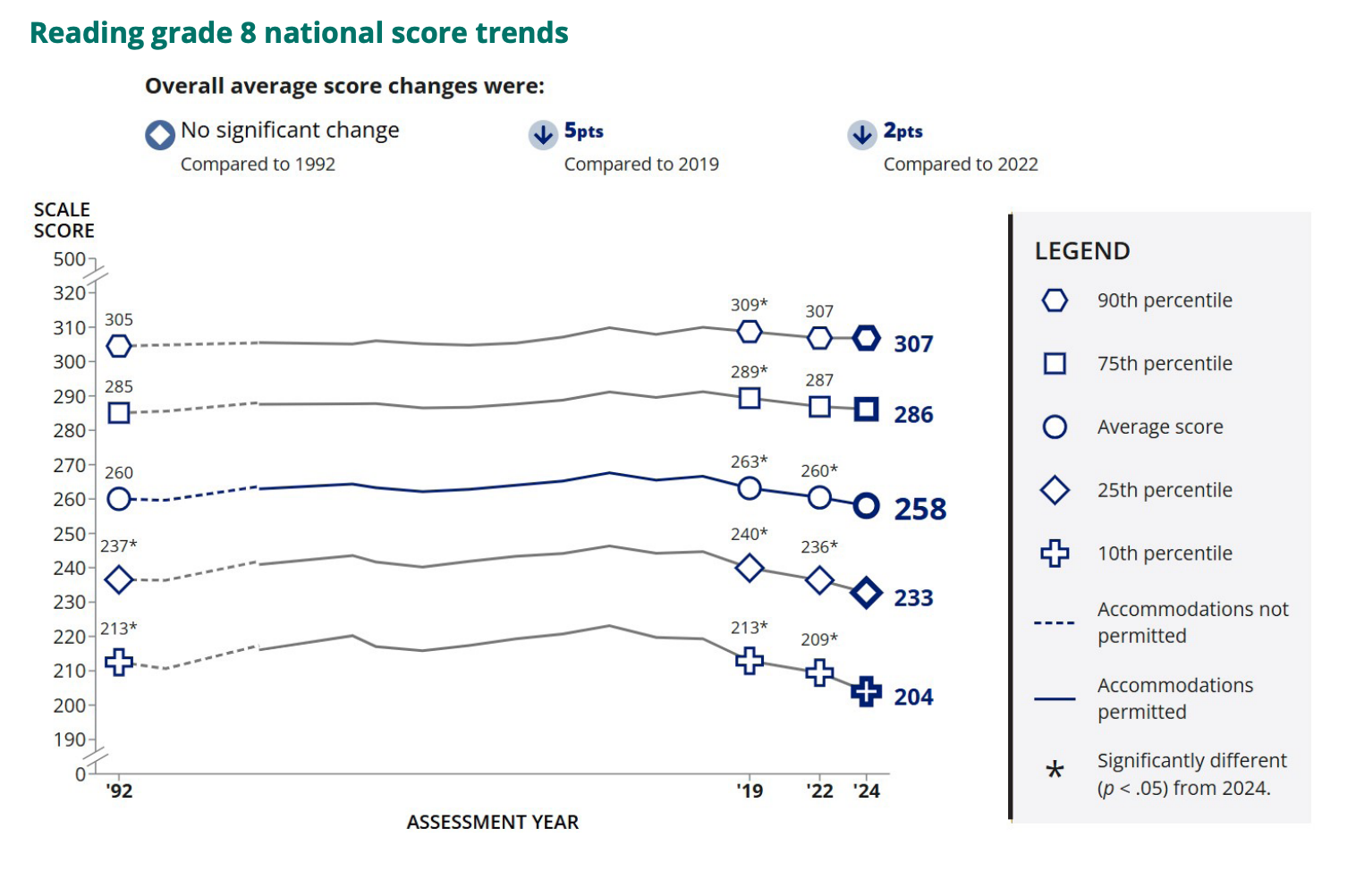
Nationally, the news coming in shows trouble ahead: In January, for example, the National Assessment of Educational Progress, known as the Nation’s Report Card, showed that average eighth grade scores in 2024 were below those of 2019 and didn’t budge from 2022, when scores were the lowest in more than 20 years. Worse, the gaps between high and low achievers widened.
Tennessee, though, was one of five jurisdictions where the percentage of eighth graders scoring proficient in math — meaning they were able to handle challenging tasks like calculating square roots, areas and volumes — increased from 2022 to 2024. That reflects a longer-term trend: Since 2011, Tennessee has climbed from the 45th-ranked state to the 19th for average eighth grade math scores.
