
The U.S. Department of Education recently released a draft proposal of regulatory language that outlines how short-term programs could become — and remain — eligible for the newly created Workforce Pell Grants.
The Workforce Pell program will allow students in programs as short as eight weeks to receive Pell Grants. It was created as part of the massive spending and tax package that Republicans passed this summer and takes effect in July 2026.
The Education Department released the draft proposal ahead of negotiations next week to hash out the regulatory language governing how the program will operate.
In a process known as negotiated rulemaking, stakeholders representing different groups affected by the regulations are to meet Monday to begin discussing the policy details of the Workforce Pell program. Participants include students, employers and college officials.
If they reach consensus on regulatory language, the Education Department will have to use that when formally proposing regulations for Workforce Pell. If the stakeholders don’t reach consensus, the agency will be free to write its own regulations.
The draft proposal outlines the steps state officials will have to take for workforce programs to begin qualifying for Workforce Pell Grants and what student outcome metrics they would need to hit to remain eligible for the grants.
The massive budget bill expands Pell Grants to certain workforce-training programs lasting between eight to 15 weeks. For programs to be eligible, governors must consult with state boards to determine if they prepare students to enroll in a related certificate or degree program, meet employers’ hiring needs, and provide training for high-skill, high-wage or in-demand occupations, among other requirements.
Under the Education Department’s draft proposal, each state’s governor would work with its workforce development board to establish which occupations are considered high-skill, high-wage or in-demand and publicly share how the state made those determinations. Governors would also have to seek feedback from employers to develop a written policy for determining whether programs meet local hiring needs.
As established in the spending bill, short-term programs must then receive approval from the Education Department’s secretary before they can qualify for Workforce Pell. Under the statute, programs have to exist for at least one year before they can get approval.
The Education Department’s proposal adds that the secretary wouldn’t be able to approve a program until “one year after the Governor determines that the program met all applicable requirements.”
This means that “all programs would need to wait an additional year before becoming eligible, even if they had already existed for more than a year,” according to a Thursday analysis of the draft from James Hermes, associate vice president of government relations at the American Association of Community Colleges.
AACC plans to work with negotiators to push for that provision to be changed, Hermes said.
Under the Education Department’s draft language, programs would need to maintain a job placement rate of 70% to remain eligible during the first two years of the Workforce Pell program. But after the 2027-28 award year, they would need 70% of their graduates to specifically land jobs in fields for which they’re being trained, according to the proposal.
During each award year for Workforce Pell, the statute bars programs from posting tuition and fee prices that are higher than the “value-added” earnings of their students. It calculates that difference by subtracting 150% of the federal poverty line from the median earnings of students who completed their program three years prior.
To make that calculation, the Education Department proposed first checking whether that cohort contains at least 50 students. If not, it would look back up to two more years to see if the program meets that benchmark. If the program still misses that threshold, it will look back one more year to achieve a cohort of 30 students.
If looking back those additional years doesn’t yield data from at least 30 students, the Education Department would not complete the “value-added” calculation, according to the draft. However, the agency’s proposal doesn’t address how that would impact a program’s eligibility for Workforce Pell.

As the U.S. Department of the Interior prepares to take on a greater role in administering federal funding for tribal colleges, institutional leaders fear financial uncertainty and losing long-standing trust with the Education Department.
The grant program is one of dozens the Education Department reshuffled to other federal agencies late last month in yet another effort by Secretary Linda McMahon to trim down its duties and ultimately dismantle the department. Through an interagency agreement, the Department of the Interior will now manage tribal colleges’ Title III funding, while ED retains oversight and policymaking responsibilities, according to an Education Department announcement.
Trump administration officials argue the move makes sense. The Department of the Interior, home to the Bureau of Indian Education, already oversees tribal K–12 schools and two tribal higher ed institutions, Haskell Indian Nations University in Kansas and Southwestern Indian Polytechnic Institute in New Mexico. The Department of the Interior also already administers higher education scholarships for Native students and other grant funding for tribal colleges.
Secretary of the Interior Doug Burgum said in the announcement that his department will assume administrative responsibilities “for enhancing Indian education programs, streamlining operations, and refocusing efforts to better serve Native youth and adults across the nation.”
The American Indian Higher Education Consortium said in a statement that it’s monitoring the policy shift and plans to work closely with the Department of the Interior “to ensure stability and continuity” for institutions and their students.
