Hi all. Today, HESA is releasing the eighth edition of The State of Postsecondary Education in Canada, co-authored by myself and HESA’s Jiwoo Jeon and Janet Balfour. Many thanks to our partners – Pearson, Studiosity, Duolingo, Capio, Element451 and Riipen – for supporting this year’s edition.
You probably don’t need to actually read this year’s edition to know that the state of postsecondary education in Canada is a bit perilous. And the reason for this, quite simply, is that public funding for higher education has been stagnant for well over a decade now.
At one level, of course, it is possible to look at public funding in Canada and proclaim that nothing is wrong. As Figure 1 shows, public spending on higher education has stayed relatively constant over the past fifteen years in inflation-adjusted dollars. Individual provinces may have seen swings up or down in their spending, but collectively the ten provinces have spent a collective $20 billion/year or so on higher education since about 2011-12 (excluding transfer payments from the federal government), and the federal government has spent about $10 billion/year.
Figure 1: Federal and Provincial Own-Source Expenditures in Respect of PSE Institutions, Canada, in $2023, 2007-08 to 2023-24, in Billions
So, at one level it is possible to shrug off the problem. But that requires eliminating a lot of context. Let’s see how Canadian funding looks when we put it into various types of contexts.
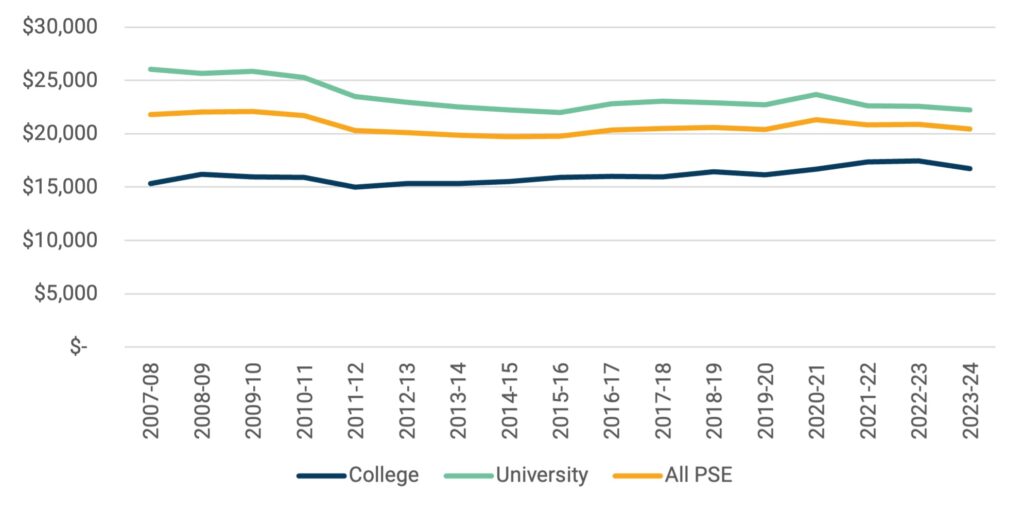
If we describe public funding in per-student terms, as in Figure 2, what you see is a mixed picture. Total public funding per full-time equivalent domestic student has dropped by about 6% since 2009, and for university students by about 15%. Complicating this figure is the fact that per-student funding for college students has risen somewhat, however, this is due not to extra funding but rather to a very significant drop in the number of domestic students enrolled in colleges. Whether this is due to a reduction of interest in college programs among Canadians, or a deliberate move away from Canadian to international students on the part of colleges is difficult to answer, but in either event, the rise in funding per college student is a function of fewer students rather than more funding.
