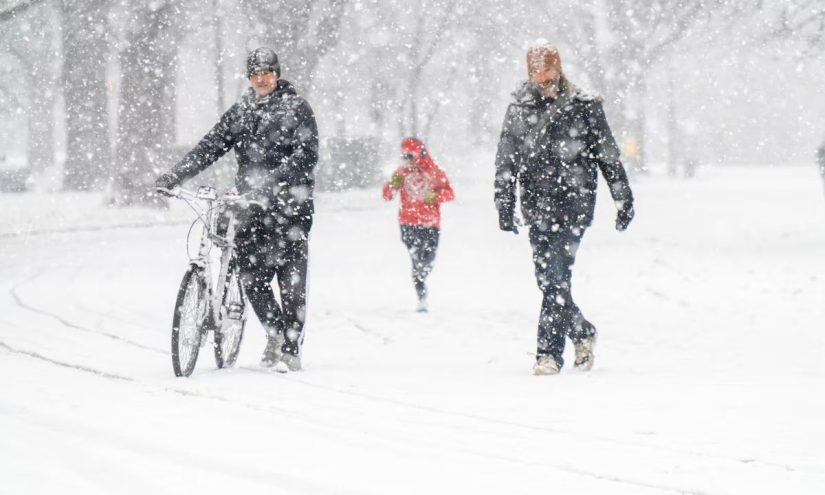
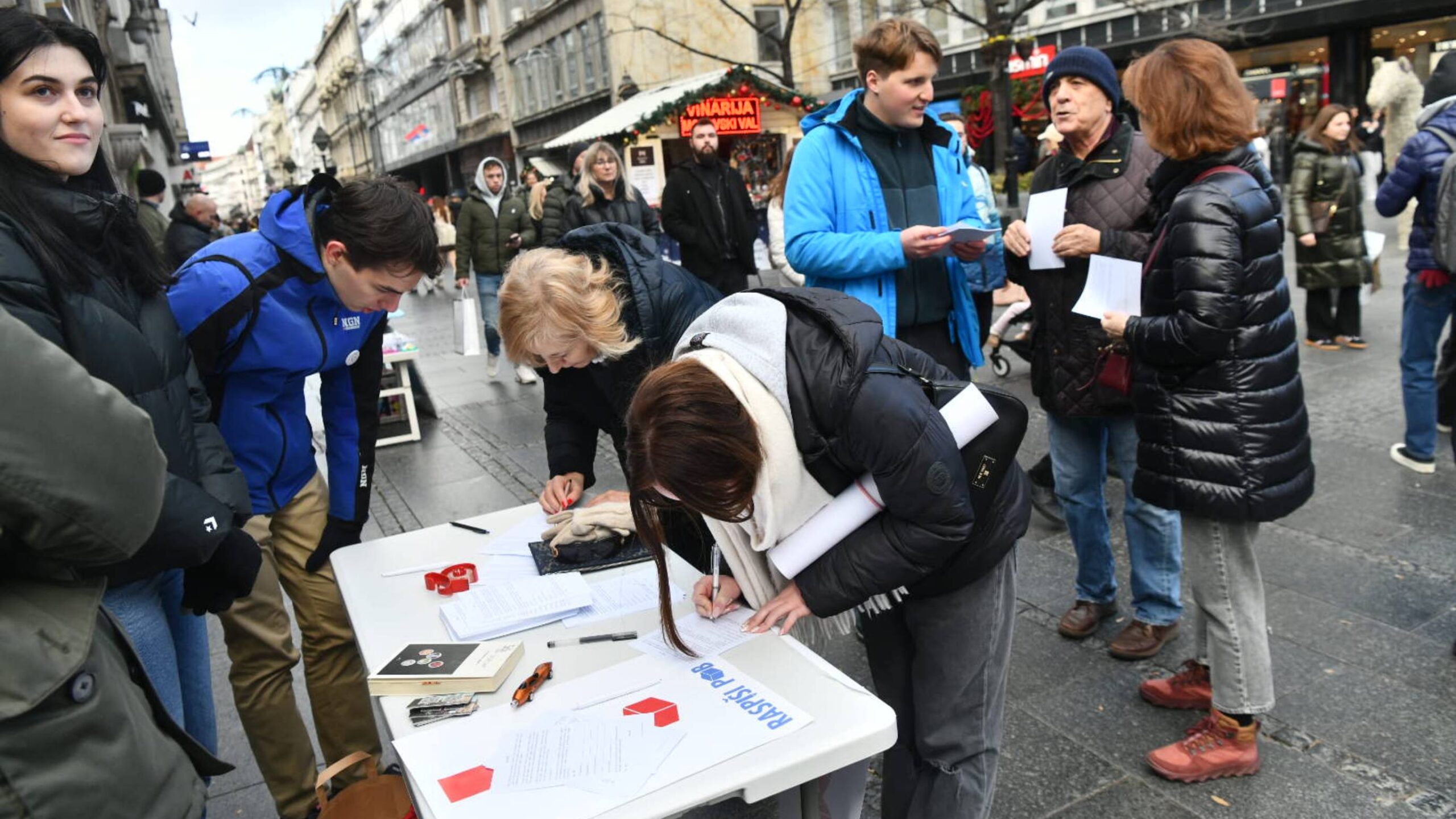
This past weekend, braving freezing weather, Serbian students set up nearly 500 stands in dozens of cities, towns and villages across the country. They’ve not been selling Christmas trinkets – they’ve been collecting signatures.
The action, titled “Raspiši pobedu” (Declare Victory) was less a petition, more a test of support. After more than a year of campus blockades, protests drawing hundreds of thousands, and awareness-raising marches across the country, they wanted to know – does Serbia actually want the elections we’ve been demanding?
Jana, a first-year philosophy student staffing one of the Belgrade stands, told AFP:
We are counting to get a rough idea of how many people support us.
The answer, by all accounts, was emphatic. In Niš alone (Serbia’s third largest city), more than 17,000 signatures were collected. In Kraljevo (a city in south-central Serbia), 16 stands had to print additional materials due to demand. Across the country, the queues kept coming.
Political science professor Nebojša Vladisavljević sees the students entering a new phase of mobilisation:
The goal is to turn the support gained through protests into votes and an electoral victory.
![]()
As has often been the case, the protest action has been well timed. On our Christmas Day (Serbia itself follows the Julian calendar), a court had ruled there were no grounds to further prosecute the former construction minister suspected of a “serious crime against public safety” in connection with the Novi Sad canopy collapse that killed 16 people and triggered the entire movement.