“AIHEC will continue to advocate for approaches that uphold the federal government’s trust and treaty obligations to Tribal Nations and protect the vital role of TCUs in advancing Tribal sovereignty and student success,” the statement read.
Despite reassurances, tribal college leaders are leery of the upcoming change.
Stephen Schoonmaker, president of Tohono O’odham Community College in Arizona, said he understands the logic of the shift, given tribal colleges already have a strong relationship with the Bureau of Indian Education.
But the department also proposed cutting more than 80 percent of tribal colleges’ funding earlier this year, from roughly $127 million last year to about $22 million this year.
Congress didn’t approve the cut, but the proposal “was an existential threat to tribal colleges,” Schoonmaker said.
He believes institutions like his are safest when they have grants coming from multiple federal agencies. That way, if one agency cuts funding, there are still federal dollars flowing in from elsewhere.
“Putting everything under one basket that could be just cut all at once is not reassuring,” he said.
Even though he’s had positive experiences working with the BIE, he said he’s jarred by the uncertainty.
“With this administration, there is a propensity to shuffle things around and make a flurry of proposals, some of which get headway, some of which get dropped almost immediately,” Schoonmaker said, “and it makes it challenging to plan, to ensure for our students and for our employees and for our communities that we serve that the way we’ve been structured, the way that the trust and treaty obligations work … will continue to be honored.”
The administration hasn’t shared a transition plan with tribal college leaders, adding to their worries, said Chris Caldwell, president of the College of Menominee Nation in Wisconsin.
According to Caldwell, tribal college leaders are most concerned about the future of the funding mechanisms and support that has historically come from the Department of Education. “We want to make sure that those are retained or even increased,” Caldwell said.
He also questions how much the BIE will listen to tribal college leaders in its decision-making. For example, its proposal to slash tribal college funding came shortly after a listening session with institutional leaders, he said.
At the same time, he’s buoyed by the fact that bipartisan support not only saved colleges from proposed cuts, but it increased their funding; the Education Department funneled a historic one-time tranche of funds to tribal colleges, redirected from grants for other minority-serving institutions, earlier this year. Contributions from philanthropist MacKenzie Scott, including a $10 million gift to the College of Menominee Nation, have also offered some extra stability.
“I have been on roller coasters, but never a roller coaster like this,” Caldwell said. But “I think that strong bipartisan support bodes well for us, even in the midst of this restructuring.”
Twyla Baker, president of Nueta Hidatsa Sahnish College in North Dakota, said what’s most concerning to her is that the interagency agreement came as a “total surprise.”
“Tribes, tribal nations, tribal educators should have known about this,” she said. They “should have had input on this well before any type of moves should have been made, before any type of interagency agreements should have been signed … Consultation should have happened and needs to happen quickly if we’re going to continue on this path.”
She also has her doubts about ED shifting responsibilities over to the Department of the Interior. She said tribal college leaders have worked to develop expertise within the Education Department about their institutions and now it feels like that effort was for naught.
“You’re kind of pulling the rug out from under us,” she said. “And that structure, the regularity of how business is done, is going to be dismantled. You can’t just shove it over to somebody else’s responsibility and expect it to work well.”
She worries the transition could affect students if services and resource allocation are interrupted.
“That type of interruption can be pretty untenable for small schools in rural areas, which is what a lot of us are.”
Whatever happens, Baker said the transition is “a diversion of energy that didn’t necessarily have to happen where we could have been just focusing on our missions.”
The Bureau of Indian Education has come under fire in the past for its negligent oversight of K–12 schools and the two higher ed institutions in its care.
Members of Congress held a heated hearing last year in which many accused the Bureau of Indian Education of responding slowly or inadequately to student and employee complaints at Haskell Indian Nations University, including reports of sexual assault. Some Kansas lawmakers even proposed removing Haskell from federal control.
The BIE has also historically drawn criticism for poor academic outcomes, limited reporting, inadequate technology and deferred maintenance backlogs at its K–12 schools, ProPublica reported. A 2014 report by Sally Jewell, interior secretary under President Barack Obama, and former Education Secretary Arne Duncan called the BIE a “stain on our Nation’s history.” The report denounced the agency for producing “generations of American Indians who are poorly educated” and promised to undertake reforms.
