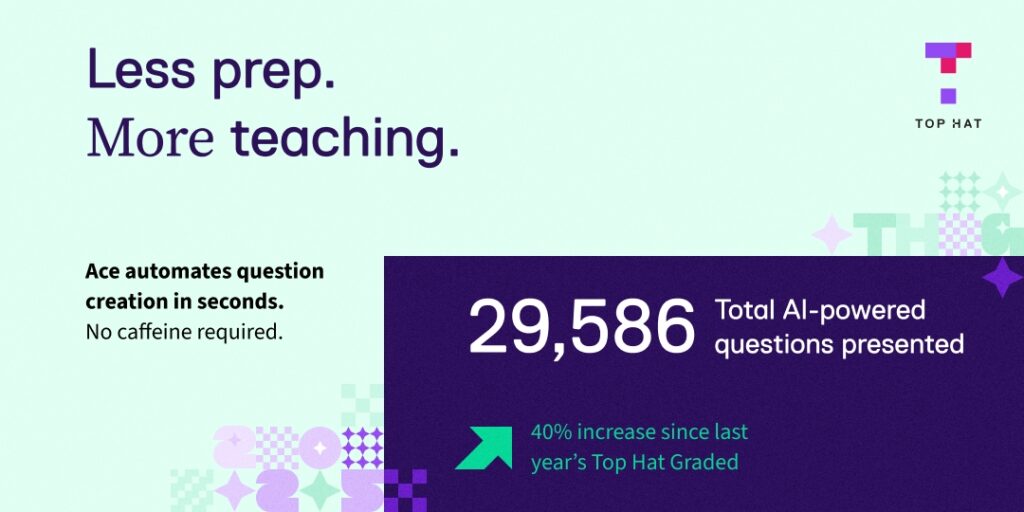
As the back-to-school season begins, educators and students alike are stepping into classrooms that look and feel increasingly different from just a few years ago. Technology is no longer just a supporting tool–it is a central part of how learning is delivered, personalized, and measured. From AI that helps teachers design lessons and personalize learning, to adaptive learning platforms that meet students where they are, education technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace.
Innovation is at the forefront this year, with districts embracing tools that support academic growth, streamline workflows, and foster deeper engagement. AI-powered tutoring, immersive experiences, and tools that enhance collaboration are just a few of the technologies entering classrooms and lecture halls. These resources are not only helping educators save time but also are equipping students with critical thinking, problem-solving, and digital skills they will need for future careers.
As schools balance new opportunities with challenges around implementation, equity, and data privacy, industry leaders and educators are offering valuable insights into what’s next. Teachers are sharing how these tools reshape day-to-day instruction, while technology providers are highlighting trends that will shape the coming year. Together, these perspectives paint a picture of a learning landscape that is both dynamic and adaptable, where innovation is guided by the shared goal of supporting student success.
This back-to-school season, the conversation is not just about new devices or apps, but about how technology and thoughtful innovation can transform education for all learners–making 2025 a year of possibilities, progress, and promise.
This school year, career and technical education (CTE) won’t just be an elective, but will be a priority. As more districts recognize the powerful outcomes tied to CTE, we’ll see a shift in graduation requirements to reflect what students actually need for their futures. That might mean rethinking four years of traditional math in favor of math courses that are career-aligned to specific career pathways. Administrators and superintendents are paying attention and for good reason. The data shows CTE not only boosts student outcomes, but also brings relevance back to learning.