Since then, three investigations have been launched. Only one has resulted in an indictment confirmed by a court – and now another avenue of accountability has closed.
A week earlier, thousands had gathered in Novi Pazar – Serbia’s youngest town demographically, with a majority Bosniak Muslim population – for the first protest of its kind there. The immediate cause was brutal – Momčilo Zelenbaba, who travelled 190 kilometres from Jagodina to attend, explained:
I came because 200 students lost their status and 30 professors lost their jobs.
Dženana Ahmetović, a student protester, framed the stakes:
We are here today to send a message to Serbia that we fight for an interim management and the survival of our university. This concerns all of us, not only Novi Pazar.
The Novi Pazar students had become famous across Serbia after walking for 16 days – one day for each victim – to join the anniversary commemoration in Novi Sad on 1 November. Now they were paying the price for that solidarity – and students from across the country were coming to stand with them in return.
![]()
Nearly two-thirds of citizens, regardless of political affiliation, see snap elections as a way out of the crisis. For now, President Vučić has said elections won’t be held before late 2026. The students have other plans.
No easy framing
Back in January 2025, I wrote about the student protests as they called their first general strike – and at the time, I hedged, suggesting you could “pretty much flip a coin” on whether the movement would bring down the government or fizzle out over concerns about the academic year.
It turns out I was too cautious. The students didn’t just survive – they’ve forced the question of snap elections onto the agenda and positioned themselves as a serious electoral force.