(Tony Dearman, director of the Bureau of Indian Education since 2016, told ProPublica that the BIE has undergone changes since then, including a more direct process to inspect school buildings, make major purchases and enter into contracts.)
In a statement to Inside Higher Ed, the Department of the Interior described its new responsibilities toward tribal colleges as an “opportunity to better serve Native youth” and emphasized plans to solicit tribal college leaders’ input during the transition.
“As we move forward with efforts to improve the coordination and delivery of Native American education programs, the Bureau of Indian Education will continue to engage closely with tribes and education partners to ensure their perspectives inform our work,” the statement read.
“We value the input we receive from tribes and stakeholders, and we remain dedicated to building a future where Native students have the tools, support, and opportunities they need to thrive for generations to come.”

The settlement in the Sweet v. McMahon case stems from a class-action lawsuit filed during the first Trump administration that accused the Education Department of stonewalling decisions on applications for borrower defense to repayment, a federal program that provides debt relief to students defrauded by their colleges.
The settlement divided borrowers into three groups.
It granted automatic relief to the first group, which was composed of roughly 200,000 borrowers who attended one of the 151 colleges listed by the department. The list was dominated by for-profit institutions, including both large chains that had shuttered and still-operating colleges.
The second group was promised timely decisions, or automatic relief if the Education Department didn’t meet certain deadlines. The agency told the court earlier this year it had resolved many of those cases, and will provide another update in December.
And the last group — which is now facing a potential delay — is composed of the 207,000 people who filed over 251,000 borrower defense claims after the settlement had been struck but before it received final court approval.
The Biden administration’s Education Department promised to make timely decisions on their cases — or else provide automatic relief to them by Jan. 28 of next year. Now, the department under President Donald Trump is requesting to move that deadline back to July 2027.
In a Nov. 6 court filing, the agency said it lacked the resources to quickly issue decisions on such a large pool of applications.
“The Department has not received the resources that are needed to adjudicate post-class applications — Congress repeatedly ignored requests for funding to increase staffing to the levels the Department deemed necessary to fully implement the settlement,” the agency said, adding that its Federal Student Aid office “has instead seen staffing dwindle at the time when resources for postclass adjudication are most needed.”
Trump signed an order to close the Education Department to the “maximum extent appropriate and permitted by law” and has asked Congress to reduce its funding.
The Education Department has cut its staff roughly in half under Trump and moved to outsource its programs to other federal agencies without first seeking congressional approval — a move some say could be a violation of the law.
The department said it is now adjudicating about 1,500 borrower defense applications each month for the final settlement group. As of Oct. 31, it had issued decisions on almost 54,000 of the final group’s applications.
It projected that roughly 193,000 borrower defense applications covered by the settlement would still lack decisions by the January deadline. Those borrowers’ outstanding loan balances total $11.8 billion, the Education Department said in court documents. It also said about half of the group’s borrower defense claims have so far been denied.
In a statement Wednesday, Under Secretary of Education Nicholas Kent the Trump administration is requesting more time so taxpayers aren’t “burdened with discharges for ineligible borrowers.”
“Although the Department has complied with the Court’s deadlines in good faith, the upcoming January deadline is unreasonable,” Kent said. “Without adequate time to review each outstanding borrower defense case, taxpayers could be forced to shoulder $6 billion in windfall discharges for ineligible borrowers, based on the Department’s current adjudication patterns.”
In response to the Education Department’s request, lawyers for the borrowers slammed the department’s request.
“Less than 12 weeks before the deadline, the Department reveals that not only is it behind schedule to meet that deadline, it never had a prayer of meeting the deadline,” they said. “Out of more than 251,000 Post-Class applications, it has adjudicated fewer than 54,000 — barely one-fifth.”

The U.S. Department of Education’s plans to move core programming to other agencies is illegal and harmful to K-12 and higher education students, educators and families, according to an amended lawsuit filed Tuesday.
Brought forth by a broad coalition of school districts, employee unions and a disability rights organization, the amended complaint seeks to halt the outsourcing of Education Department programs.
“Taking away the services and supports students rely on will irreparably hurt children, families, educators, schools, and communities, in states across the nation,” said a Tuesday statement by Democracy Forward, which is representing the plaintiffs in the case. “The Department of Education offers important support to educators and communities throughout the nation and the unlawful attempts to shut down the Department are nothing less than an abandonment of the future of our country.”