—Edson Barton, CEO, YouScience
Throughout my administrative experience, it has become increasingly evident that many educational preparation programs fall short in emphasizing the importance of fostering connection and relevance in learning from the student’s perspective. Too often, the pedagogical approach positions educators as drivers of a rigid, outdated instructional model, centered on the teacher in a highly directive role, rather than as reflective facilitators willing to ride alongside students on a learning journey. To shift this reality, I take every opportunity to embrace and share the practices promoted by PBLWorks, which offer a framework where students not only learn content and skills but do so in ways that are connected to their own interests and community. Through the Project Based Learning (PBL) methodology, learning becomes more personal, meaningful, and accountable, with expected learning products that showcase depth in student understanding and growth. Every school-age child has personal experiences from which to make connections, and with PBL, we are better equipped to serve all children effectively. While traditional testing data has its own importance in driving strategic moves, the outcomes derived from the application of learning are immeasurable in their long-term impact on career readiness. In our MSAP Norwalk implementation, shifting the approach requires more than updating curriculum units, it also demands a redefinition of the educator’s role as a collaborative team member in the classroom. Educators must evolve into co-learners and creative engineers of dynamic, student-centered learning environments. They must become comfortable with uncertainty and confident in guiding student discovery. Such a workshop-like classroom environment is essential for authentic PBL, which demands both deep preparation and flexible facilitation. Here, success is defined not only by content mastery but also by the authentic application of knowledge and skills. Importantly to note, the teacher is also a learner in this dynamic process. Ultimately, quality teaching and learning is measured not by the delivery of instruction but by the evidence of student learning. As I have grown in my leadership and implementation of the PBL framework, the phrase “I taught it, but they didn’t get it” is beyond obsolete, replaced by a continuous cycle of reflection, refinement, and real-world, relevant outcomes. Learning is represented dually in personalized student exemplars and in improved results on high-stakes assessments.
–Victor Black Ed.D., Magnet School Assistance Program (MSAP) Norwalk Project Director, Norwalk Public Schools, Connecticut
Learning is fundamentally about meaning-making. It’s a dynamic human process that involves our whole selves. It involves the brain as well as emotions, attitudes and beliefs, relationships, environments, and contexts. AI can’t make meaning for you. If the AI makes the meaning for you, you haven’t learned anything–that is the core of distinguishing between what is useful AI that is going to advance learning, and what is hype that could actually be counterproductive and destructive to learning.
– Auditi Chakravarty, CEO, AERDF
Welcome to your teaching journey. As we begin the 2025-26 school year, I want to extend my heartfelt welcome to our new educators. Your passion and fresh perspectives are invaluable assets to our learning community. I encourage you to remember that teaching is about building relationships. Get to know each student, learn their interests, challenges and dreams. Strong connections create the trust necessary for meaningful learning. Don’t hesitate to lean on your colleagues and mentors. Teaching can feel overwhelming, but you’re never alone. Seek guidance, share resources and collaborate whenever possible. Be patient with yourself as you find your rhythm. Focus on progress, not perfection, and celebrate small victories along the way. Most importantly, never lose sight of why you chose this profession. You have the power to change lives, one student at a time.
–Dr. Debra Duardo, Superintendent of Schools, Los Angeles County & Board Member, Association of Latino Administrators and Superintendents (ALAS)
Hello, new teachers! As a 32-year veteran of teaching, I vaguely remember those first few days and weeks, but I do remember being thoroughly overwhelmed. So, my first piece of advice is to find yourself a mentor who can help you navigate the waters. Second, think outside the box. Educational technology has exploded in the last few years and us old people can’t keep up. Find something that works and immerse yourself in it. May I make a suggestion? Creation over consumption. Let’s give an example. VR is amazing. You and your students can “visit” places that you would never be able to take them on a field trip. Awesome! Do it! But I have found that creating our own VR experiences by integrating ClassVR with tools like ThingLink or DelightEx brings a whole new level of engagement and understanding. My last piece of advice? Love it! Love those kids. They need you. Bond with your colleagues. You need each other. You got this. I’m happy you’re part of the team.