But the path from those January blockades to this past weekend’s signature campaign has been anything but straightforward, and the story is harder to tell than the familiar framing would suggest.
Western media, when it has covered the protests at all, has often reached for a familiar narrative – plucky pro-European youth versus authoritarian regime backed by Russia.
Vučić himself encouraged this framing, repeatedly claiming the protests were a Western-orchestrated “color revolution” and that:
…President Putin had clearly explained everything he needed to know about it in just three sentences.
But the students who occupied faculties across Serbia weren’t waving EU flags. In fact, when a group tried to raise the EU flag during a vigil in Belgrade, they were surrounded, shouted at, and forced to leave – while Orthodox crosses, references to Kosovo, and students wearing traditional šajkača caps became common features of the protest aesthetic, while the organisers said nothing.
Academics have called this “depoliticization as strategy” – the deliberate bracketing of partisan and ideological markers to claim moral legitimacy in an environment where all political institutions are compromised.
This is a movement that has rejected the regime but also rejected the opposition, that demanded elections but refused to endorse any candidate, that cycled to Strasbourg to petition the European Parliament, but wouldn’t let anyone carry a European flag at home.
When opposition leaders attempted to join protests, they were met with suspicion and outright rejection – student “plenums” have explicitly asked political parties to stay away, banned party insignia, and have refused to let politicians speak.
![]()
One student in the documentary Wake up, Serbia! puts the generational logic directly:
Our parents fought during the ’90s and 2000. They accomplished something. They brought in democracy. Now we have problems with democracy. Now it’s our turn to fight to make it less corrupt.
Another is emphatic about rejecting old divisions:
We don’t care if the guy representing us is gonna be a Catholic, a Muslim, Christian, Indian guy, whatever. We want to change this system and we don’t want to focus on bringing back Kosovo or seeing who is Croatian in our friend group and who is from Bosnia. We don’t care about that. We care about the current situation in Serbia.
The academic analysis puts it formally:
…what appeared as an ‘anti-political’ stance was more accurately an anti-partisan strategy, shaped by the authoritarian context that rendered conventional political participation ineffective.
The students claimed to be about “justice, not politics.” And yet they articulated explicitly political demands – accountability, resignations, investigations, and eventually snap elections.
The tensions were real. While the plenums formally disavowed ideological branding, progressive-leaning groups and pro-EU civil society actors were marginalised, sometimes physically removed – even as nationalist symbols were tolerated. The documentary captures one revealing exchange about violence:
We don’t want to be responsible for violence as an organization of students.
But you want violence?
Yes, I literally answered that. I don’t want to be labeled as an aggressive student. I would love to be labeled as an aggressive citizen.
And the challenges of direct democracy are frankly acknowledged:
The process of making decisions is very, very slow. Show up to the plenary session, and then we debate for 4 and a half hours and come to no conclusion. Okay, let’s have another plenary session. 4 hours, no conclusion.
What the regime threw at them
Throughout 2025, the government’s response has drawn on every tool in the authoritarian playbook – and a few that seemed improvised on the spot.
Violence
On 15 March, somewhere between 275,000 and 325,000 people gathered in Belgrade for the “15th for 15” protest – the largest mass demonstration in modern Serbian history. At 19:11, the crowd fell into commemorative silence. What happened next remains contested, but accounts from those present are astonishing. Ivana Ilic Sunderic, a veteran of Serbian activism:
I have been going to protests for 30 years but I’ve never heard anything like this. A sound rolling toward us, a whiz… very frightening, like a sound from hell.
![]()
Evidence surfaced of a US-made Long Range Acoustic Device mounted on a Gendarmerie vehicle. Interior minister Ivica Dacic dismissed the devices as “loudspeakers available on eBay.” Vučić issued a high-stakes ultimatum:
If there was a single piece of evidence that a sound cannon was used against demonstrators, then I would no longer be president.
In June, the human rights organisation Earshot published forensic analysis concluding it was highly likely that protesters were subjected to a targeted attack using a directional acoustic weapon. Vučić remains president.