In a statement emailed to K-12 Dive on Wednesday, Madi Biedermann, deputy assistant secretary for communications at the Education Department, said, “It’s no surprise that blue states and unions care more about preserving the DC bureaucracy than about giving parents, students, and teachers more control over education and improving the efficient delivery of funds and services.”
On Nov. 18, the Education Department announced it was developing interagency agreements with other federal agencies to support six programs, including with the U.S. Department of Labor to handle the management of about $28 billion in K-12 funding for low-income school districts, homeless youth, migrant students, academic support, afterschool programs, districts receiving Impact Aid and other activities.
Another interagency agreement places about $3.1 billion in institution-based grants for postsecondary education programming at the Labor Department.
The moves add to a partnership the Education Department created with the Labor Department earlier this year to take over the management of federal career and technical assistance programs. Democratic lawmakers, during a Nov. 19 House Education and Workforce subcommittee hearing, said several state CTE programs ran into funding delays due to a new grant management process at the Labor Department.
While the Education Department does not yet have formal plans to move the management of special education, civil rights enforcement and federal student aid out of the agency, those options are still being explored, a senior department official said during a press call on Nov. 18.
Even when programming shifts under the interagency agreements, the Education Department would still be the agency responsible for these programs, with the partner agencies taking on much of the daily operations.
The Trump administration has said the continual downsizing of the Education Department is meant to reduce federal bureaucracy and give states more autonomy over spending allocations.
During a White House press conference Nov. 20, U.S. Education Secretary Linda McMahon said there’s been a “hard reset” of the country’s educational system. “That reset was a campaign promise from President Trump to send education back to the states and end Washington’s micromanagement of education once and for all,” McMahon said.
Critics, however, say the disruptions from shifting agency responsibilities, along with Education Department staff reductions and delays in grant funding, is causing havoc for K-12 and higher education systems.
The updated complaint in Somerville v. Trump, which was consolidated with New York v. McMahon, was brought against the Education Department by groups of states, school districts and teacher unions. The Arc of the United States is now an additional plaintiff in the case.
The cases were heard earlier this year before district and appeals courts, which issued and upheld injunctions blocking the administration’s actions. In July, the U.S. Supreme Court granted the Trump administration’s request for a stay allowing the changes at the Education Department to take place for now.
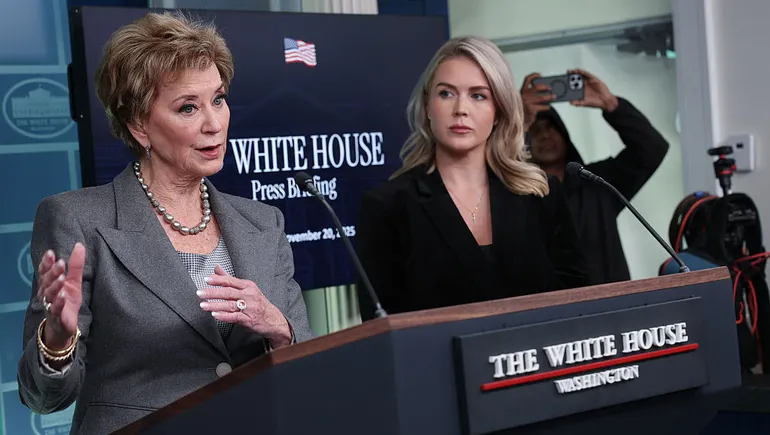

Trump administration officials took major steps toward dismantling the U.S. Department of Education last week, announcing they were moving several programs to other federal agencies.
Those include moving TRIO and Gear Up grants — programs that help low-income students prepare for and persist through college — to the U.S. Department of Labor, according to an agency fact sheet. Also moving to the Labor Department are grant programs that help higher education institutions bolster their academics and financial stability.
The amount billionaire philanthropist MacKenzie Scott has donated to colleges since mid-October. Scott is on another gifting spree, giving hundreds of millions of dollars to over a dozen historically Black colleges and universities and at least one tribal college.

Reaction to the U.S. Department of Education’s announcement this week that it is shifting management of a handful of programs to other federal agencies ranged from celebration to condemnation.
The moves fulfill “a promise made and a promise kept to put students first and return education to the states,” said Rep. Burgess Owens, R-Utah, on X on Tuesday.