–Craig Dunlap, Blended Learning Teacher, Yealey Elementary School, Kentucky
I began teaching 25 years ago, and thirteen years ago I was introduced to Project-Based Learning (PBL). From that moment, I “enrolled.” PBL is not just a strategy, it’s a mindset. It transformed not only my students, but also me as an educator. Through engaging in and witnessing PBL, I have learned that it changes the way students view their education and their place in school. They no longer see themselves as passive recipients of information, but as active learners with a voice, a purpose, and a sense of belonging. PBL builds their self-efficacy, ignites their curiosity, and turns learning into a lifelong journey. Because learning in PBL is authentic, engaging, and connected to real life, every student can access it, every student feels valued, and every student has the chance to succeed. Most importantly, every student has the opportunity to be seen and to see themselves reflected in their education, their classrooms, and their school community. And while my primary goal as an educator has always been my students, I must say that PBL also transforms teachers in deeply positive ways. Unlike a scripted, one-size-fits-all curriculum, PBL gives teachers full autonomy to design, to create, and to make learning relevant. It allows us to become problem-solvers, innovators, and true professionals. As PBL teachers, we model exactly what we want from our students. PBL isn’t about checking boxes; it’s about unleashing your craft as an educator and showing your students what authentic, meaningful work looks like. What I have come to believe, after years of teaching and leading, is that PBL is not just a method of instruction, it’s a way of seeing students, teachers, and learning itself. It is the path that allows students to fall in love with learning, and teachers to love their craft. And once you experience it, it’s hard to ever imagine teaching any other way.
–Beth Furnari, Principal, P-TECH Norwalk in Norwalk Public Schools, Connecticut
For new district administrators, don’t chase every shiny object. Education is full of vendors promising silver bullets. Anchor your decisions in what solves your district’s problems, not in what looks flashy. Additionally, remember to prioritize relationships over initiatives. People will follow your lead if they believe you value them, not just their output. When you prioritize relationships, oftentimes the initiatives naturally follow. For example, our district’s performing arts manager came to me with the idea of virtual set design knowing I’d be open to his ideas and willing to try something new.
–Tim Klan, Administrator of Information and Instructional Technology, Livonia Public Schools, Michigan
In today’s educational landscape, our instructional strategies must evolve to meet the needs of digital-native learners. While traditional resources have their place, we recognize that deep engagement often requires more immersive and interactive experiences. To bridge this gap, our school district has strategically implemented virtual reality (VR). For the past five years, our schools have been utilizing the ClassVR platform by Avantis. This technology has proven to be a powerful tool for transcending the physical limitations of the classroom. The moment students see the VR kits arrive, a visible excitement builds for the learning ahead. These curated experiences are not simply virtual field trips; they are pedagogical springboards that empower students to explore historical eras, global locations, and complex scientific concepts. Most importantly, VR provides a unique medium for fostering essential skills in observation, critical analysis, and content creation.
–Kyle Kline, Director of Digital Learning, Twin Lakes School Corporation, Indiana
In the 2025 to 2026 school year, we will see a greater push for ongoing, explicit instruction in foundational literacy skills for older students. Most students need ongoing, developmentally appropriate, explicit literacy instruction in upper elementary and middle school, but very few of them receive it. Most students in grades 4-8 do not receive explicit instruction for crucial foundational skills that older students need to develop, like decoding multisyllabic words. More often than not, teachers in grades 4-8 lack the resources, time, or training to provide explicit instructional support to help their students continue to grow as readers. Giving teachers what they need to support their students will certainly be part of the solution, along with more targeted interventions that provide support to students where they need it.
– Rebecca Kockler, Executive Director, AERDF’s Reading Reimagined Program
After decades of progress narrowing gender gaps in STEM, the pandemic may have set girls back significantly–and the gap is likely to grow wider unless schools and policymakers act quickly. New NWEA research reveals that pandemic-era setbacks hit middle school girls hardest in math and science, erasing decades of progress. With fewer girls now enrolling in 8th-grade Algebra–a key gateway to advanced STEM coursework–there’s a real risk that fewer young women will pursue STEM in high school, college, and careers. To reverse this trend, schools will need to closely monitor gender participation in key STEM milestones, expand access to advanced coursework, provide early interventions and academic supports, and examine classroom practices to ensure girls are being actively engaged and encouraged in math and science. Without these steps, the future STEM talent pipeline will be less diverse and less equitable.