By June, on Vidovdan – the national holiday commemorating the 1389 Battle of Kosovo, freighted with nationalist symbolism – riot police charged a largely peaceful protest of 140,000 people, using pepper spray, shields and batons. Student Luka Mihajlović became a symbol of the crackdown – beaten and arrested while standing calmly with hands raised.
![]()
Institutional warfare
The government adopted amendments to the Higher Education Law in March, promising a 20 per cent budget increase and 50 per cent tuition fee reduction – but in parallel came Regulation 5/35, altering the ratio of teaching to research hours from 20:20 to 35:5.
Because research was no longer compensated, and blockades prevented teaching, professors supporting the protests would receive only 12.5 per cent of their usual salary – roughly €70 a month:
This is obviously a try to break us down, but we are trying to endure and to support our students in spite of the punishments.
By May, a government Working Group was drafting yet another Higher Education Law – this one allowing foreign universities to operate without local accreditation while receiving state subsidies, and introducing a voucher system forcing state faculties to compete with private ones.
Jelena Teodorović (an Associate Professor at the Faculty of education, University of Kragujevac) warned of:
…a fierce fight for financing that would force faculties to make studying faster and easier, ultimately resulting in worthless knowledge and worthless diplomas.
Vučić, in Niš, made his preferences clear:
Private faculties have shown to be significantly more stable and serious.
A BIRN (Balkan Investigative Reporting Network) investigation published in December documented systematic retaliation – hundreds fired or demoted, over 100 teachers and 25 school directors dismissed for supporting the protests, and criminal charges launched against University of Belgrade rector Vladan Đokić.
![]()
Last week, thousands gathered in Novi Pazar after the university administration revoked student status for 200 students absent due to protests and dismissed 30 professors. One public sector worker describes the coercion around pro-government rallies:
We have a rally tomorrow, are you going? I’m not going. But, your contract is expiring.
Counter-mobilisation
Throughout 2025, the government has maintained a surreal counter-protest camp known as “Ćaciland” – part propaganda tool, part dark comedy. One student on the inhabitants argues they’re not students:
They are adults. There are people 50 plus years old. It’s so transparent that they are protected by the government and actually sent there by the government.
Another describes attempts to interview residents:
People were interviewing people in the camp and they were like, “Oh, no, no, no, no.” Hiding their faces, being embarrassed. And the ones who spoke were like, “Oh yeah, I’m not going to the faculty for the past 2 years. I just came here.” Like, €200 a day – that sounds like a good deal.
![]()
Some say the camp’s composition was, in fact, more sinister than laughable:
Members of the brigade that was dismembered after Milošević left in 2000 – the brigade that actually killed Prime Minister Zoran Đinđić – the veterans of that brigade are right now supporting the students 2.0.
Co-option
The regime has repeatedly tried to reframe itself as being on the same side as the students – just against “lower-level corruption.”
Vučić launched what he branded a new “anti-corruption offensive,” conveniently timed to coincide with the peak of protests. Pro-government commentators began echoing student demands for transparency, presenting Vučić as a fellow enemy of the oligarchs. Several mid-level officials were dismissed, and state media framed these changes as evidence that the president was listening.
![]()
During a visit to Sremska Mitrovica, Vučić declared:
I trust these young people. I trust them more than those who put them up to this. People will no longer tolerate it – that is why they want us to change. They do not want those who destroyed the country to come to power. They want none of them. But they do want us – different, better, changed.
The European dimension
On 3 April, eighty students set off on bicycles from Novi Sad, beginning a 13-day journey to Strasbourg. Their stated mission:
For the world to hear the voice of Serbia. For European institutions to put pressure on the authorities.
It was a pragmatic calculation, not an ideological embrace – the students needed external pressure that the regime couldn’t suppress domestically.
![]()
Their letter to French President Emmanuel Macron combined political clarity with poetic determination:
We are not here to complain, but to remind you that hope still moves – and sometimes, it moves on two wheels. We refused to give up; every turn of the pedals was a protest against fear.