Jeanne Allen, founder and CEO of the Center for Education Reform, applauded the federal education management shifts in a Tuesday statement. “It won’t be seamless, and it won’t succeed unless the new agencies clearly communicate with states, communities, and parents about their new flexibility — how funds can be better spent, and how to avoid getting snared in fresh compliance traps. But shifting power closer to communities is the right direction.”
But opponents say the transfers will create more burdens and inefficiencies.
MomsRising, a grassroots organization focused on economic security and anti-discrimination practices against women and moms, called the moves “reckless, harmful, and unlawful” in a Wednesday statement.
“Further dismantling the Department of Education will undermine learning opportunities for children in every state, harming families and undermining our workforce, our economy, and our country as a whole for generations to come,” MomsRising said.
Although management of special education, civil rights enforcement and federal student aid is not moving out of the Education Department, the agency is still exploring the best options for the structure of those activities, a senior department official said during a press call on Tuesday.
The six new interagency agreements will help “break up the federal education bureaucracy, ensure efficient delivery of funded programs, activities, and move closer to fulfilling the President’s promise to return education to the states,” the Education Department said in a Tuesday statement.
Management of career and technical education moved out of the Education Department to the U.S. Department of Labor earlier this year. CTE and K-12 administrative organizations had voiced reservations, saying they feared CTE would lose its education and career exploration focus and that programming would be driven solely by workforce needs.
Interagency agreements and other cross-agency collaborations have been used by the Education Department in the past, under both Democratic and Republican administrations. These practices typically have broad support, because they address alignment on specific programs between two or more agencies through shared funding and programming.
Tuesday’s announcement was significant for the large-scale movement of certain core programs out of the agency. Included in the new partnerships is an IAA with the U.S. Department of Labor to handle the management of about $28 billion in K-12 funding for low-income school districts, homeless youth, migrant students, academic support, afterschool programs, districts receiving Impact Aid, as well as other activities.
This partnership, the Education Department said, would streamline the administration of K-12 programs and align education programs with DOL’s workforce programs to improve the nation’s education and workforce systems.
Denise Forte, president and CEO of EdTrust, a nonprofit that seeks to eliminate economic and racial barriers in schools, said in a Tuesday statement that the changes will exacerbate hardships faced by underserved students.
“These new directives only serve to further distance students — particularly students of color, those from low-income backgrounds, students with disabilities, and multilingual learners — from educational opportunities,” Forte said. “The other agencies that are now charged with protecting students’ educational civil rights simply do not have the relationships, expertise, or staff capacity to do so.”
On the flip side, the America First Policy Institute applauded the changes in a Thursday statement, saying the move would “preserve program service levels and responsiveness while reducing costs and giving states more flexibility to meet the needs of students and families.”
While many organizations and individuals praised or criticized the shift in management, several others said they want more details about logistics and exactly what would change.
For example, would the education secretary need to call the labor secretary if a decision needs to be made? And what agency would be tapped by staff seeking policy or procedure clarifications? This scenario was brought up by Braden Goetz — senior policy advisor at the Center on Education and Labor at New America and a previous director of the policy and research team in the Office of Career, Technical, and Adult Education at the Education Department — during a Wednesday House Education and Workforce subcommittee hearing on CTE.
Goetz predicted that state officials in North Dakota, which passed a public charter school bill this year, will now need to seek clarity from the Labor Department on understanding Education Department regulations for charter schools.
“Good luck to them,” Goetz said.
The senior Education Department official on Tuesday’s press call said more details about operations and staffing for the IAAs will be better known in the coming weeks or months.

McMahon has said the recent government shutdown proved that the Education Department isn’t necessary.
Photo illustration by Justin Morrison/Inside Higher Ed | Anna Moneymaker/Getty Images | Pete Kiehart for The Washington Post via Getty Images
The Education Department is planning to move TRIO and numerous other higher education programs to the Labor Department as part of a broader effort to dismantle the agency and “streamline its bureaucracy.”
Instead of moving whole offices, the department detailed a plan Tuesday to transfer certain programs and responsibilities to other agencies. All in all, the department signed six agreements with four agencies, relocating a wide swath of programs.