– Dr. Megan Kuhfeld, Director of Growth Modeling and Analytics, NWEA
Reliable, longitudinal student data is critical to drive strategic action. As federal support for education research is scaled back and key data collection efforts remain uncertain, districts and states may find themselves without trusted information to guide decisions. In the absence of these investments, schools will need to rely more heavily on research organizations and data partners that can offer the longitudinal insight and analytical capacity schools need to understand where students are, where they’re headed, and how to support them. With academic recovery proving slower and more uneven than expected, schools need evidence-based insights to navigate this complex landscape. Expect a growing shift toward research-backed, nonpartisan data sources to fill the vacuum and support smarter, more equitable decision-making.
– Dr. Karyn Lewis, Vice President of Research and Policy Partnerships, NWEA
As cybersecurity becomes an increasing risk for K-12 districts this year, it’s more critical than ever that IT leaders establish a culture of security at the start of the school year. Schools are continuously working to maintain 1:1 technology without compromising user safety or straining budgets, and asset tracking and inventory management is an integral part of that process. With shrinking IT teams working to track thousands of devices across schools, having a centralized asset management system allows districts to avoid costly surprises and manage devices more efficiently. It helps them to monitor device location and application use, make targeted and data-backed incident response decisions, and identify assets potentially affected by a security breach. It also streamlines the inventory auditing process, which allows school IT teams to track and manage the maintenance and updating needs of deployed devices, both of which function to improve security. Cyberattacks are not only becoming more frequent, but more complex and it’s time for schools to safeguard their technology by investing in smarter, more resilient solutions that protect learning environments and support long-term success.
—Bill Loller, Chief Product Officer, Incident IQ
As a new principal, your most important work is building relationships. That includes building and strengthening the trust with your staff, as well as your parents and families. Take the time to make those connections, to listen to people and get to know them. In Hawaii, we have a term “ahonui” which means “waiting for the right moment.” As a principal, you need to know when it’s the right time to act and when it’s the right time to listen. As a new leader, it’s natural to have a sense of urgency: You have a long list of things you want to do to help kids be safe and learn, but to do that you first need to honor what has been done so far. By getting to know the people who make up your school community you’ll learn how you can enhance it. To help build my relationship with my teachers, especially the new ones, we have an onboarding day the day before teachers report back. This is my chance to introduce them to some of the things that we have going on and the structures we have in place to support them as they teach. We introduce them to some tech tools that our school has that others don’t, like the AI-powered tutoring app SuperTeacher–but we try not to overload them because we understand that for a new teacher (or even a teacher who’s new to our school) it can be overwhelming if we just upload a lot of initiatives and must-dos and expectations. Instead, we get to know each other, and my vice principal and I share the theme we’ve come up with for each school year. Our theme for this year is “alu i ka hana me ke kuana’ike like,” which means “to join together in the work with a unified mindset.”
– Derek Minakami, Principal, Kāneʻohe Elementary School, Honolulu, HI
Through my years of teaching, I have found myself talking less and listening to students more. It’s important to make space for student voices to help create richer discussions and more meaningful learning experiences that connect to their own lives. At the same time, grounding those experiences in strong scientific practices ensures that learning is both engaging and rigorous. As a new school year begins, I encourage every teacher to connect the learning happening in your classroom to potential career paths and help students see the real-world impact of what they’re studying.