But researchers have struggled to determine which interventions were most effective in helping students recover. A June 2024 study that looked at different strategies came to no conclusion because the strategies weren’t comparable across districts, said Dan Goldhaber of the nonprofit American Institutes for Research. In March, the Trump administration eliminated nearly all staff at the Department of Education unit that runs the Nation’s Report Card, which educators and researchers worry could make it even harder to compare how students in different states and districts perform and draw lessons about what works.
In the absence of systematic research, attention has turned to states like Tennessee and districts like Weakley and Putnam where kids have climbed out of an academic hole. At Martin Middle School, the percentage of students meeting grade level expectations on the state math exam cratered during the pandemic, falling from 40 percent in 2019 to 24 percent in 2022. But in 2024 that number jumped to 43 percent.
Related: Data science under fire: What math do high schoolers really need?
Weakley County sits in the state’s northwest corner, its flat farmland populated with small towns of mostly modest ranch homes. The county is poorer than most in the country, with a median household income under $50,000.
When the first federal Covid relief money arrived in early 2020, the district had to choose what to prioritize. Weakley focused on hiring staff who could help kids recover lost learning — instructional coaches for each school to focus on teaching strategies, plus subject-area coaches like Baker, whose role the district created in 2021. “Bottom line, we decided people over things,” said school system Director Jeff Cupples.
Research indicates that coaching can make a big difference in student outcomes. A 2018 study summarizing the results of 60 prior studies found that coaching accelerated student learning by the equivalent of four to six months, according to Brown University associate professor Matthew Kraft, who led the research team. In a survey of Tennessee school districts last year, 80 of 118 that responded said they employ math coaches.

In 2022, Martin Middle made another big change, nearly doubling the time kids spend in math class. In place of a single 50-minute class are two 45-minute periods that the school calls “core” and “encore,” with the encore session meant to solidify what students get in the first.
On an overcast March day, Becky Mullins, a longtime math and science teacher who’s also assistant principal, helped sixth graders in her encore class calculate area and volume. On a screen at the front of the classroom, she pulled up problems many of them had trouble with in their core class taught by math teacher Drew Love. One asked them to calculate how many cubes of a certain volume would fit inside a larger prism. “What strategy have you learned from Mr. Love on how to solve this problem?” she asked.
Related: One state tried algebra for all eighth graders. It hasn’t gone well
When a student in the back named Charlie raised his hand and said he was stuck, Mullins pulled up a chair beside him. They worked through the procedure together, and after a few minutes he solved it. Mullins said helping students individually in class works far better than assigning them homework. “You don’t know what they’re dealing with at home,” she said.
Martin Middle seventh grader Emma Rhodes, 12, said individual help in her sixth grade encore class last year helped her through fractions. Her encore teacher was “very hands on,” said Rhodes. “It helps me most when teachers are one on one.”
Yet studies of double-dose math show mixed results. One in 2013 found a double block of algebra substantially improved the math performance of ninth graders. Another a year later concluded that struggling sixth graders who received a double block of math had higher test scores in the short term but that those gains mostly disappeared when they returned to a single block.
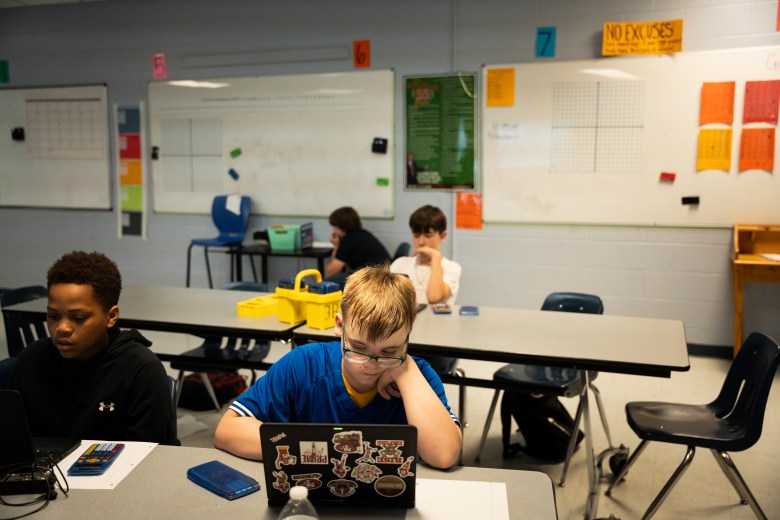

Weakley and Putnam County staff also credit the systematic use of student achievement data for helping their middle schoolers rebound. Tennessee was a pioneer in the use of academic data in the early 1990s, devising a system that compiles fine-grained details on individual student achievement and growth based on state test results. Both Weakley and Putnam teachers use that data to pinpoint which skills they need to review with which students and to keep kids motivated.