For instance, the Labor Department is set to take over most of ED’s higher education programs, which include grants that support student success, historically Black colleges and universities, and other minority-serving institutions. Meanwhile, the State Department will handle Fulbright-Hays grants as well as those administered by the International and Foreign Language Education office. Indian Education and programs for tribal colleges are moving to the Interior Department.
Several of the offices that have overseen these grant programs were gutted in recent rounds of layoffs, but any staff members who are still managing them will move to the other agencies. ED also has sought to defund some of the grants, deeming them unconstitutional, so it’s not clear what is moving to the other agencies.
The agreements were signed Sept. 30—the day before the government shut down. ED officials expect the transition to take some time.
No programs, however, have been moved from the Office for Civil Rights, the Office of Federal Student Aid or the Office of Special Education and Rehabilitation Services. The department is still “exploring the best plan” for those offices, a senior department official said in a press call Tuesday afternoon.
“These partnerships really mark a major step forward in improving management of select programs and leveraging these partner agencies’ administrative expertise, their experience working with relevant stakeholders and streamlines the bureaucracy that has accumulated here at ED over the decades,” the senior department official said. “We are confident that this will lead to better services for grantees, for schools, for families across the country.”
Education Secretary Linda McMahon hinted at the sweeping announcement in a social media post Tuesday morning. The secretary posted an ominous video of a ticking clock followed by President Ronald Reagan urging Congress to dissolve the Department of Education. The video ended with a flickering screen that read “The Final Mission,” an echo of her first letter to Education Department staff in which she outlined how she would put herself out of a job.
President Donald Trump directed McMahon in March to close down her department “to the maximum extent appropriate and permitted by law.”
Liz Huston, a White House spokesperson, applauded the announcement describing it as a “bold, decisive action to return education where it belongs—at the state and local level.”
“The Trump Administration is fully committed to doing what’s best for American students, which is why it’s critical to shrink this bloated federal education bureaucracy while still ensuring efficient delivery of funds and essential programs,” she said in a statement.
These moves are the most significant steps McMahon has taken beyond the layoffs to comply with the president’s directive.
Congress has pressed McMahon multiple times to acknowledge that neither she nor the president can fully shut the department down without lawmakers’ approval. But when addressing these concerns, McMahon has made a point to note that shutting the department and its programs down entirely is different than dismantling bureaucracy and co-managing operations with other cabinet-level departments.
The department official echoed this Tuesday when talking with reporters, saying that policy and statutory oversight of the programs will still rest with employees at the Department of Ed. But execution of processes, particularly as it pertains to grants, will be managed by other agencies.
“Education has broad authority under several statutes to contract with other federal agencies to procure services, and the department has had that authority since its inception,” the official said. “We at the Department of Ed have engaged with other partner agencies over 200 times through [inter-agency agreements] to procure various services of other partner agencies over the years—even the Biden administration did it.”
The department has already moved Career, Technical and Adult Education to the Department of Labor. McMahon has said that effort was essentially a test run to see how other agencies could handle the department’s responsibilities. Democrats in Congress have decried the plan to move CTE to Labor as illegal.
Many of the department’s offices have already experienced dramatic disruptions this year, as McMahon used two reductions in force to cut the head count of her staff by more than 50 percent. The latest mass layoff, which took place during the government shutdown, has since been enjoined by a federal court. President Trump also agreed to return affected employees to “employment status” administration when he signed a stopgap bill to temporarily end the 43-day shutdown.
But it remains unclear whether those staff members have returned or will ever return to work. Multiple sources told Inside Higher Ed that the language of the bill may allow Trump to leave employees on paid administrative leave until the bill is no longer effective on Jan. 30 and then re-administer the pink slips.
Prior to Tuesday’s announcement, many higher education experts as well as current and former ED employees were hesitant to declare the department dead. Some said as long as the department and its functions remain codified, it will still be alive. But one former staff member put it this way: “If you take the major organs out of a human, do you still have a human or do you have a corpse?”
Amy Laitinen, senior director of the higher education program at New America, a left-leaning think tank, said moving the offices to other federal agencies would not save tax dollars.
“It fractures and weakens oversight of those dollars, it’s duplicative and it’s wasteful,” she said. “How are you tracking student outcomes to ensure taxpayer dollars are well spent when all of the entities responsible are scattered to the wind? For example, separating the agency in charge of financial aid policy (OPE) from the entity responsible for financial aid implementation (FSA) makes no sense.”

