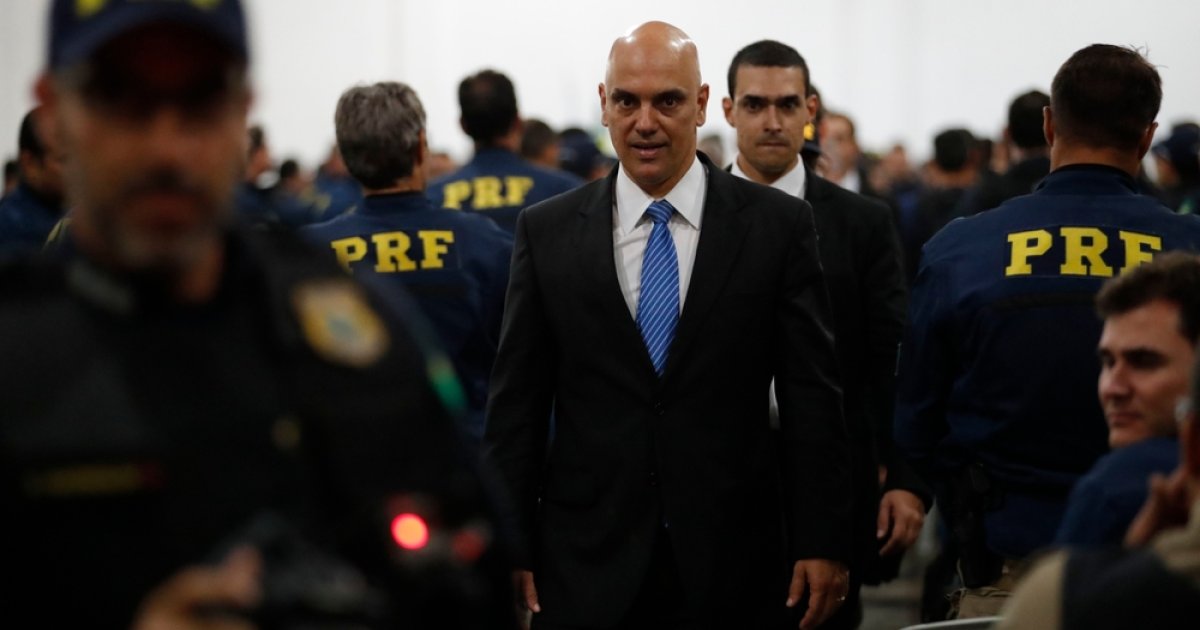
Alexandre de Moraes, the polarizing Brazilian Supreme Court Justice, is no friend to free speech. Though he is a popular figure within Brazil among those who see him as a protector of democracy, he has aggressively wielded his authority to censor, especially on the internet, with little transparency.
From his position in Brazil’s Supreme Court, de Moraes has doggedly pursued wide swaths of speech and speakers off and on the internet, as well as the tech companies hosting them. In a highly public incident last year, Brazil blocked X — and even threatened VPN users accessing it with massive fines — over the company’s noncompliance with de Moraes’ orders.
The actions of de Moraes, and Brazil’s Supreme Court more broadly, have repeatedly drawn the ire of the Trump administration. But chief among President Trump’s grievances is the prosecution of his political ally, former Brazilian President Jair Bolsonaro, who is accused of attempting a coup to overturn his 2022 election loss to President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva.
How has the Trump administration responded?
Last month, the administration enacted a series of punishments against Brazil’s leadership and de Moraes specifically. In a July 30 executive order, Trump announced tariffs and other sanctions due to Brazil’s prosecution of Bolsonaro and other actions that “conflict with and threaten the policy of the United States to promote free speech and free and fair elections at home and abroad.” The order follows Trump’s weeks-earlier threat of tariffs over the “witch hunt” against Bolsonaro.
Secretary of State Marco Rubio also revoked the visas of de Moraes “and his allies on the court” and their families. And under the Global Magnitsky Human Rights Accountability Act, usually reserved for the most serious human rights abuses, the Department of the Treasury announced sanctions targeting any of de Moraes’s U.S. assets.
Unprincipled, partisan free speech advocacy is no free speech advocacy at all
There is plenty to debate about how to best protect free speech on the global internet, and around the world more generally, and what actions the United States can take in its defense. But, even though Brazil’s adversarial relationship with free expression is deeply alarming, it’s impossible to ignore the incongruity of the Trump administration putting itself in the position of diagnosing and treating government censorship.
Physician, heal thyself.
The opening months of Trump’s second term in office have offered a nonstop, headspinning bonanza of violations, threatened and enacted, against Americans’ First Amendment rights.
I write regularly in the Free Speech Dispatch about the myriad threats to freedom of expression, from Russia to the UK to India to Hong Kong. It’s painfully, brutally clear we need leadership to push back against the wave of global repression that threatens all of our rights. But that leadership must practice what it preaches and avoid simply using concerns about free speech as a pretext to fight partisan political battles. On both counts, this administration has failed.
You will make no converts to the free speech cause by proving right the critics who suspect its advocates are guided by partisan aims, not principled ones. Instead, you will breed cynicism and harm the very cause you claim to support.
This same posturing marred Vice President JD Vance’s objections to European censorship, an ugly trend that’s in dire need of principled critiques. Instead, Vance claimed that under Trump, the “new sheriff in town,” the administration “may disagree with your views, but we will fight to defend your right to offer them in the public square.”
Well, unless you’re CBS/Paramount, law firms, The Wall Street Journal, the Washington Commanders, CNN, The New York Times, protesters, Media Matters, James Comey’s seashells, “propaganda,” academic and medical journals, pollster Ann Selzer and The Des Moines Register, The Associated Press, international students, flag burners, Harvard, Columbia, or the many other universities and academics under threat.
The ugly reality is that the U.S. is rapidly ceding its moral authority to criticize foreign governments’ censorship, like that emanating from Brazil’s Supreme Court, when its own president and agencies are gleefully flouting the First Amendment and free speech principles day in and day out.
Perhaps most baffling was the administration’s objection to the Brazilian government’s targeting of Paulo Figueiredo, a Brazilian journalist, and “U.S. resident, for speech he made on U.S. soil.” Readers may also be able to think of some more government officials targeting immigrants legally residing in the U.S. for protected speech made on U.S. soil — and they’re doing so from our White House and State Department, not thousands of miles away.
Global censorship is a real challenge, and it’s only getting worse. But until the U.S. removes the censorial beam from its own eye, we may find that other nations are unmoved by our criticisms and cures. Or, they may perhaps even be interested in doling them out to us.