Figure 2: Per-student Spending by Sector, Canada, in $2023, 2007-08 to 2023-24
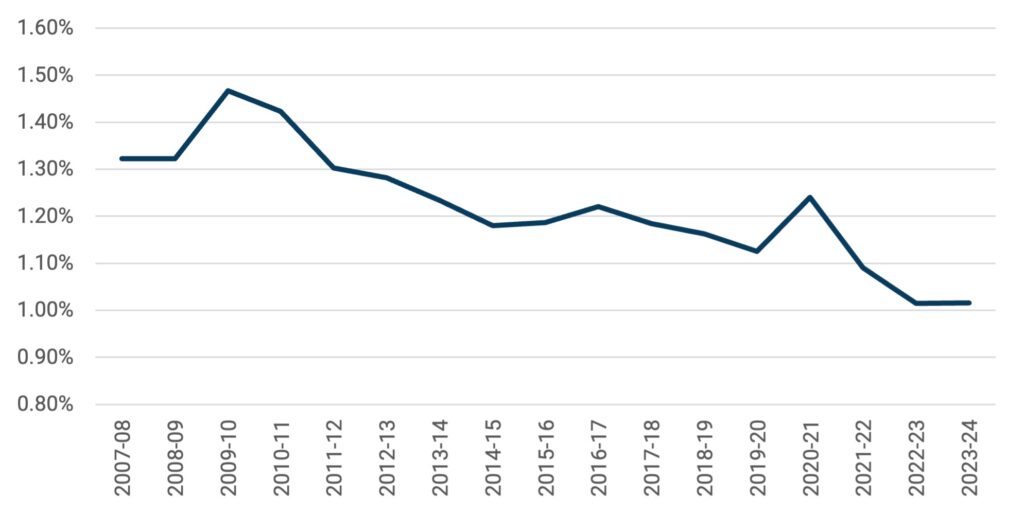
If we describe public funding as a percentage of the country’s economy, the picture looks significantly worse. Prior to the recession of 2008-09, public funding on postsecondary education was about 1.3% of GDP, which was substantially above the level seen across other industrialized countries (about 1.0%, according to the OECD). Briefly, that number popped up during the Great Recession, partly because spending increased but also partly because GDP stagnated. Since then, however, spending has stayed constant while GDP has grown. The result is that public spending on postsecondary has fallen to the OECD average of 1% – and the financial advantage our system once held over competitor nations has largely disappeared.
Figure 3: Public Spending on Postsecondary Education as a Percentage of GDP, in $2023, 2007-08 to 2023-24
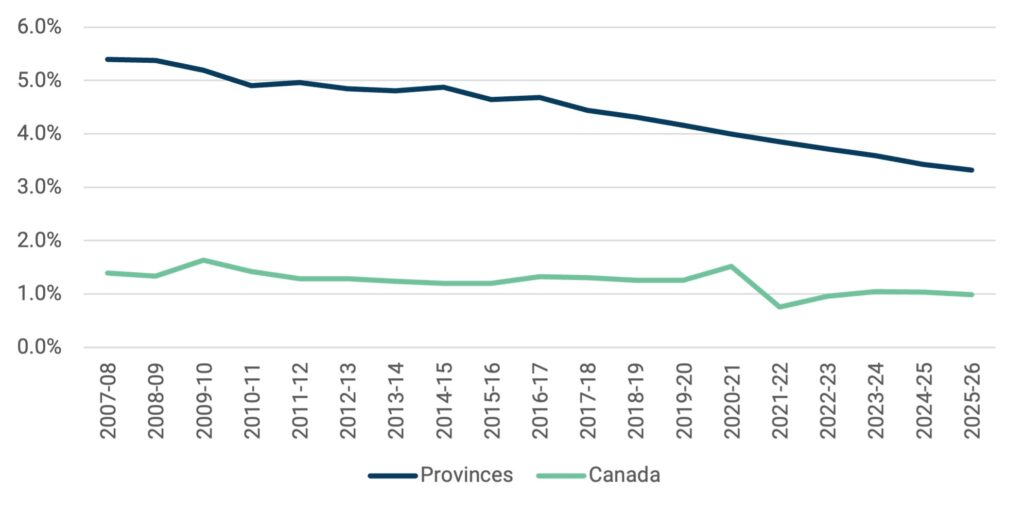
We can also look at these figures in per-inhabitant terms. There was a point in the late 00s where Canada had about 33 million inhabitants and public sources spent $30 billion per year on postsecondary education. Fifteen years and seven million new inhabitants later, we’re still spending $30 billion per year. That results in a 21% reduction in spending on universities and colleges per inhabitant from public sources, as shown in Figure 4. In Figure 5, we look at postsecondary spending as a percentage of government budgets. Again, we see a case of spending on postsecondary institutions falling consistently because overall government expenditure is rising quickly. In the past fifteen years, aggregate provincial spending on postsecondary has fallen as a percentage of total provincial expenditures from 5.4% to just 3.3%; for federal spending it has fallen from 1.6% to just 1%.