Federal education staff are returning to work after a weeks-long federal government shutdown that halted many U.S. Department of Education activities ended Wednesday. However, the agreed-upon plan to open the government is only temporary.
The continuing resolution signed into law Wednesday funds federal education programs at fiscal year 2025 levels. This temporary spending plan expires Jan. 30, unless Congress agrees to a more permanent budget before that deadline.
The deal nullifies the reduction-in-force notices sent to 465 agency employees on Oct. 10. The Education Department is also prohibited from issuing additional RIFs through the end of January and must provide back pay to all employees who did not receive compensation during the shutdown.
Government shutdown is over, and we’re baaackkkkk!
But let’s be honest: did you really miss us at all? pic.twitter.com/erql7eLOeG
— U.S. Department of Education (@usedgov) November 13, 2025
In a statement to K-12 Dive on Thursday, the Education Department said that it “brought back staff that were impacted by the Schumer Shutdown,” in a reference to Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer, D-N.Y.
In Senate floor remarks Nov. 10, Schumer said, “The last 41 days have exposed the depths of Donald Trump’s cruelty. He shut the government down longer than any president in American history and took innocent kids, veterans, and federal workers as political hostages, all because he refuses to do anything — anything — to fix the healthcare crisis and instead keeps pushing policies that will cut people’s coverage even more.”
The statement from the Education Department added that the “Department will follow all applicable laws” and that all employees coming off furlough are back to active duty.
However, the American Federation of Government Employees Local 252, which represents more than 2,700 U.S. Department of Education employees, said the return to work for agency staffers has been “rocky.”
Rachel Gittleman, president of AFGE 252, said in a statement Thursday afternoon that employees have not received official notices from the Education Department’s human resources office to return to work. Rather, they are relying on text messages from supervisors or colleagues. Gittleman added that many employees named in the October firings are locked out of their computers and do not have access to agency email.
“This disorganization and chaos only further demoralizes the hardworking public servants at the Education Department that have faced threats, harassment, illegal firings — and 44 days without paychecks,” Gittleman said.
The shutdown — the longest in U.S. history — began Oct. 1 after Congress reached an impasse on spending for FY 2026. While day-to-day K-12 and higher education operations stayed mostly unaffected, the federal shutdown put a pause on Office for Civil Rights investigations, new grant-making activities and technical assistance support.
Still, some disruptions trickled down to early childhood programs and K-12 school systems.
The National Association of Federally Impacted Schools, in a Nov. 7 statement, warned that delays in Impact Aid payments, which help school systems that are located in areas with non-taxable federal property, were “destabilizing school districts across the country.”
NAFIS Executive Director Cherise Imai said that funding delays were not only inconvenient, they were “dismantling student support systems and threatening the stability of entire communities.”
The association said a survey of 90 federally impacted school districts found that more than one-third were feeling budget pressures, with many cutting programs, freezing hiring and drawing on reserves to stay open.
Early in the shutdown, it was expected that athletics and extracurricular activities at Department of Defense Education Activity schools would be paused, but those events were later deemed excepted activities during the lapse in appropriations.
Although the federal government has reopened, uncertainty remains. According to a Nov. 10 posting by Tara Thomas, senior government affairs manager at AASA, The School Superintendents Association, “the agreement does not provide superintendents with any additional certainty regarding education funding for the 26-27 school year.”
Staffing levels at the Education Department remain quite lean as well due to layoffs, buyouts and attrition that occurred prior to the shutdown. According to a court filing from Nov. 12, the total number of Education Department employees is 2,536, down from 4,133 when Trump was inaugurated Jan. 20.
In early childhood education, the shutdown caused nearly 10,000 children to temporarily lose access to federally supported Head Start centers after funding lapsed, according to the National Head Start Association.
Head Start provides early childhood education services for children from low-income families. NHSA said the shutdown caused thousands of parents to lose child care services and cut access to healthy meals at the same time federal benefits for the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program expired Nov. 1.
In a Thursday statement, Yasmina Vinci, executive director of NHSA, credited the Head Start workforce for using emergency funds, working without pay and working with community partners to keep most Head Start programs open.
“This shutdown exposed how deeply we rely on a workforce that is underpaid, overextended, and yet unwavering in its commitment to our nation’s most vulnerable children,” Vinci said.