Related: Inside the new middle school math crisis
A four-hour drive east of Weakley in Putnam County on a day in early March, seventh grade math teacher Brooke Nunn was reviewing problems students had struggled with. Taped to the wall of her classroom was a printout of her students’ scores on each section of a recent test in preparation for the Tennessee state exam in April. One portion of that exam requires students to work without calculators. “This non-calculator portion killed them, so they’re doing it again,” Nunn said of the exercises they’re working on — adding and subtracting negatives and positives, decimals and fractions.
The data on her wall drove the lesson and the choice of which students to have in the room at Prescott South Middle School, where she teaches. Starting about 10 years ago, the district began requiring 90 minutes of math a day, split into two parts. In the second half, teachers pull out students in groups for instruction on specific skills based on where the data shows they need help.
Teachers also share this data with students. In a classroom down the hall, after a review lesson, fellow seventh grade math teacher Sierra Smith has students fill out a colorful graphic showing which questions they got and which they missed on their most recent review ahead of the state test. Since Covid, apathy has been a challenge, district math coach Jessica Childers said. But having kids track their own data has helped. “Kids want to perform,” she said, and many thrive on trying to best their past performance.
The district is laser focused on the state tests. It created Childers’ math coach role in 2019 with district funds and later other instructional coach jobs using federal pandemic relief money. Much of Childers’ job revolves around helping teachers closely align their instruction with the state middle school math standards, she said. “I know that sounds like teaching to the test, but the test tests the standards,” said Childers.
Something in what the district is doing is working. It’s not well off: The share of its families in poverty is 4 percent higher than the national average. But at all six district middle schools, the percentage of students meeting expectations on the state math exam was higher in 2024 than in 2019, and at all six the percentage was above the state average.
Goldhaber, the AIR researcher, speculated that the focus on testing might help explain the rebound in Tennessee. “States have very different orientations around standards, accountability and the degree to which we ought to be focused on test scores,” he said. “I do believe test scores matter.”
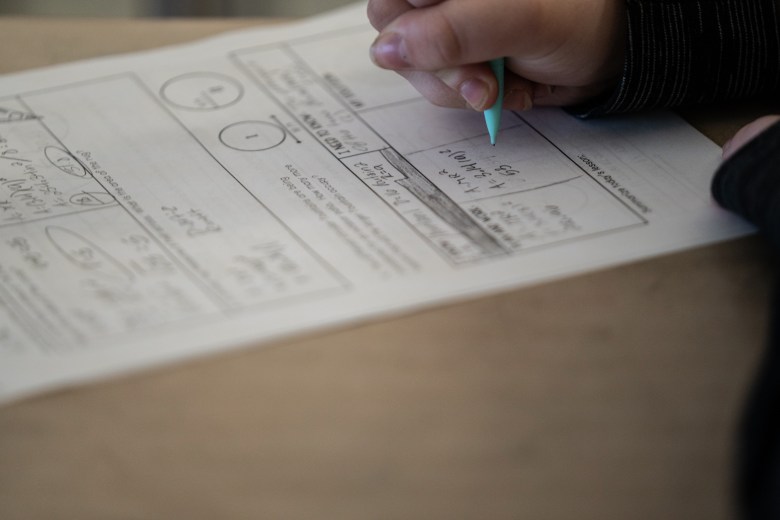

If Trump administration layoffs hamstring the ability to compare performance across states, successful strategies like those in the two districts might not spread. Weakley and Putnam have taken steps to ensure the practices they’ve introduced persist regardless of what happens at the federal level. Most of the federal Covid relief dollars that paid for academic coaches in both districts stopped flowing in January, but both have rolled money for coaches into their budgets. They also say double blocks of math will continue.
Cupples, the Weakley superintendent, worries about the effect of any additional federal cuts — without federal funds, the district would lose 90 positions and 10 percent of its budget. It would be “chaos, doom, despair,” he said, laughing. “But one thing I’ve learned about educators — as one myself and working with them — we overcome daily,” he said.
“It’s just what we do.”
Contact editor Caroline Preston at 212-870-8965, via Signal at CarolineP.83 or on email at [email protected].
This story about math recovery was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for the Hechinger newsletter.