–Mike Montgomery, Natural Resources Teacher, Littleton Public Schools EPIC Campus (recently featured in the “Building High-Impact CTE Centers: Lessons from District Leaders” e-book)
Everyone is working with fewer resources this school year. As the number of bilingual and multilingual students continues to grow, it will be important for teachers to be creative and resourceful in how they are using those limited resources to support ELL students. For example, they can look outside their school for resources and partnership opportunities with businesses, non-profit associations and higher education institutions. They can also seek out grant funding that is specific for bilingual students. Multilingualism is a superpower, but English language learners face unique barriers that can put them at a disadvantage compared to their native-English-speaking peers. It is critical to continue to advocate for these students and be creative in finding ways to help them grow this superpower. Teachers: you will be key to ensuring shifting policy decisions and uncertain budgets don’t result in our most vulnerable students being left behind.
–Ulysses Navarrete, Executive Director, Association of Latino Administrators and Superintendents (ALAS)
As we begin this new academic year, I want to thank you for the incredible work you do each day to inspire and shape the minds of our students. In times when our nation–and especially Los Angeles–faces critical conversations about democracy and social justice, your role is more important than ever. Let us empower our students to think critically, question thoughtfully, and express their voices in meaningful ways–whether through essays, art, letters, or dialogue. Together, we have the opportunity to guide them toward becoming informed, compassionate, and courageous leaders who can influence the future. Your dedication matters, and the impact you make will be felt far beyond the classroom walls.
–Ruth Perez, Ed.D., Deputy Superintendent, Los Angeles County Office of Education & Board Member, Association of Latino Administrators and Superintendents (ALAS)
One thing we often hear from school districts is that after they purchase new technology, there is a lag in implementation. To ensure technology products improve teaching and learning in year one, I recommend district IT leaders work with companies that act as true partners with the district, offer built-in professional development, and provide opportunities for schools to learn best practices from each other. To help with adoption, districts can handle implementation in small increments to not overwhelm teachers, enlist classroom innovators who can lead the charge on integrating new technologies, and offer opportunities for teachers to learn from others who are implementing the technology.
–Gillian Rhodes, Chief Marketing Officer, Avantis Education, creators of ClassVR
Students learn best when they are engaged. My advice to new teachers is to find new, innovative ways to make learning relevant to real life. This will help students get more out of their lessons and prepare them for the world. Technology is a powerful way to do this. Providing immersive experiences such as through virtual or augmented reality can help teachers connect classroom concepts with real-world experiences. Whether it’s virtually touring ancient ruins, traveling through a blood vessel to learn about the circulatory system, or visiting a job site to learn about that career path–immersive experiences like these can help improve student-engagement and take instruction to the next level.
–Gillian Rhodes, Chief Marketing Officer, Avantis Education, Creators of ClassVR
While school safety conversations often focus on rare but severe emergencies, day-to-day medical incidents remain among the most frequent challenges schools face. From asthma attacks and allergic reactions to seizures, many medical emergencies occur away from the nurse’s office or outside traditional classrooms, making rapid response crucial. This school year, we will see the continued prioritization of real-time alert systems that enable immediate action in medical emergencies. Location-aware tools and mapping technology, such as the strategic placement of AEDs, help responders quickly locate life-saving equipment and reach incident scenes without delay. Since teachers and staff are often the first to respond, they need easy and accessible ways to summon help quickly.
—Dr. Roderick Sams, Chief Development Officer, CENTEGIX
Reading fluency is a foundational skill for lifelong learning, even more so in an ever-changing, technology-based world. As such, supporting students in developing their reading fluency goes beyond building in time for practice. It is important for new and experienced teachers alike to understand that students need access to high-quality, research-based curriculum; differentiated lessons and small groups; multi-level systems of support; and well-implemented, quality instructional technology. It is also important for teachers to implement a repertoire of strategies and tools to specifically support literacy development. While there is no substitute for a differentiated reading lesson taught using high-quality curriculum by a highly-qualified educator, instructional technology is an excellent resource to further support student learning! When implemented effectively, and paired with teacher-led lessons, instructional technology platforms allow teachers to track student growth in real time, provide differentiated supports that target the needs and goals of individual students, and extend learning beyond teacher-led lessons. In a world of staffing shortages, larger class sizes, and ever-changing demands on educators, instructional technology can be an excellent supplemental support to further student achievement and learning. Building fluent readers sets our students up for success far beyond the classroom, empowering them to continue to challenge themselves and grow into the future with confidence and skills to succeed in a society with careers and livelihoods that will surely look very different from what we now see.