Figure 4: Public Spending on Post-Secondary Education Institutions Per Inhabitant, in $2023, 2007-08 to 2023-24
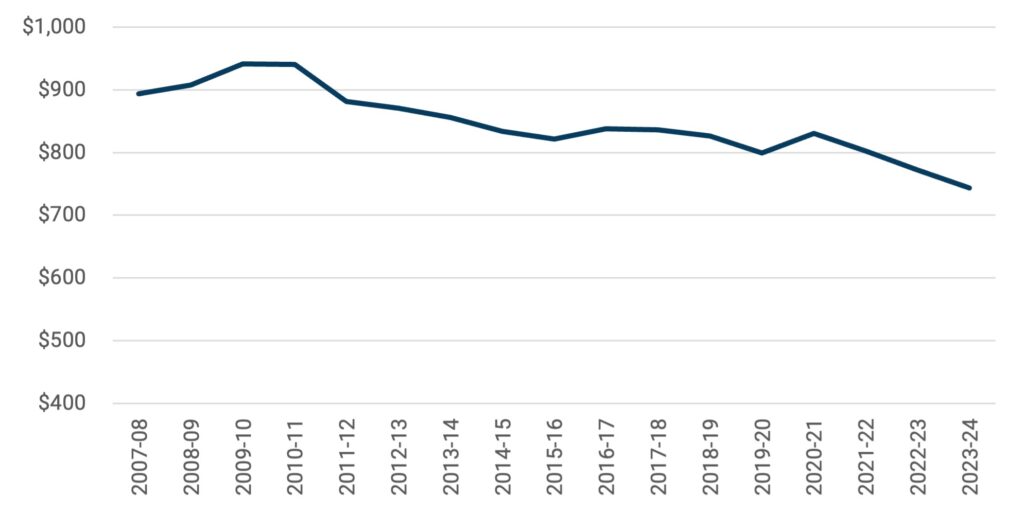
Figure 5: Public Spending on Postsecondary Education Institutions as a Percentage of Total Government Spending, Federal and Provincial Governments, in $2023, 2007-08 to 2023-24
In other words: we have been able – just — to keep our public investments in higher education level with inflation. But we have only been able to do so because our population is larger, and our economy has grown over the last fifteen years, and we can do so with less relative effort. Had we kept up funding on a domestic per-student level with where it was in the immediate aftermath of the Great Financial crisis, post-secondary education system would have an extra $2.1 billion. If we had kept funding on postsecondary education level with overall population growth we would have invested another $7.3 billion. If we’d had funding for postsecondary institutions level with GDP growth we would have invested another $13.6 billion. And if we had kept it level with the overall growth in program spending, we would have invested another $19.1 billion. So, depending on the measure chosen, we are anywhere from $2-20 billion short of where we would be had we kept our spending levels of the late 00s/early 10s.
But, you say, isn’t this true everywhere? And aren’t we at least better than the United States?
It is certainly true that Canada is in a pattern that would seem familiar both to residents of Australia and the United Kingdom. These three countries have all followed roughly the same path over the past decade and a half, combining stagnant public funding with slightly growing domestic numbers, paid for by an absolute free-for-all with respect to international students paying market tuition rates. All three countries looked like they had made a good deal at least for as long as the international student boom lasted.
But take a look at our biggest competitor, the United States. During the financial crisis of 2008-9, funding for postsecondary institutions tumbled by over 10%. But then, in just the eight years between 2012 and 2020, funding for higher education grew by a third – from about $150B (US) per year to over $200B/year. In fact, for all we hear about cuts to funding under Trump (not all of which may come true, as at the time of writing the Senate seems quite intent at least on reversing the billions of proposed cuts to the National Institutes of Health), even if all the proposed cuts were to come through, total US spending on higher education would be roughly 20% higher than it was in 2008-09, while Canada’s would be more or less unchanged. And of course, in the United States domestic enrolments are falling, meaning that in per- student terms, the gap is even more substantial.