The European Parliament responded in May with a resolution acknowledging the “legitimacy of student protest demands” and calling for an investigation into the sonic weapon allegations – 419 votes in favour. European Commissioner for Enlargement Marta Kos:
Corruption and irresponsibility are the two main triggers of the protests. They also represent the motive for dissatisfaction due to a lack of democracy, the enslavement of the media, and the impunity of politicians.
By October, the Parliament had adopted what was described as the “harshest ever” resolution towards the Serbian regime – 457 votes in favour, featuring express support for student demands, denunciation of state repression, explicit condemnation of sonic weapons and Pegasus spyware, and a call for an EU fact-finding mission. MEP Irena Joveva said that the time of impunity for autocrats in Belgrade was coming to an end:
We see this grotesque irony that those who order beatings call the beaten people Nazis, inventing fake ćaci students, while real students are bleeding for democracy.
The regime’s media apparatus weaponised every European intervention, accusing the students of “selling out to Brussels” and labelling them “traitors.” Students who had carefully distanced themselves from ideological affiliation found themselves simultaneously supported by EU progressives and demonised by nationalist-authoritarian actors – their rhetorical insistence on neutrality was becoming increasingly untenable.
The electoral gambit
In April, moving from demands for accountability to wider demands, student plenums issued a declaration that changed the terms entirely:
Government corruption is so deeply rooted that no functional reform is possible within the current institutional framework. Only new elections – conducted under fair and monitored conditions – can open the path to justice.
The students had gone from demanding investigations to demanding regime change.
![]()
November 1st marked a year since the canopy collapse. At exactly 11:52 AM, tens of thousands stood in 16 minutes of silence – one minute for each victim. Independent observers placed the Novi Sad crowd at approximately 100,000. Dijana Hrka, mother of 27-year-old victim Stefan, addressed the crowds:
I need to know who killed my child so I can have a little peace. I am looking for justice. I want no other mother to go through what I am going through.
A giant banner unfurled on Petrovaradin Fortress:
See you tomorrow and every other day until there is justice.
Vučić issued a rare televised apology:
I apologize – both to students and to protesters, as well as to others with whom I disagreed.
![]()
The students were unmoved. State-owned Serbian Railways suspended train traffic to Novi Sad on the day of the protest, citing an alleged bomb threat.
Student plenums have now announced support for a civic electoral list while emphasising that students themselves won’t appear as candidates – they demand independent monitoring, transparent campaign financing, and genuine media pluralism, but they still refuse to endorse any party. Sociologist Zoran Gavrilović:
We are witnessing the formation of a serious electoral player, because the students have become Vučić’s most serious competitor.
The open question
The academic analysis identifies both the strength and the risk:
…without institutional continuity, moral mobilization risks dissipation. Without mechanisms to translate civic power into structural change, legitimacy may erode once the moment passes.
One student puts it plainly:
This has outgrown the student-led protests. We can do everything still – all of the organisation, the logistics – but we can’t do it all on our own. We need help for this next step.
Another on the long game:
We have to wake up as many people as we can until the next elections so that we can actually win. And if the election gets stolen again like they did in 2000, then we can violently protest.
And another, more hopefully:
You’re not aware of how many people have been woken up from a very long sleep here in Serbia. We are the students that managed to wake up the whole nation. Now it’s up to the citizens of Serbia to decide what will happen next.
For those of us who follow student movements, there are lessons here – though perhaps not the ones we expected. The power of decentralisation is real – the movement was almost impossible to decapitate through targeted arrests or co-option precisely because it had no leaders. The importance of tactical evolution is also clear – from blockades to silent vigils to 24-hour road closures to bicycle journeys to signature campaigns, each phase wrong-footed the authorities.
But the limits of “depoliticisation” have also been visible. Refusing to build political infrastructure, rejecting alliances with compromised but potentially useful actors, tolerating some ideological currents while excluding others – the movement may have constrained its own transformative potential.
This weekend’s signature campaign suggests they know this. The paradox now is whether a movement built on rejecting politics can win at it.