–Sam Schwartz, Associate Principal, La Causa Charter School, a Fluency Innovator Grant recipient
As a science teacher, I believe there is no replacement for hands-on learning experiences, so I suggest starting each year with an activity where students make measurements using tools or items around the classroom. This way, once students are given access to data-collection sensors and probeware for scientific investigations throughout the year, they have a better understanding and appreciation for why we use the technology. When it comes to labs and measurements, even for inquiry-based experiments, teachers should always do their own dry run of the data-collection process first. This allows teachers to see any stumbling blocks in the collection process and have a data set to refer to during the class discussion. Also, a class set of data gives students a basis of comparison when they are looking at their own data-collection practices and it allows students who may have been absent or unable to collect data at the time to still engage in the analysis process.
–Kathleen Shreve, Physics Teacher, Homestead High School, California & Member, Vernier Trendsetters Community
There’s incredible untapped potential in the wealth of data that schools already collect. Districts are sitting on years of attendance patterns, assignment completion rates, and family engagement metrics–all of which could predict which students need support before they hit crisis mode. With federal benchmarks unreliable and new assessments being expensive, 2025-26 is going to be the year districts finally turn inward to the data they already have. The challenge isn’t collecting more information–it’s making existing data actionable for teachers and families.
– Dr. Joy Smithson, Data Science Manager, SchoolStatus
As a new teacher starting the school year, remember that you can’t pour from an empty cup. Take care of yourself first—set clear work hours, protect time for rest, and don’t feel guilty about saying no when needed. Building relationships with colleagues and families is important, but healthy boundaries make those connections stronger and more sustainable. Start small: be approachable, communicate clearly, and show consistency. When you balance self-care with professionalism, you’ll create space to thrive both inside and outside the classroom.
–Betsy Springer, Instructional Coach, Gull Lake Community Schools & a Teacher Leader Impact Award winner
High school attendance is in crisis, and it’s about to force the conversation we’ve been avoiding for decades. When nearly 30 percent of high schoolers are chronically absent, we’re seeing clear signals that many students need different pathways to engagement and success. The districts that survive this attendance crisis will be the ones brave enough to completely reimagine what high school looks like, with flexible schedules that let students apprentice during traditional school hours and partnerships with local employers who can show students why their education matters.
– Dr. Kara Stern, Director of Education, SchoolStatus
The start of every school year is charged with possibility, with students and educators alike bringing energy, curiosity, and the excitement of new connections. That momentum can be a powerful tool as schools work to strengthen their Project Based Learning (PBL) practices. The insight is simple: PBL succeeds when schools build a culture where questions are encouraged, collaboration is natural, and feedback is welcomed. Without that culture, projects risk becoming just activities or separating into silos. With it, PBL becomes transformative–helping students see themselves as capable learners and community members who are encouraged to ask what’s possible and empowered to act. My advice is to use the energy of the new year to establish that culture early. Invite students and teachers to share their thinking openly, model vulnerability by sharing your own work-in-progress, and normalize feedback as a gift. When we frame PBL not only as project-based learning, but as possibility, belonging, and love, we create the conditions where authentic learning thrives, and we sustain that momentum from the first day of school through the last.
–Taya Tselolikhina, Director of District and School Leadership, PBLWorks
Laura Ascione is the Editorial Director at eSchool Media. She is a graduate of the University of Maryland’s prestigious Philip Merrill College of Journalism.
Latest posts by Laura Ascione
(see all)