Figure 6: Indexed Real Public Spending on Postsecondary Institutions, Canada vs. US, 2011-12 to 2023-24 (2011-12 = 100)
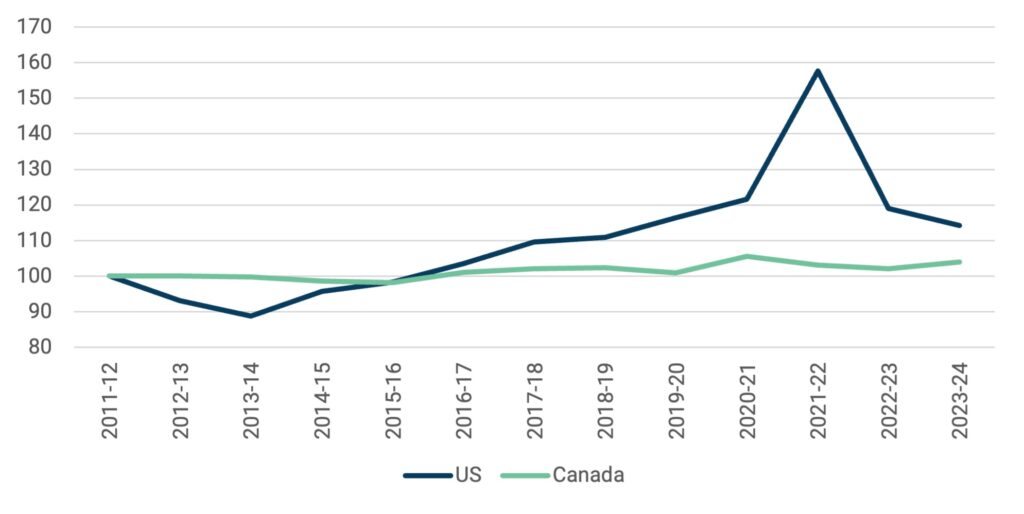
In sum: Canada is not alone in seeing significant falls in higher education spending, but few countries have seen declines in quite as an across-the-board fashion, for quite as long, as we have. Canada began the 2010s with one of the best-funded tertiary education systems in the world, but, quite simply, governments of every stripe at both the federal and provincial levels have been systematically squandering that advantage for the past 15 years. We had a genuine lead in something, an advantage over the rest of the world. But now it is gone.
So much for the past: what about the future? Well, it depends a bit on where you stand. The federal Liberals came back to power on a platform which was the least science-friendly since 1988. They promised money for postsecondary education, but most of it was either for apprenticeship grant programs which they themselves had deemed poor value for money just last year, or for programs to switch apprenticeship training from public colleges to union-led training centres – as crass a piece of cash-for-union endorsements as one can imagine. (The only saving grace? The losing Conservatives promised the unions even larger bribes). What they promised for science, for direct transfers to public universities and colleges, was a pittance in comparison.
Moreover, following the election, in the face of a set of tariff threats from the Trump Administration, the federal and provincial governments united in a program of “nation-building” which revolved entirely around the notion that national salvation was to be found in programs which “produced more goods” and “gets them to markets” (i.e. non-US markets, meaning ports) more quickly. The idea that the country might pivot to services, to a more knowledge-intensive economy in which university and college research efforts might be seen as useful, was apparently not even considered. Rather, the country rushed head-first into the familiar – but in the long-term disastrous – role being hewers of wood and drawers of water.
Now, hewing wood and drawing water has traditionally been Canada’s lot, and one could argue that historically have not fared so very badly by focusing on this core competence. But it is worth remembering the Biblical origin of this phrase, in the book of Joshua. A group of Canaanites known as the Gibeonites had not been entirely truthful when signing a treaty with the returning Israelites; claiming to be a nomadic people rather than a settled one (which would have led to them being exterminated). When the Israelites discovered the deception, many wanted the Gibeonites killed; instead, Joshua decided that they should hew wood and draw water for the Israelites instead. That is to say, they fell into bondage. The political analogies in today’s Trumpian world should be obvious.
To return to higher education: things look pretty bleak. Investment is falling. Governments are unwilling either to spend more on higher education, or to permit institutions to generate money on their own through tuition fees. Their idea of economic growth is, at best, out of the 1960s: sell more natural resources to foreigners. The idea of making our way in the world as a knowledge or science powerhouse, a spirit that infused policymaking at both the federal and provincial level in the early 2000s, has simply disappeared. Colleges might see some boosts in funding over the coming years for vocational programming, although it’s likely that they will need to scrap with private-sector unions for the money; the likelihood is that universities will see real decreases in funding. The fate of the promised increase in research spending in the 2024 budget seems especially at-risk.
The path to a better Canada does not lie in becoming better hewers of wood and drawers of water. It lies in developing new industries based on cutting-edge knowledge and science. Spending on postsecondary students, on its own, does not guarantee that these new industries will come into existence. But the absence of spending on postsecondary education certainly guarantees that they will not.
The country has a choice to make. And right now, we seem to be choosing poorly.